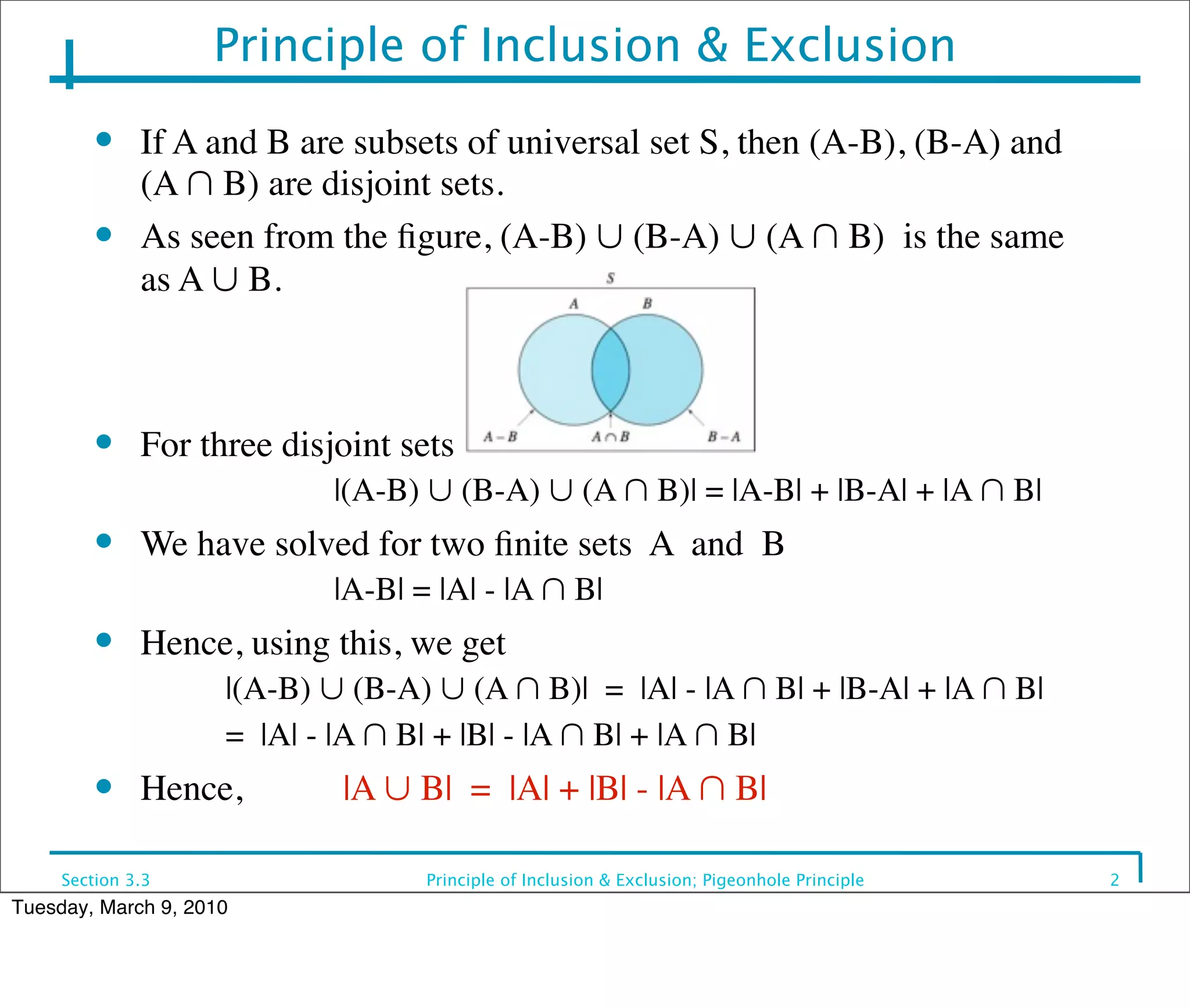
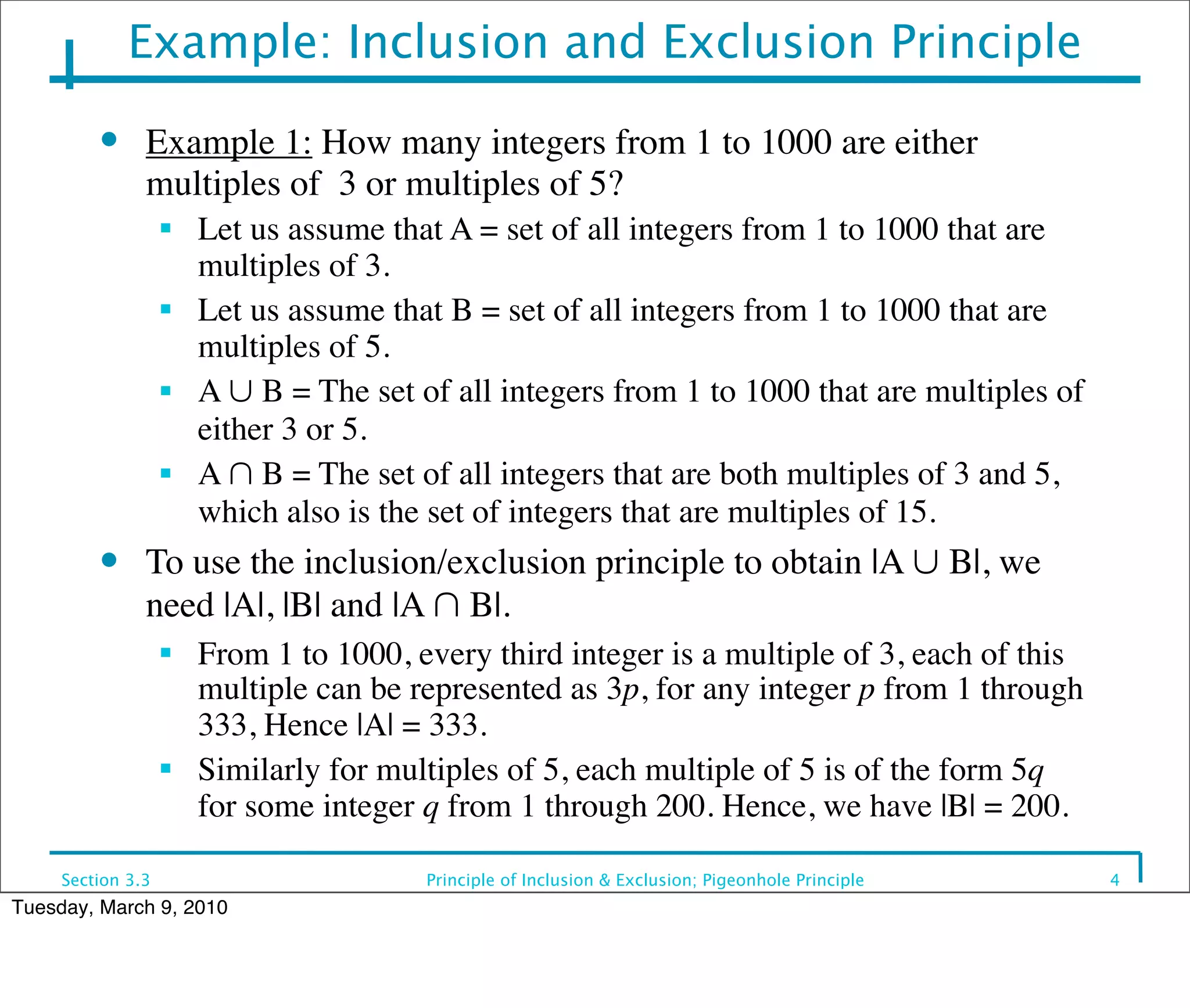
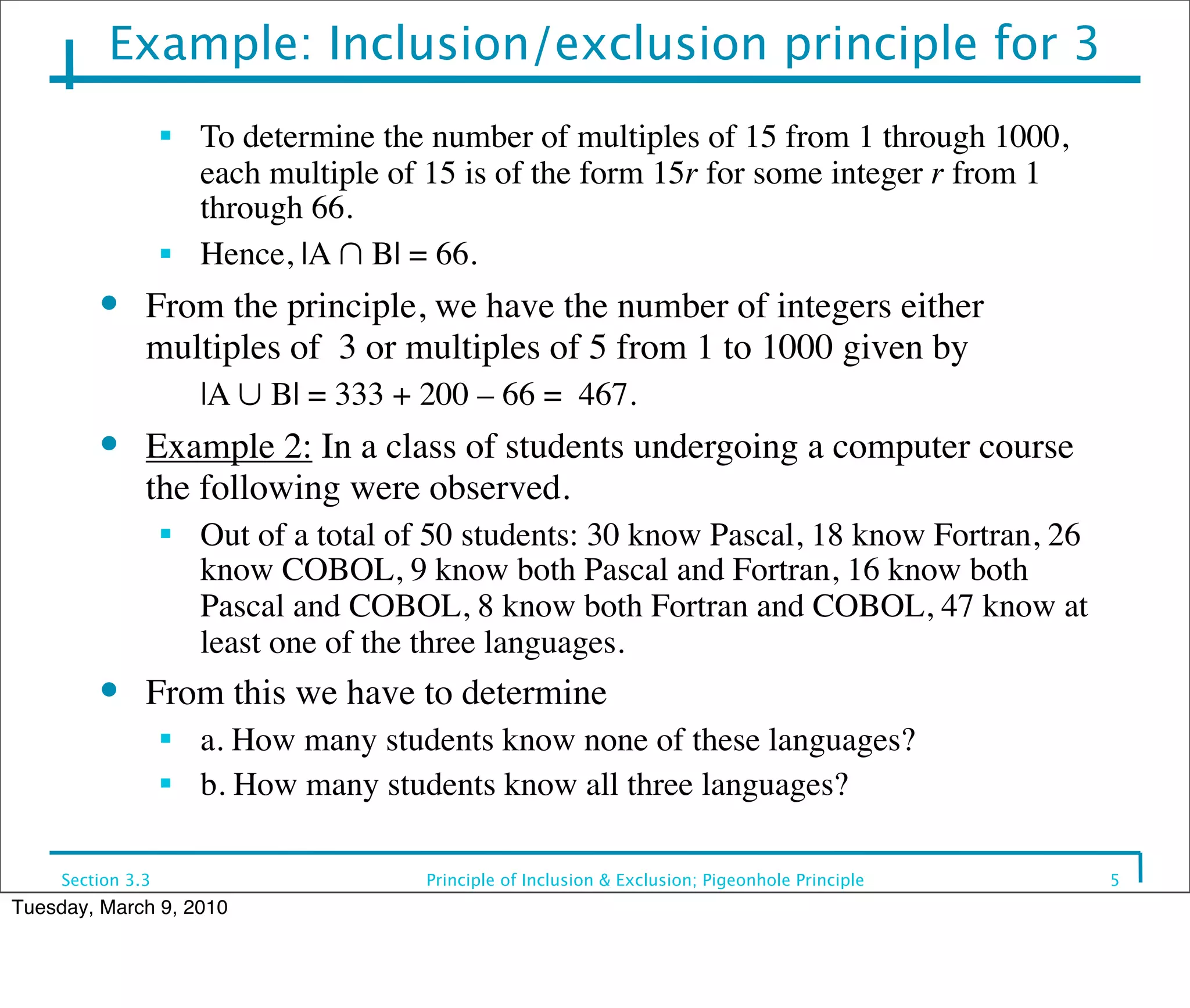
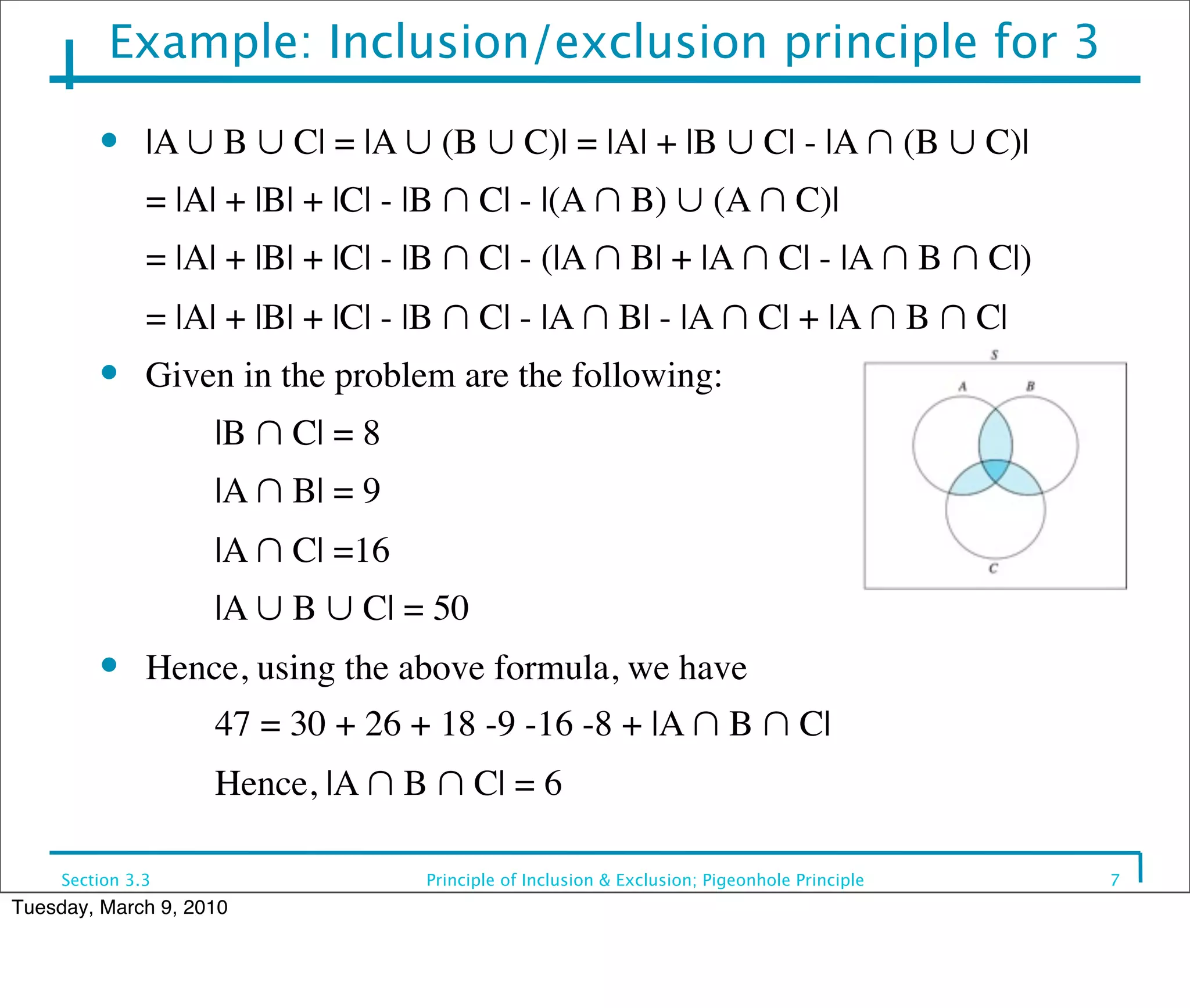
