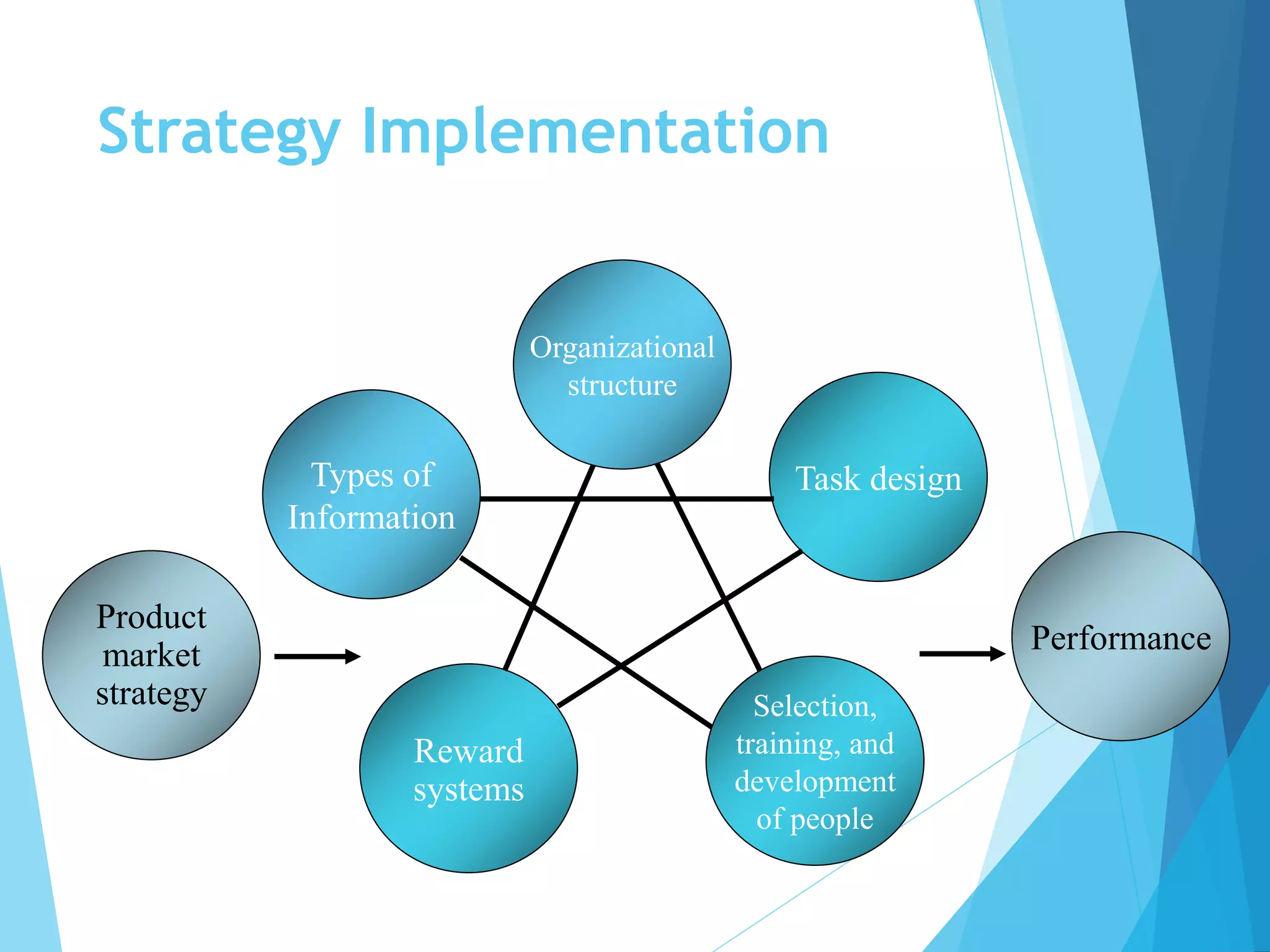
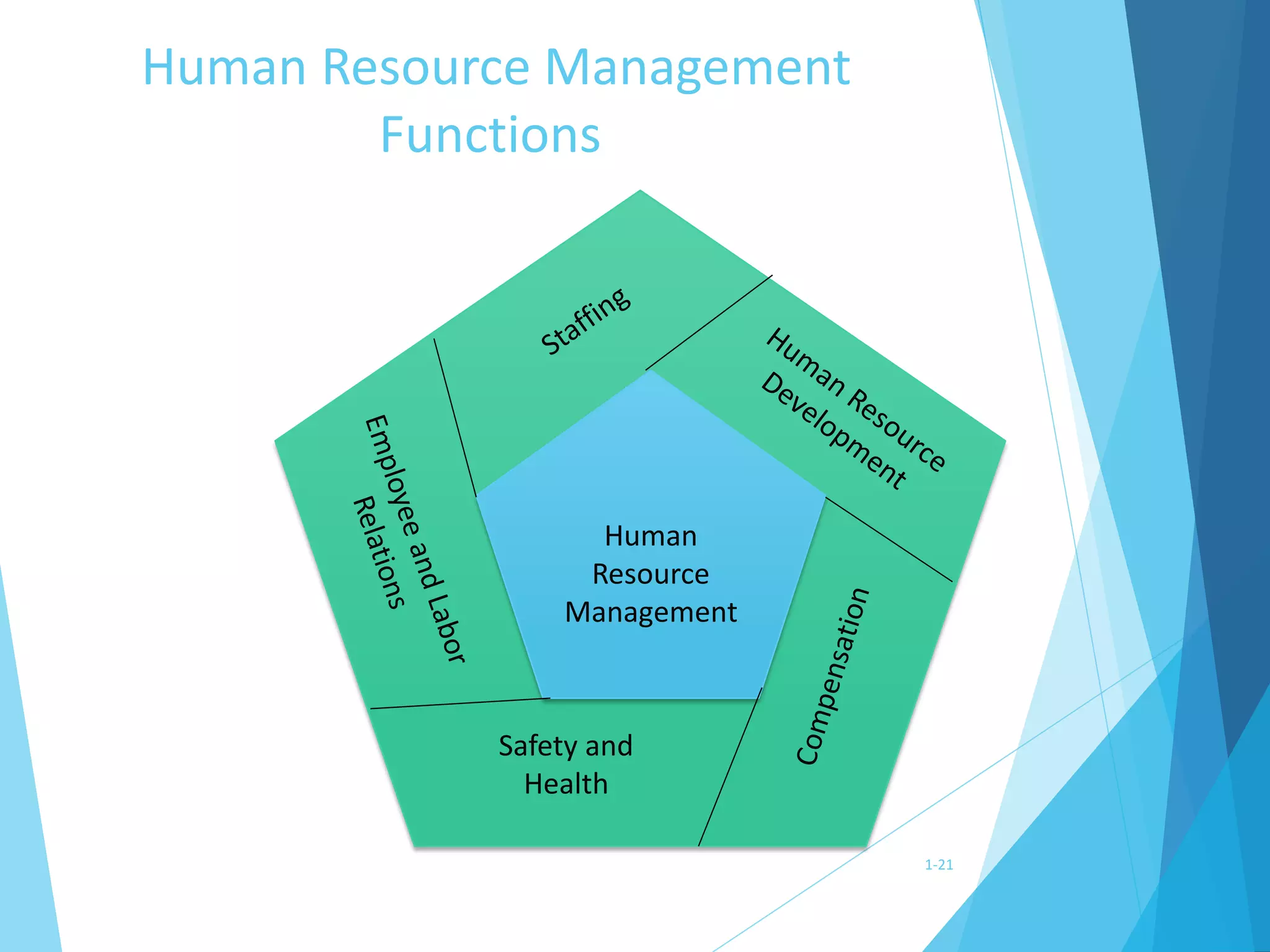
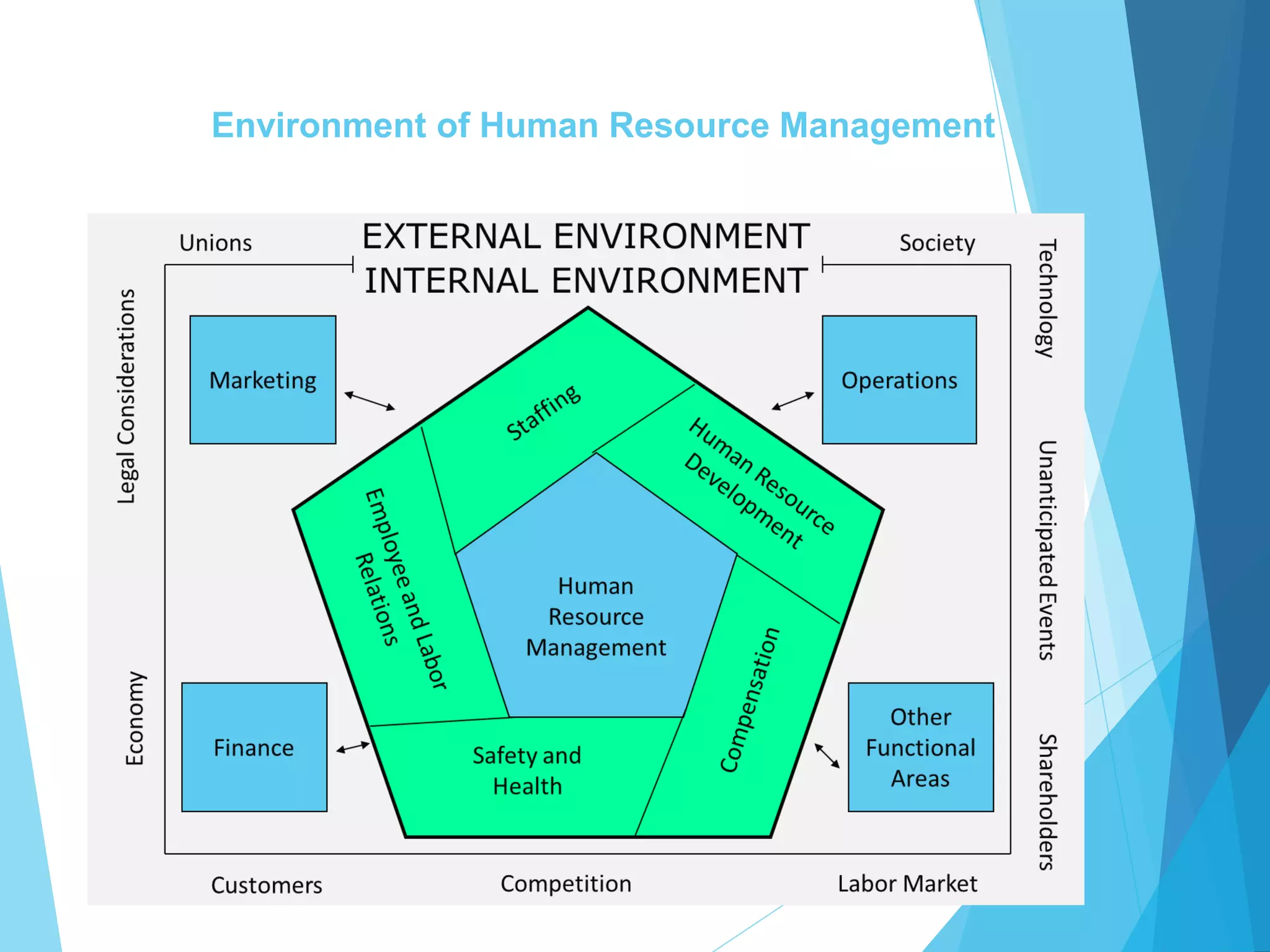
This document discusses various perspectives on strategy and strategic human resource management. It provides definitions of strategy from several scholars, such as Mintzberg, Quinn and Purcell. It also defines strategic management and strategic HRM. The document outlines different types of strategies, including business, operations and resource strategies. It discusses the role of HR in strategy formulation and implementation. Finally, it presents models of strategic HRM and discusses advantages and disadvantages of taking a strategic approach to HRM.