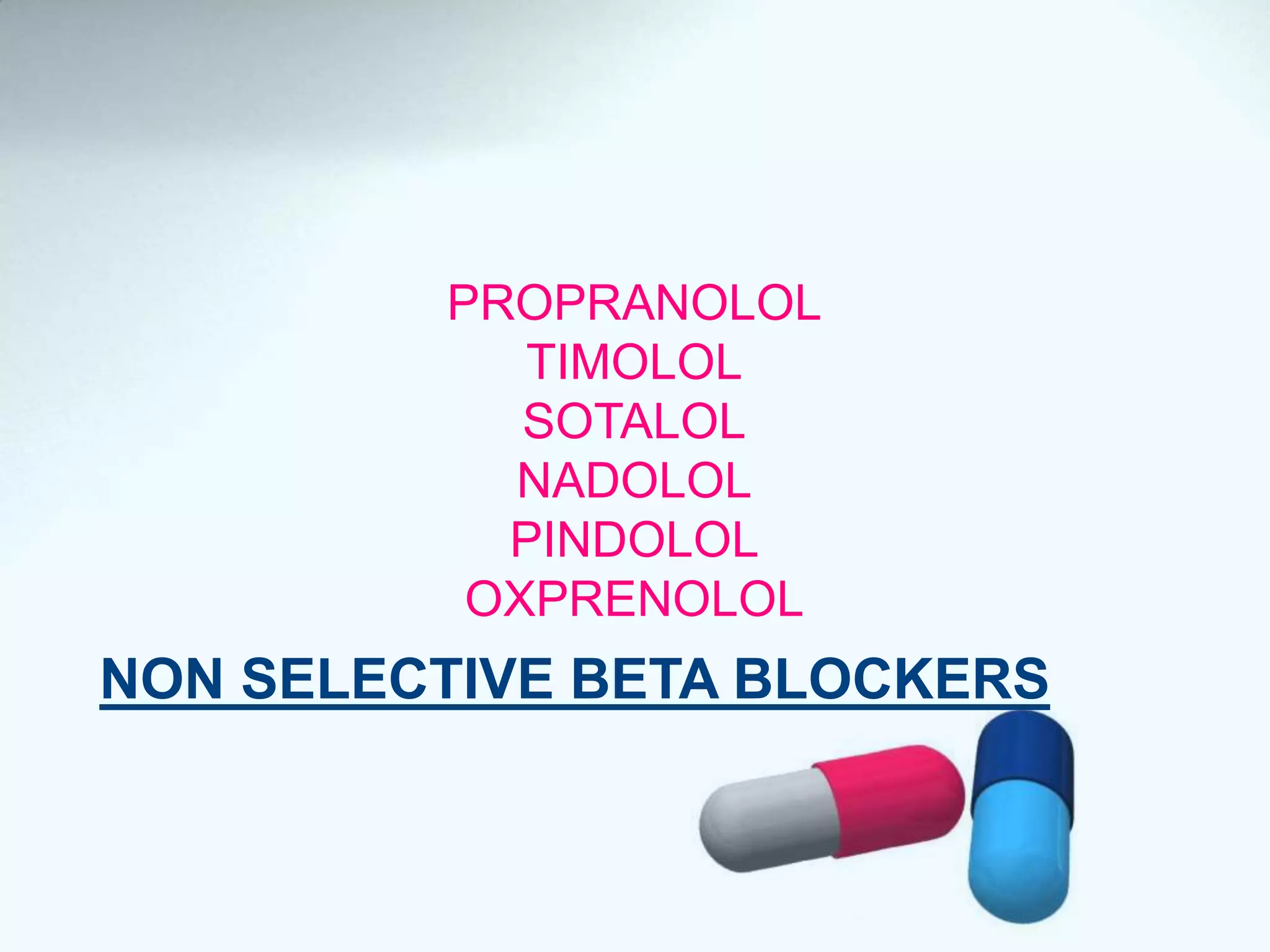
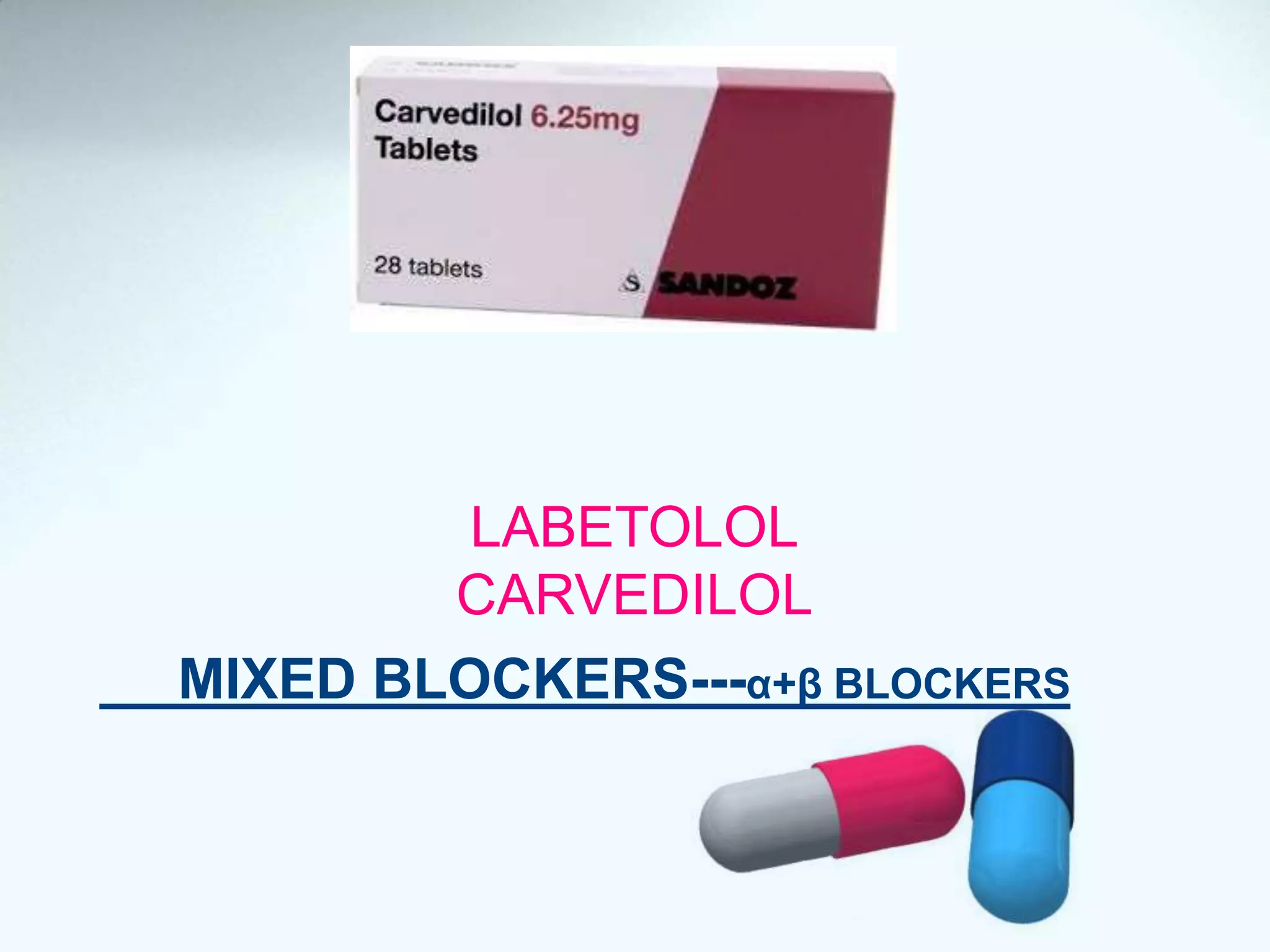
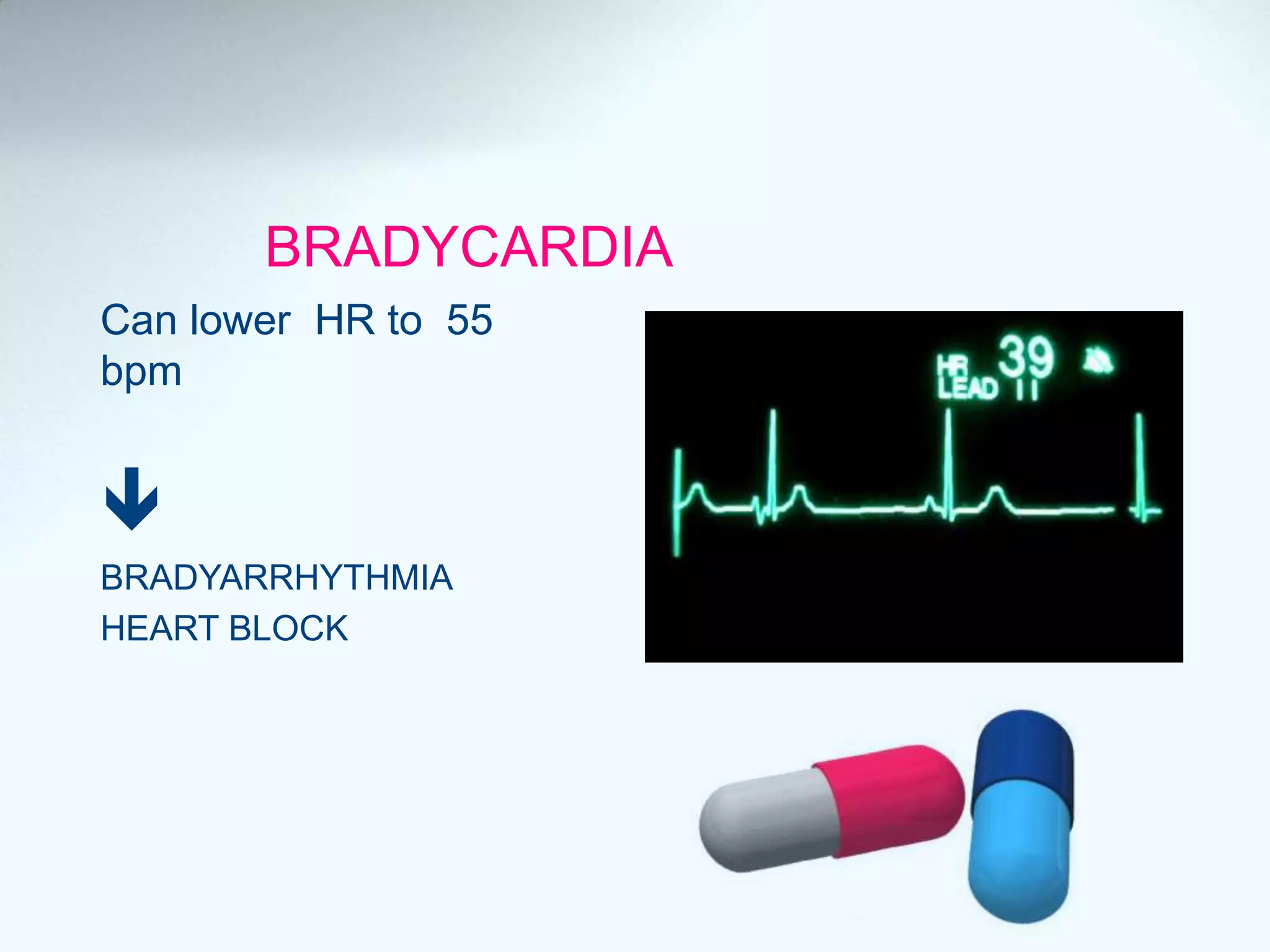
