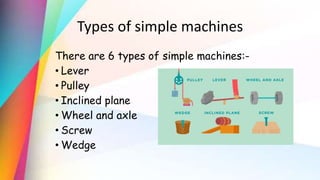
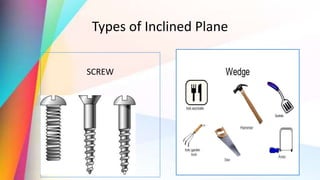
Force can push or pull objects and cause them to move, stop, change speed or direction. Gravity and friction are two main types of forces. Gravity pulls objects toward the center of Earth while friction resists the motion of objects. Simple machines like levers, pulleys, inclined planes and wheels make work easier by reducing the amount of force needed. Different forms of energy include light, heat, sound, electrical and various natural resources like solar, wind and hydro energy which are used to power homes and generate electricity.