More Related Content
Similar to Gram_positive___Ch 21.ppt (20)
More from AhmedAlshwahin (7)
Gram_positive___Ch 21.ppt
- 1. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
1
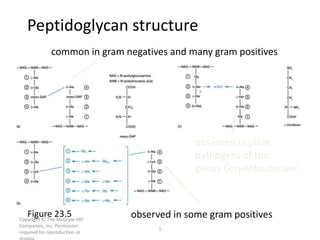
Figure 23.5
common in gram negatives and many gram positives
observed in some gram positives
observed in plant
pathogens of the
genus Corynebacterium
Peptidoglycan structure
- 2. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
2
Genus Micrococcus
• aerobic, catalase-positive rods that occur in
pairs, tetrads or irregular clusters
• usually non motile
• often pigmented yellow, orange or red
• widepsread in soil, water, and on human skin
• does not undergo morphological
differentiation
- 3. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
3
FamilyStaphylococcaceae
• contains 4 genera
• facultatively anaerobic, nonmotile, gram-
positive cocci
• usually form irregular clusters
• normally associated with warm blooded
animals in skin, skin glands and mucous
membranes
- 4. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
4
Figure 23.13
- 5. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
5
Pathogenic Staphylococcus
• Staphylococcus epidermidis
– common skin resident
– sometimes responsible for endocarditis and for
infections of patients with lowered resistance
• e.g., wound infections, surgical infections, and
urinary tract infections
- 6. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
6
Antibiotic Resistant Staphylococci
• resistance to methicillin
– Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
(MRSA)
• obtained from genetic elements received from other
organisms
• resistance to vancomycin, the “drug of last
resort”
- 7. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
7
Staphylococcus aureus
• produces the virulence factor coagulase
– causes blood plasma to clot
• produces a-hemolysin
– toxin which lyses cells
• major cause of food poisoning
– recently >1,000 school children in Texas had
staphylococcal food poisoning caused by eating
improperly handled chicken
• found on nasal membranes and skin, and in
gastrointestinal and urinary tracts
- 8. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
8
nonmotile
facultative and
strict anaerobes
homolactic
fermentation
Lancefield grouping system –
based on polysaccharide and
techoic acid antigens in cell wall
or between cell wall and plasma
membrane
Streptococci
- 9. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
9
a-hemolysis
– incomplete lysis of red blood cells
– seen as greenish zone around colony on blood agar
b-hemolysis
– complete lysis of red blood cells
– seen as clear zone around colony on blood agar
Table 23.5
- 10. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
10
Figure 23.17
- 11. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
11
Enterococci and lactococci
- 12. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
12
Figure 23.18
- 13. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
13
Important streptococci, enterococci,
and lactococci
• Streptococcus pyogenes – streptococcal sore throat,
acute glomerulonephritis, and rheumatic fever
• Streptococcus pneumoniae – lobar pneumonia and
otitis media
• Streptococcus mutans – dental caries
• Enterococcus faecalis – opportunistic pathogen
(urinary tract infections and endocarditis)
• Lactococcus lactis – production of buttermilk and
cheese
- 14. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
14
Family Leuconostocaceae
Genus Leuconostoc
• facultative, gram-positive cocci
• carry out heterolactic fermentation via
phosphoketolase pathway
• carry out heterolactic fermentation using
phosphoketolase pathway
• isolated from plants, silage and milk
• play a role in food spoilage
- 15. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
15
Figure 23.15
- 16. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
16
Phospho-
ketolase
pathway
Figure 23.16
- 17. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
17
Importance of Leuconostoc
• wine production
• production of sauerkraut and pickles
• production of buttermilk, butter, and
cheese
• synthesis of dextrans (L. mesenteroides)
• involved in food spoilage
– tolerate high sugar concentrations
– grow in heavy syrup
- 18. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
18
Class Bacilli
• large variety of gram-positive
organisms
• contains two orders, Bacillales and
Lactobacillales , 17 families and over
70 genera
- 19. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
19
Bacillus subtilis
• type species
• used as model organism for cellular
differentiation, division and other
processes
• its genome was one of first to be
sequenced
• has families of genes expanded by gene
duplication
• 10 integrated prophages or remnants of
prophages
• various species produce antibiotics
- 20. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
20
Other important species of Bacillus
• B. cereus – food poisoning
• B. anthracis – anthrax
• B. thuringiensis and B. sphaericus – used as
insecticide
– parasporal body – solid protein crystal that
contains toxin
- 21. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
21
Figure 23.9
- 22. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
22
parasporal
body
endospore
Figure 23.10 (a)
- 23. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
23
Endospores
– have a complex structure containing a coat,
cortex, and inner spore membrane surrounding
the protoplast
