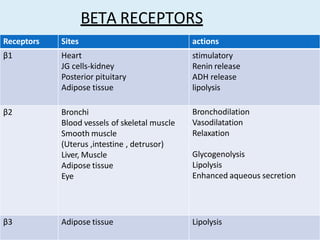
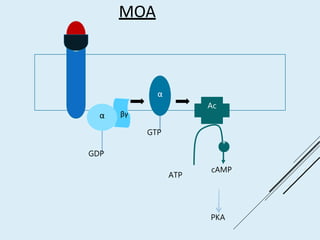
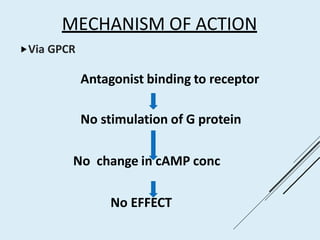
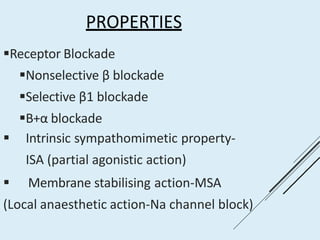
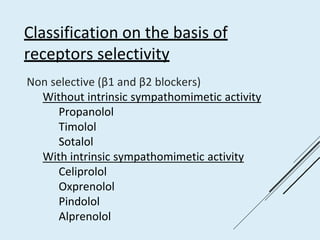
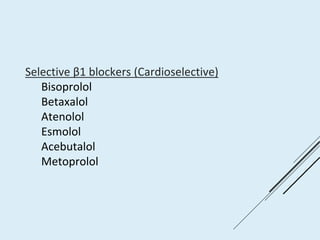
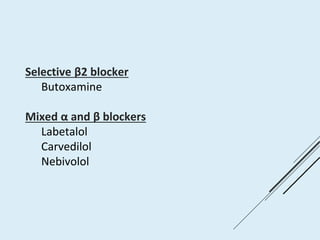
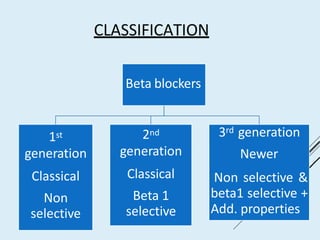
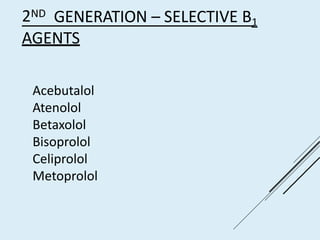
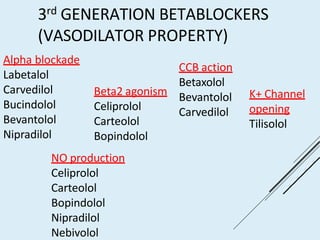
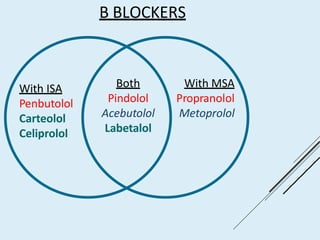
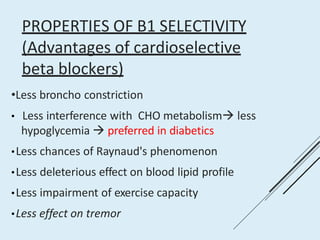
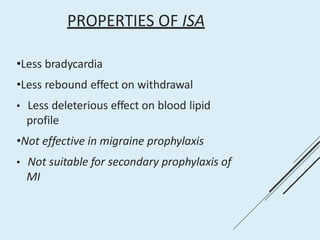
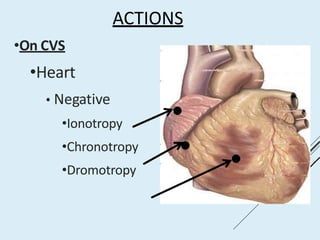
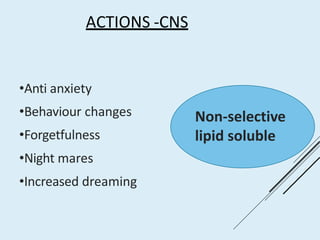
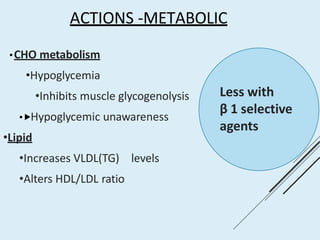
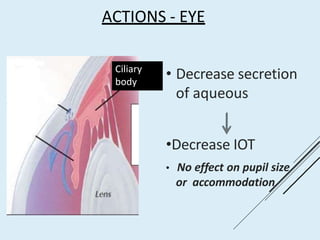
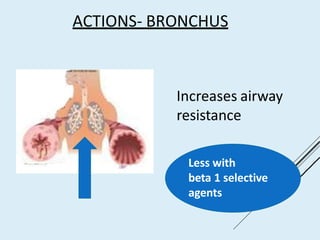
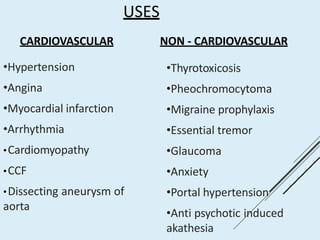
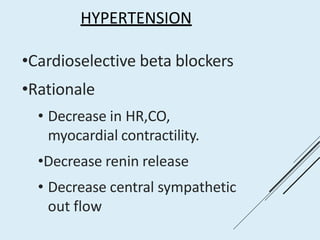
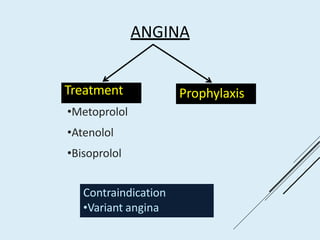
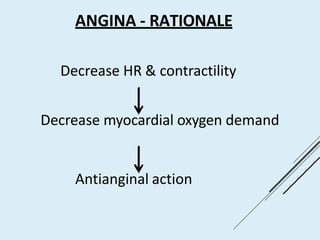
