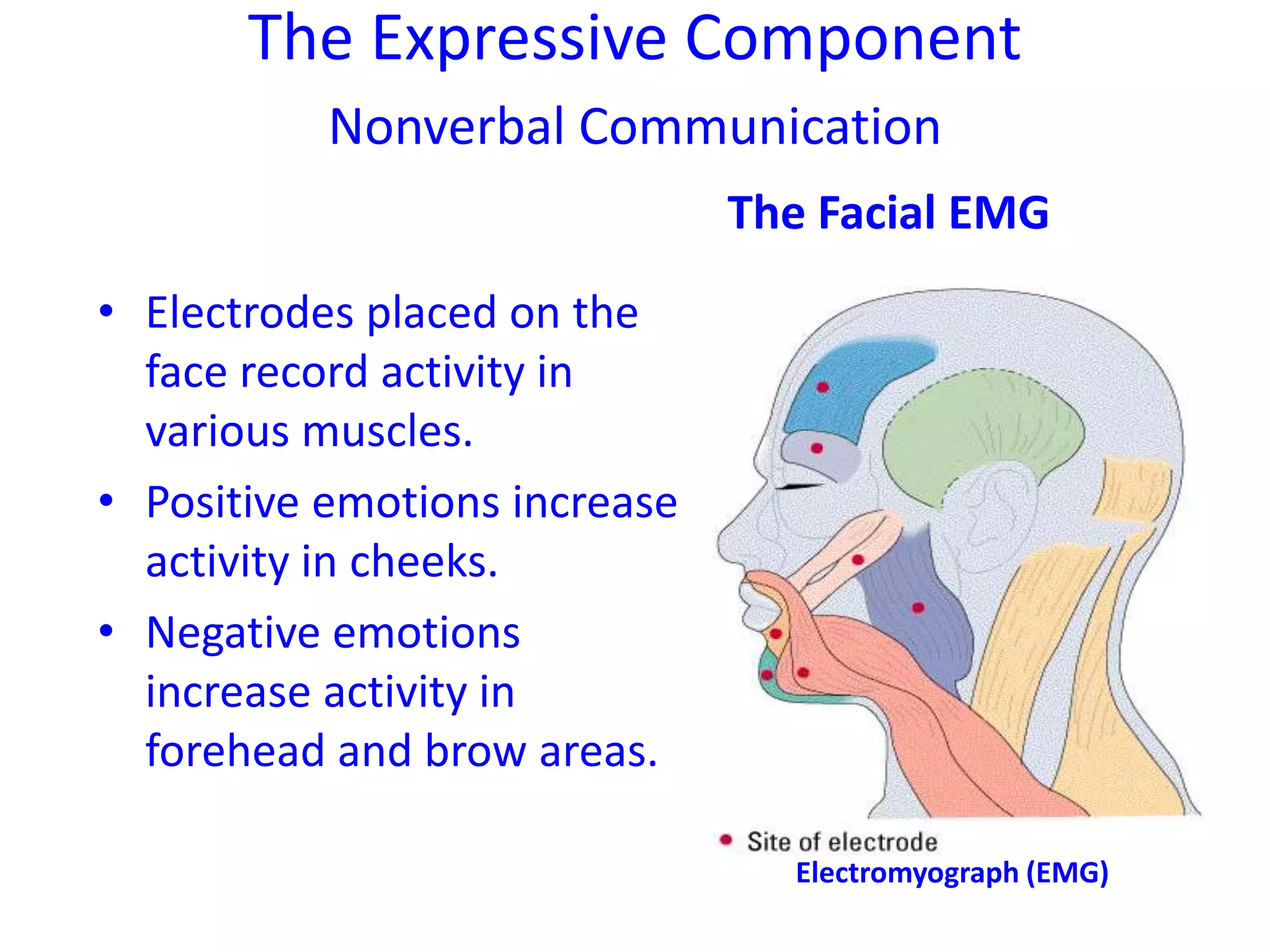
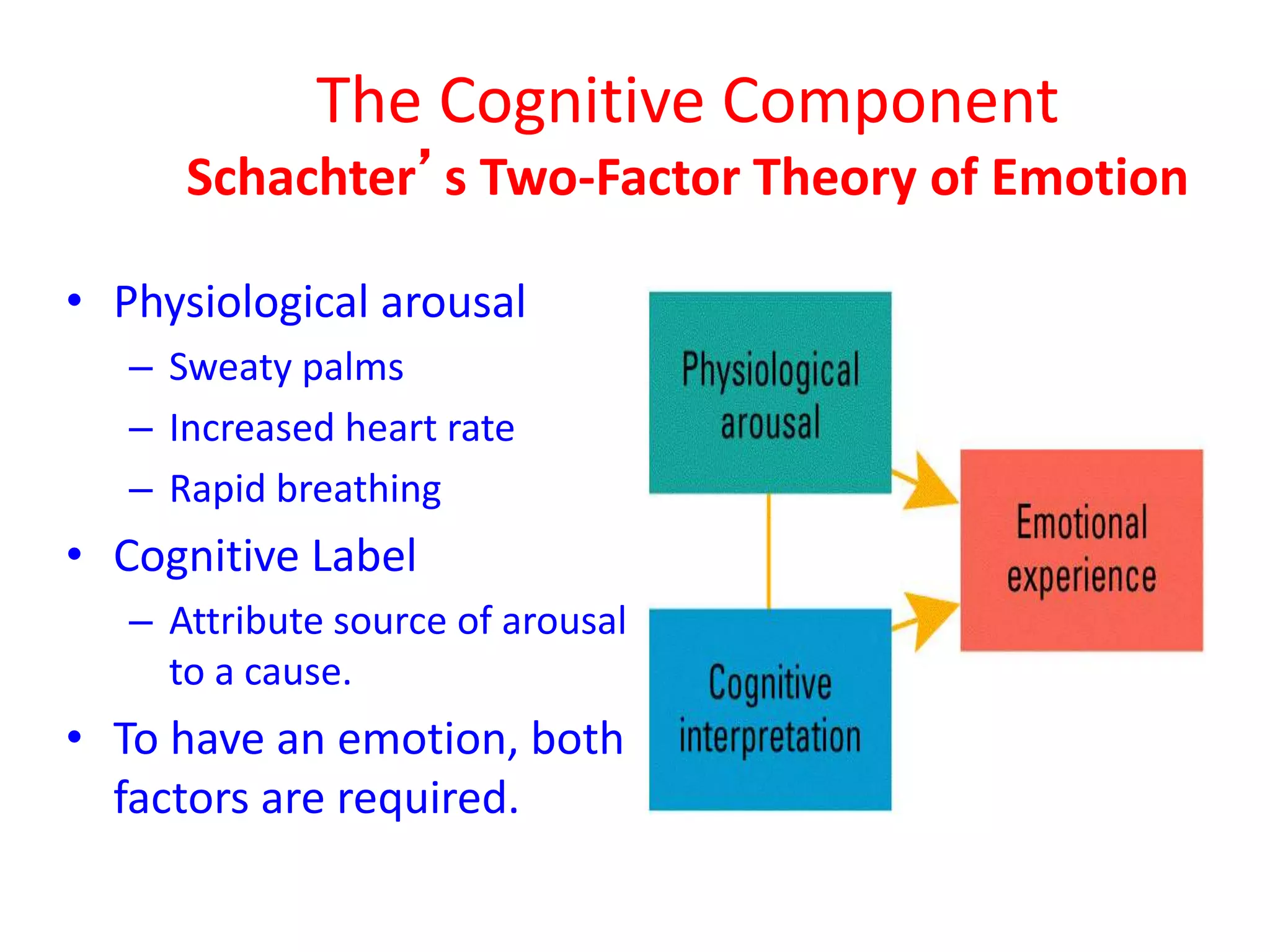
There are three components of emotion: physiological, expressive, and cognitive. The physiological component involves arousal in the body and brain areas involved in emotions. The expressive component is the nonverbal expression of emotions through facial expressions and body language. The cognitive component involves how people interpret and label their physiological arousal and emotional experiences.