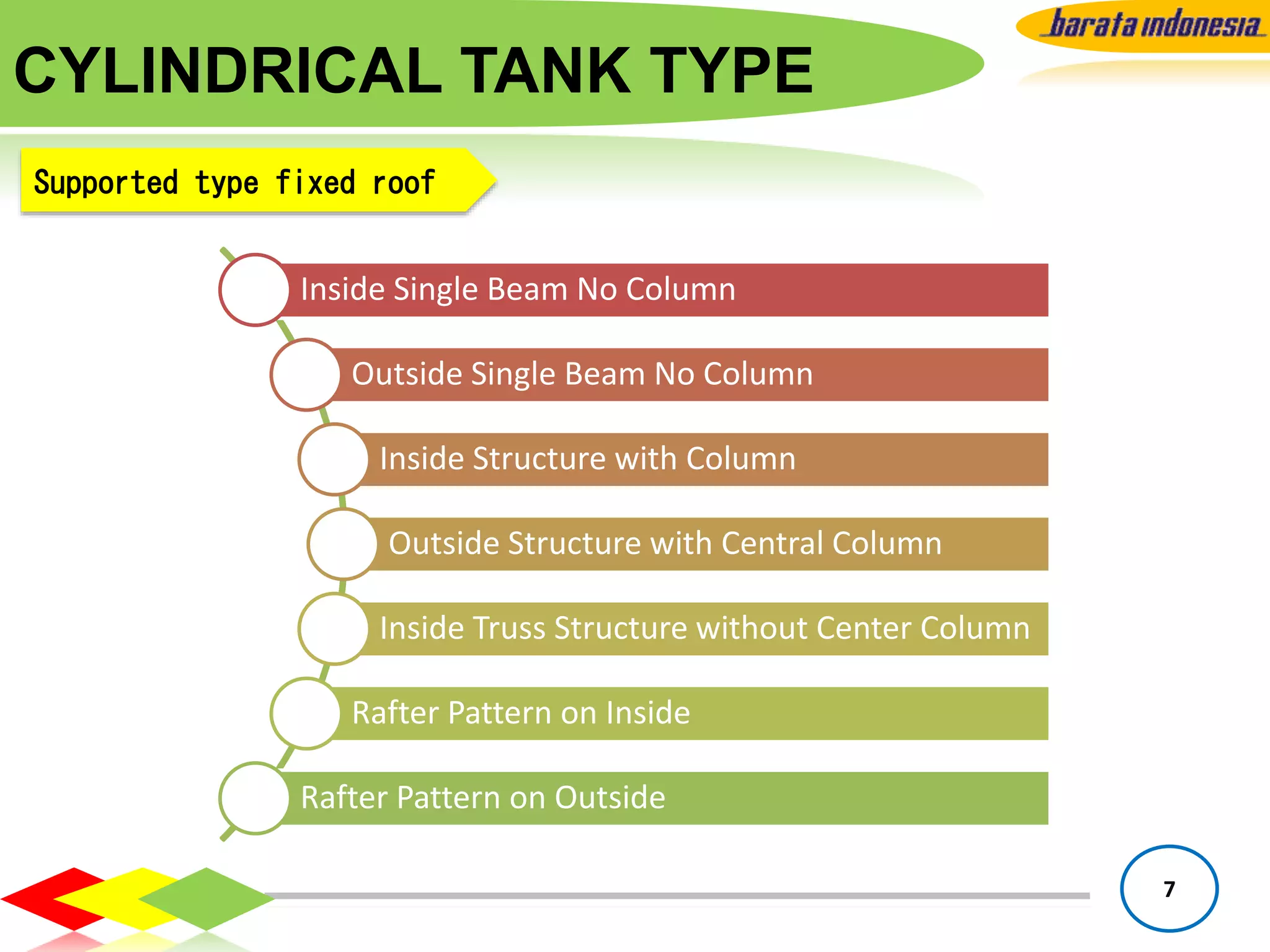
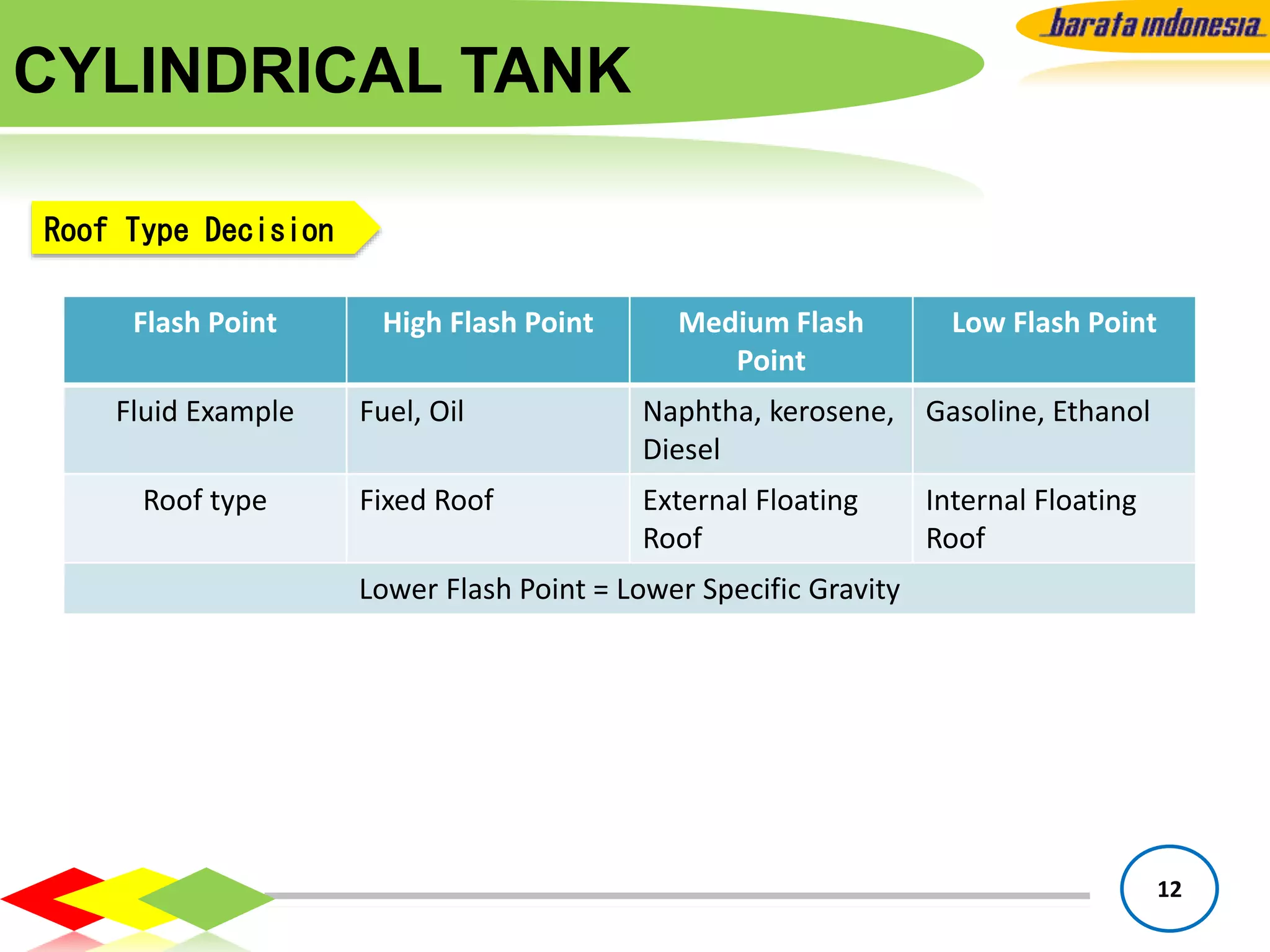
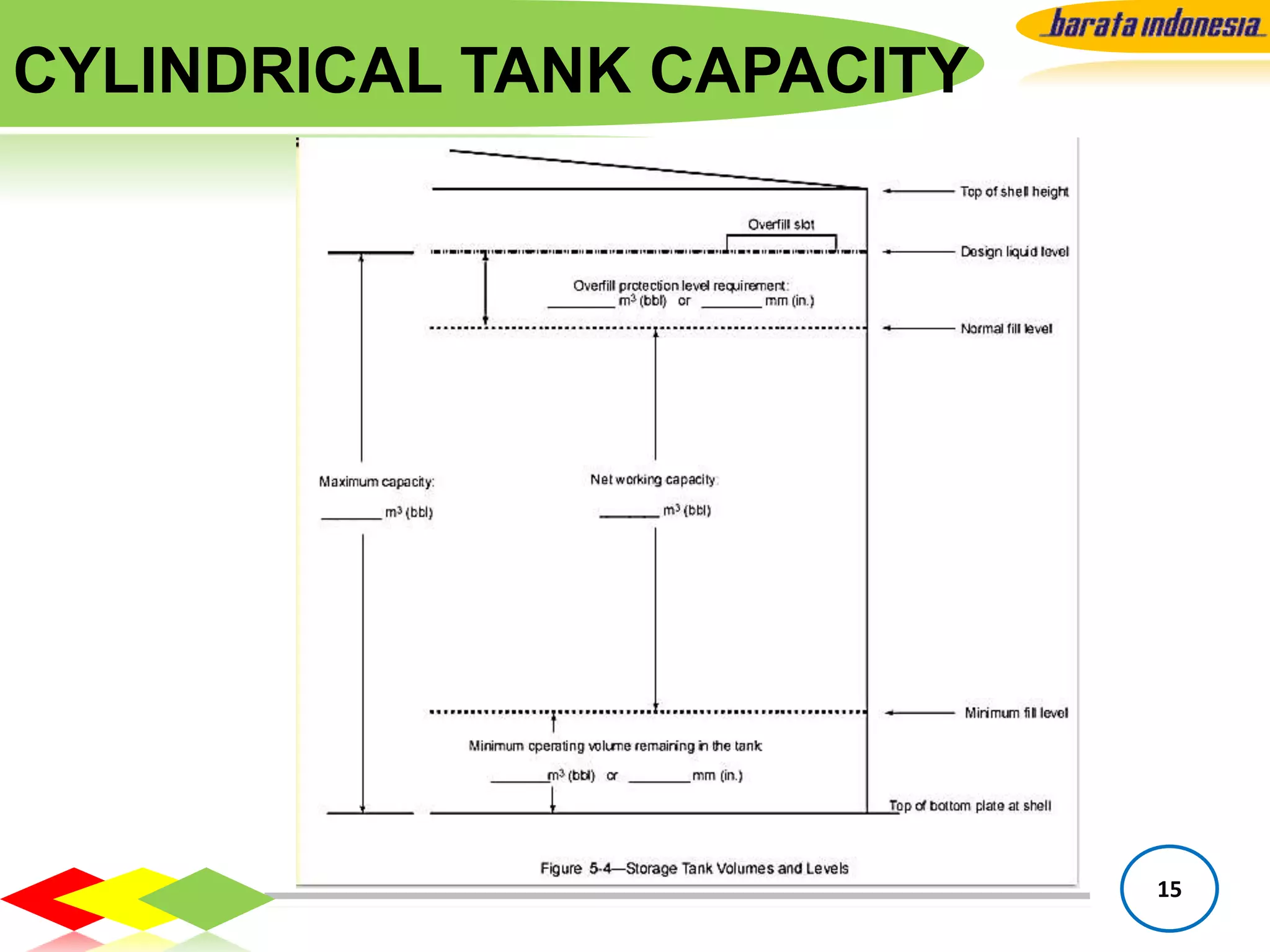
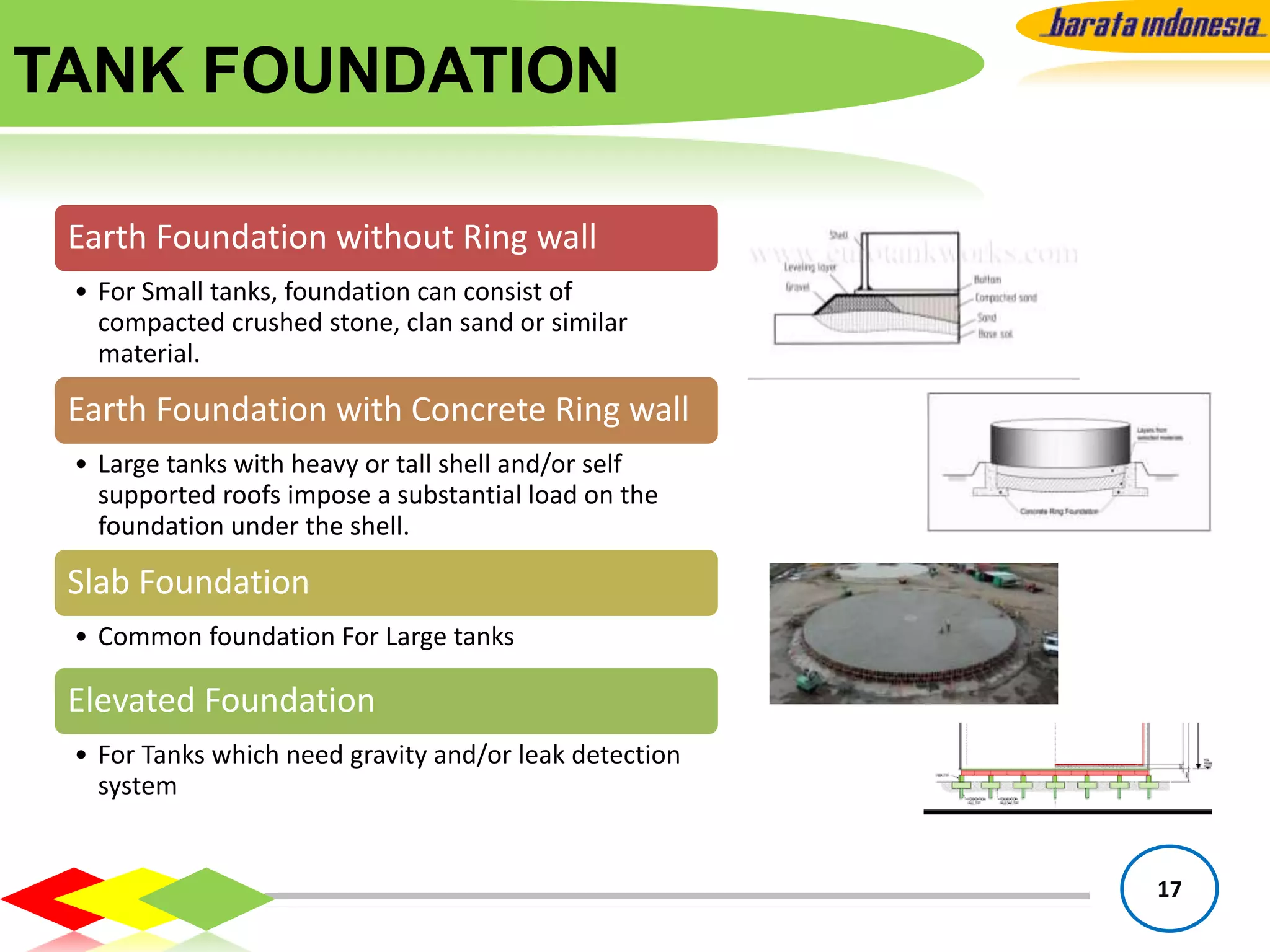
The document provides information on storage tank design based on API 650 standards. It discusses the different types of storage tanks including their shapes, sizes, and applications. The two main types are atmospheric storage tanks and pressurized storage tanks. Cylindrical tanks are the most common and can have different roof types like fixed, floating, or cone/dome roofs depending on the stored liquid's flash point. Material selection, tank capacities, accessories, foundations, and important notes about containment are also covered.