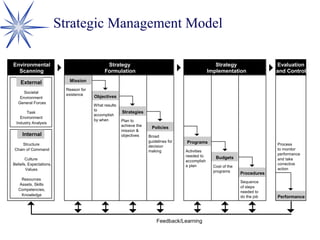
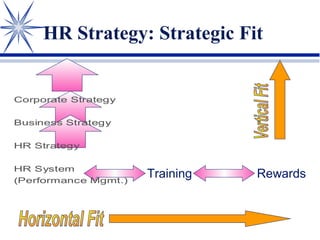
The document discusses strategic human resource management (HRM). It defines strategic HRM as ensuring the organization has skilled, engaged employees to achieve competitive advantage. The three key propositions of strategic HRM are that human capital plays a strategic role, HR strategies should integrate with business plans, and individual HR strategies should cohere. The roles of HR managers include translating vision into meaningful formats, acting as change agents and strategic partners. Strategic HRM involves environmental scanning, strategy formulation, implementation, evaluation and control. The goals are to enhance organizational performance and have HR proactively participate in strategic decision making.