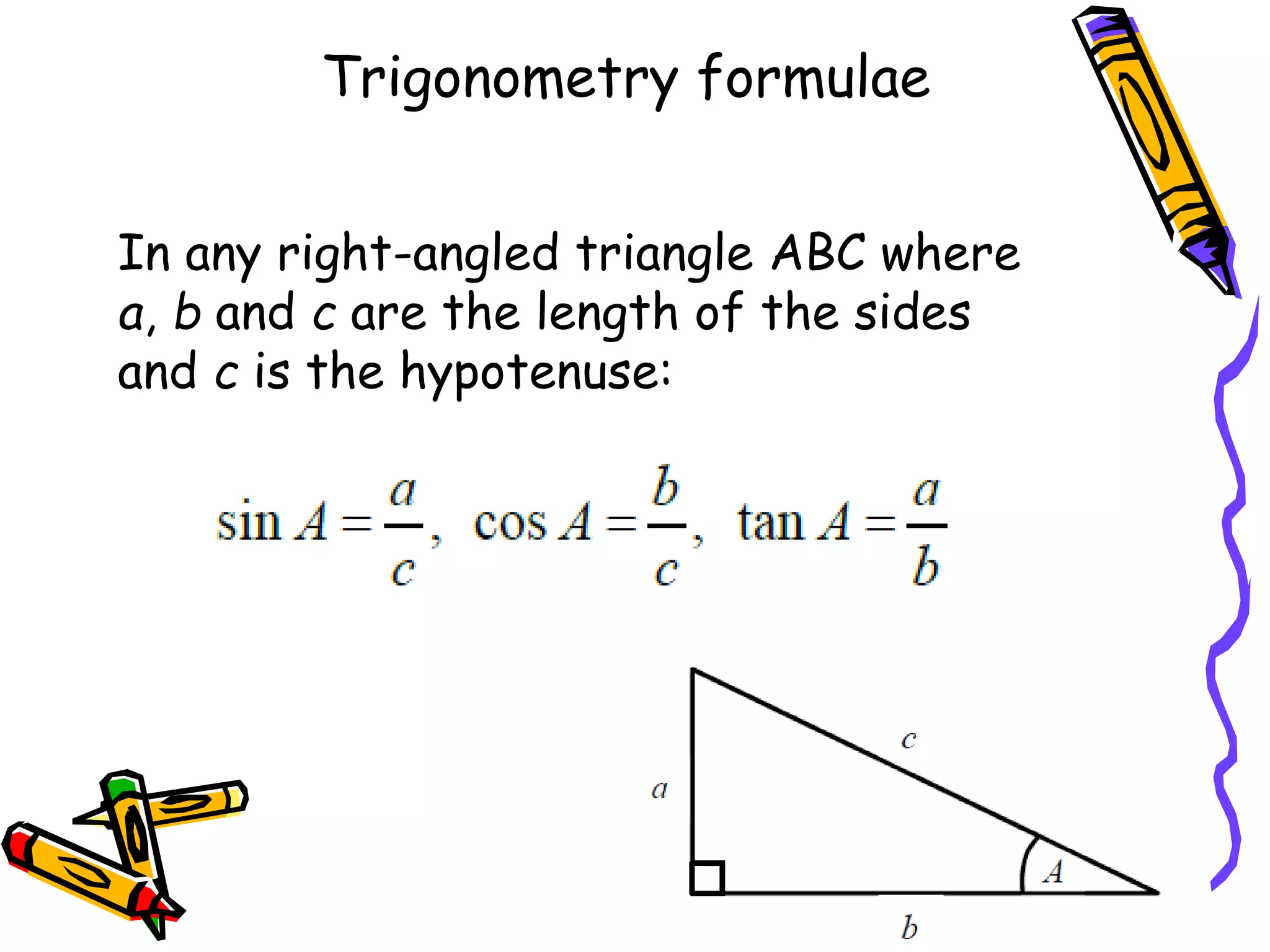
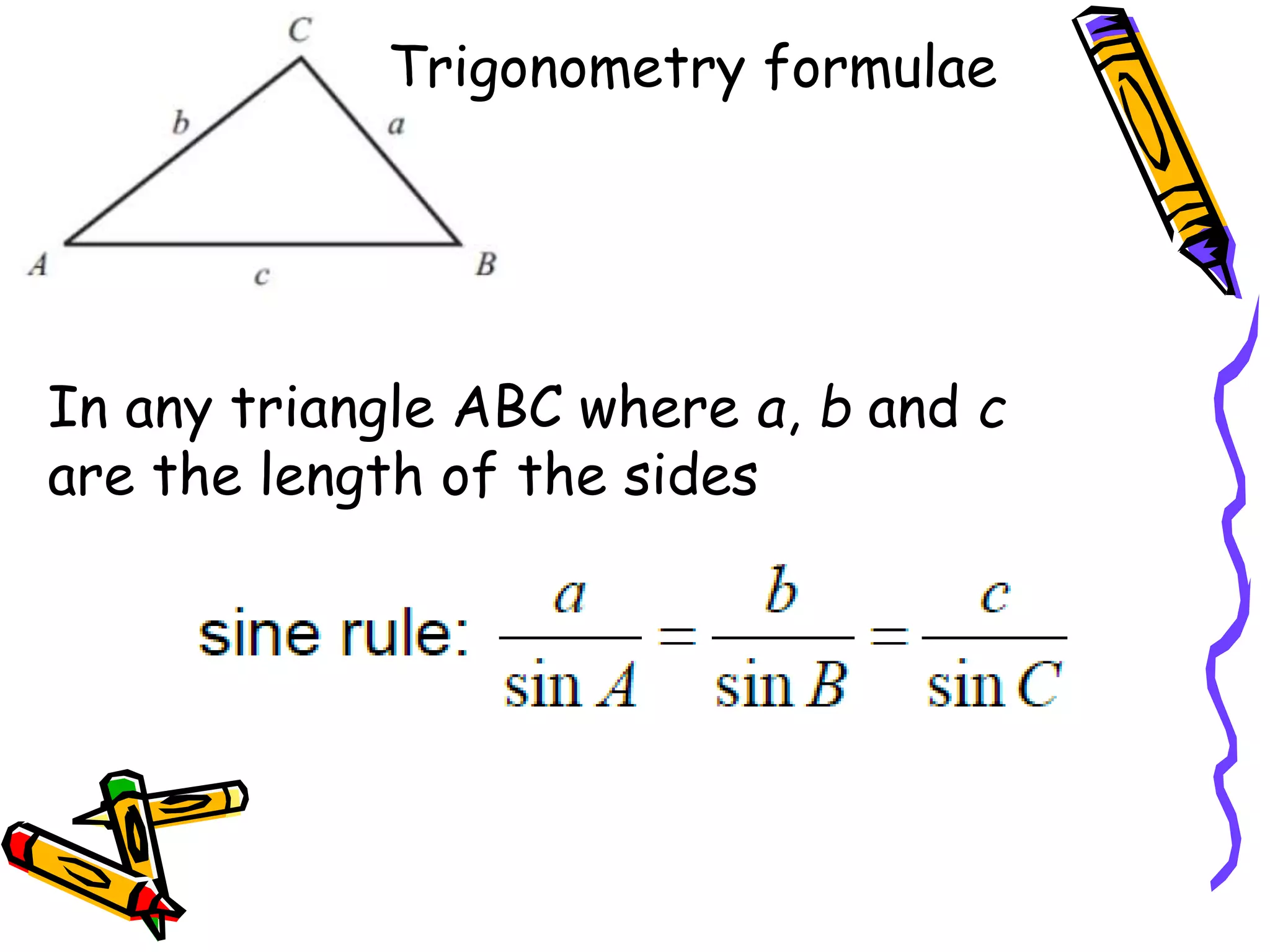
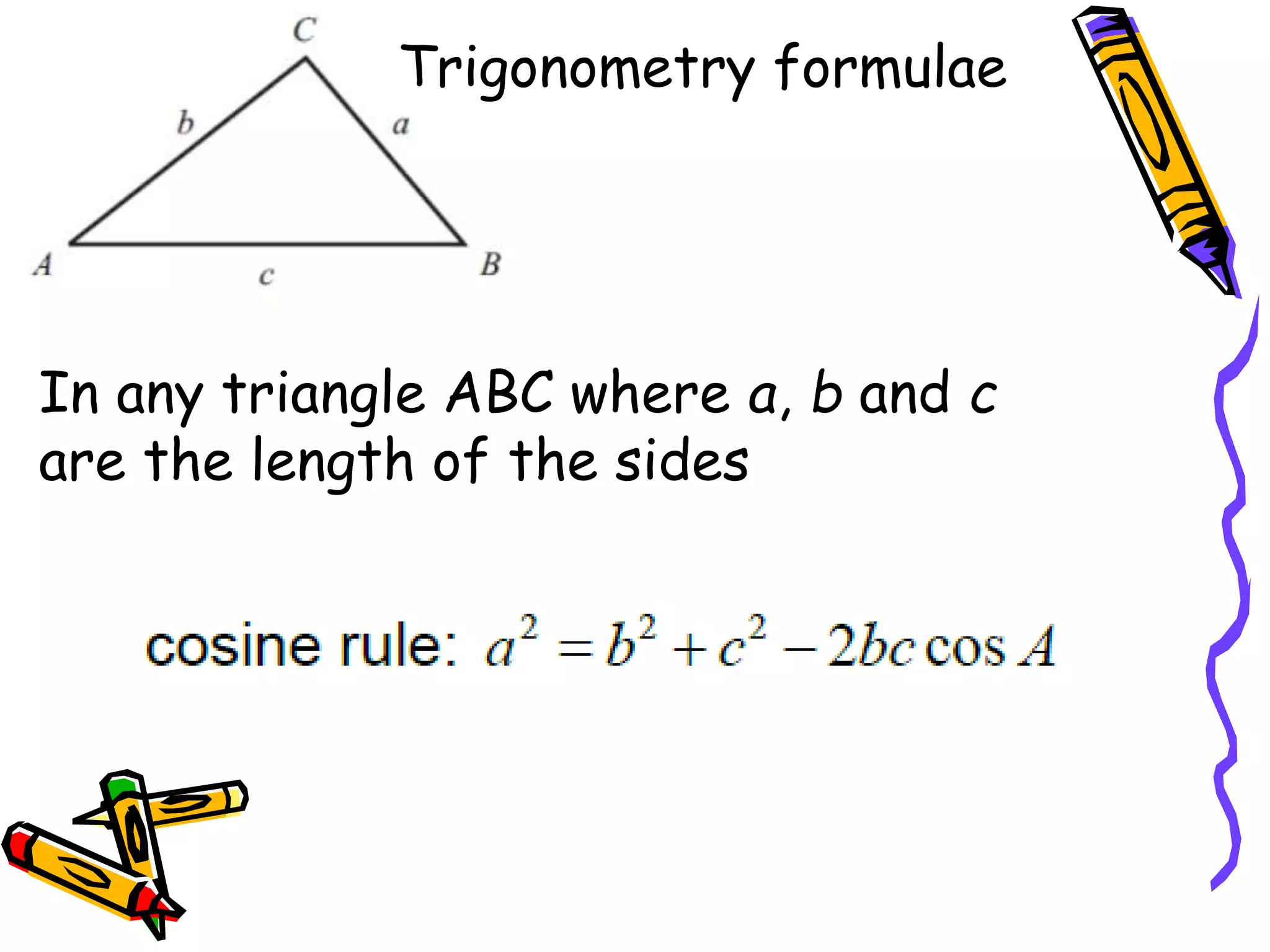
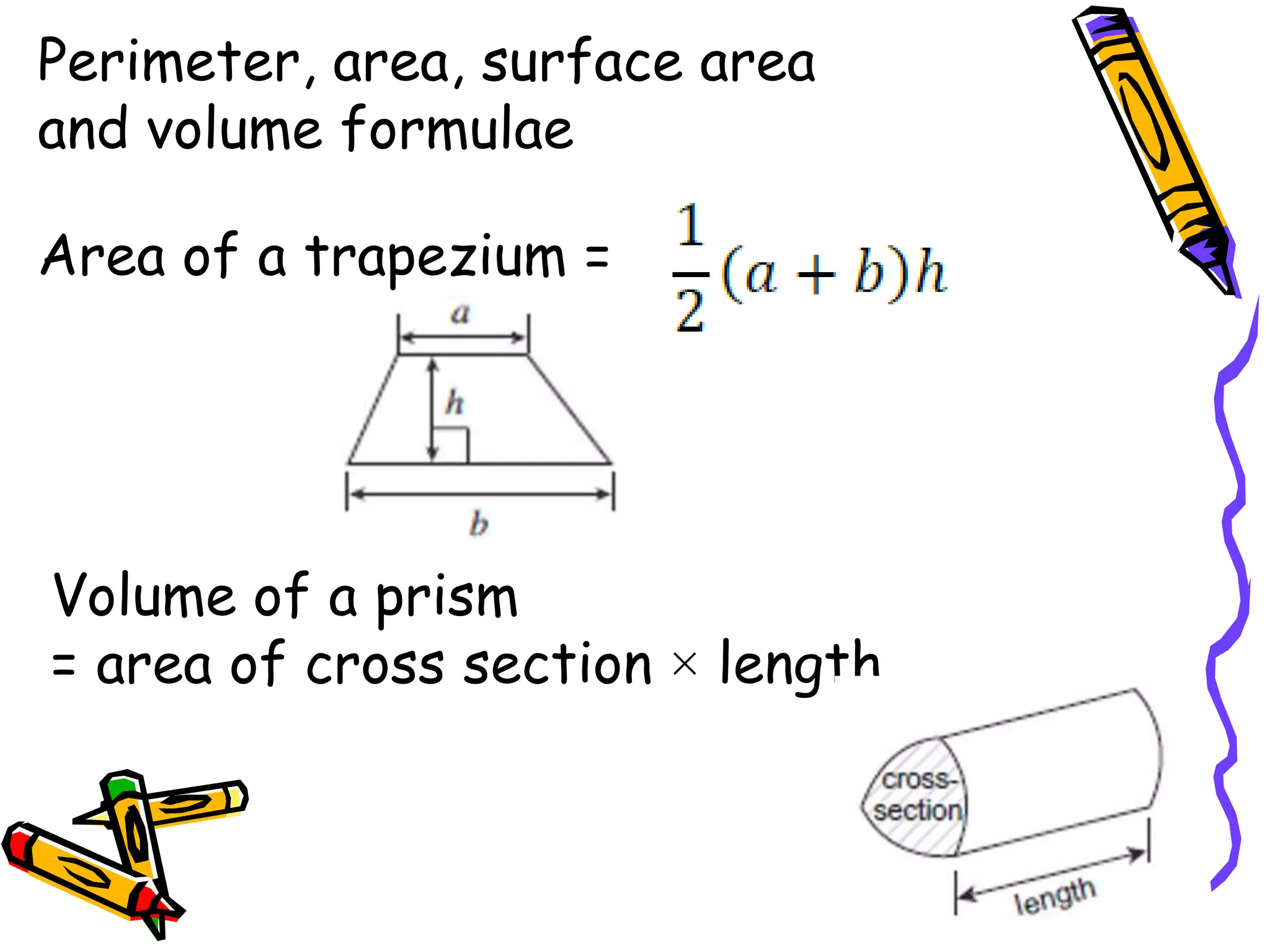
