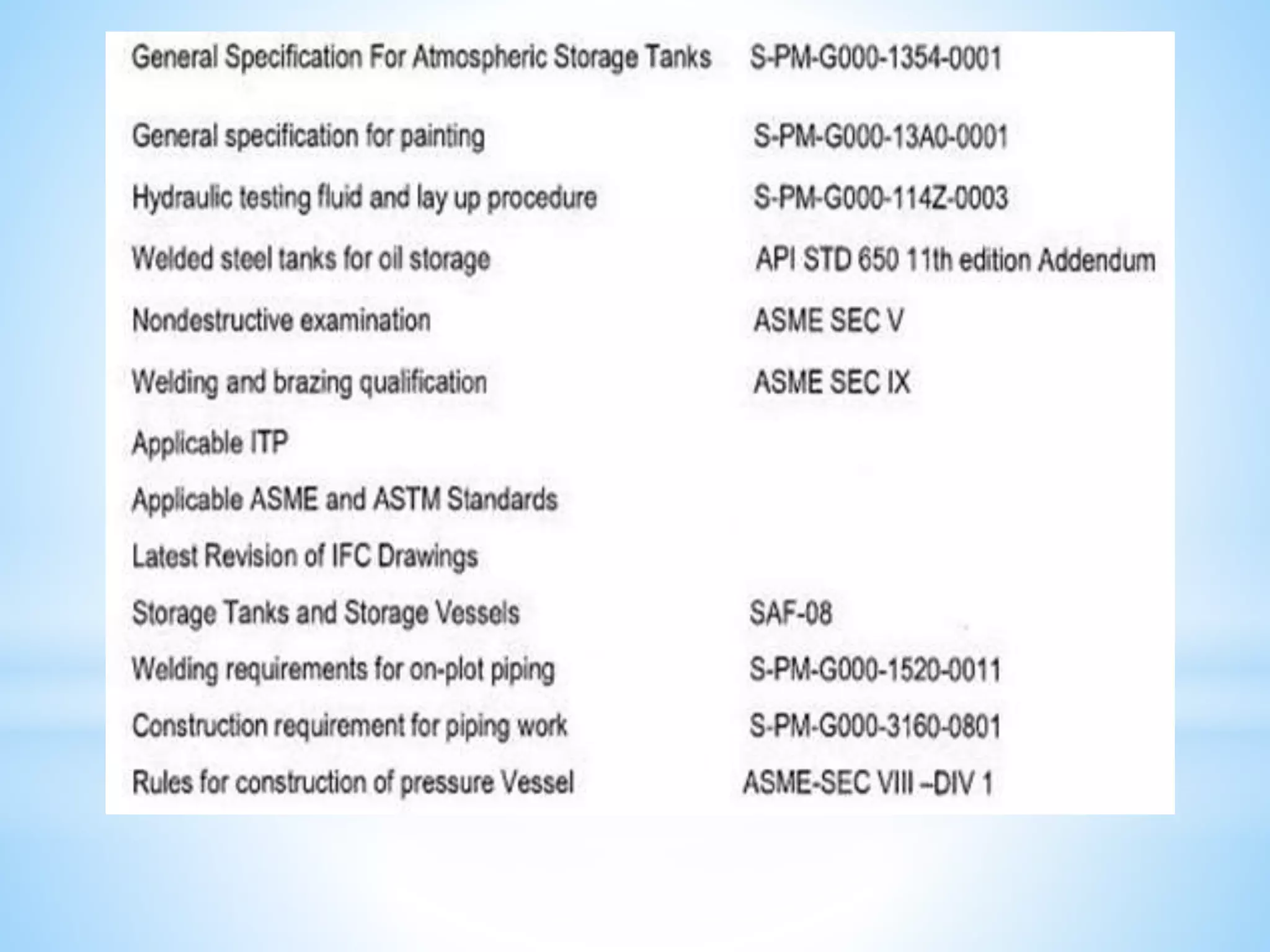
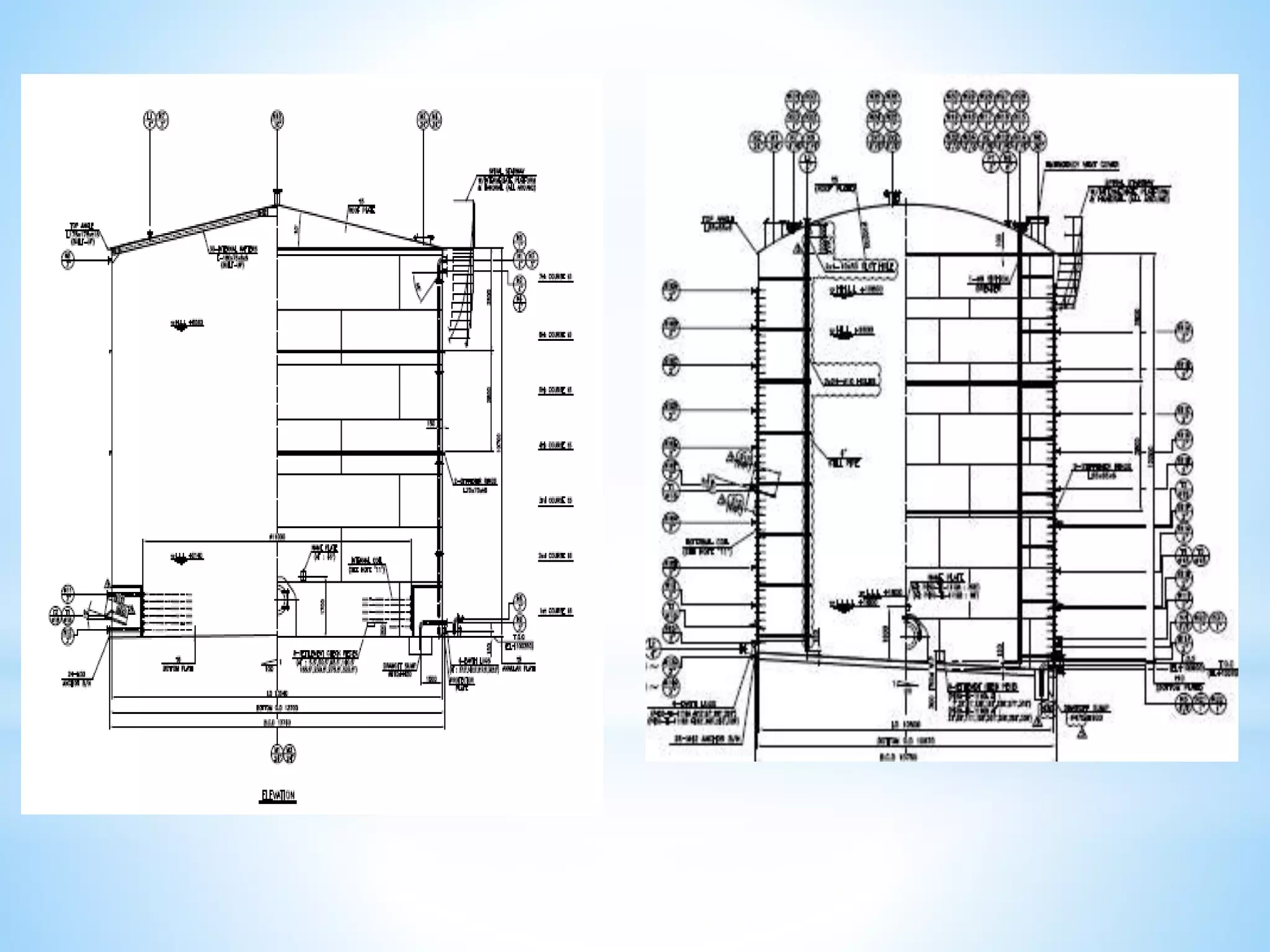
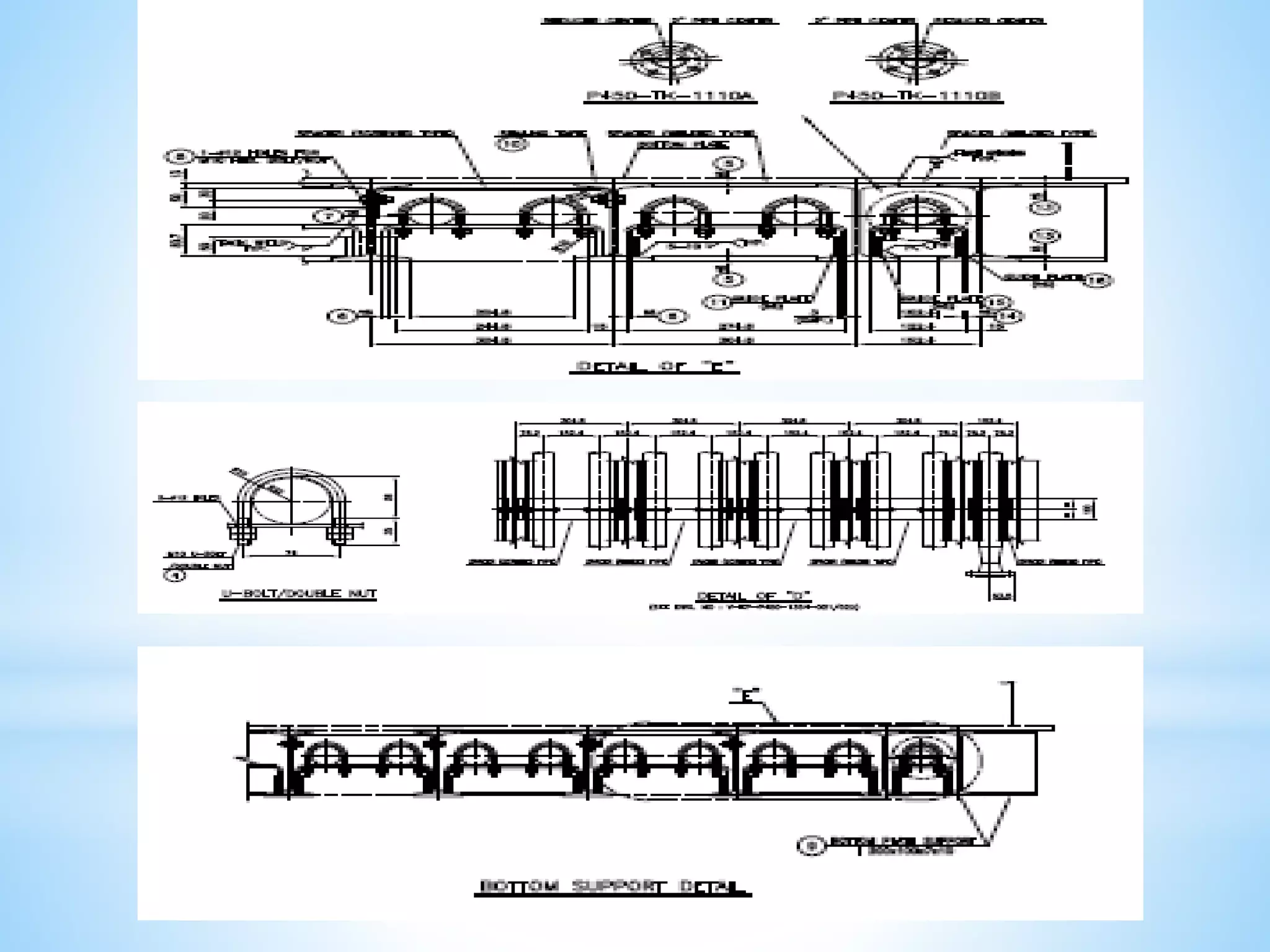
