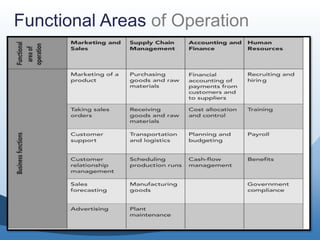
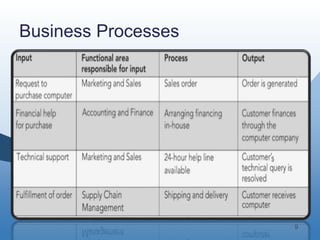
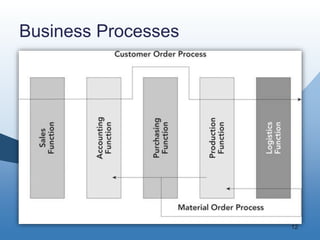
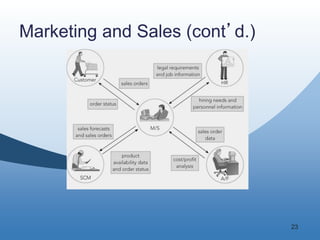
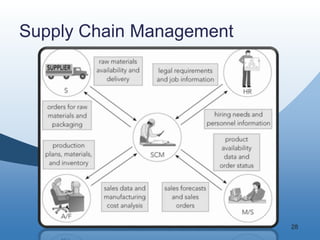
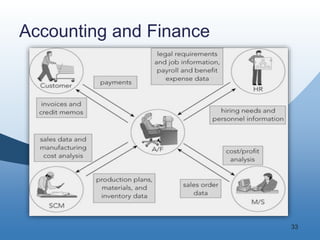
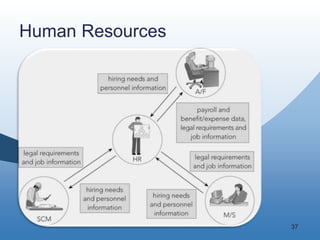
The document discusses the key functional areas of a business - marketing and sales, supply chain management, accounting and finance, and human resources. It explains that each functional area requires data from the others to perform their operations and business processes. An integrated information system, such as one provided by enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, allows the different functional areas to share a common database and ensures accurate and timely sharing of data between areas. This coordination of information is important for the success of the company's business processes and overall operations.