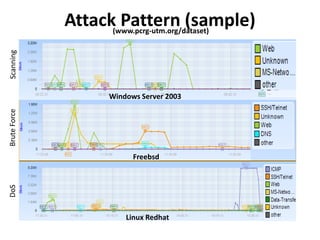
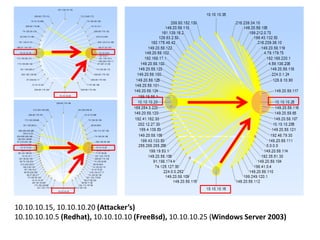
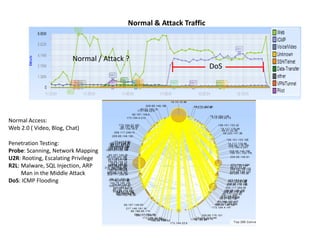
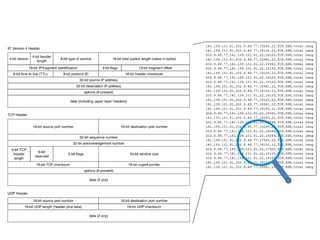
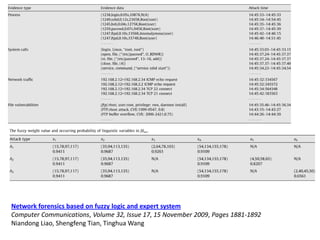
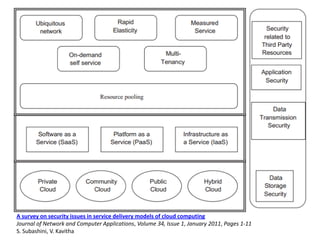
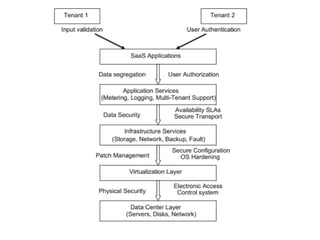
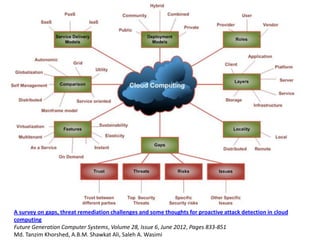
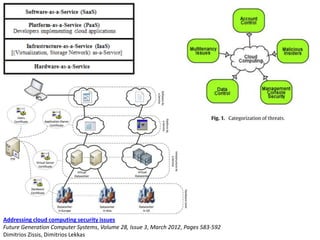
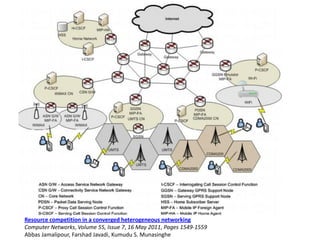
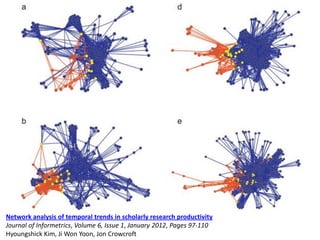
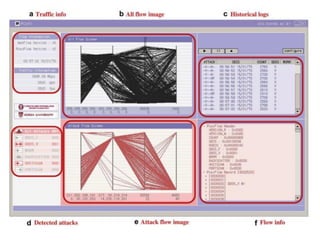
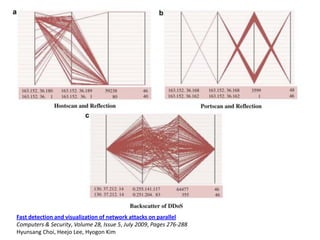
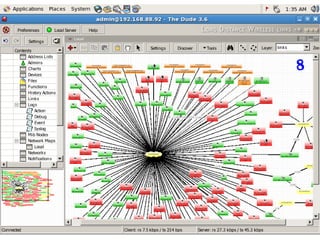
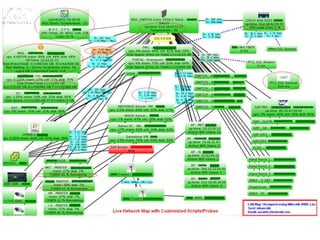
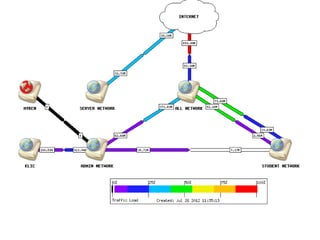
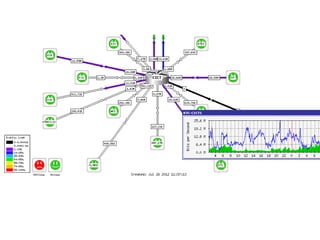
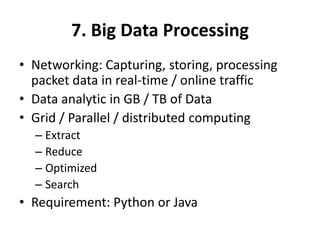
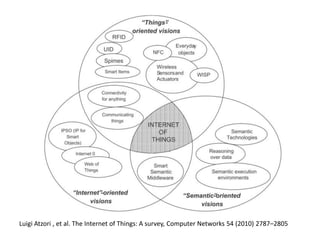
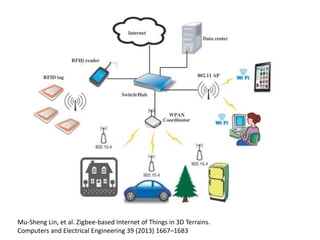
This document discusses several challenges and future trends in network security, including network attacks, forensic investigation, cloud computing, heterogeneous networks, network graphs, network management, big data processing, and the Internet of Things. It provides examples of existing research and identifies opportunities for new research in tools and methods for defense, data analysis, clustering/classification, security mechanisms, privacy, quality of service, monitoring, and data processing in these domains.