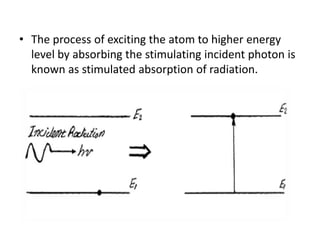
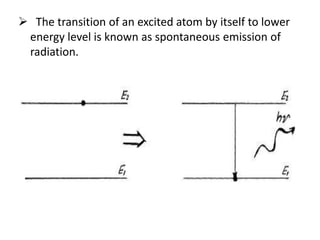
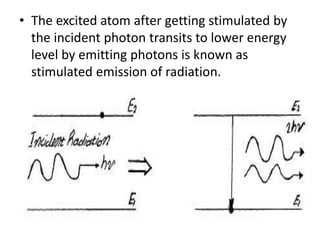
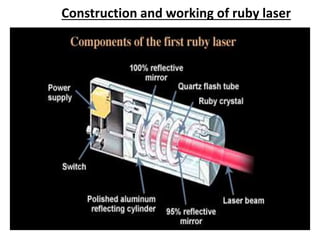
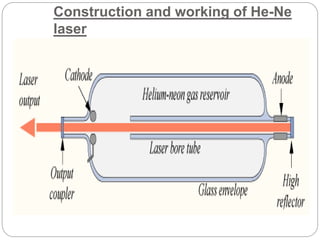
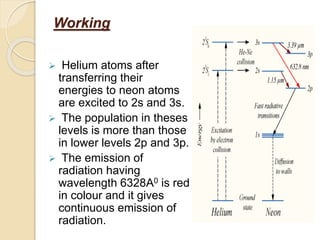
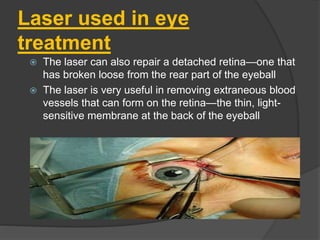
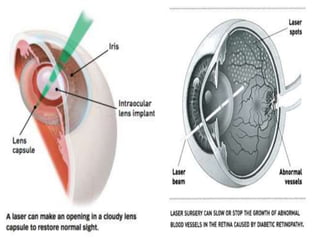
This document discusses lasers, including their principle of operation through stimulated emission, types of lasers such as solid state, gas, and semiconductor lasers. It describes the construction and working of ruby and He-Ne lasers. Applications of lasers in communication, industry, medicine, and military are covered. Advantages such as precision cutting and disadvantages like cost and health hazards are summarized.