Scalp Anatomy
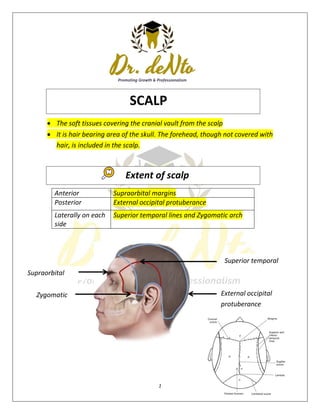
- 1. 1 Supraorbital margins Zygomatic arch The soft tissues covering the cranial vault from the scalp It is hair bearing area of the skull. The forehead, though not covered with hair, is included in the scalp. Anterior Supraorbital margins Posterior External occipital protuberance Laterally on each side Superior temporal lines and Zygomatic arch Superior temporal External occipital protuberance SCALP Extent of scalp
- 2. 2 S - Skin C - Connective tissue (superficial fascia) A - Aponeurosis L - Loose Areolar Connective Tissue (subaponeurotic layer) P - Pericranium Skin The skin of scalp is characterized by plenty of hair follicles, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. Firmly attached to the epicranial aponeurosis through dense fascia Abundance sebaceous glands Sebaceous cyst are common Connective tissue Binds skin to subjacent aponeurosis The superficial fascia is characterized by dense connective tissue. It contains the blood vessels and nerves of the scalp. The fibrous strands in the superficial fascia are fixed to the walls of the blood vessels. This The musculoaponeurotic layer consists of two parts: i. Epicranial aponeurosis (galea aponeurotica) ii. ii. Muscular part composed of frontal and occipital bellies of the occipitofrontalis muscle. Structure
- 3. 3 factor prevents retraction of the blood vessels, when injured. Hence, scalp wounds bleed profusely. The bleeding in the scalp is controlled by application of direct pressure of the digit or by placing the surgical sutures. Inflammation cause little swelling but are much painful Aponuerosis and muscle The galea aponeurotica covers the vault like a helmet. EPICRANIAL APONUEROSIS It is freely movable on the pericranium along with the overlying and adherent scalp and fascia. On each side it is attached to the superior temporal lines. Anteriorly ,it receives the insertion of the frontalis. Posteriorly ,receives insertion of the occipital bellies and attached to the external occipital protuberance. OCCIPITOFRONTALIS LOOSE AEREOLAR TISSUE The subaponeurotic layer (fourth layer) forms a potential space filled with loose areolar tissue beneath the aponeurotic layer. The emissary veins, which communicate the veins of the scalp with the intracranial venous sinuses, pass through this space. This space is closed on all sides except anteriorly, where it extends into the upper eyelid It is known as the dangerous area of scalp. It Extends anteriorly into the eyelids. Posteriorly to the highest and superior nuchal lines and on each side to the superior temporal lines. PERICRANIUM Loosely attached to the surface of the bones,but is firmly adherent to the sutures where the sutural ligaments bind the pericranium to the endocranium.
- 4. 4
- 5. 5 Arteries supplying the scalp are branches of either the external carotid artery or the ophthalmic artery which is a branch of the internal carotid artery. External carotid arteries o Occipital arteries o Posterior auricular arteries o Superficial temporal arteries Internal carotid arteries o Supratrochlear arteries o Supraorbital arteries 1. The following arteries supply the anterior quadrant: i. Supratrochlear ii. Supraorbital The above two arteries are the branches of the ophthalmic artery (a branch of internal carotid artery). iii. Superficial temporal artery is the terminal branch of external carotid artery. 2. The following arteries supply the posterior quadrant of scalp i. Posterior auricular ii. Occipital artery The above two arteries are branches of external carotid artery. Arterial Supply of the Scalp
- 6. 6 Veins draining the scalp follow a pattern similar to the arteries. a. The supratrochlear and the supraorbital vein unite at the medial angle of eye to form angular vein. b. The superficial temporal vein joins the maxillary vein to form retromandibular vein. c. The posterior division of retromandibular vein unites with the posterior auricular vein to form external jugular vein. d. The occipital vein drains into the suboccipital venous plexus. Which lies beneath the floor of the upper part of the posterior triangle, the plexus in turn drains into the vertebral veins or internal jugular vein. Of the deep parts of the scalp o Via emissary veins that communicates with the dural sinuses o Emissary vein connect the extracranial veins with the intracranial venous sinuses to equalize the pressure, the veins are valveless. o Parietal emissary vein, which passes through parietal foramen and communicates with the superior sagittal sinus. o Mastoid emissary vein, which passes through mastoid foramen and communicates with the sigmoid sinus. Venous Drainage of the Scalp
- 7. 7 The lymphatics in the occipital region initially drain to occipital nodes which drain into upper deep cervical nodes. lymphatics from the upper part of the scalp drain in two directions o Posterior to the vertex of the head they drain to mastoid nodes. o Anterior to the vertex of the head they drain to pre-auricular and parotid nodes. Lymphatic Drainage
