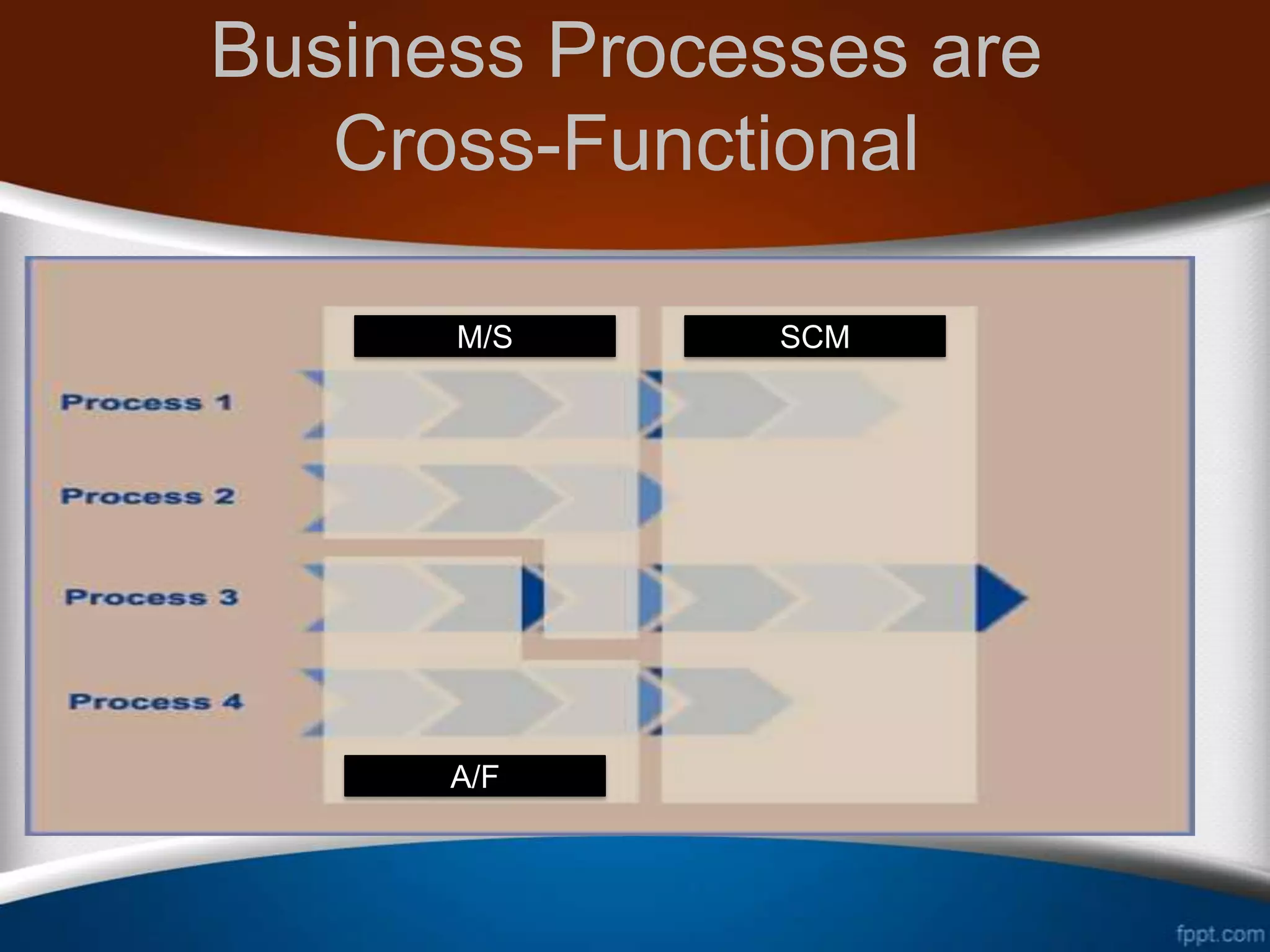
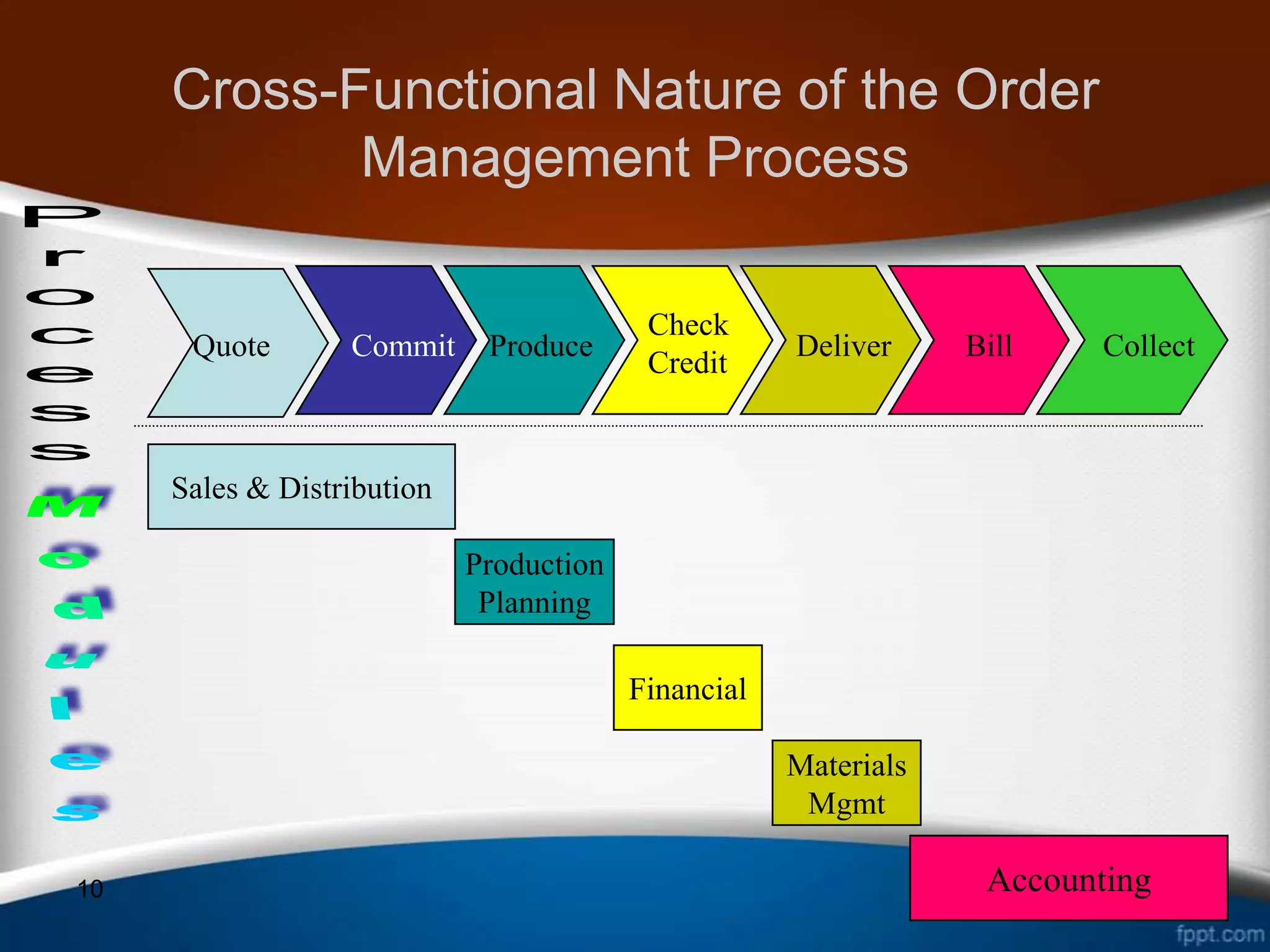
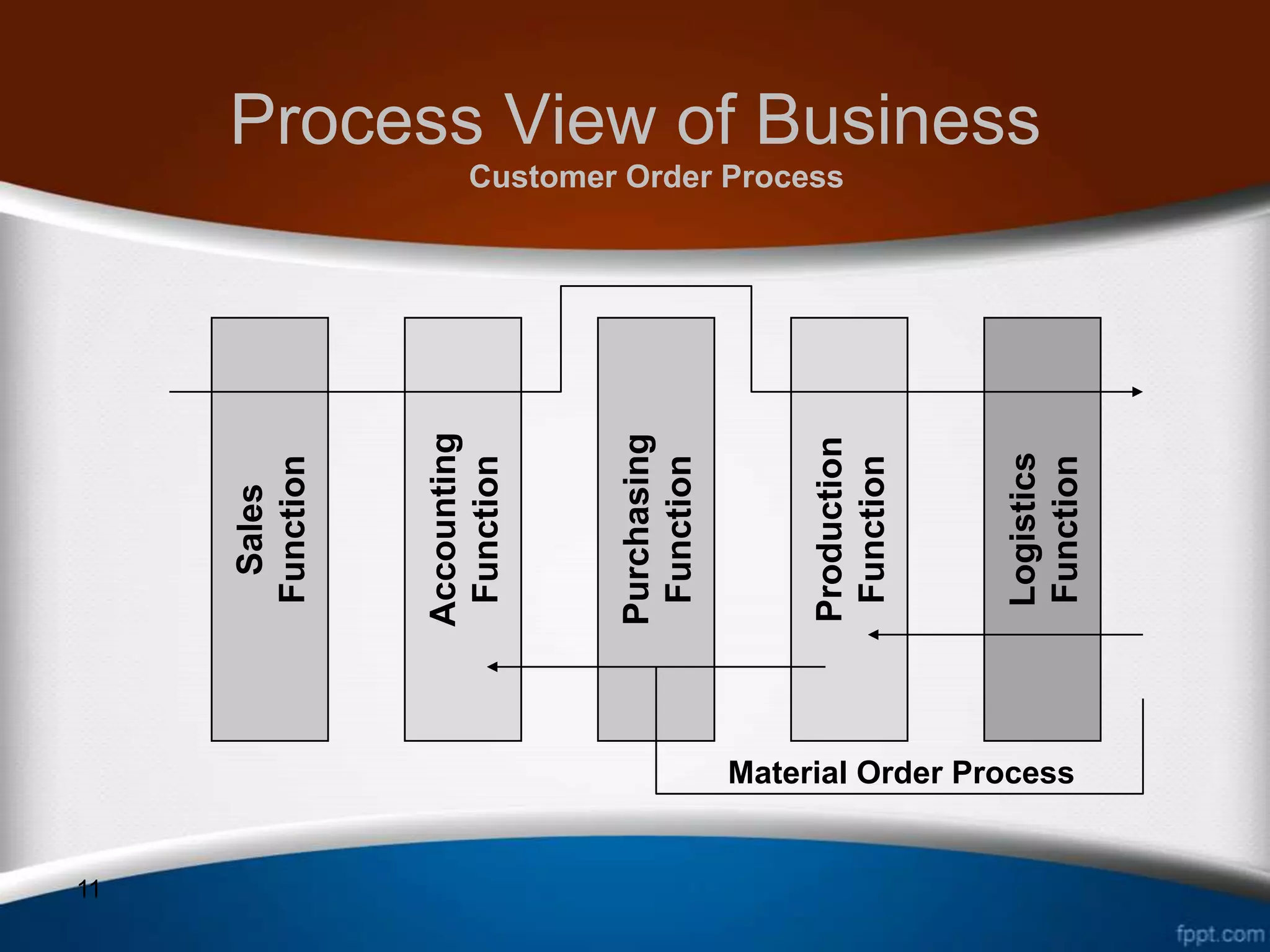
