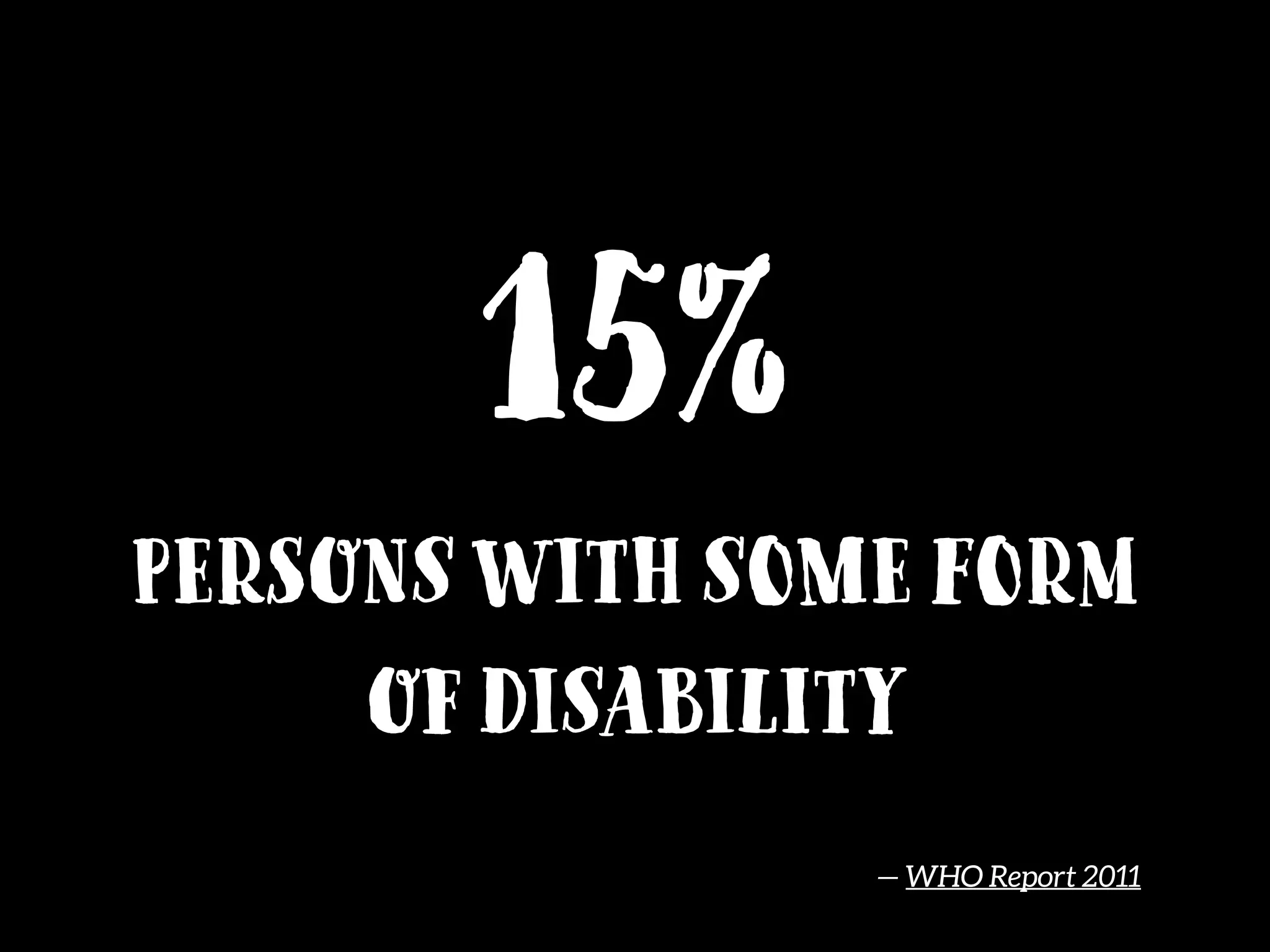
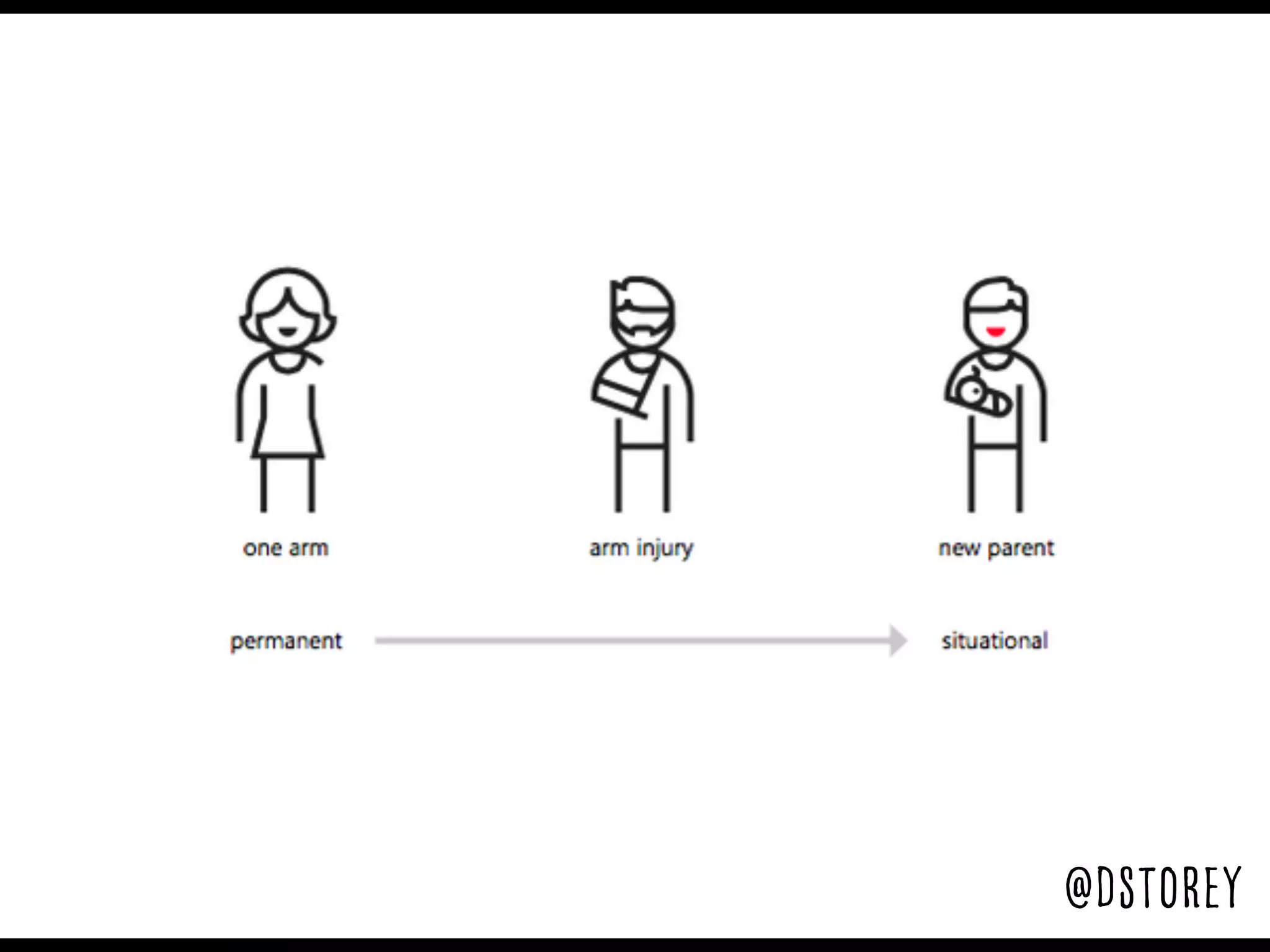
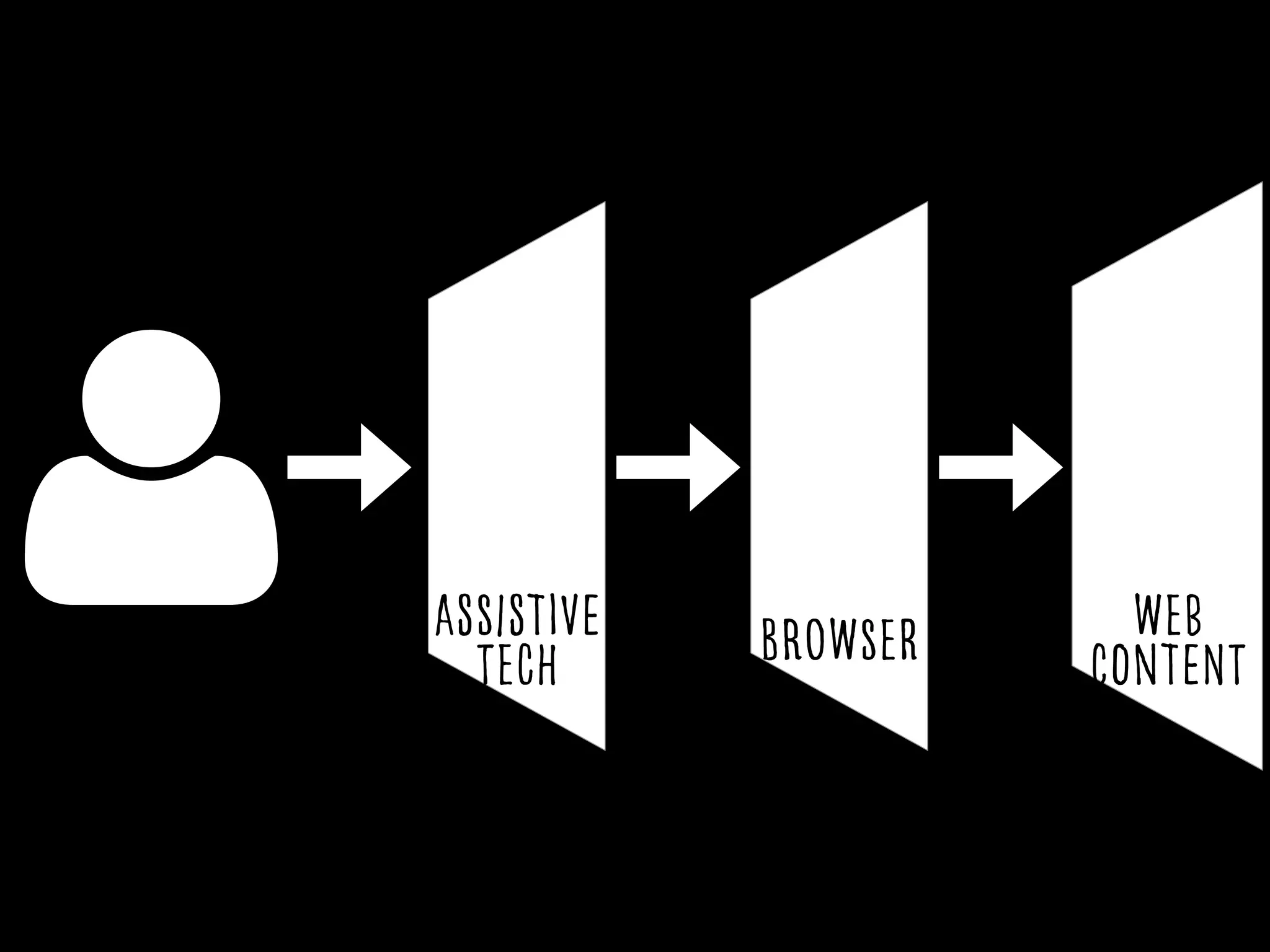
