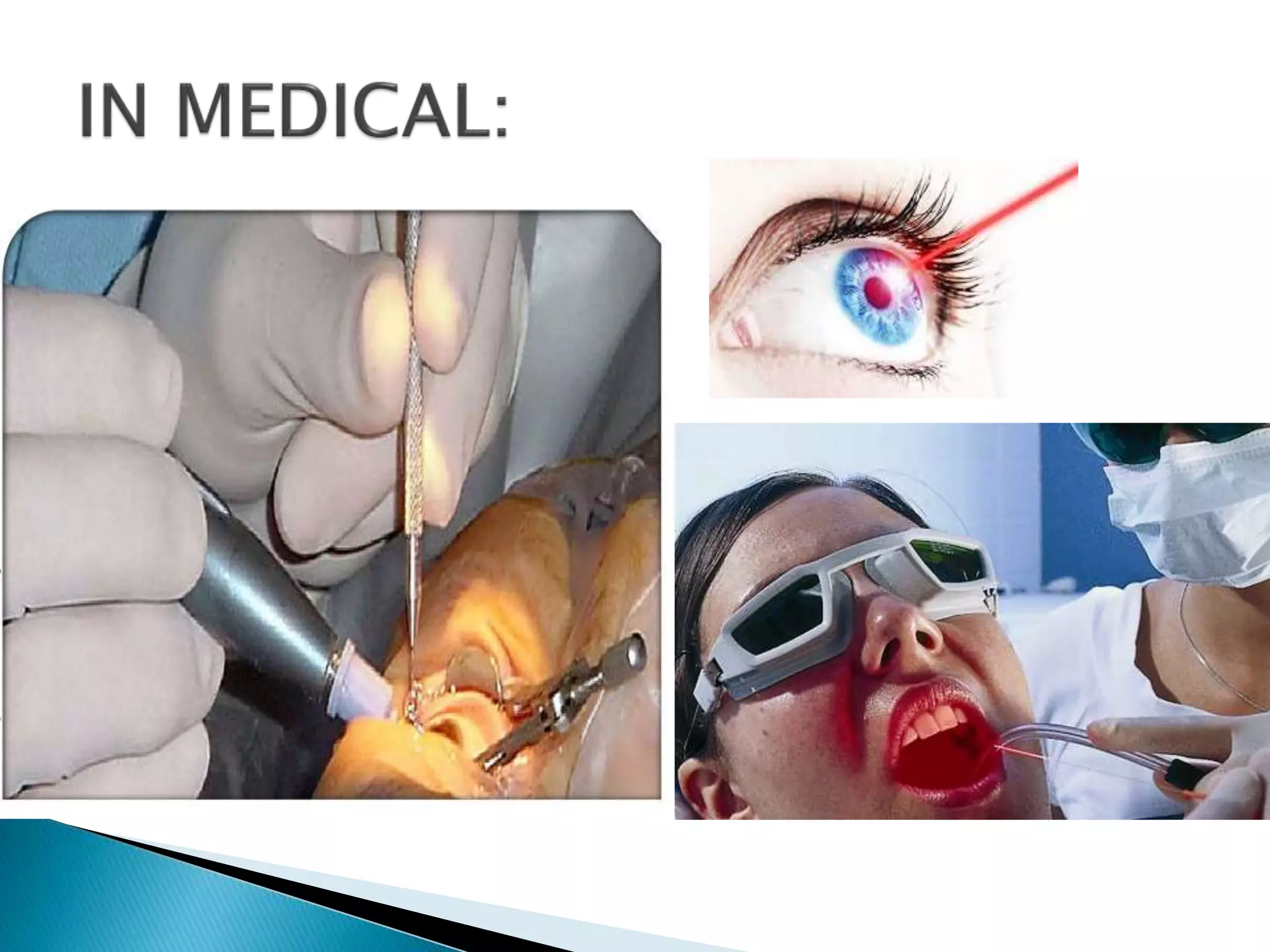
This document discusses lasers and their applications. It defines lasers as optical devices that generate intense beams of coherent light through stimulated emission. Lasers are then described as having special properties like traveling long distances without spreading out. The document proceeds to list several applications of lasers, including in manufacturing, medicine, metrology, data storage, communications, displays, spectroscopy, microscopy, energy technology, and the military. Specific examples are provided for some of the applications.