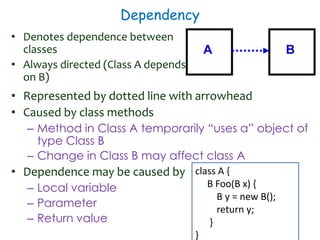
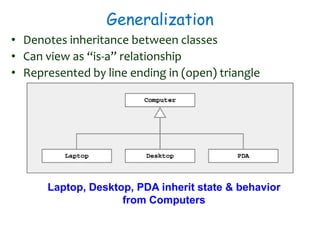
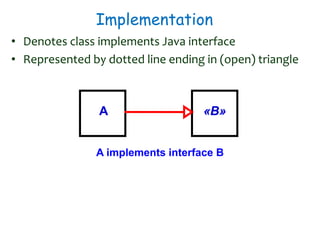
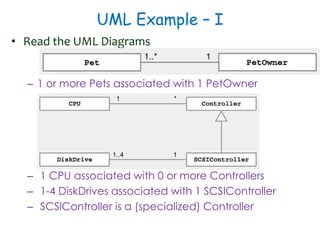
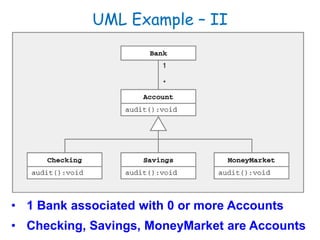
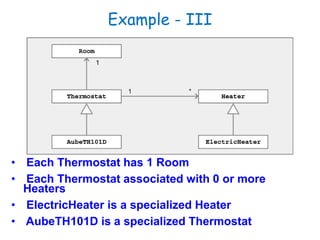
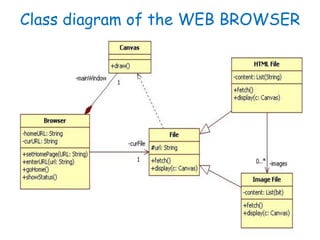
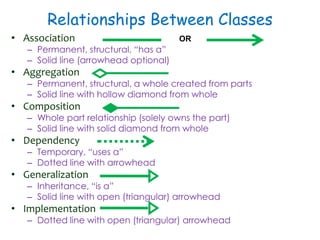
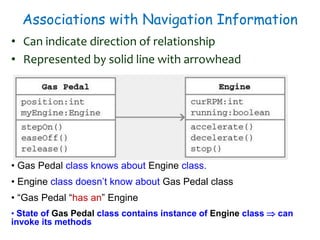
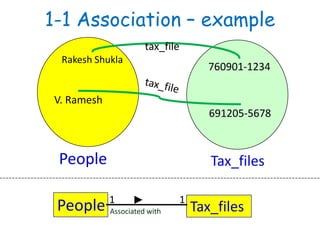
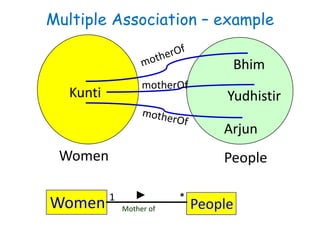
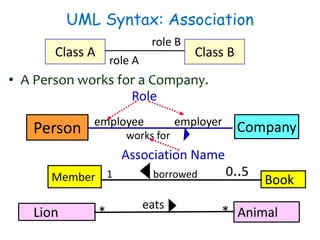
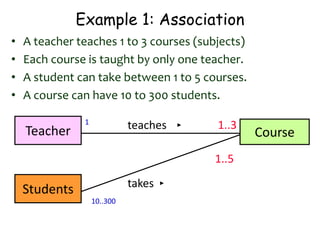
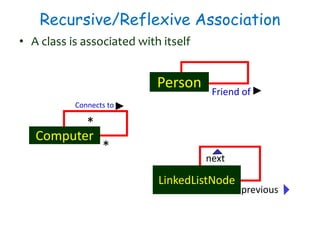
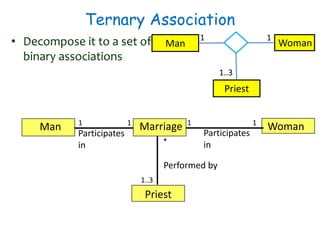
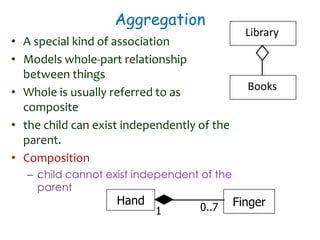
The document discusses UML class diagrams and their components. It defines a class diagram as representing entities with common features as rectangles divided into compartments for the class name, attributes, and operations. It provides examples of how different relationships like association, aggregation, and generalization are depicted. Key points include that association represents a "has-a" relationship, aggregation a whole-part relationship where parts can exist independently, and generalization an "is-a" relationship of inheritance.