– dipicolinic acid is present
– heat resistant
– dormant and viable for long periods of time
- 24. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
24
Figure 23.6
- 25. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
25
Class Clostridia
• contains three orders and 11 families
- 26. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
26
Genus Clostridium
• over 100 species in distinct phylogenetic
clusters
– in future will probably be divided into several
genera
• fermentative metabolism
– ferment amino acids using Stickland reaction
• oxidation of one amino acid using another as
electron acceptor
– fermentation products responsible for
unpleasant odors associated with putrefaction
- 27. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
27
Important species of Clostridium
• C. botulinum – food spoilage (especially
canned foods); botulism
• C. tetani – tetanus
• C. perfringens – gas gangrene
• C. acetobutylicum – manufacture of
butanol
- 28. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
28
Figure 23.7
- 29. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
29
Desulfotomaculum
• anaerobic
• endospore forming
• reduces sulfate and sulfite to hydrogen sulfide
during anaerobic respiration
• stains gram-negative but in electron
micrographs is seen to have a gram-positive
cell wall
- 30. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
30
Figure 23.8
- 31. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
31
Order Lactobacillales
• also called lactic acid bacteria
• morphologically diverse
– nonsporing
– usually nonmotile
• ferment sugars for energy
– lack cytochromes
– fastidious
• contains several important genera
- 32. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
32
Order Lactobacillales
• largest genus - Lactobacillus
– sometimes coccobacilli
– grow optimally in slightly acidic conditions (pH
4.5 to 6.4)
– carry out either homolactic fermentation (via
glycolytic pathway) or heterolactic
fermentation (via pentose phosphate pathway)
- 33. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
33
Genus Lactobacillus
• widely distributed in nature
– on plant surfaces
– in dairy products, meat, water, sewage, beer,
fruits, and other materials
– normal flora of mouth, intestinal tract, and
vagina
• usually not pathogenic
- 34. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
34
Figure 23.14
- 35. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
35
Importance of lactobacilli
• fermented vegetable products (sauerkraut,
pickles, and silage)
• fermented beverages (beer, wine, juices)
• sour dough bread
• Swiss cheese and other hard cheeses
• yogurt
• sausages
• spoilage of beer, milk, and meat
- 36. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
36
Genus Listeria
• short rods
– motile by peritrichous flagella
• aerobic or facultative
– catalase positive
• common in decaying matter
• e.g., L. monocytogenes – listeriosis
– food-borne disease
- 37. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
37
Genus Caryophanon
• disk-shaped cells
• normal habitat is cow dung
- 38. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
38
Figure 23.12
- 39. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
39
Arthrobacter
• aerobic, catalase-positive rods
• respiratory metabolism
• lysine in peptidoglycan
- 40. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
40
Figure 24.7
- 41. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
41
Suborder Corynebacterineae
• has seven families with many known genera
such as
– Corynebacterium
– Mycobacterium
– Nocardia
- 42. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
42
Corynebacterium
• only genus in Family Corynebacteriaceae
• some are harmless soil and water saprophytes
• many are animal and human pathogens
– e.g., C. diphtheriae - diphtheria
- 43. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
43
• after snapping
division bacteria
often remain
partially attached
resulting in
palisade
arrangements of
cells
Figure 24.9
- 44. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
44
Genus Mycobacterium
• in family Mycobacteriaceae
– straight or slightly curved rods tht sometimes
branch or form filaments
• aerobic and catalase positive
- 45. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
45
Figure 24.10
- 46. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
46
Mycobacterial cell walls
• contain waxes with 60 to 90 carbon mycolic
acids
• acid-fast
– basic fuchsin dye cannot be removed from cell by
acid alcohol treatment
- 47. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
47
Figure 24.11
- 48. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
48
Important species of Mycobacterium
• M. bovis – tuberculosis in cattle and other
ruminants
• M. tuberculosis – tuberculosis in humans
• M. leprae – leprosy
- 49. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill
companies, Inc. Permission
required for reproduction or
49
Genus Actinomyces
• straight or slightly curved rods and slender
filaments with true branching
– may have swollen, clubbed, or clavate ends
• facultative or obligate aerobes
– require CO2 for best growth
• normal flora of mucosal surfaces (especially oral
cavity) of humans and other animals
– e.g., A. bovis – lumpy jaw in cattle
– e.g., A. israeli – most important human pathogen
• actinomycoses – ocular disease and periodontal disease
in humans
- 50. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
50
Figure 24.6