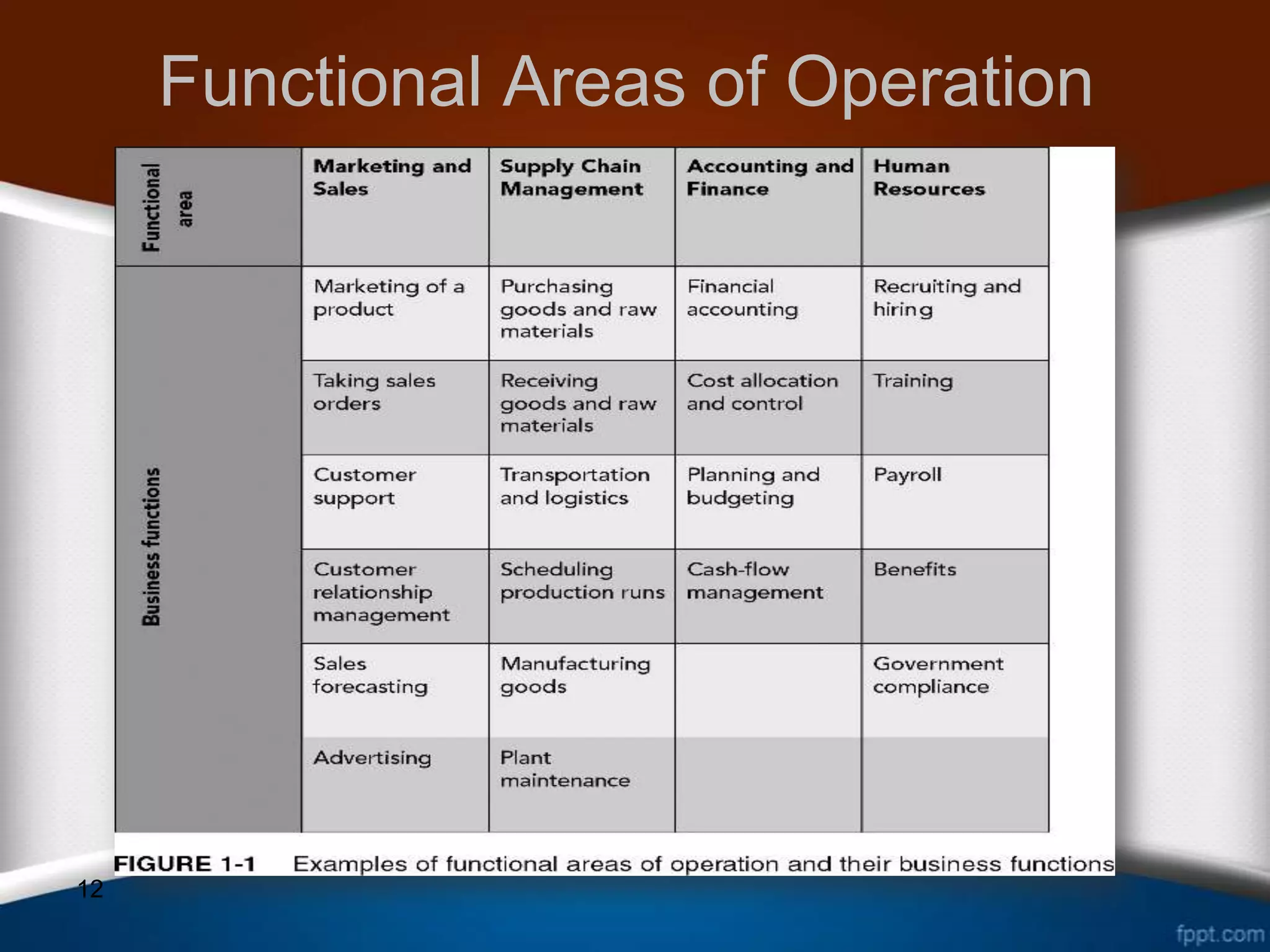
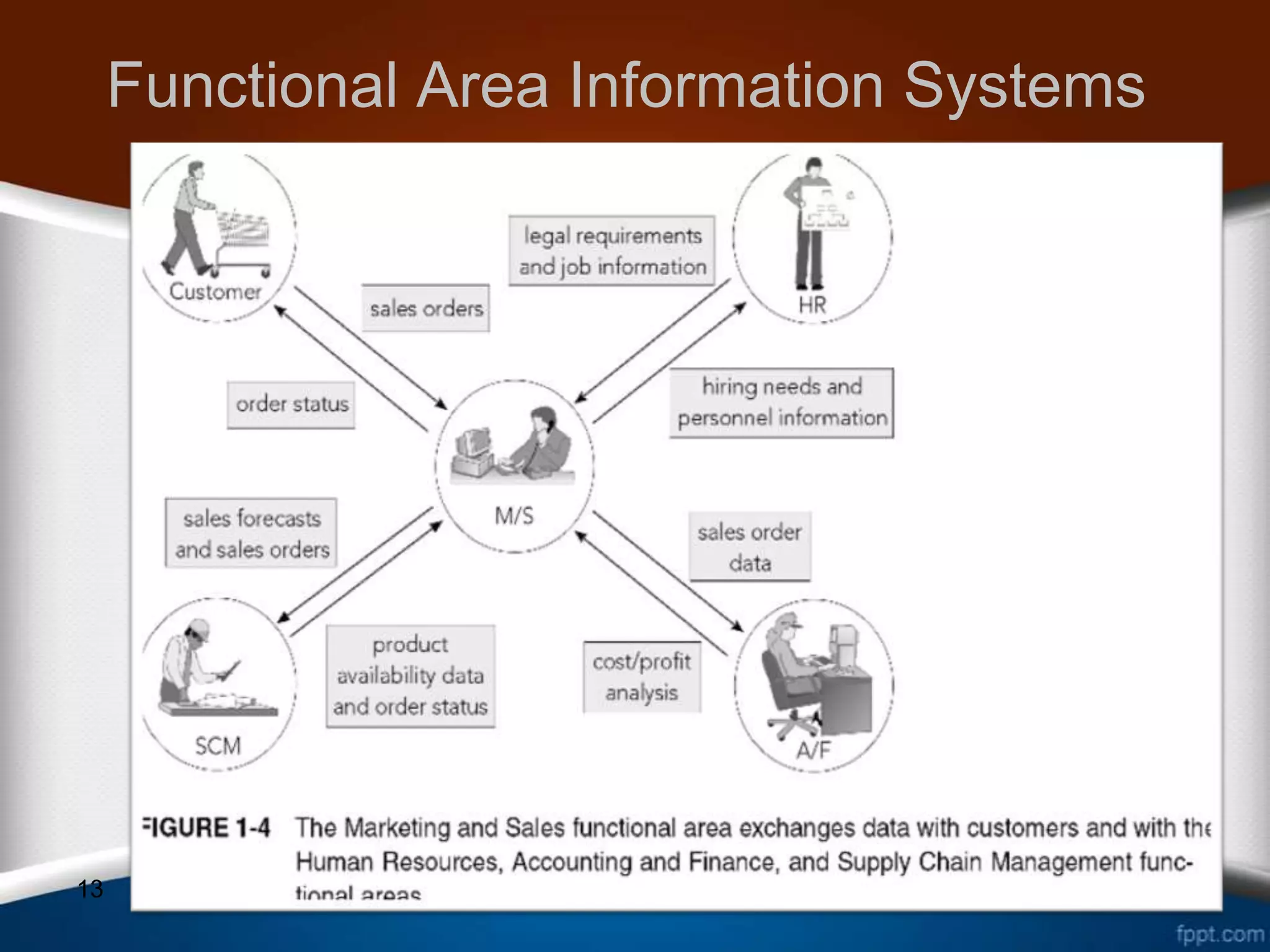
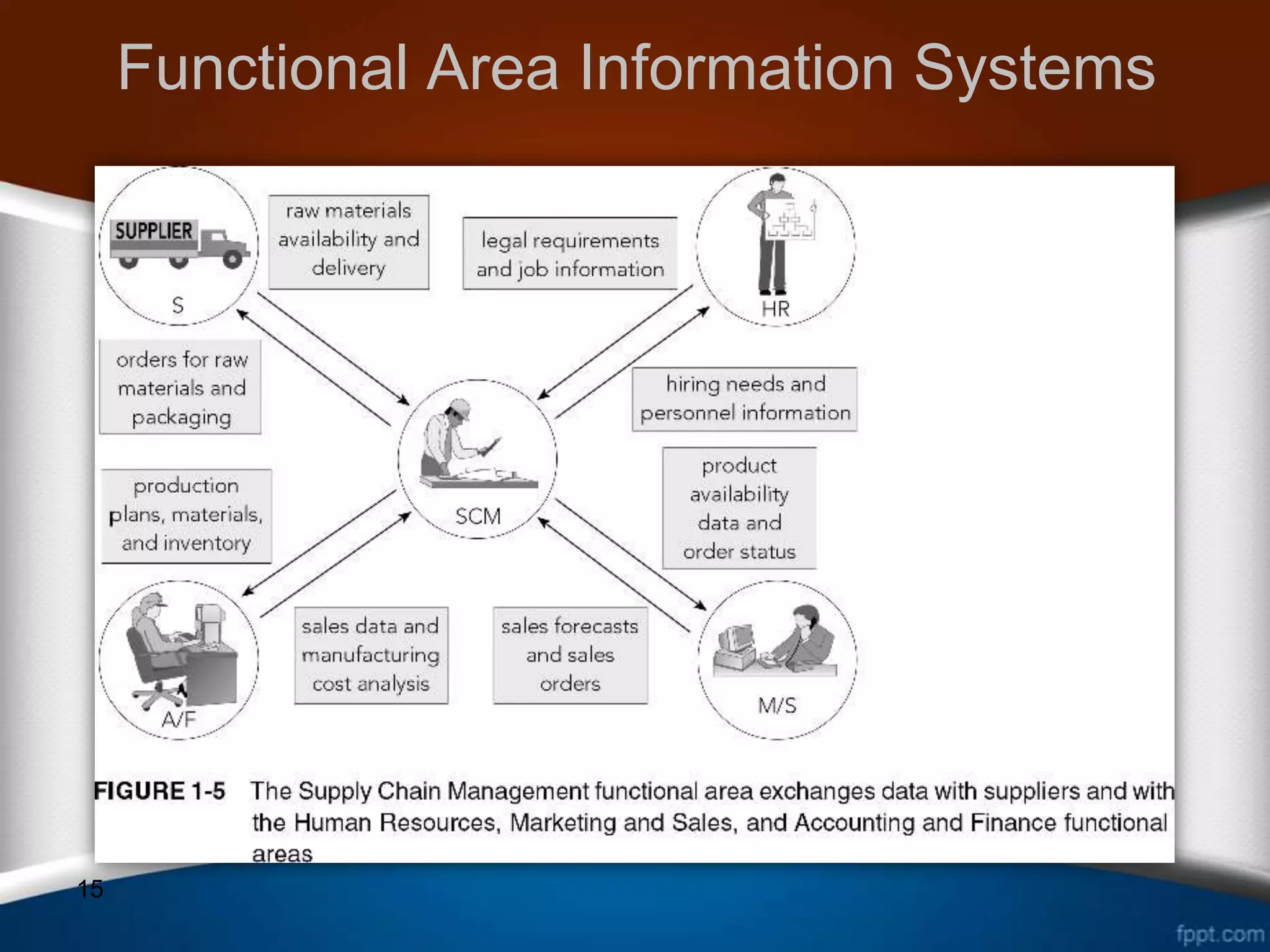
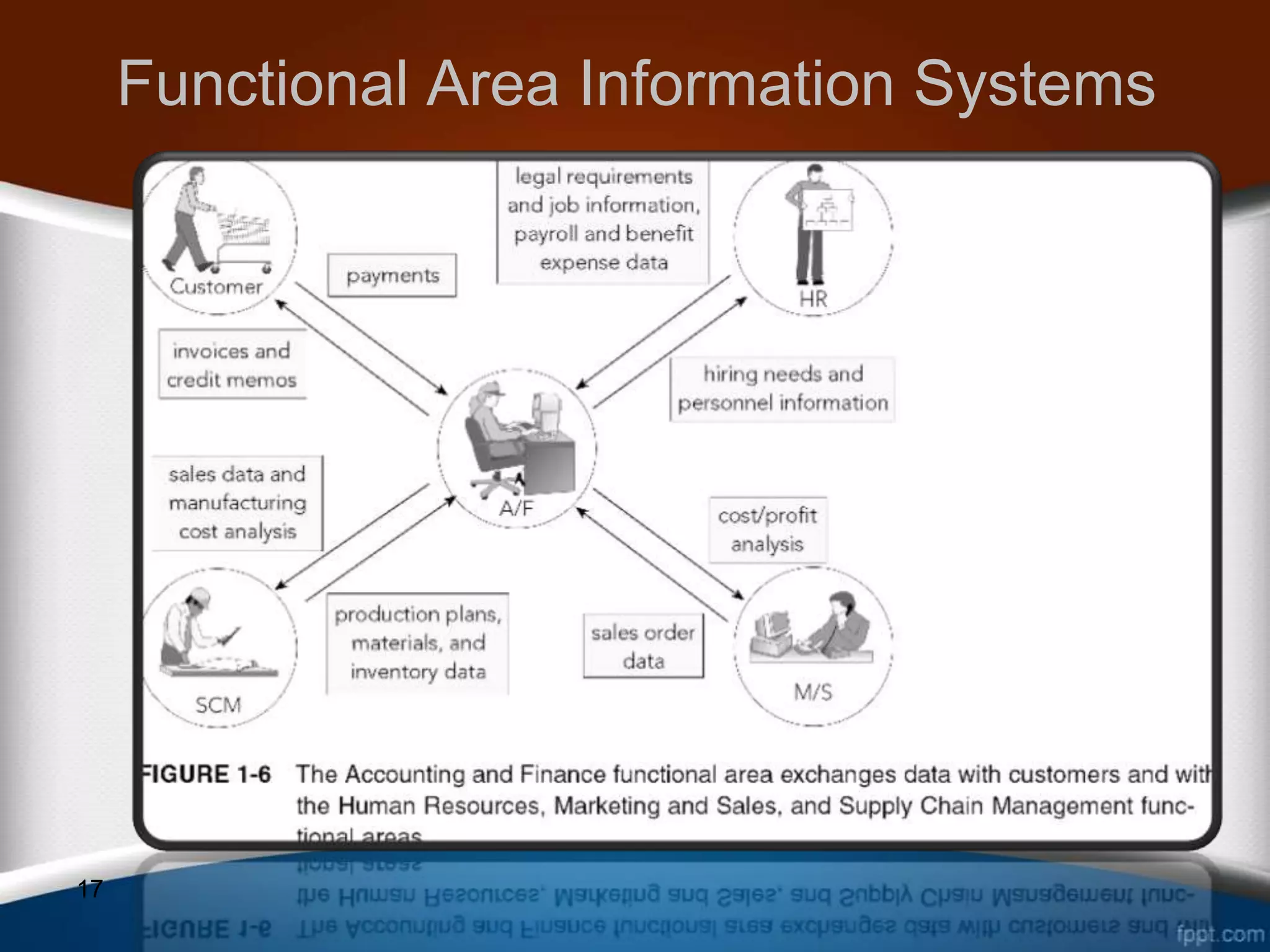
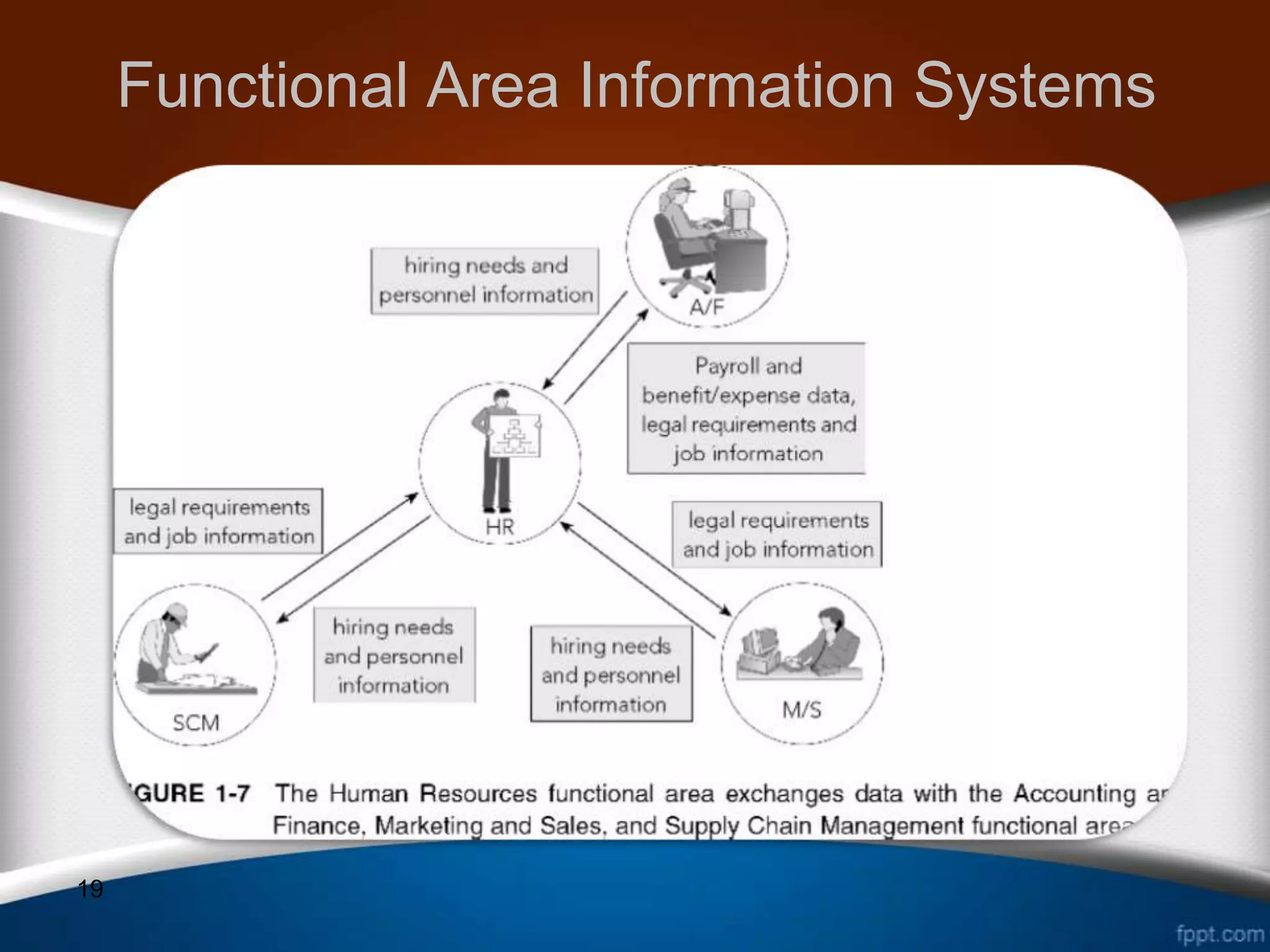
This document discusses how ERP systems integrate business functions and processes across different functional areas like marketing, supply chain, accounting, and human resources. It provides examples of common business functions and processes within each area. For instance, marketing functions include sales and identifying customer needs, while supply chain functions involve purchasing, manufacturing, and inventory management. The document also explains that ERP processes consist of interdependent steps that span multiple functional areas to transform inputs into outputs. A customer order process is provided as an example of a cross-functional business process in ERP.