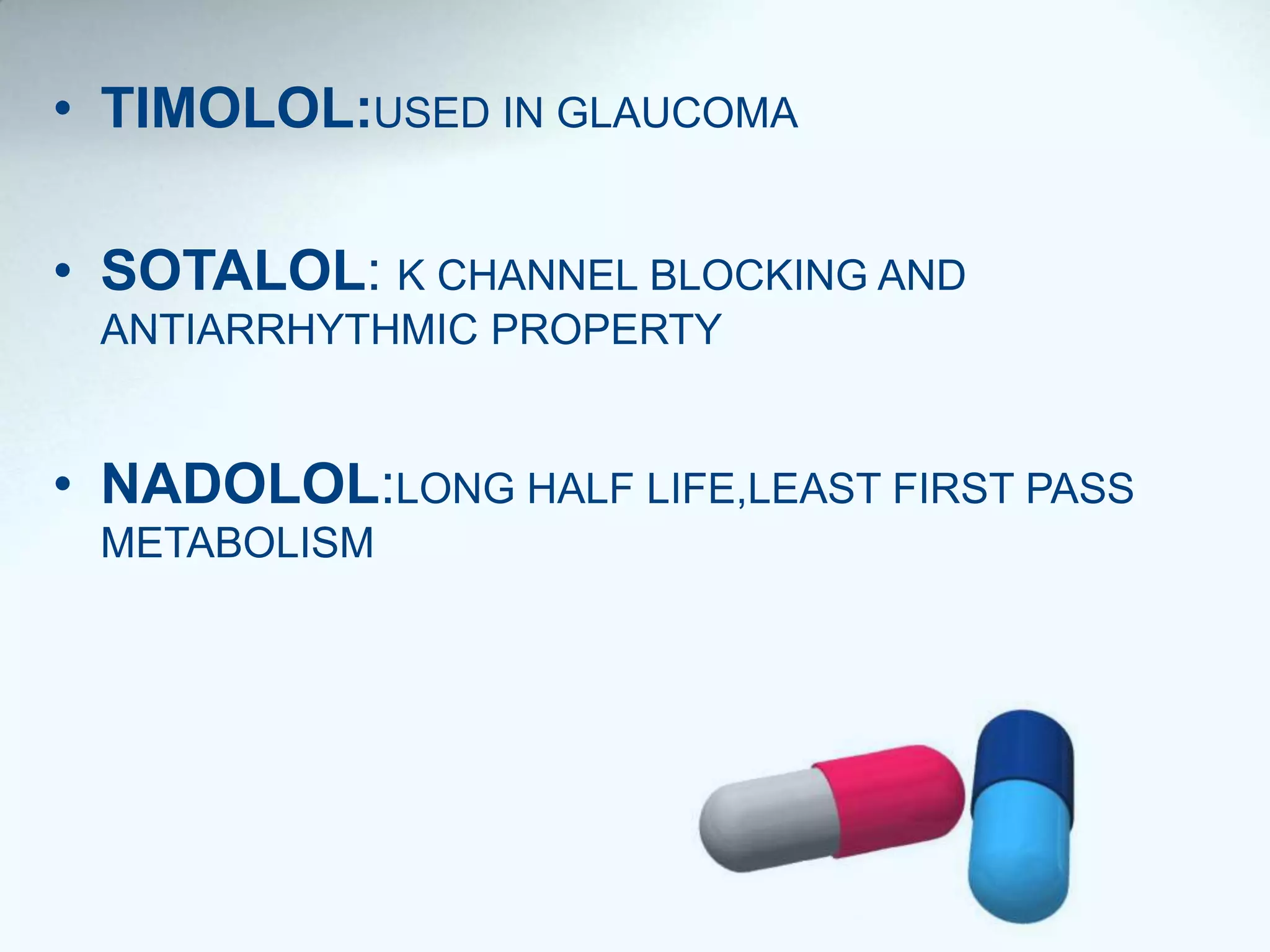
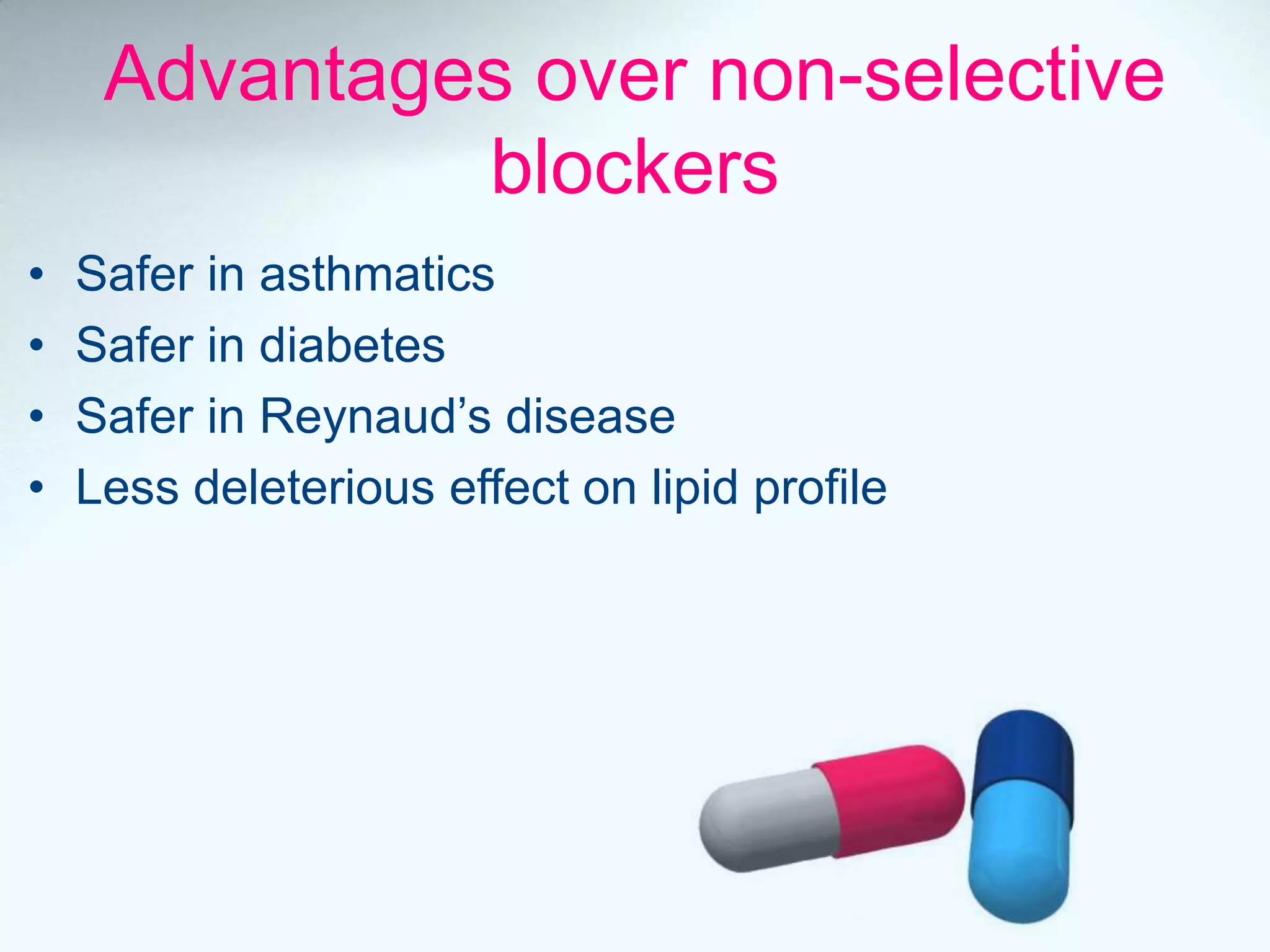