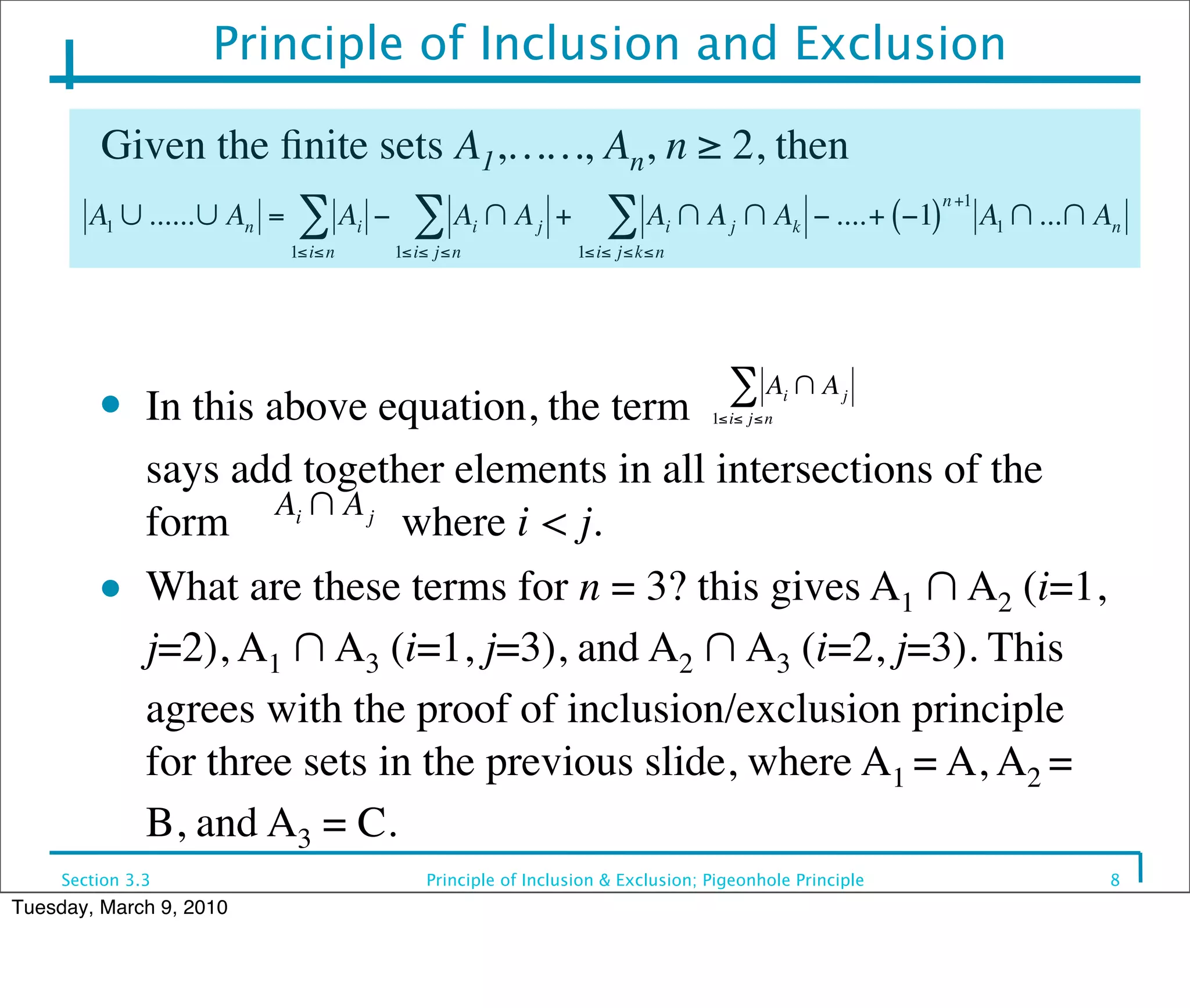
This document discusses the principle of inclusion and exclusion as it relates to set theory and probability. It begins by explaining the principle for two sets A and B, that the size of the union A ∪ B equals the size of A plus the size of B minus the size of their intersection A ∩ B. It then generalizes this to work for any number of sets. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating sizes of unions, intersections, and complements of sets. The pigeonhole principle is also introduced, which states that if more items are placed in bins than the number of bins, one bin must contain multiple items.