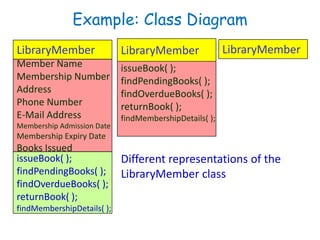
![Class Diagram
• Entities with common features, i.e.
attributes and operations.
• Represented as solid outline rectangle
with compartments for name, attributes,
and operations.
• Attribute and operation compartments
are optional depending on the purpose of
a diagram.
Window
size: Size
visibility: boolean
display()
hide()
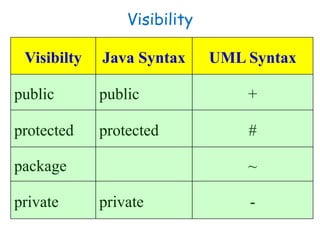
• Java Syntax UML Syntax
• Date birthday Birthday:Date
• Public int duration = 100 +duration:int = 100
• Private Student students[MAX_Size]
Students[MAX_Size]:Student](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sepase5-171112030501/85/Software-Engineering-UML-class-diagrams-3-320.jpg)
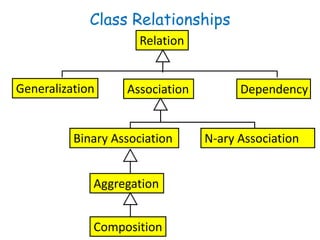

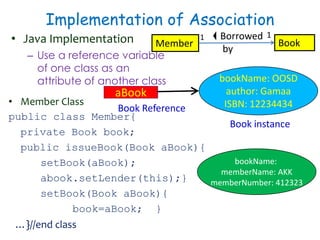

![Aggregation Implementation
public class Car{
private Wheel wheels[4];
public Car (Wheel w[4]){
wheels[0] = w[0];
wheels[1] = w[1];
wheels[2] = w[2];
wheels[3] = w[3];
}
}
Car Wheel1 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sepase5-171112030501/85/Software-Engineering-UML-class-diagrams-21-320.jpg)
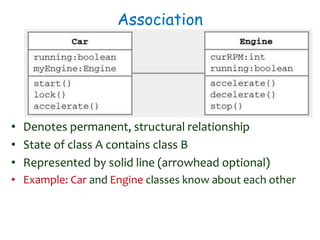
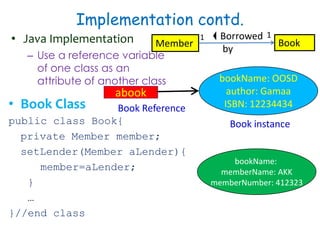
![Composition Implementation
public class Car{
private Wheel wheels[4];
public Car (){
wheels[0] = new Wheel();
wheels[1] = new Wheel();
wheels[2] = new Wheel();
wheels[3] = new Wheel();
}
}
Car Wheel1 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sepase5-171112030501/85/Software-Engineering-UML-class-diagrams-22-320.jpg)