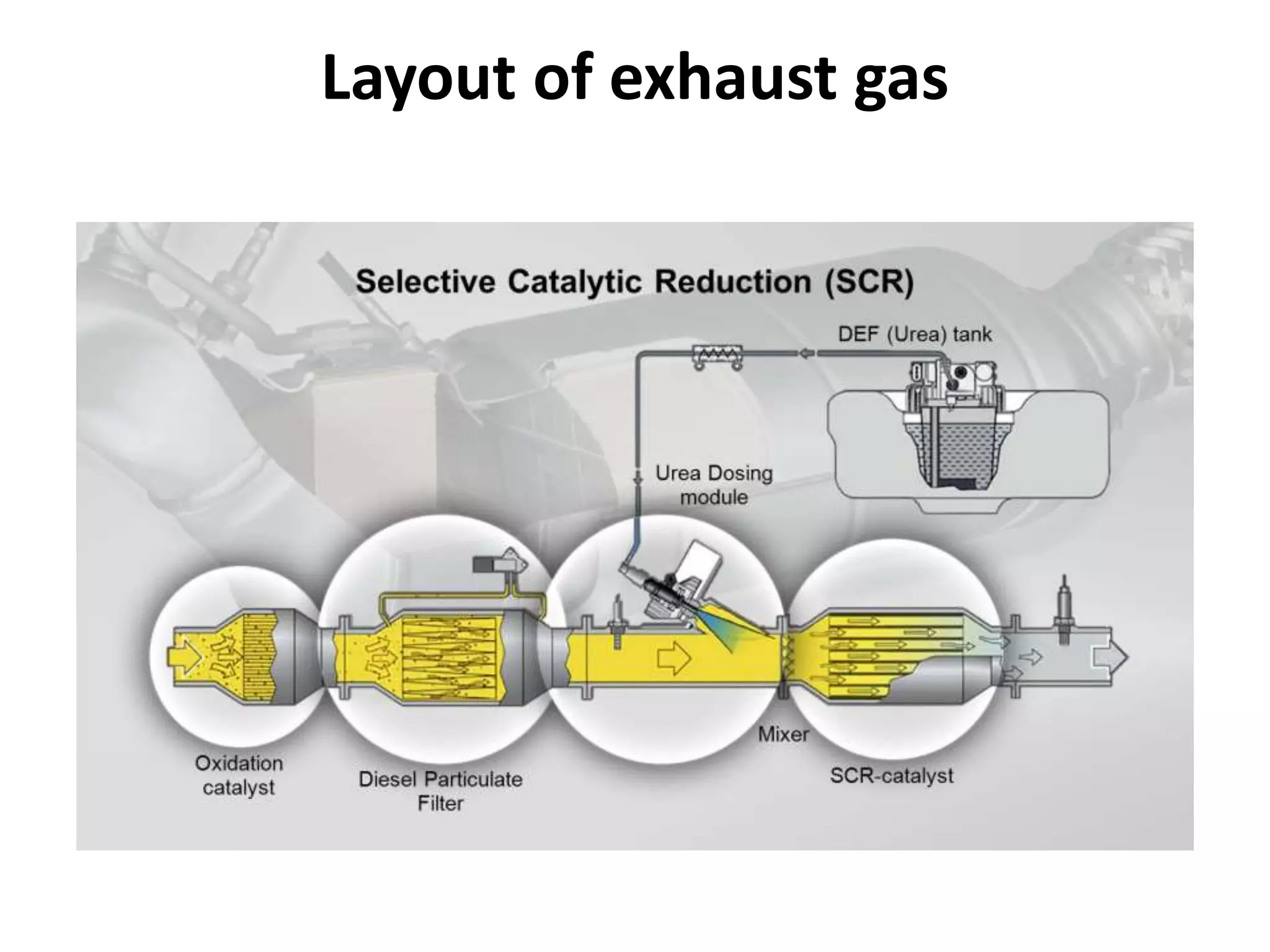
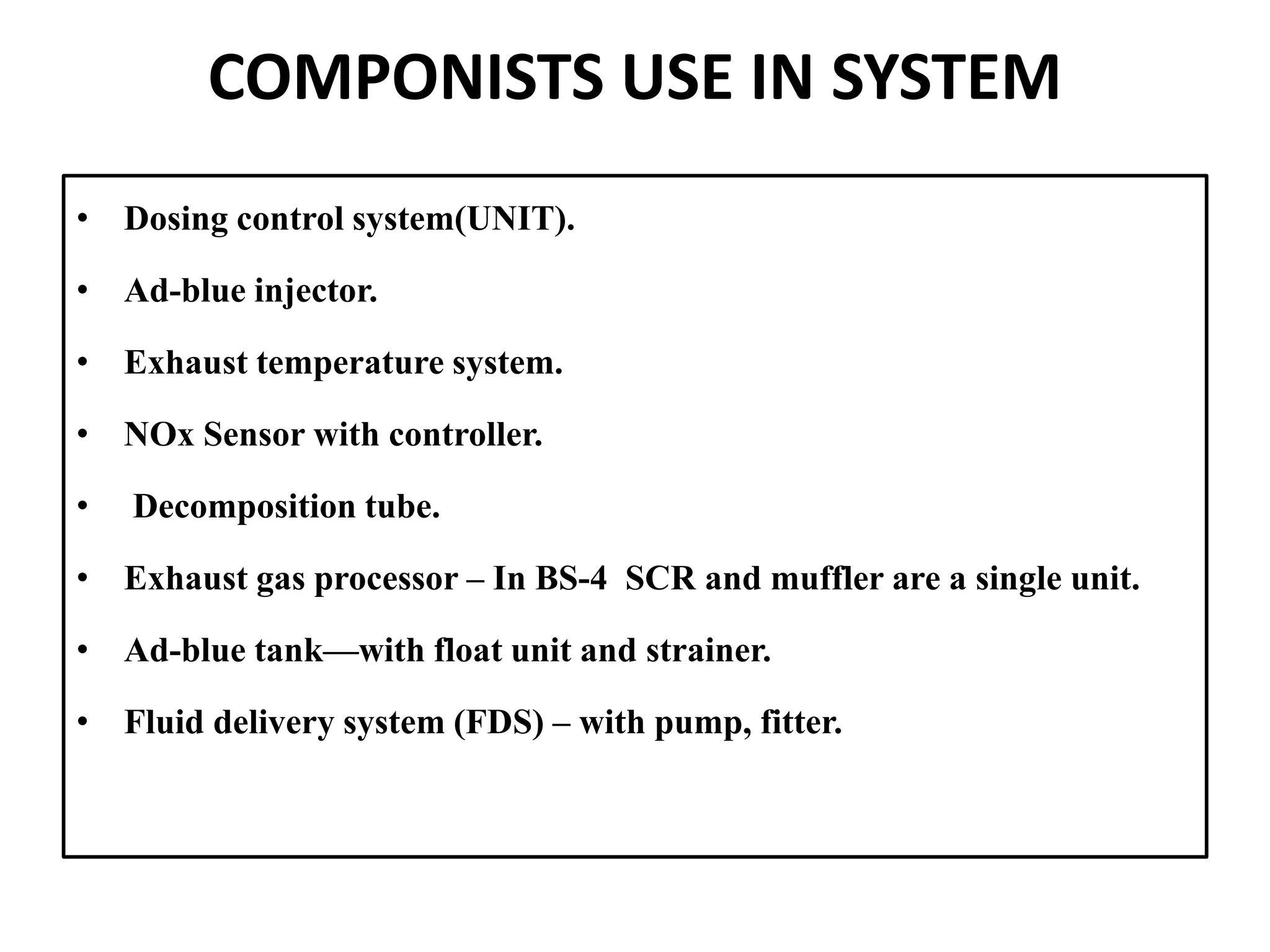
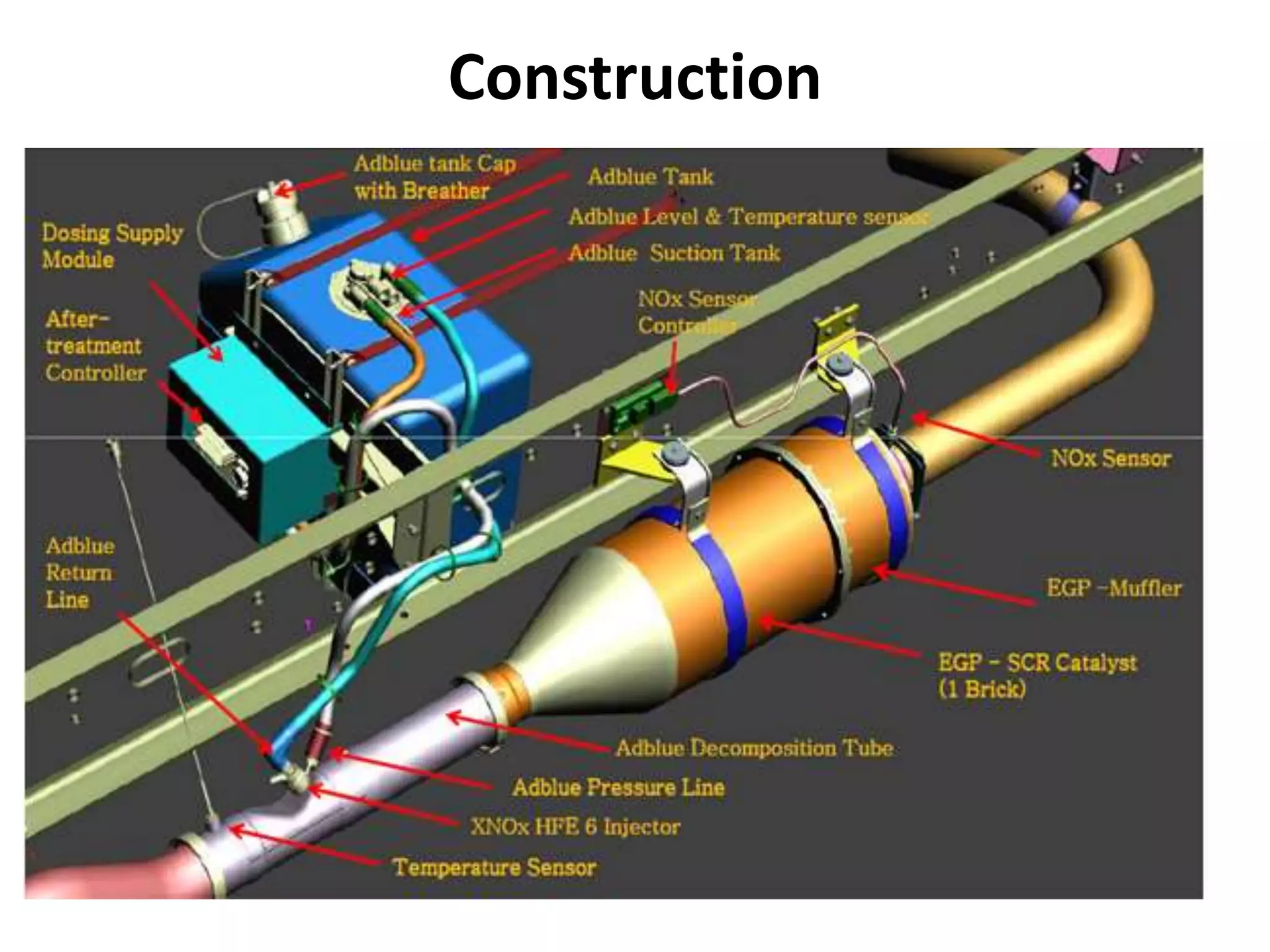
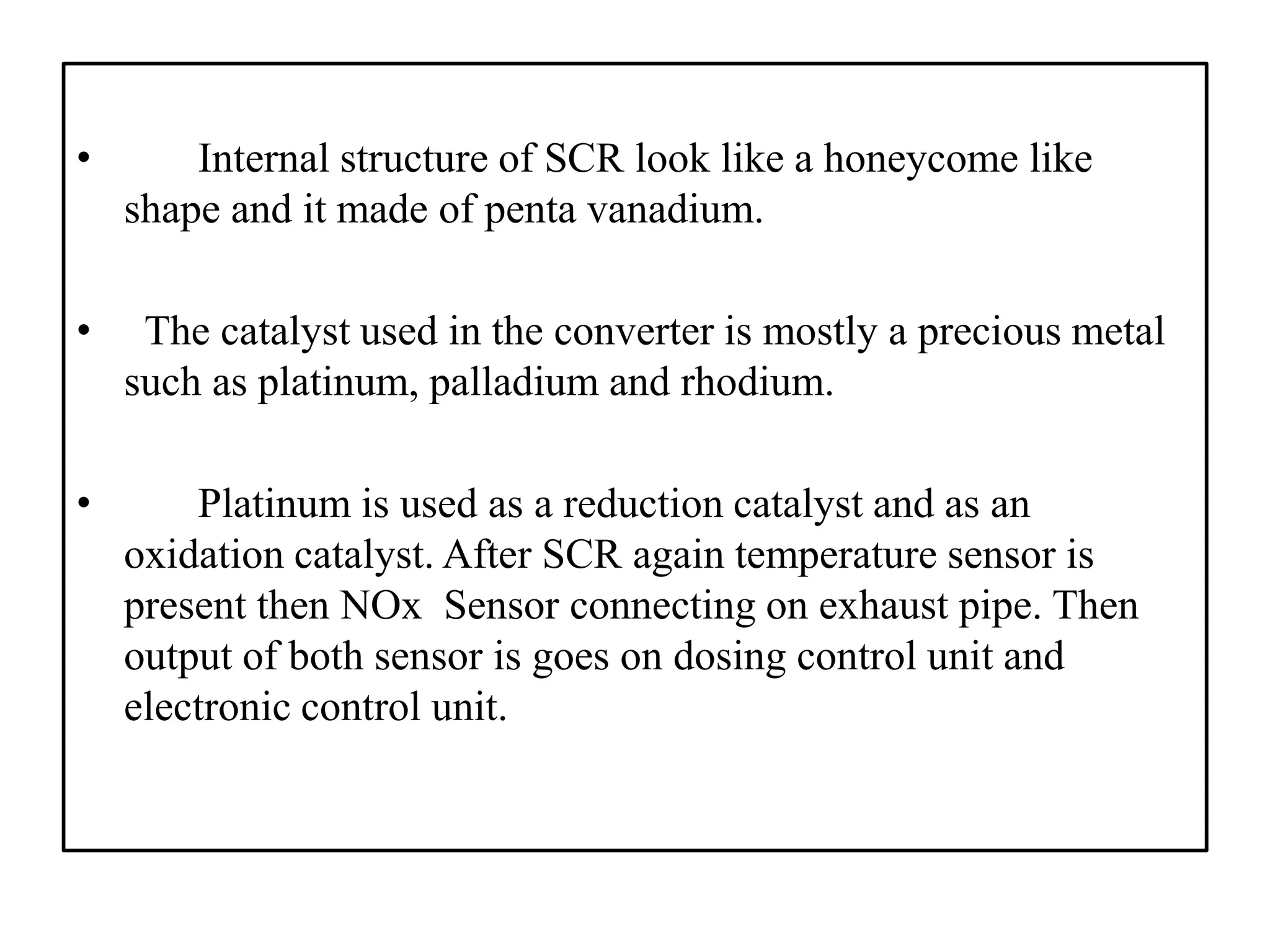