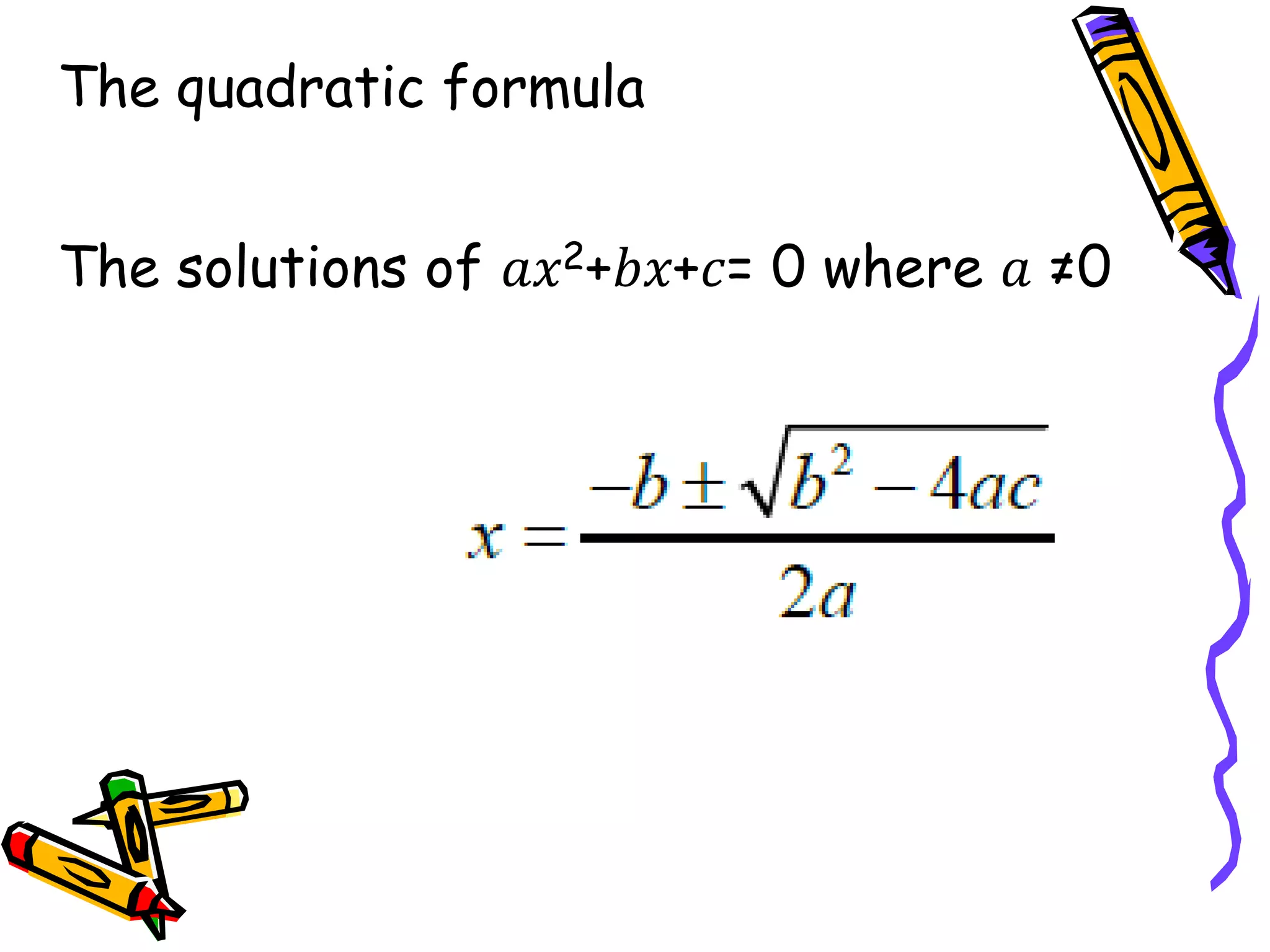The document outlines various formulae that students are expected to know, understand, or be able to use for the GCSE Mathematics exam. It presents formulae for the quadratic formula, circumference and area of a circle, Pythagoras' theorem, and trigonometry. It also lists formulae for perimeter, area, surface area, volume, compound interest, and probability that students should understand but won't be provided. Finally, it mentions kinematics formulae and calculators that may be provided or useful for questions involving various required formulae.