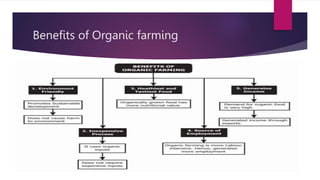
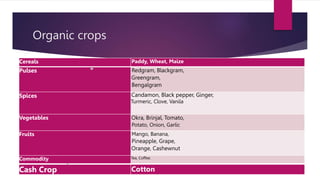
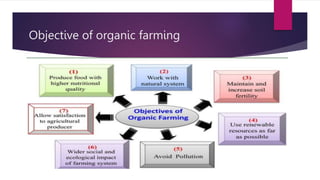
Organic farming, founded by North Bourne in the 1940s, is a cultivation method avoiding synthetic chemicals, aiming to restore ecological balance and sustainable practices. It is guided by four principles: health, ecology, fairness, and care, promoting soil fertility and reducing environmental pollution. The document outlines organic farming types, advantages and disadvantages, crops suitable for organic farming, and emphasizes its necessity for sustainable agriculture.