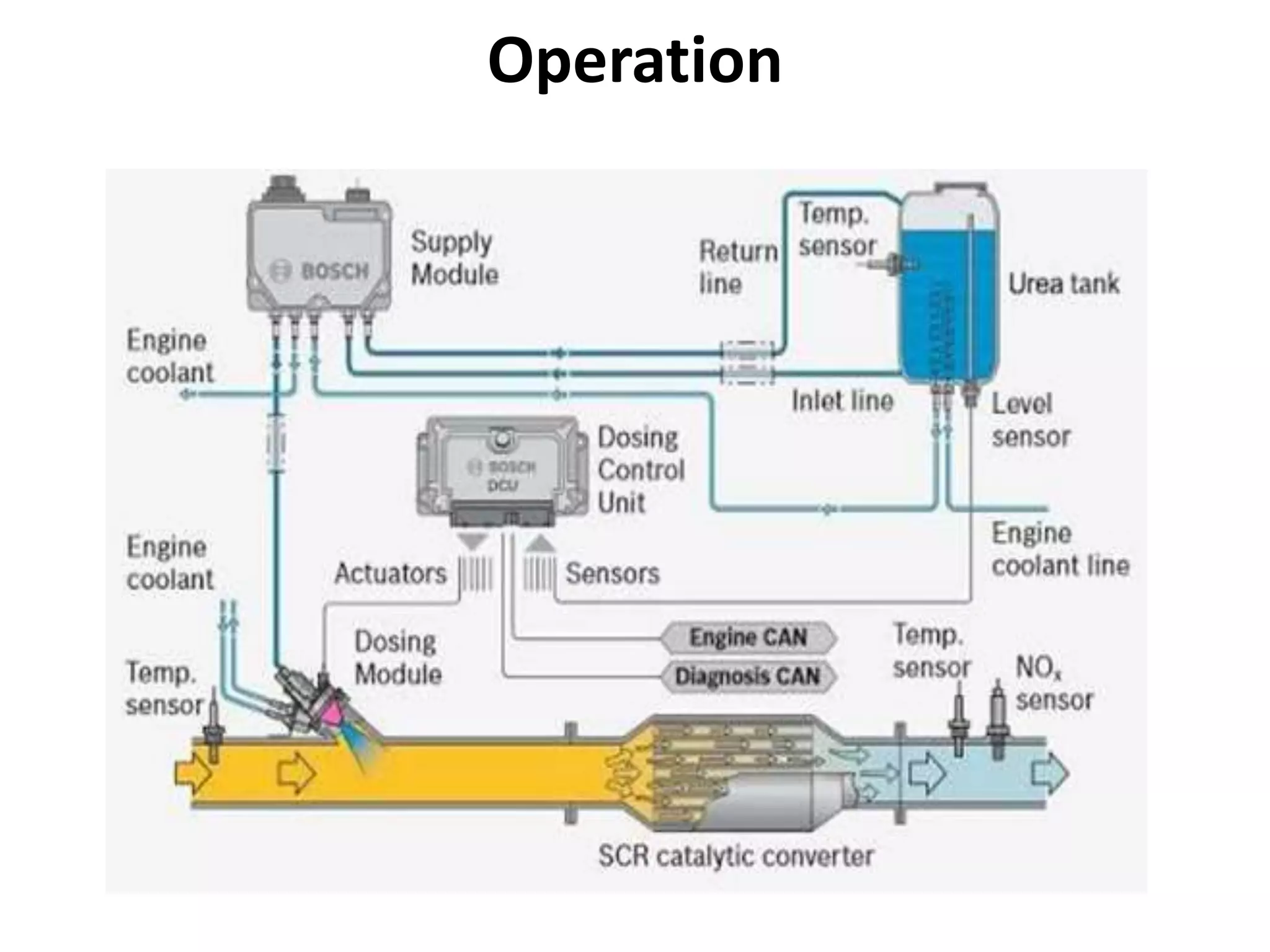
The seminar report on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) details a technology aimed at reducing nitrogen oxide emissions in diesel engines by up to 90%. It describes the system's construction, operation, and the advantages and disadvantages, noting its effectiveness in meeting stringent air quality regulations. Additionally, the document includes a comparison of pollutant emissions between BS-3 and BS-4 standards, highlighting significant reductions in hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter.