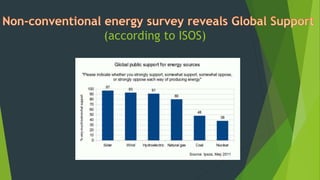
India ranked sixth in the world for total energy consumption. While India has significantly increased its installed power capacity, it is still not sufficient to meet growing demand. This growing demand and limited fossil fuel resources mean non-conventional and renewable sources of energy are important for India's future energy needs. The Indian government plans to increase renewable energy capacity to 175 gigawatts by 2022, including significant additions of solar and wind energy. Renewable sources like solar, wind, hydro, and biomass accounted for about 16% of global energy consumption and are growing rapidly due to their environmental and financial benefits compared to fossil fuels.