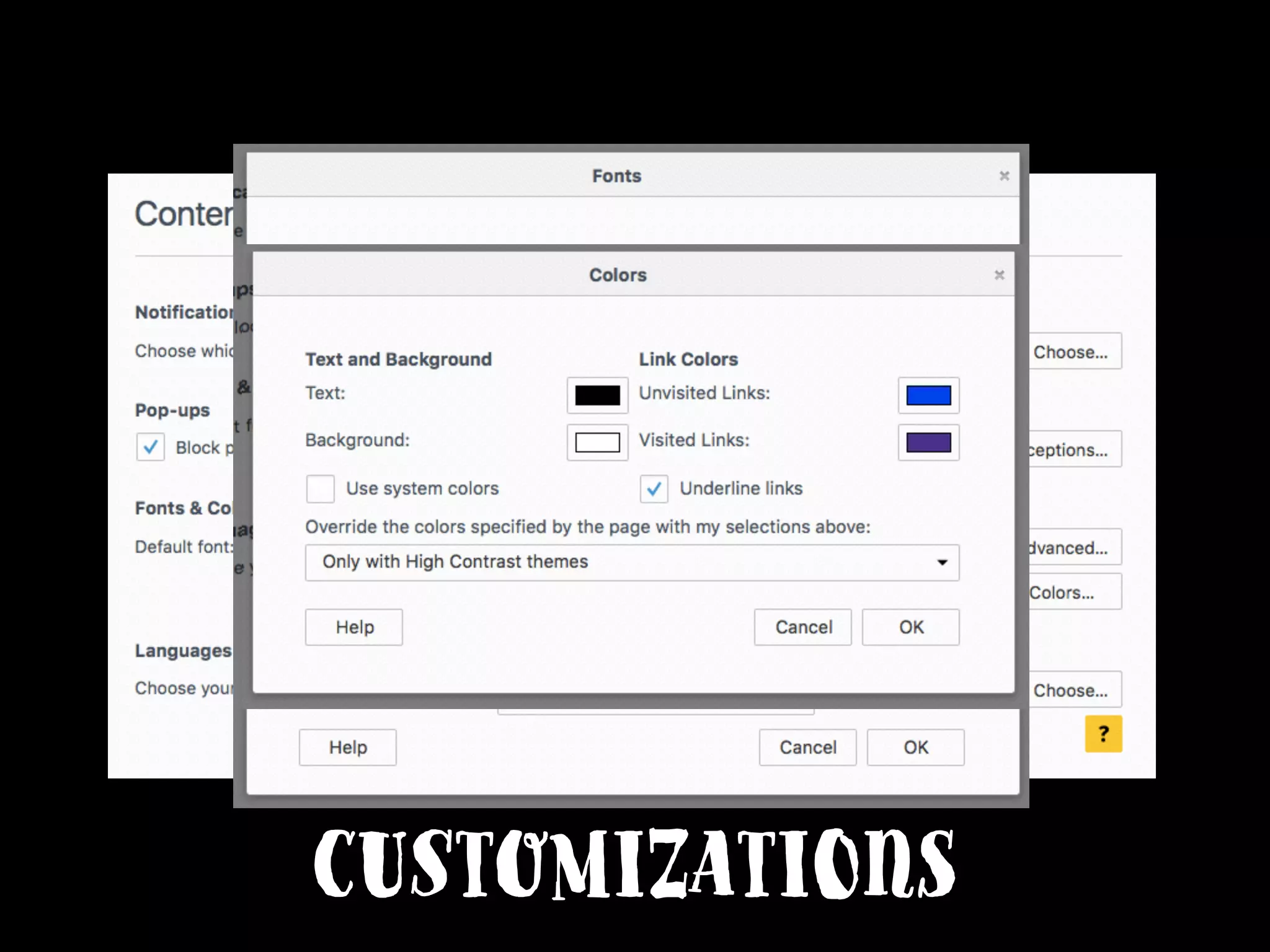
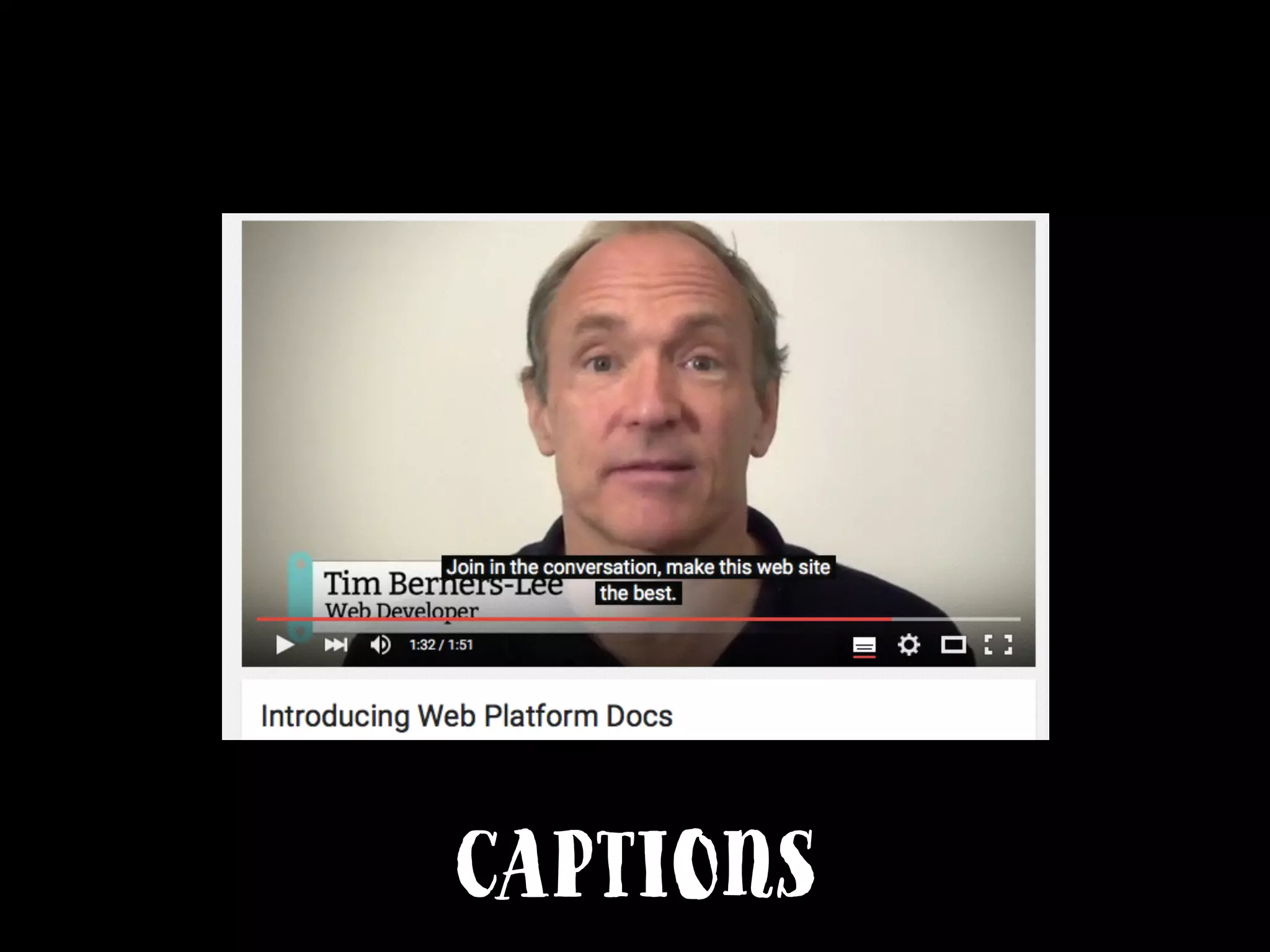
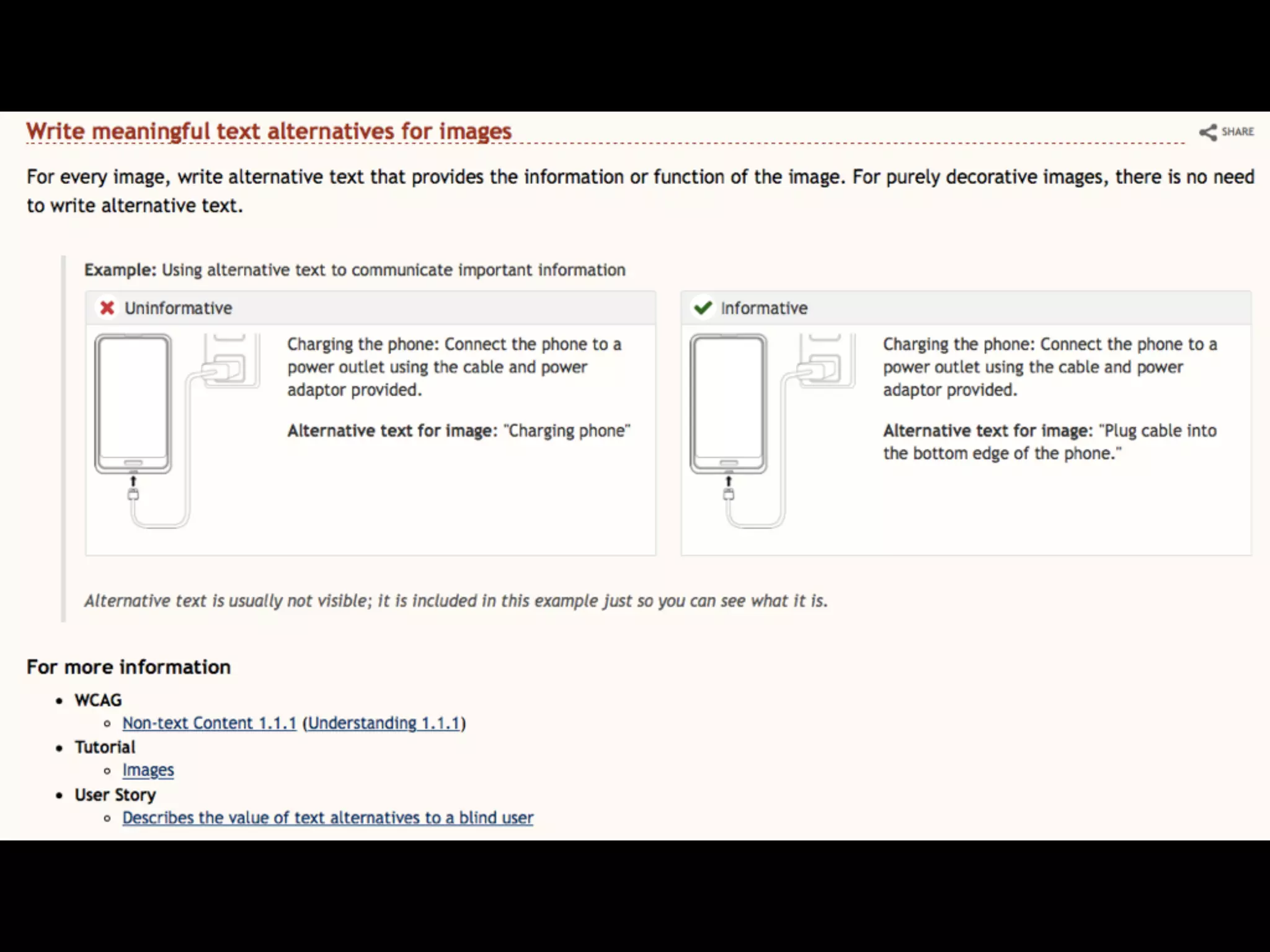
