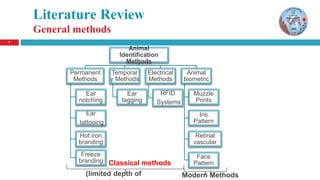
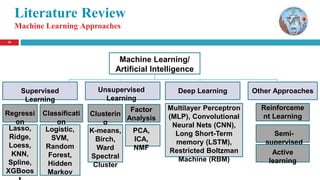
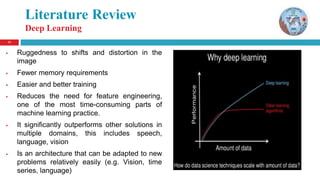
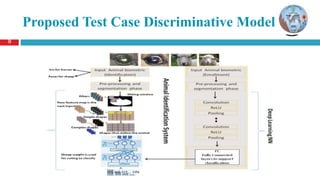
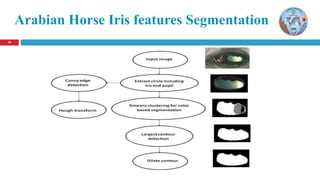
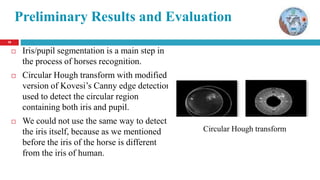
The document discusses a thesis on animal identification using machine learning, focusing on unique biometric methods for identifying Arabian horses and sheep, which traditional methods struggle with due to vulnerabilities. It outlines the problem statement, research objectives, and proposed approaches, particularly the application of deep learning techniques for real-time identification and weight estimation. The research addresses data collection challenges and evaluates performance metrics, aiming to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of animal identification systems.