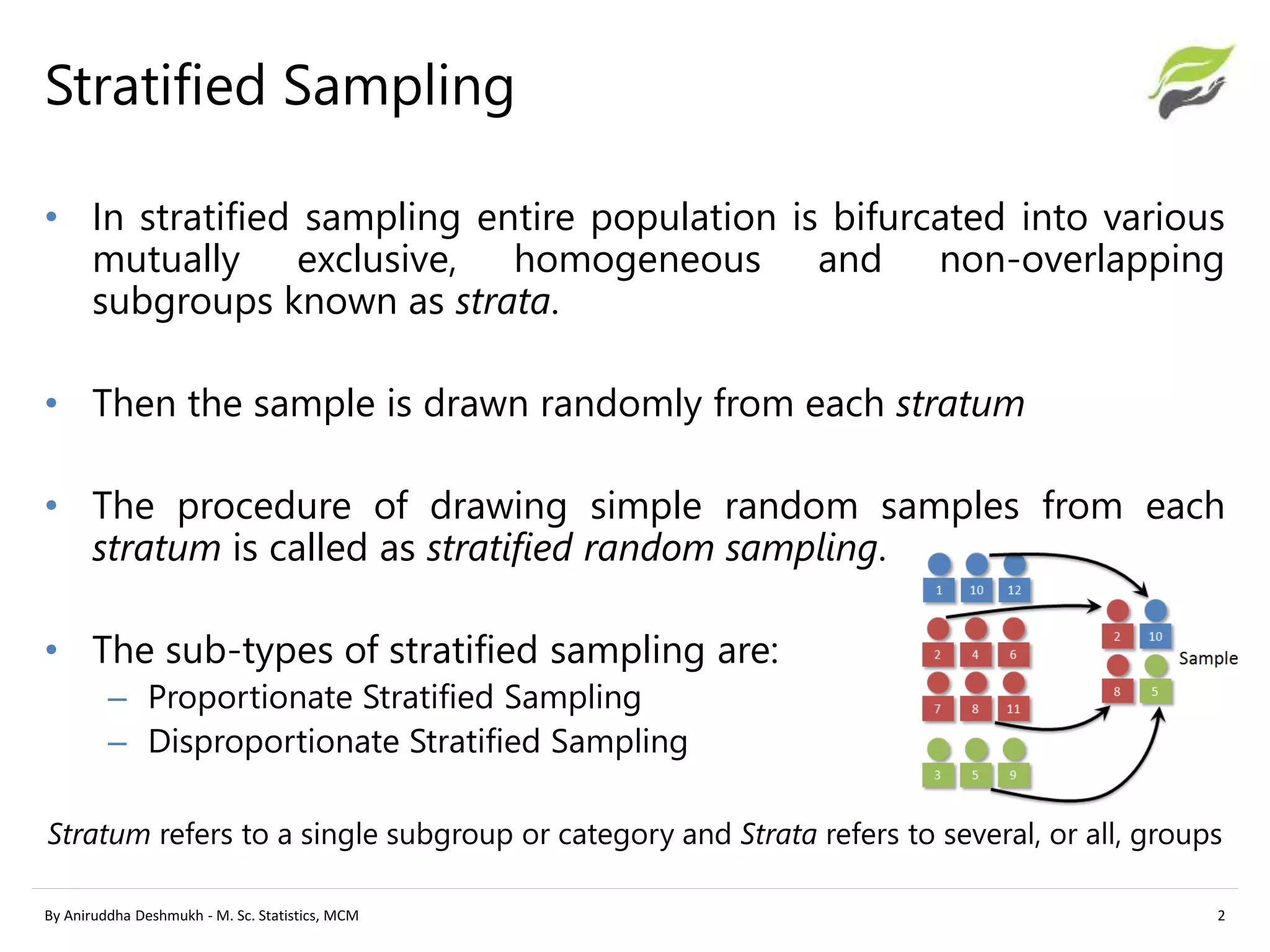
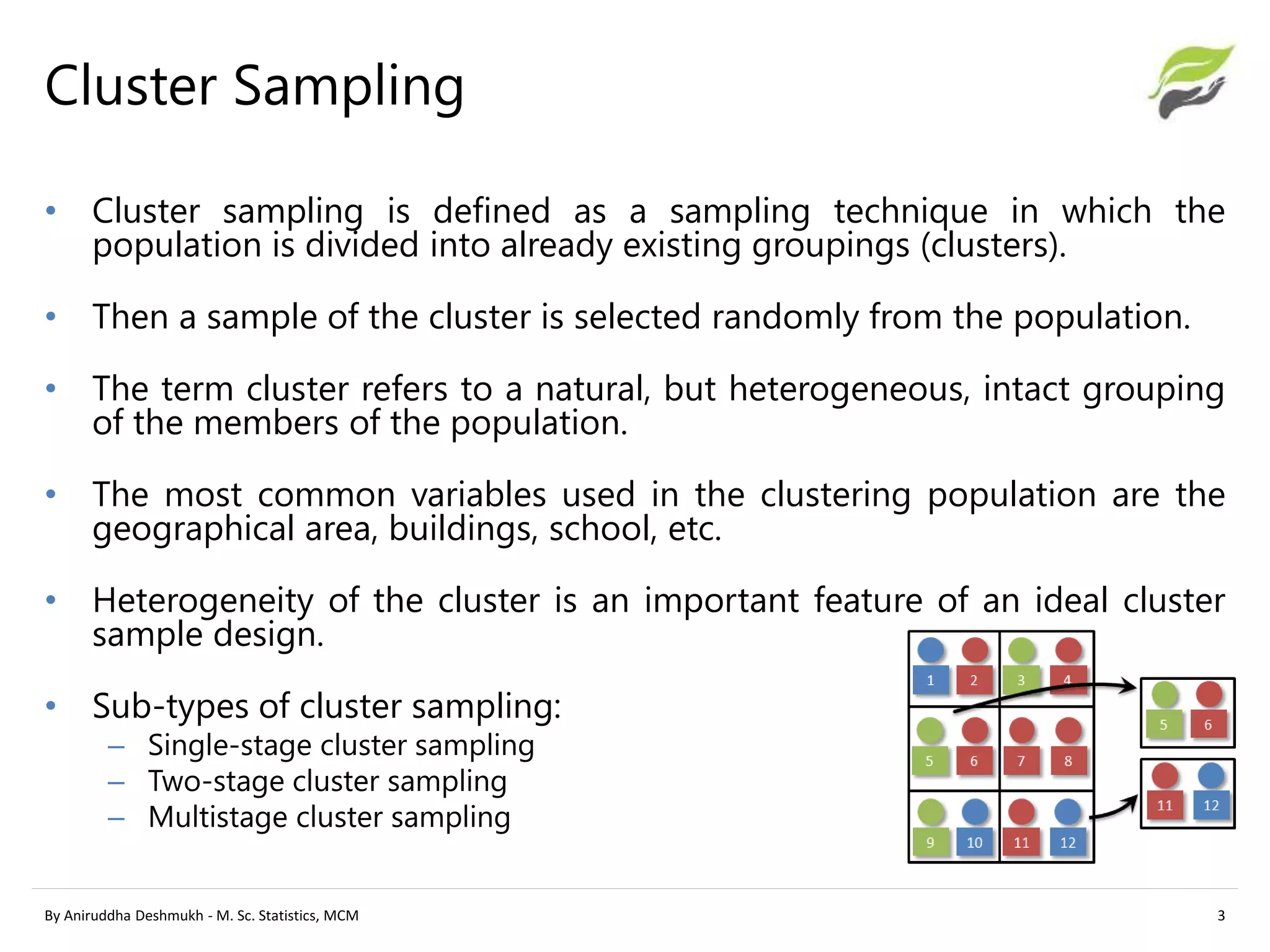
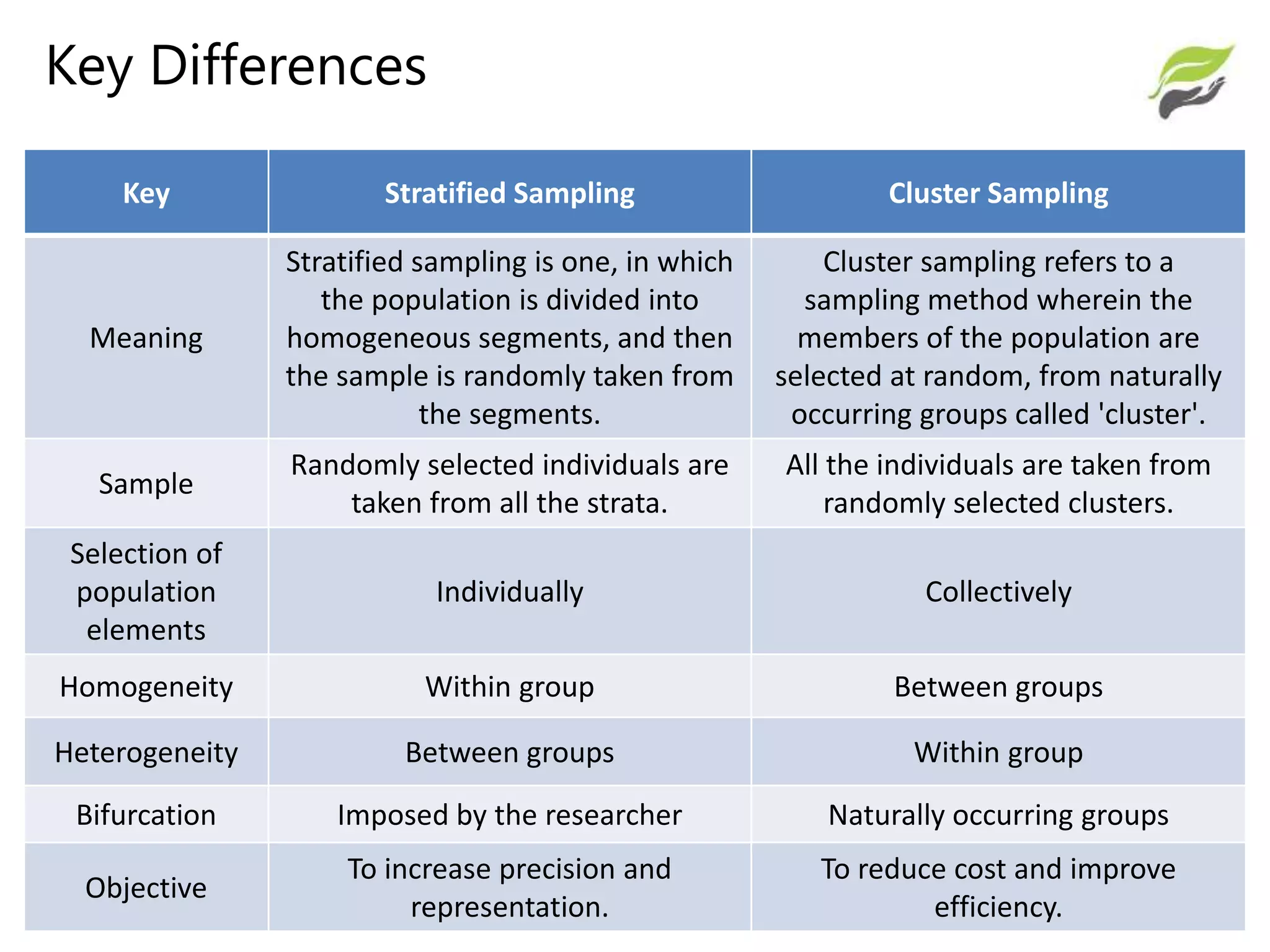
The document compares stratified sampling and cluster sampling, outlining their definitions and methodologies. Stratified sampling involves dividing a population into homogeneous subgroups and sampling from each, while cluster sampling selects entire existing groups at random. Key differences include efficiency, cost, and the time required for sampling, with stratified sampling aiming for precision and cluster sampling focusing on cost efficiency.