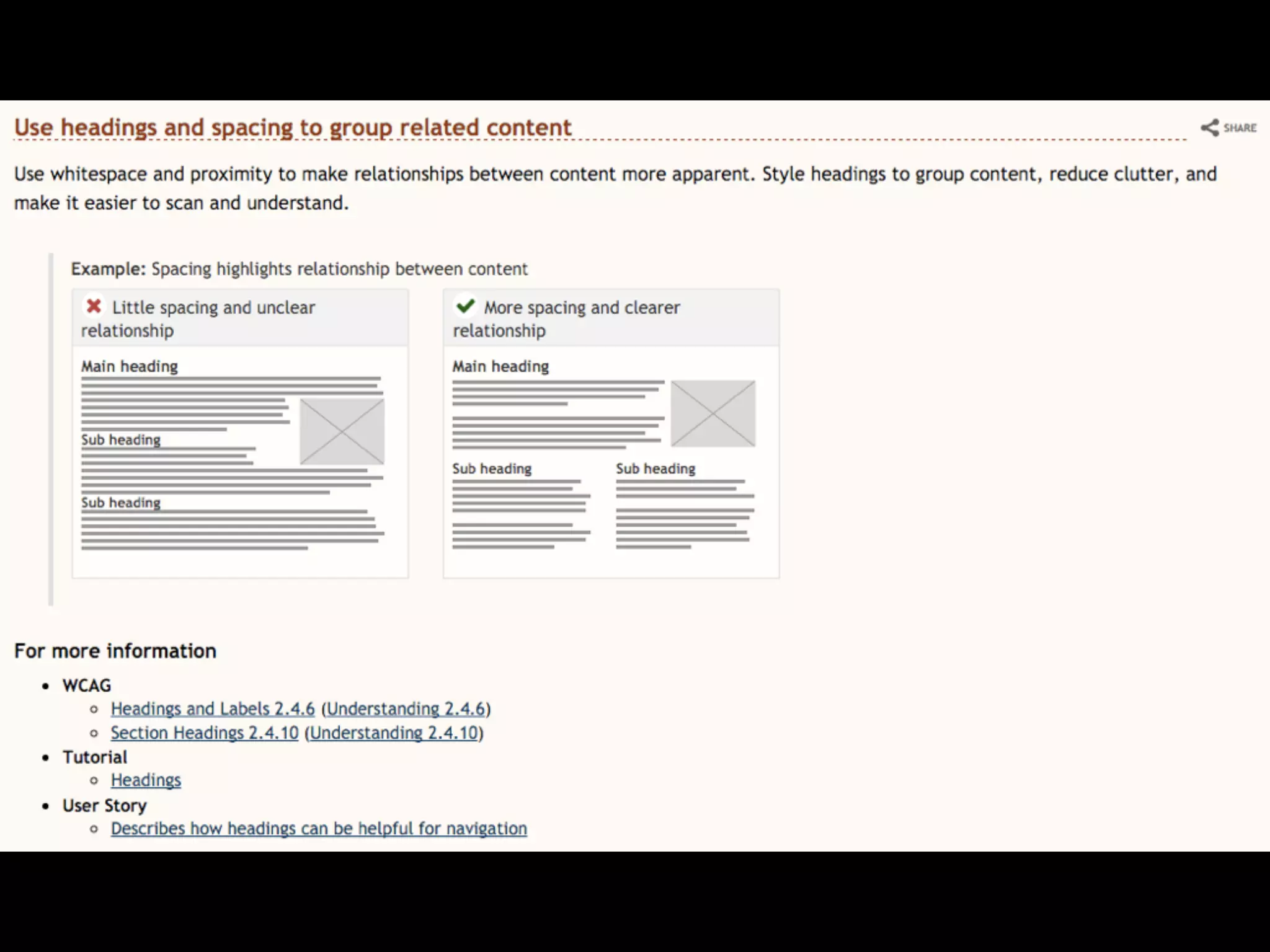
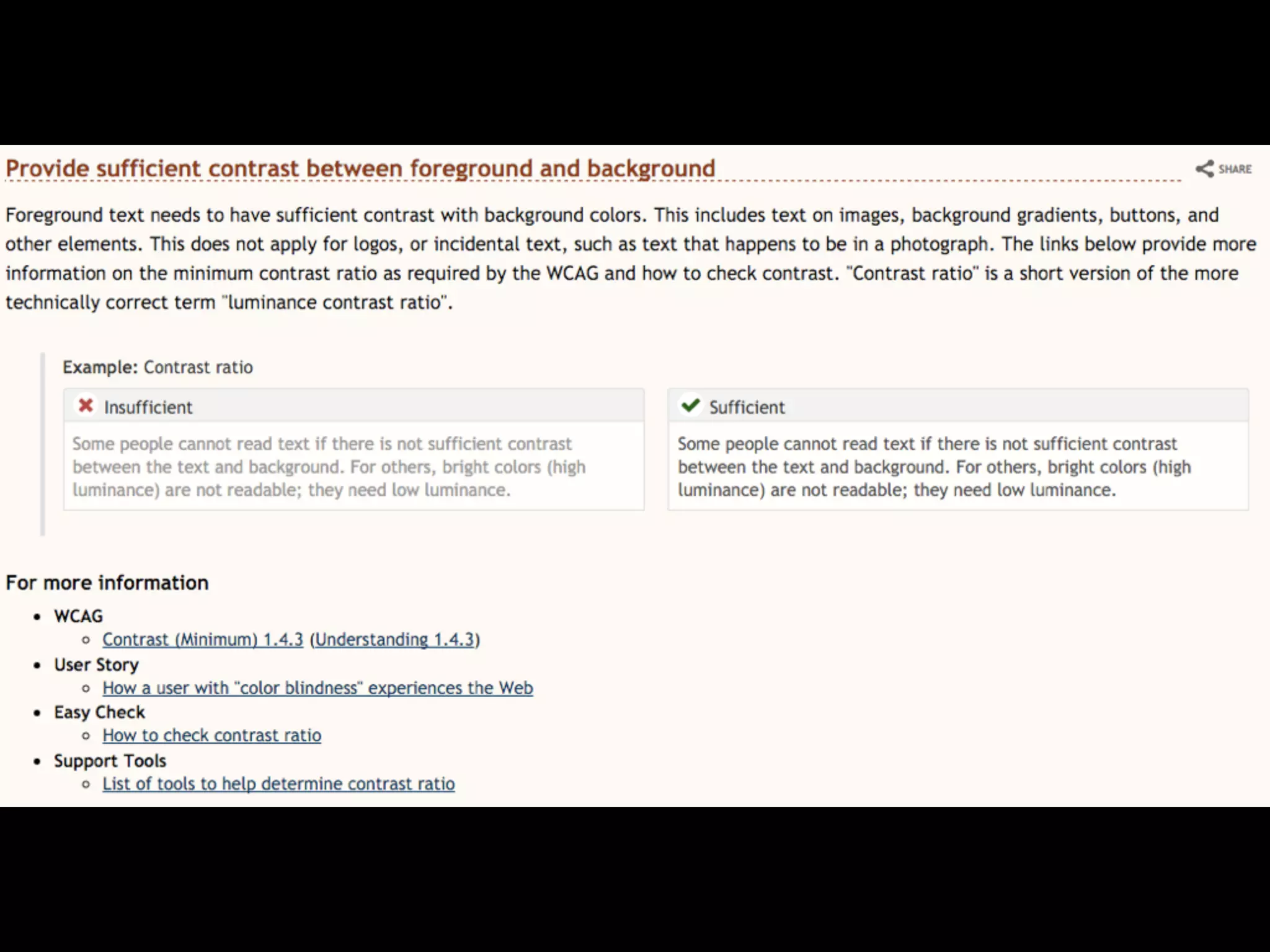
