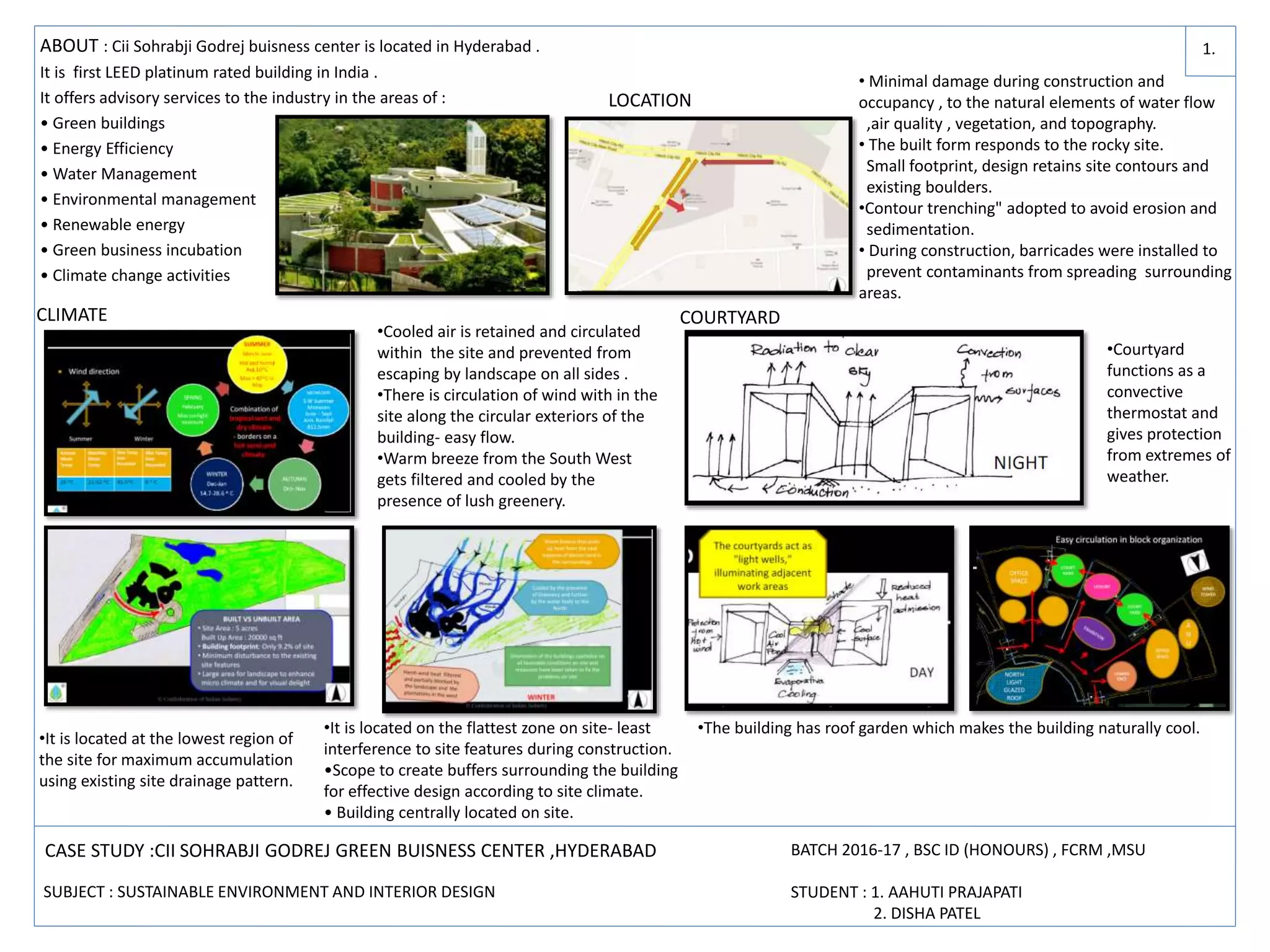
This case study summarizes the CII Sohrabji Godrej Green Business Center in Hyderabad, the first LEED Platinum rated building in India. The three story building was designed and constructed using sustainable practices. It has a small footprint to minimize environmental impact, utilizes natural lighting and ventilation, and incorporates extensive use of recycled and local materials. Rainwater is harvested and recycled water is used to reduce potable water usage by 35%. Landscaping and windcatchers help cool the building naturally and reduce energy needs.