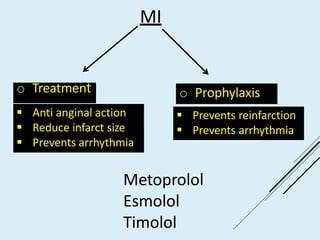
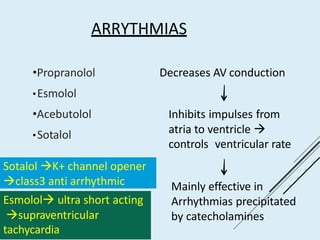
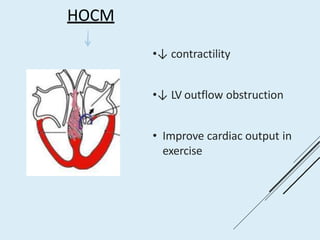
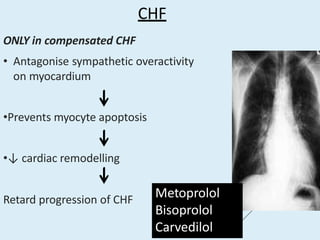
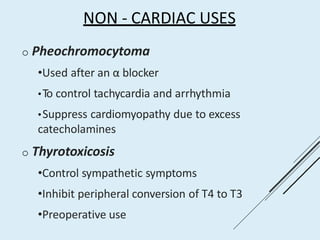
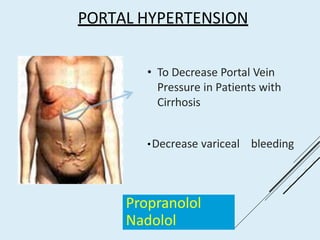
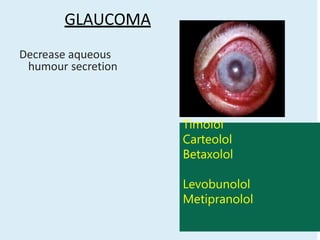
Beta blockers work by antagonizing beta receptors, inhibiting the stimulatory effects of catecholamines. They are classified based on receptor selectivity as non-selective, selective beta-1 agents, or mixed alpha/beta blockers. Common uses include hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, migraine prevention, and anxiety. Adverse effects include bradycardia, hypotension, bronchospasm, hypoglycemia, and fatigue. Contraindications include severe bradycardia, heart failure, and asthma. Overdose causes extended pharmacological effects that are treated with atropine or glucagon.