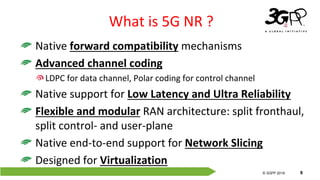
The document outlines the evolution of 5G standards through 3GPP releases, detailing the transition from Release 15 to Release 17 and the key features and enhancements in each phase. It emphasizes the significance of 5G NR, including its operation across various frequency bands and advancements in network architecture, low latency, and network slicing. Additionally, it provides an overview of future focus areas in the 5G landscape, highlighting enhancements for applications such as vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, industrial IoT, and positioning services.