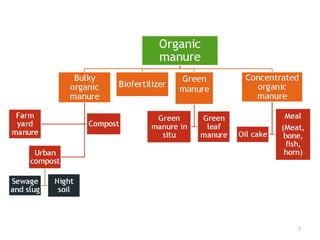
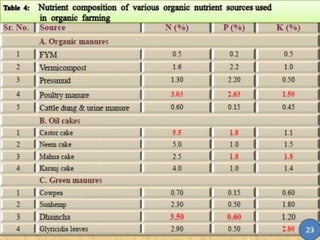
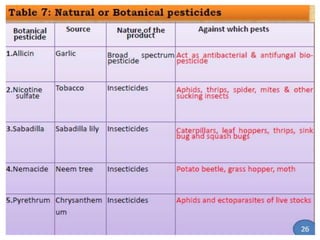
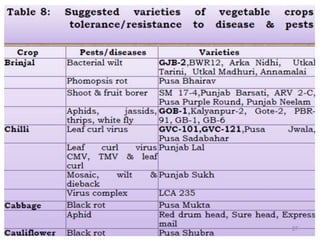
The document discusses the reasons for and principles of organic farming. It notes that conventional farming practices have led to a decline in soil quality, increase in pests, and threats to health and biodiversity. Organic farming aims to maintain healthy soil and use biological nutrients and non-chemical pest and weed management. It is more sustainable but production can be lower and nutrient release slower. Principles include using organic manures and composts produced from various waste materials and crop residues through natural decomposition processes.