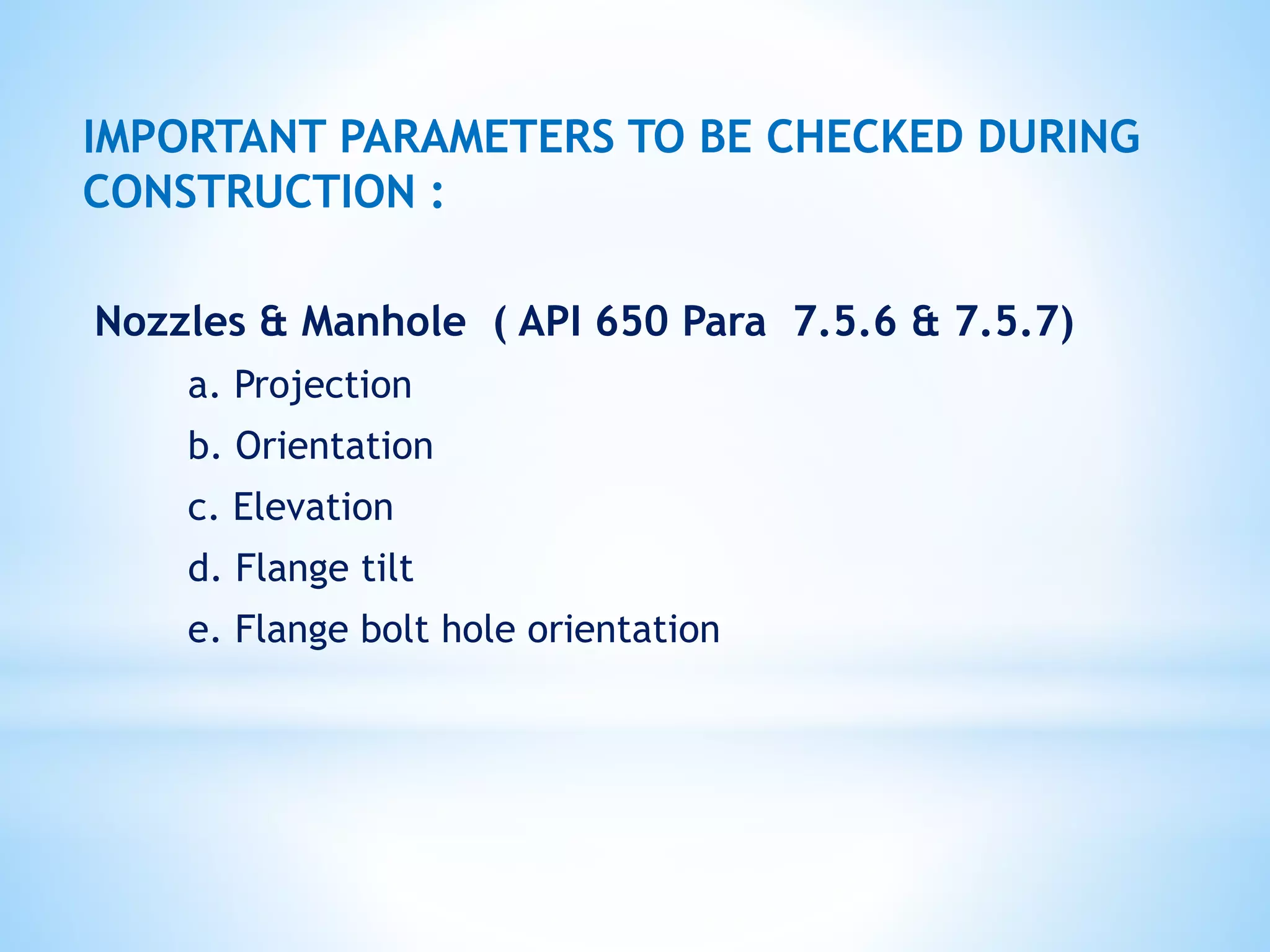
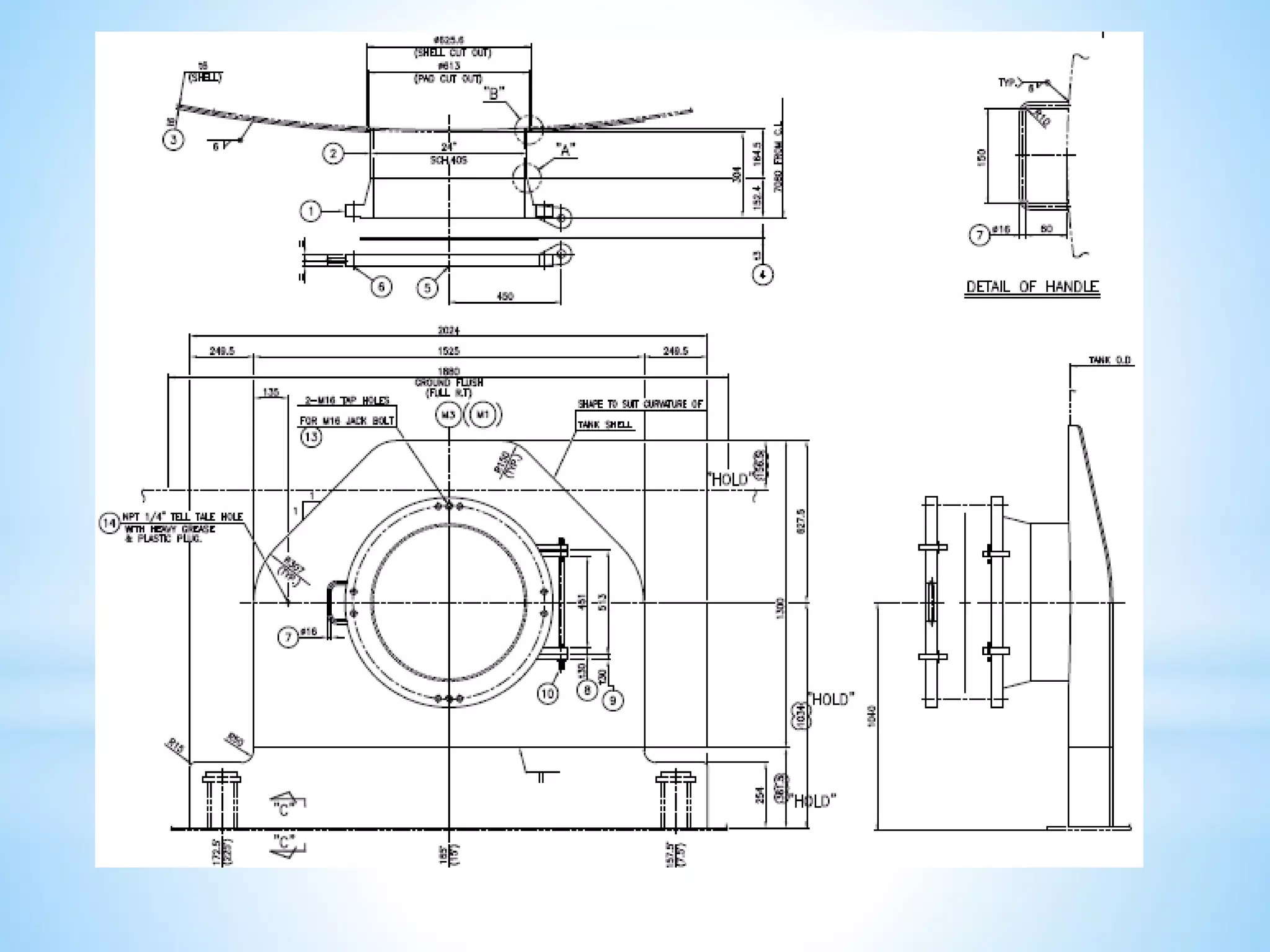
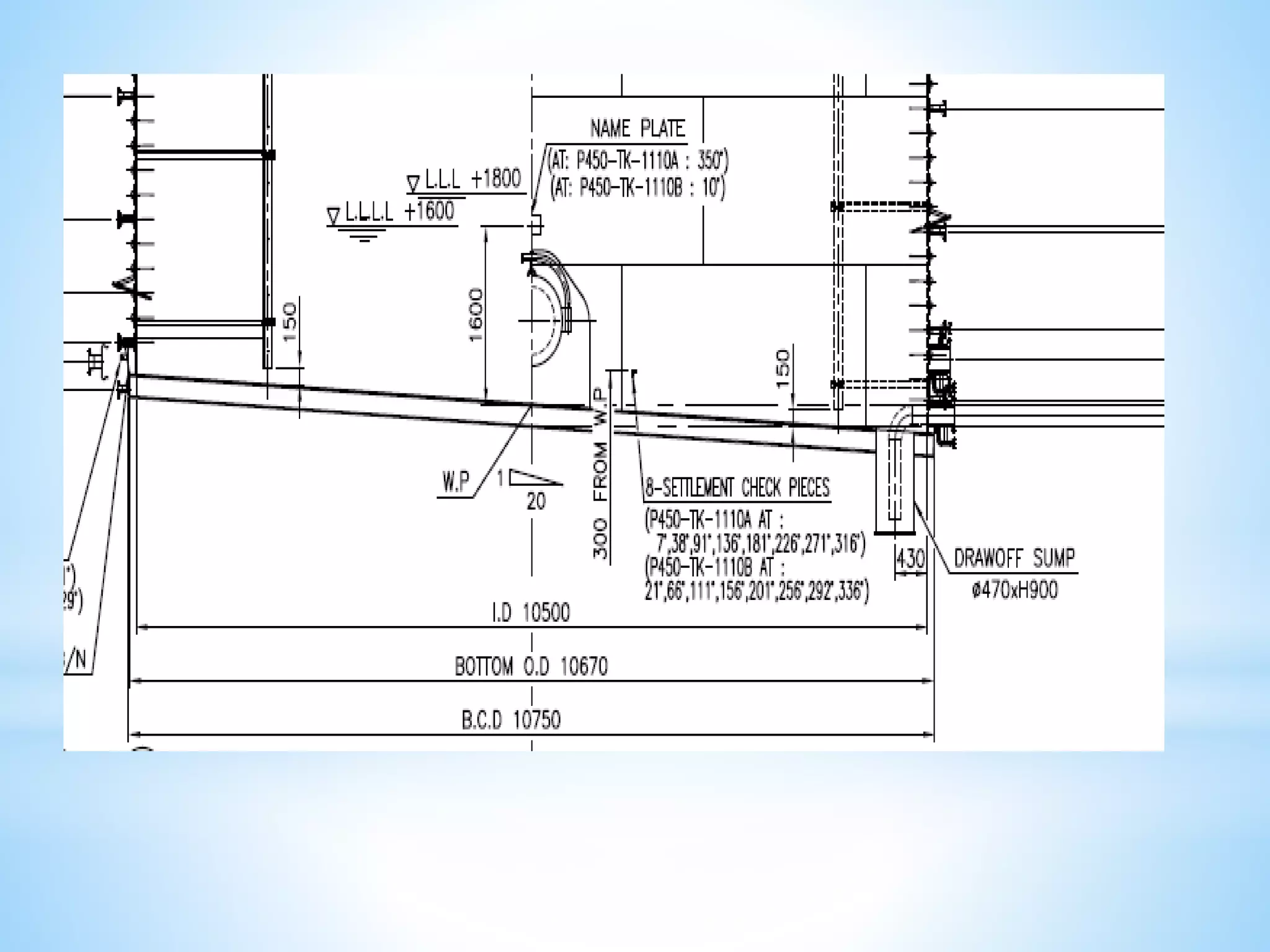
