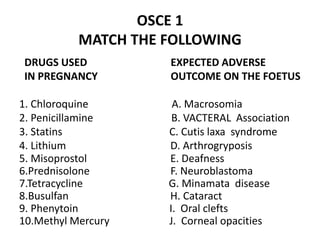
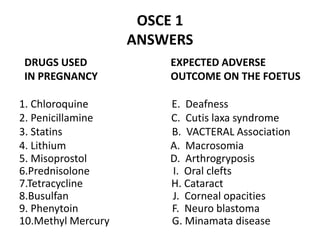
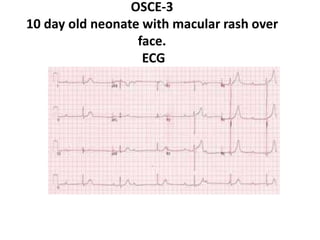
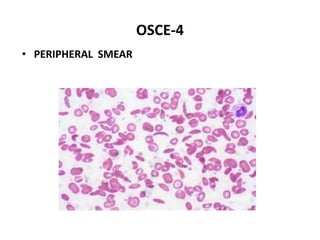
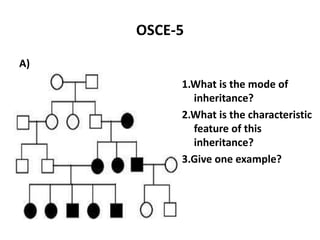
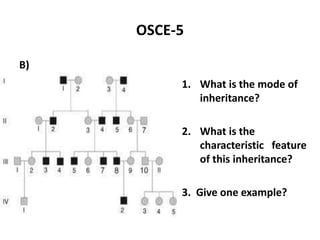
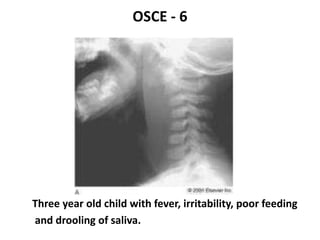
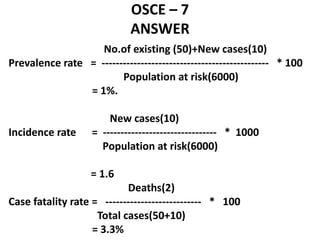
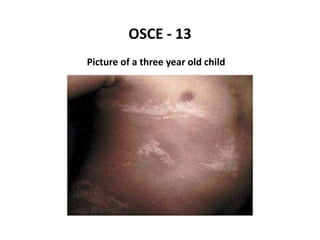
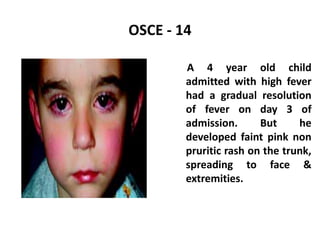
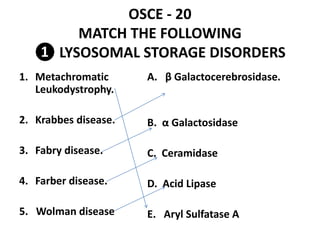
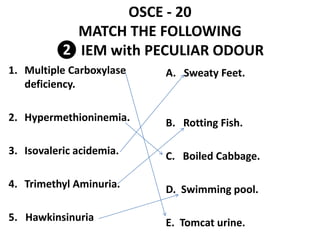
This document contains an OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination) practice exam for pediatrics. It includes 10 multiple choice matching questions that pair drugs used in pregnancy with their expected adverse effects on the fetus. It also includes several short clinical vignettes followed by 5 questions each. The vignettes cover topics like interpreting an ABG result, identifying sickle cell anemia from a peripheral smear, making a diagnosis of retropharyngeal abscess from presented symptoms, and more. The goal of the summary is to provide a high-level overview of the content and focus of the practice exam.