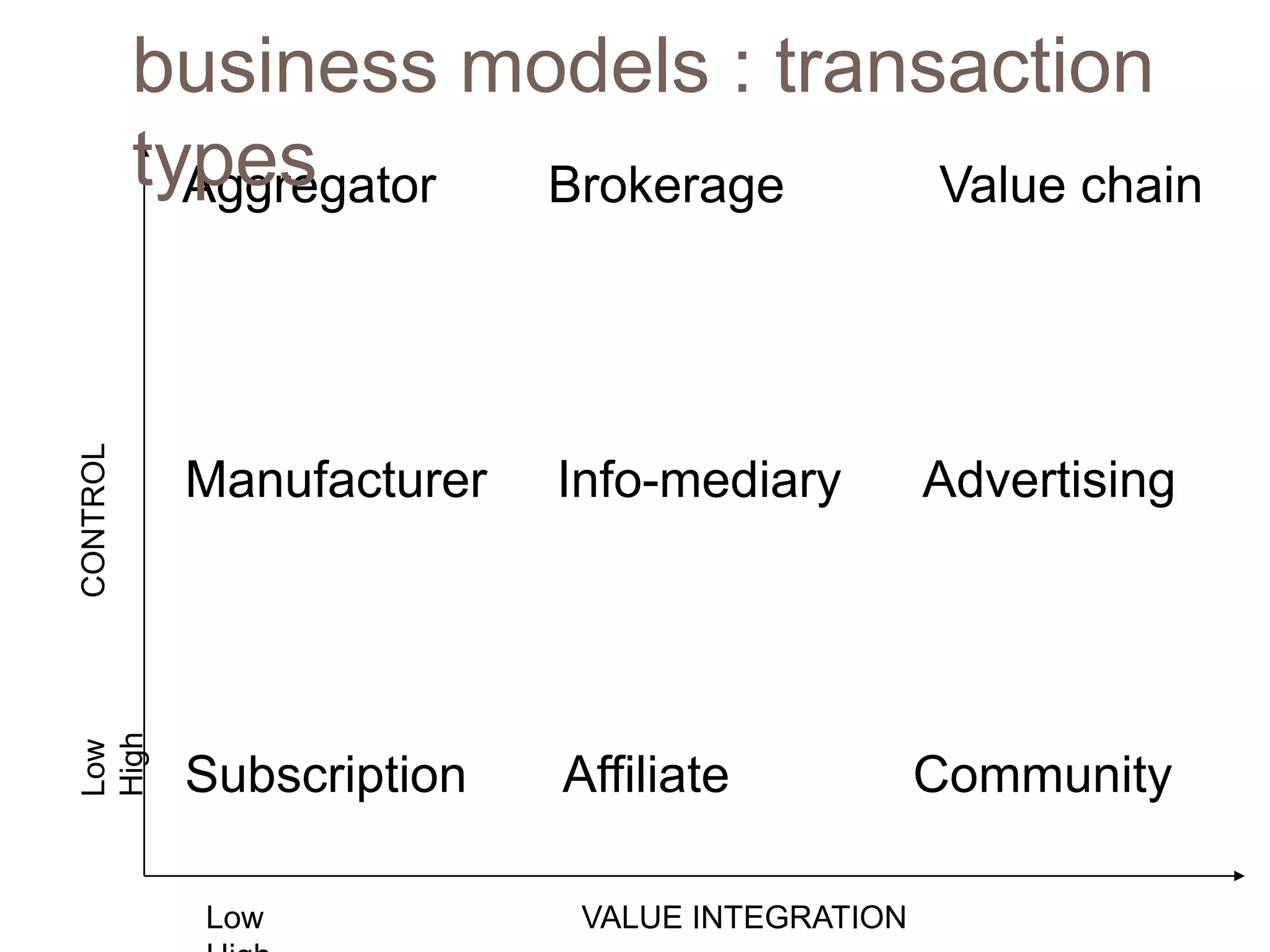
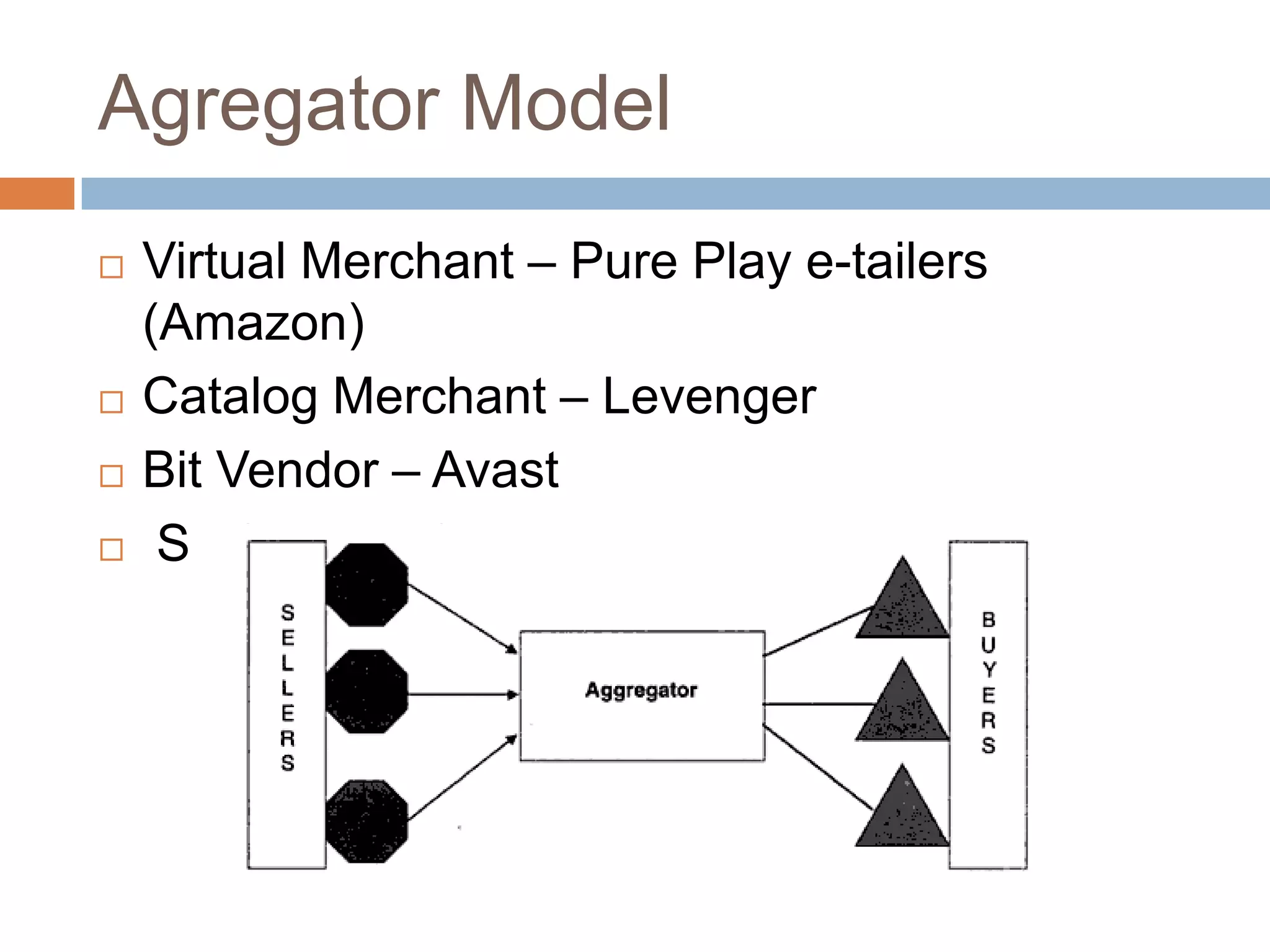
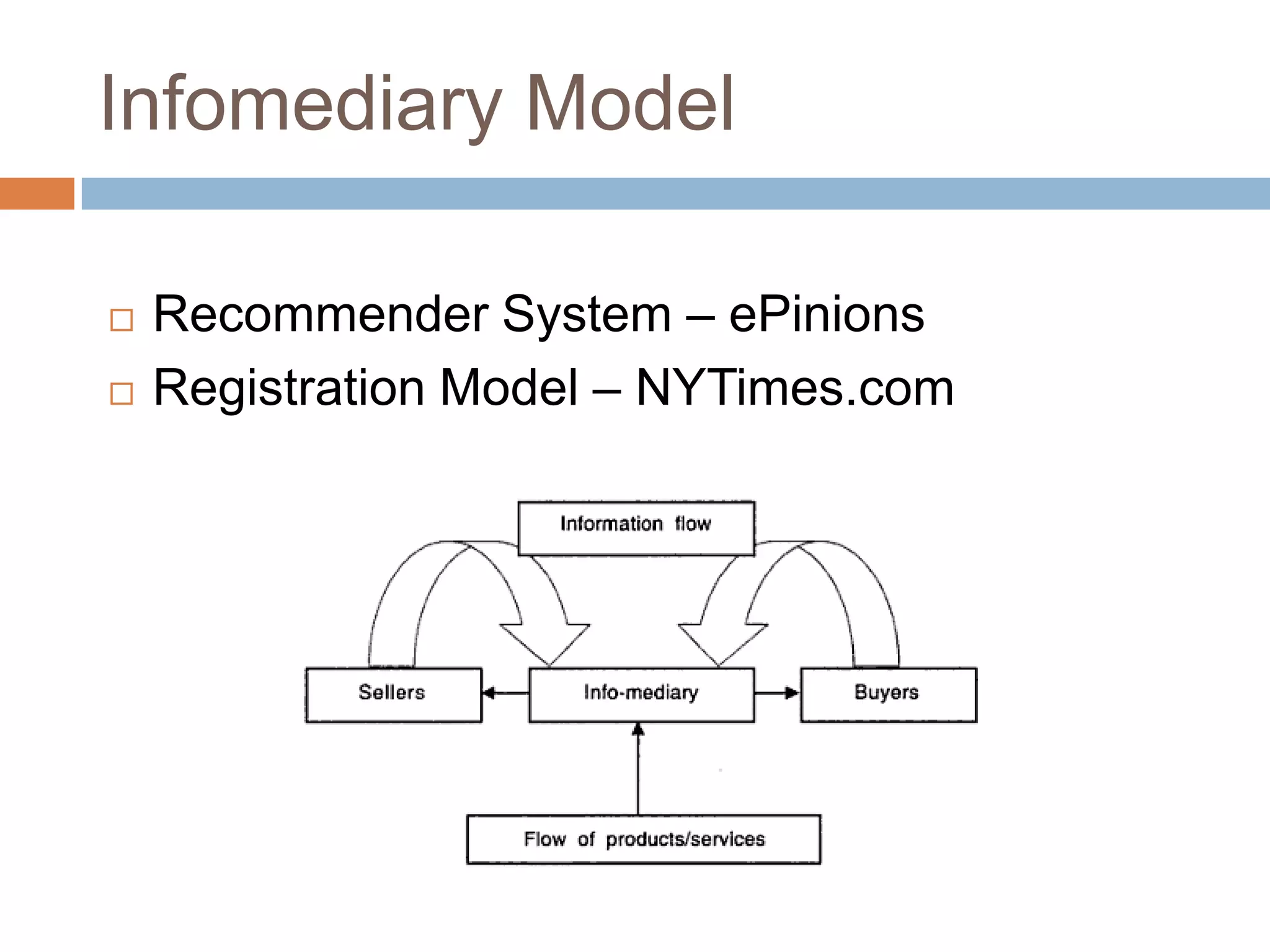
The document discusses different business models and revenue models for companies operating online, including value propositions, market offerings, resource systems, financial models like the advertising model, subscription model, transaction fee model, sales model, and affiliate model which generate revenue through various means like fees, subscriptions, sales, and referrals. It also covers different parties involved in online transactions like businesses interacting with other businesses, consumers, or both.