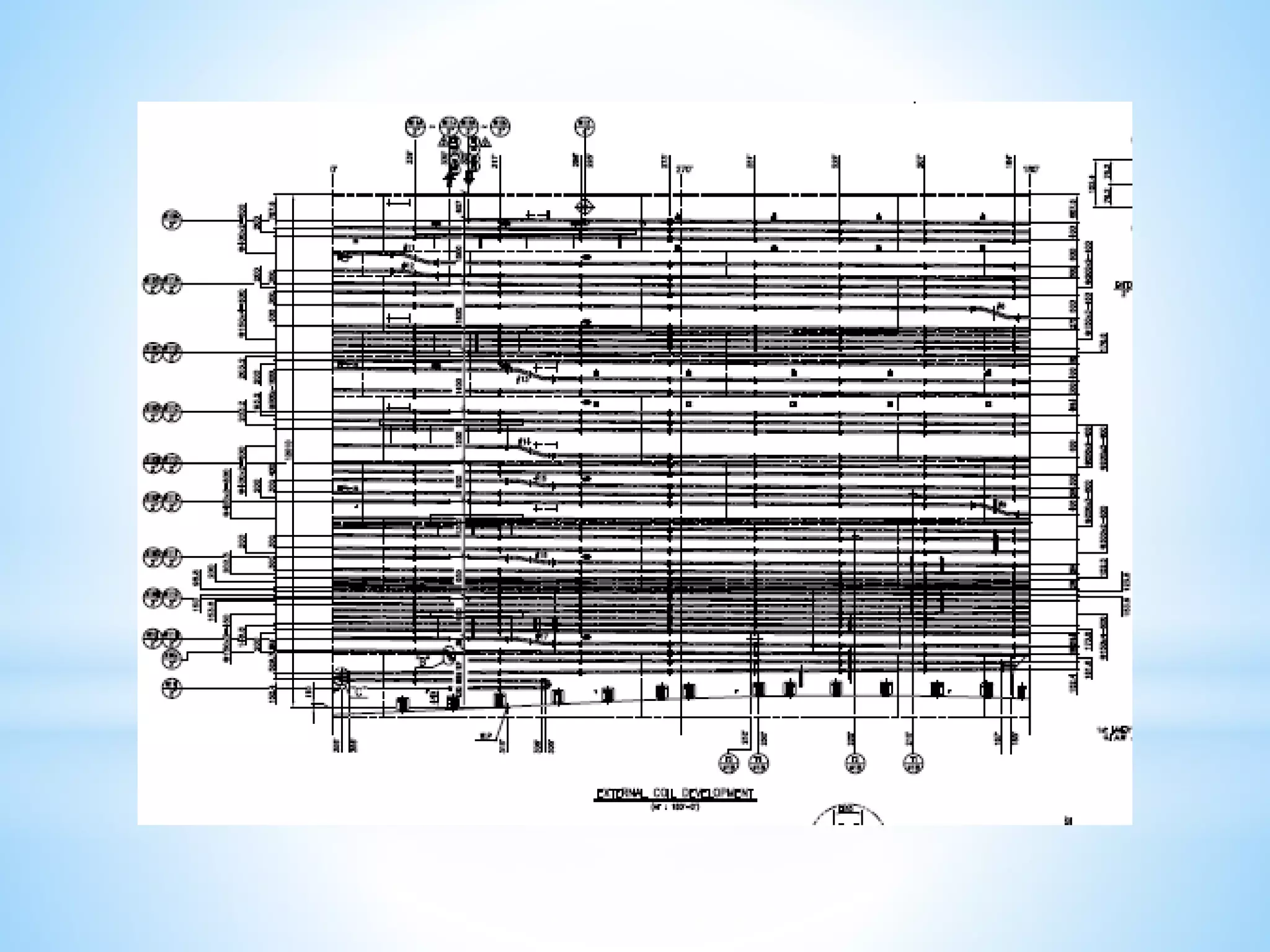
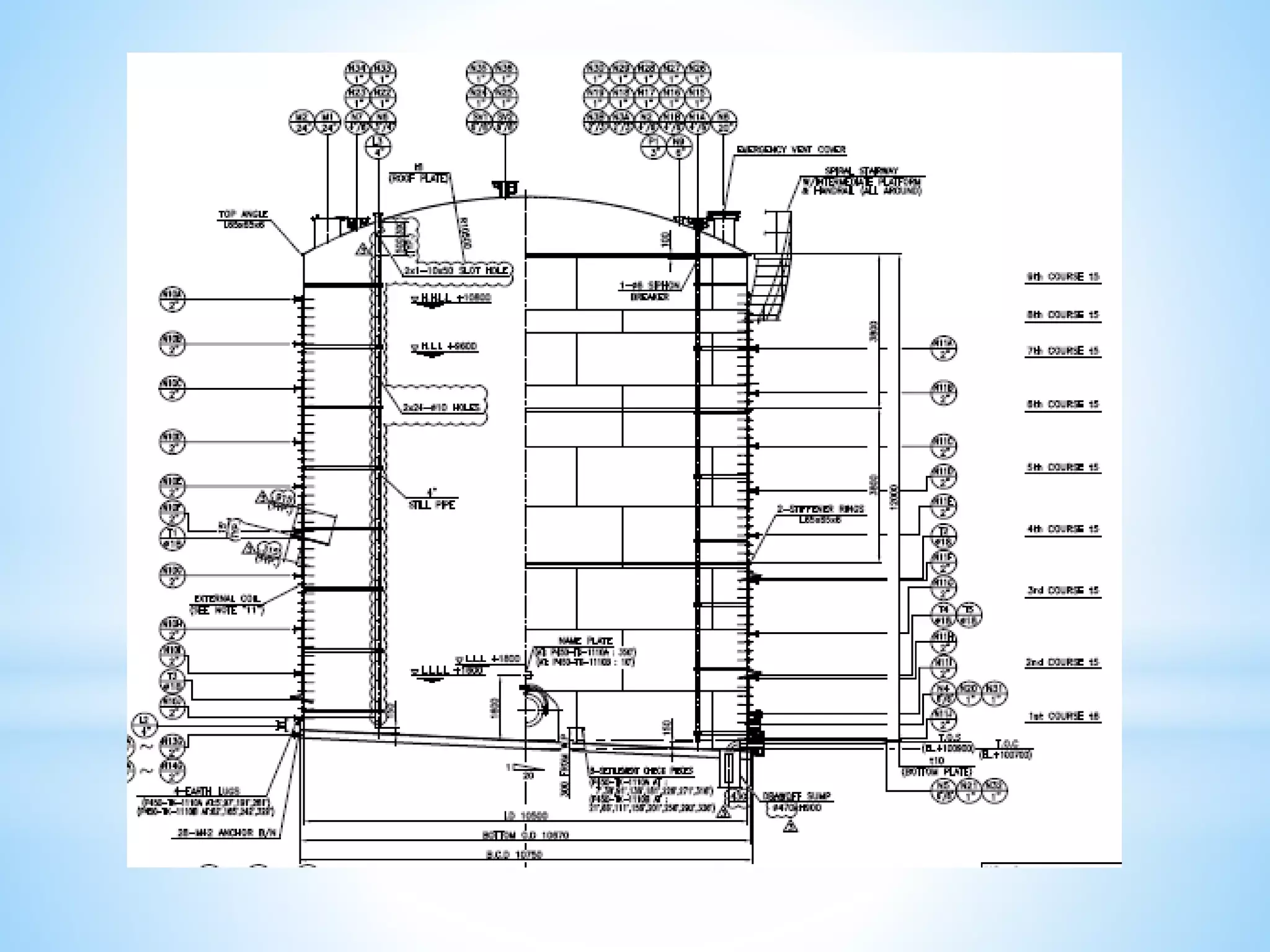
Storage tanks can be divided into two types - API 650 tanks and API 620 tanks. API 650 tanks are vertical, cylindrical tanks for atmospheric pressure. API 620 tanks are large, low-pressure carbon steel tanks with pressures up to 15 psi. There are various types of roofs including cone, dome, aluminum dome, and external floating. Important parameters to check during construction include roundness, plumbness, peaking, banding, and specifications for nozzles, manholes, and welds. Tanks undergo hydrostatic testing, roof testing, and other inspections to ensure quality and safety.