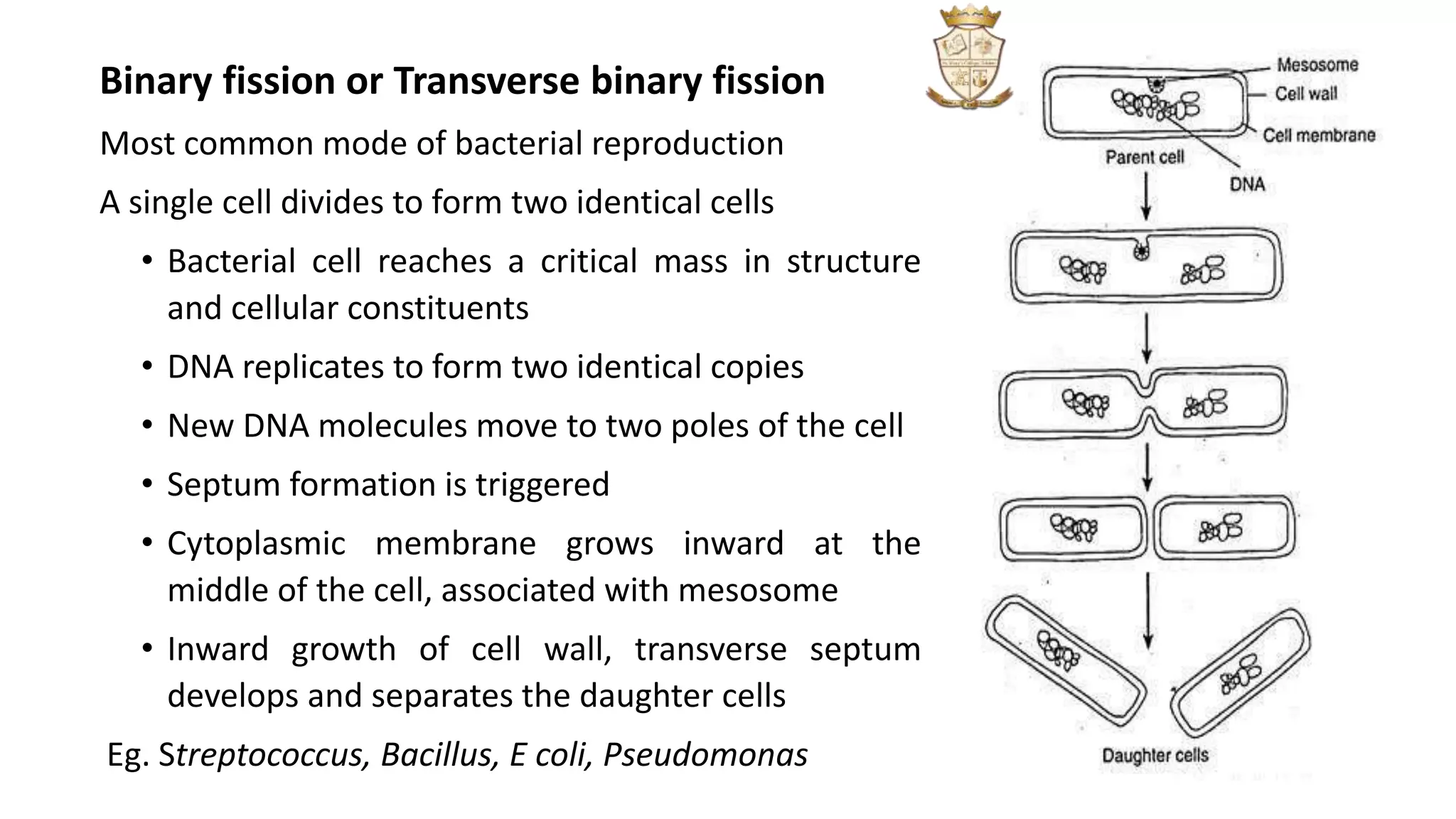
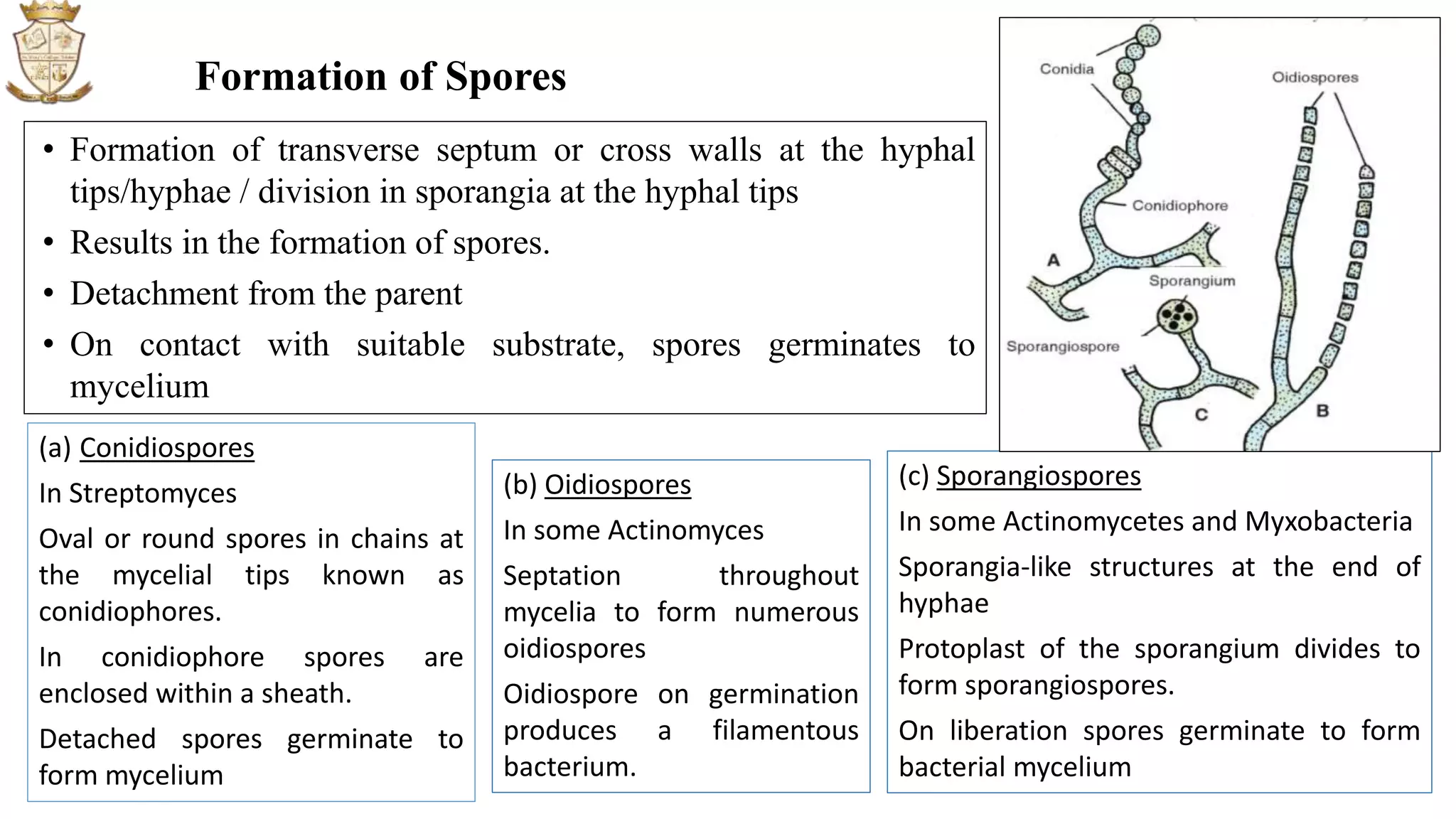
Bacteria reproduce asexually through four main modes: binary fission, budding, fragmentation, and sporulation. Binary fission, the most common mode, involves a single cell dividing into two identical daughter cells. Budding occurs when a small protuberance forms on the parent cell and eventually separates into a new cell. Fragmentation involves the parent cell breaking into multiple fragments that each develop into new bacteria. Sporulation is the formation of spores, such as conidiospores or sporangiospores, which detach and germinate into new mycelium under suitable conditions. Examples of each mode of reproduction are provided.