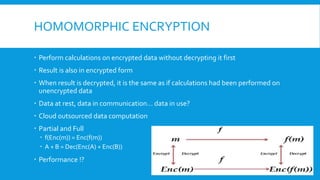
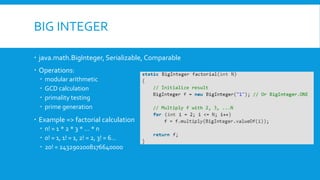
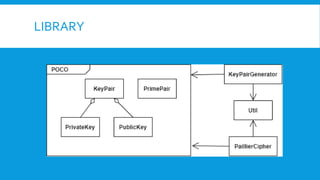
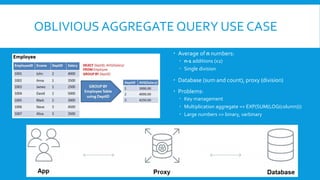
The document discusses the Paillier cryptosystem, a homomorphic encryption method allowing calculations on encrypted data while preserving the encrypted form of results. It covers its basic properties, key generation, encryption, and decryption processes, alongside its application in secure cloud computation and database queries. Additionally, it raises considerations regarding key management and performance of algorithms involved.