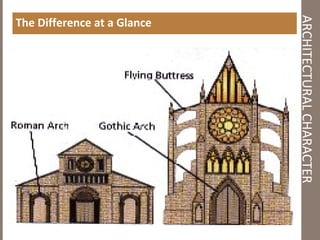
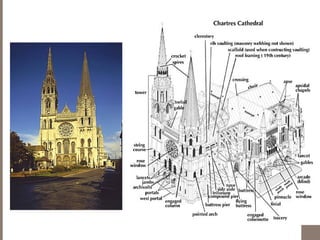
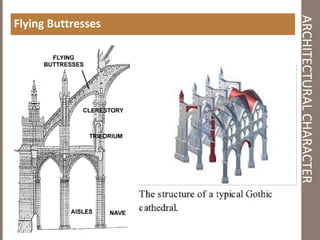
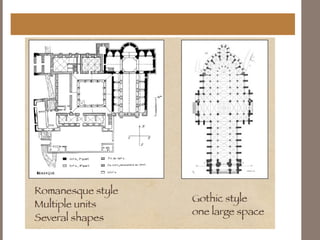
Gothic architecture originated in 12th century France and lasted into the 16th century. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, which allowed for taller buildings with larger windows and more light. Gothic architecture was used most prominently in cathedrals and churches across Europe, emphasizing verticality and light through tall spires and towers.