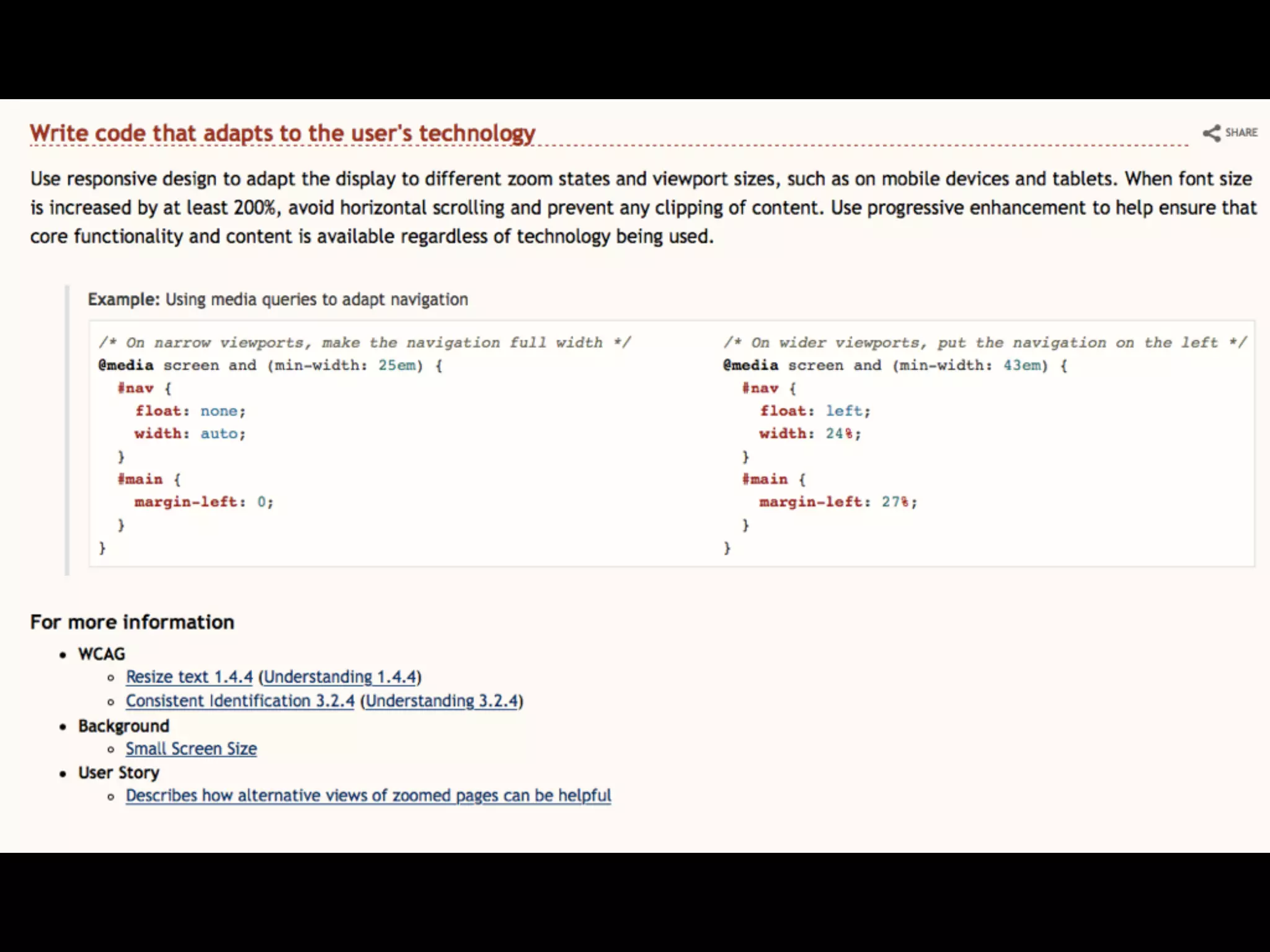
This document provides an overview of how to improve the accessibility of a website without making it overly complex. It begins by defining web accessibility and its importance for people with disabilities. It then addresses common questions about accessibility and provides resources on getting started, following guidelines, and ensuring usability. The key messages are that accessibility should be considered from the beginning, not as an afterthought, and that it leads to a better user experience for all while allowing a website to reach more people.