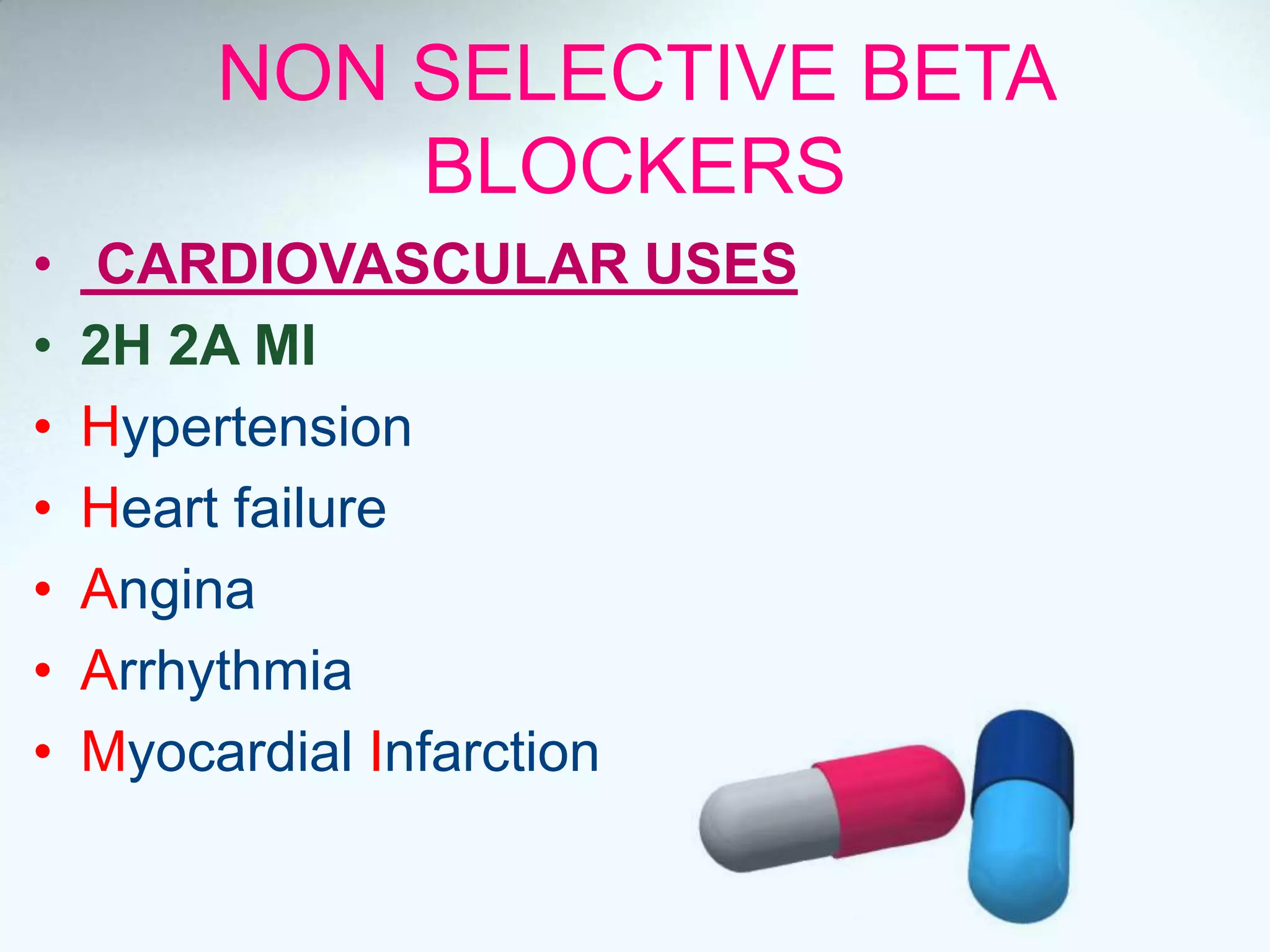
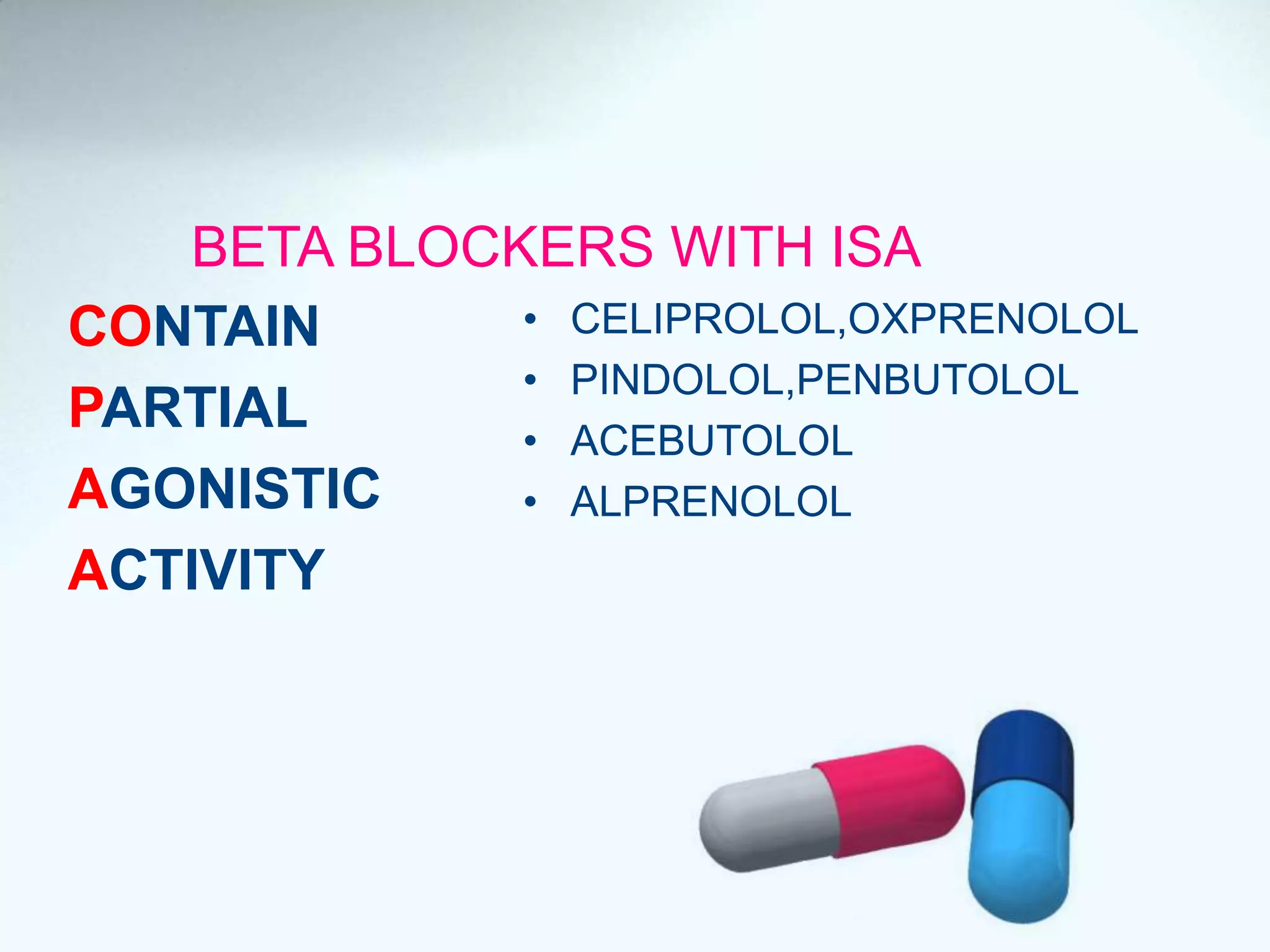
Beta blockers act on beta 1 and/or beta 2 receptors. They are classified as non-selective, selective, and mixed blockers. Non-selective blockers like propranolol block both beta 1 and beta 2 receptors. They are used for cardiovascular conditions like hypertension, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Adverse effects include bronchospasm, bradycardia, hypoglycemia, and heart failure. Cardioselective blockers mainly block beta 1 receptors. Newer blockers have improved safety profiles.