- 8. 8 Two main sources o Cranial nerves :- (anterior to ear & vertex) by trigeminal nerves o Cervical nerves:- (posterior to ear and vertex) by C2 &C3 nerves Anterior to the ears and the vertex Posterior to the ears and the vertex Sensory nerves Supratrochlear nerve Supraorbital nerve Zygomaticotemporal nerve Auriculotemporal nerve By branches of all four divisions of the trigeminal nerve Sensory nerves Great auricular nerve Lesser occipital nerve Greater occipital nerve Third occipital nerve By branches of all four divisions of the spinal cutaneous nerves (C2 and C3) Motor nerves Temporal branch of facial nerve Motor nerves Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve Nerve Supply
- 9. 9 Skin of the scalp is the commonest site in the body for sebaceous cysts as it is rich in sebaceous glands being the hairiest Cutaneous tissue of the second layer is divided into a number of loculi containing fat in which infection sends to become localised and causes severe pain. Wounds into the highly vascular second layer tend to bleed freely as the walls of the blood vessels are attached to the fibrous septa so that they cannot contract and retract to stop the haemorrhage A wound which cuts through the third layer gapes but the edges of a wound which does not penetrate the aponeurosis remain together This is because the aponeurosis is under tension because of its muscular component and retracts only when divided The emissary veins which traverse the fourth layer I.e. the subaponeurotic space connect the veins of the second layer with the intracranial venous sinuses. A superficial infection of the scalp can spread via this system to produce venous sinus thrombosis or meningitis The subaponeurontic space affords an easy plane of cleavage Blood or pus collecting in this layer tracks freely under the first three layers but cannot pass into either the superficial temporal region or the occipital region because of the attachment of the occipitofrontalis muscle. Blood can, however, spread into the upper eyelid causing a 'black eye that may form a few hours after a severe head injury. This layer is known as the 'dangerous layer as infection tends to spread readily within it. The pericranium is easily stripped up by collection of pus or blood beneath it. The affected bone in outlined as the sutural membrane limits the spread of collected fluid. This is particularly well seen in birth injuries involving the skull and causing a cephalhematoma. Caput succedaneum is the formation of swelling in the newborn skull due to stagnation of fluid in the scalp layers. This is a temporary swelling since it Clinical Application
- 10. 10 results from the venous congestion of the scalp due to compression through the birth canal. The swelling of caput succedaneum is diffuse because it is not restricted to any particular bone. It disappears within 24 hours after delivery. In newborn babies, there is slow accumulation of blood in this space, when there is intracranial hemorrhage due to fracture of the bone of vault and associated dural tear. The leakage of blood outside the cranium in the potentially large subaponeurotic space delays the symptoms of cerebral compression. Hence, the slow accumulation of blood in the fourth layer is known as Safety valve hematoma.
- 11. 11 The temple is the area between the temporal lines and the zygomatic arch which must be studied in the view of the skull or norma lateralis . The temporal fossa is a shallow depression bounded above by the superior temporal line on the frontal and parietal bones and below by the zygomatic arch. The bones taking part in the formation of the fossa are the squamous part of temporal (T), the greater wing of the sphenoid (S) and lower part of the frontal (F) and perietal (P) bones. These bones articulate at an H-shaped suture called the pterion The superior and inferior temporal lines are the duplication of the temporal line on the parietal bone. The superior temporal line marks the upper limit of the norma lateralis. Lower part of the Frontal Greater Wing of the Sphenoid Squamous part of temporal Lower part of the perietal TEMPORAL FOSSA
- 12. 12 Bounded by It contents consist of:
- 13. 13 There are six layers in this region. The first and second layers are the same as in the scalp I,e. skin and cutaneous tissue The third layer is a thin expansion of the epicranial aponeurosis of the scalp from which the auricularis anterior and superior muscles arise The fourth layer is the temporal fascia (Fig 2.7) which is attached above to the superior temporal line and below to the zygomatic arch It is a rugged membrane. The superior temporal vessels and the auriculotemporal nerve lie upon it, and it is perforated by the middle temporal artery and vein . The fifth layer is the temporalis muscle . which arises from the whole of temporal fossa. The large fan- shaped muscle converges towards the coronoid process mandible . Layers in temporal region
- 14. 14 The sixth or the last layer is the same as in the scalp i.e. pericranium. Youtube - https://youtu.be/1b40B8sgrho Facebook – De Nto