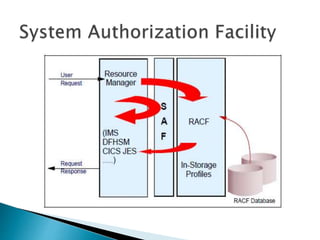
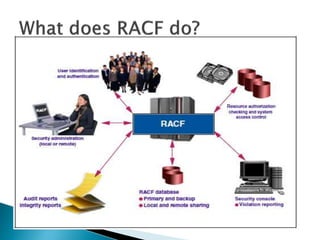
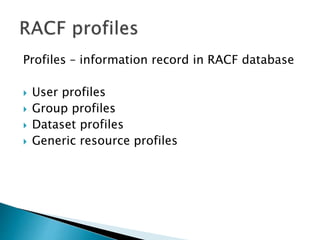
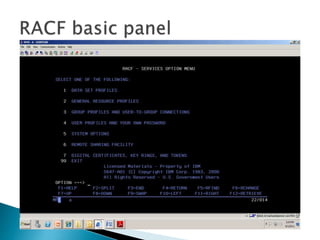
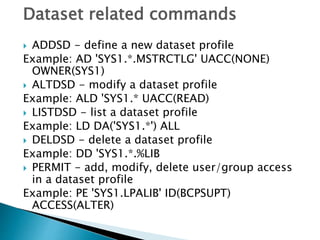
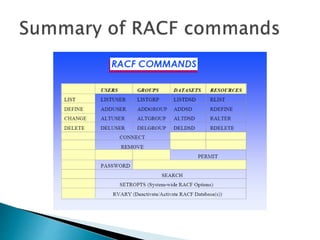
This document provides an overview of RACF (Resource Access Control Facility), an IBM product that controls access to system resources on z/OS. It describes the different types of profiles (user, group, dataset, generic) stored in the RACF database and the commands used to manage them. Authorities like SPECIAL, OPERATIONS, and AUDITOR are assigned to users and groups. RACF enforces access based on these profiles and can revoke or protect access.