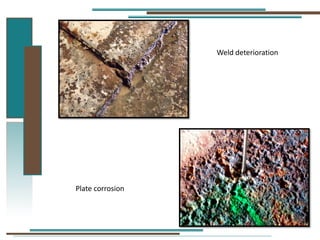
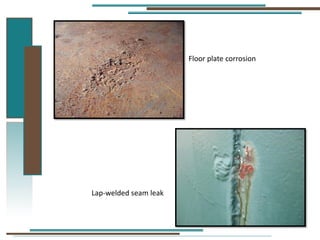
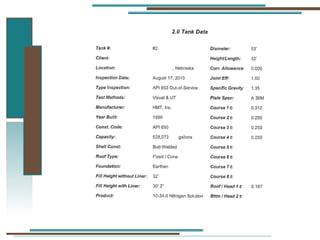
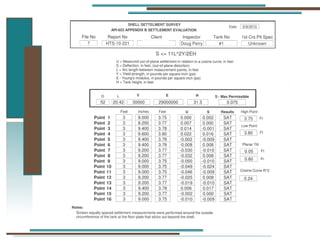
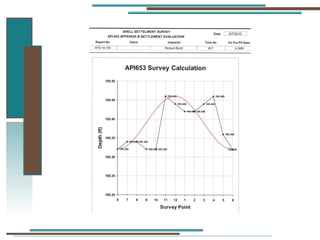
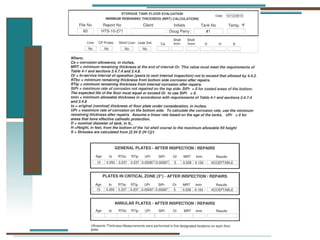
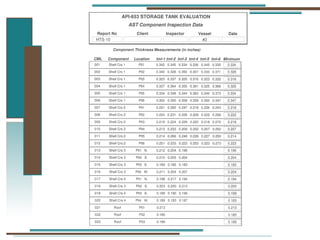
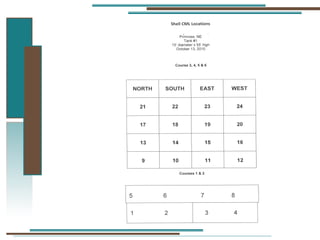
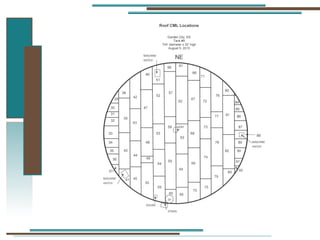
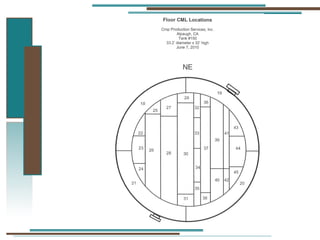
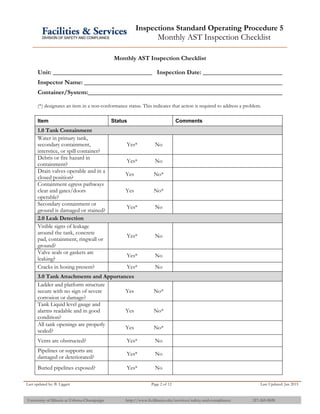
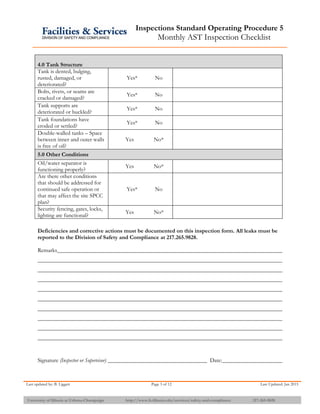
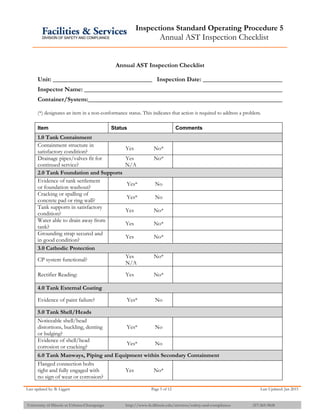
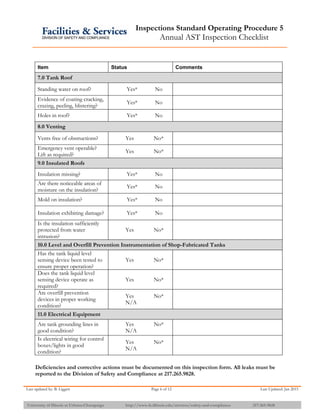
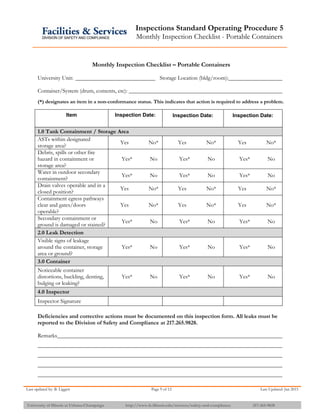
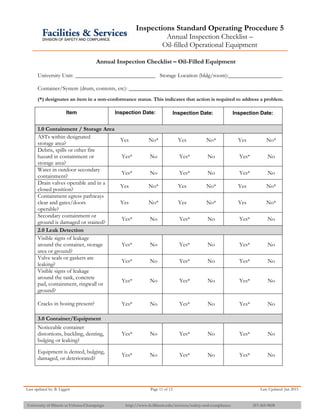
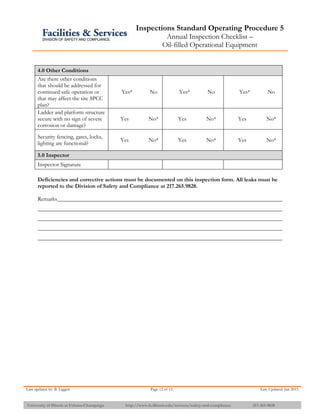
The document provides information about API 653 tank inspections, tank maintenance, and causes of tank failure. It discusses why tanks should be inspected, proper inspection protocols including inspector credentials, common inspection procedures, and providing calculations. It also discusses a common sense approach to tank maintenance and inspections. Finally, it outlines common causes of catastrophic tank failure such as improper welding procedures, lack of inspections, corrosion, and overfilling tanks.