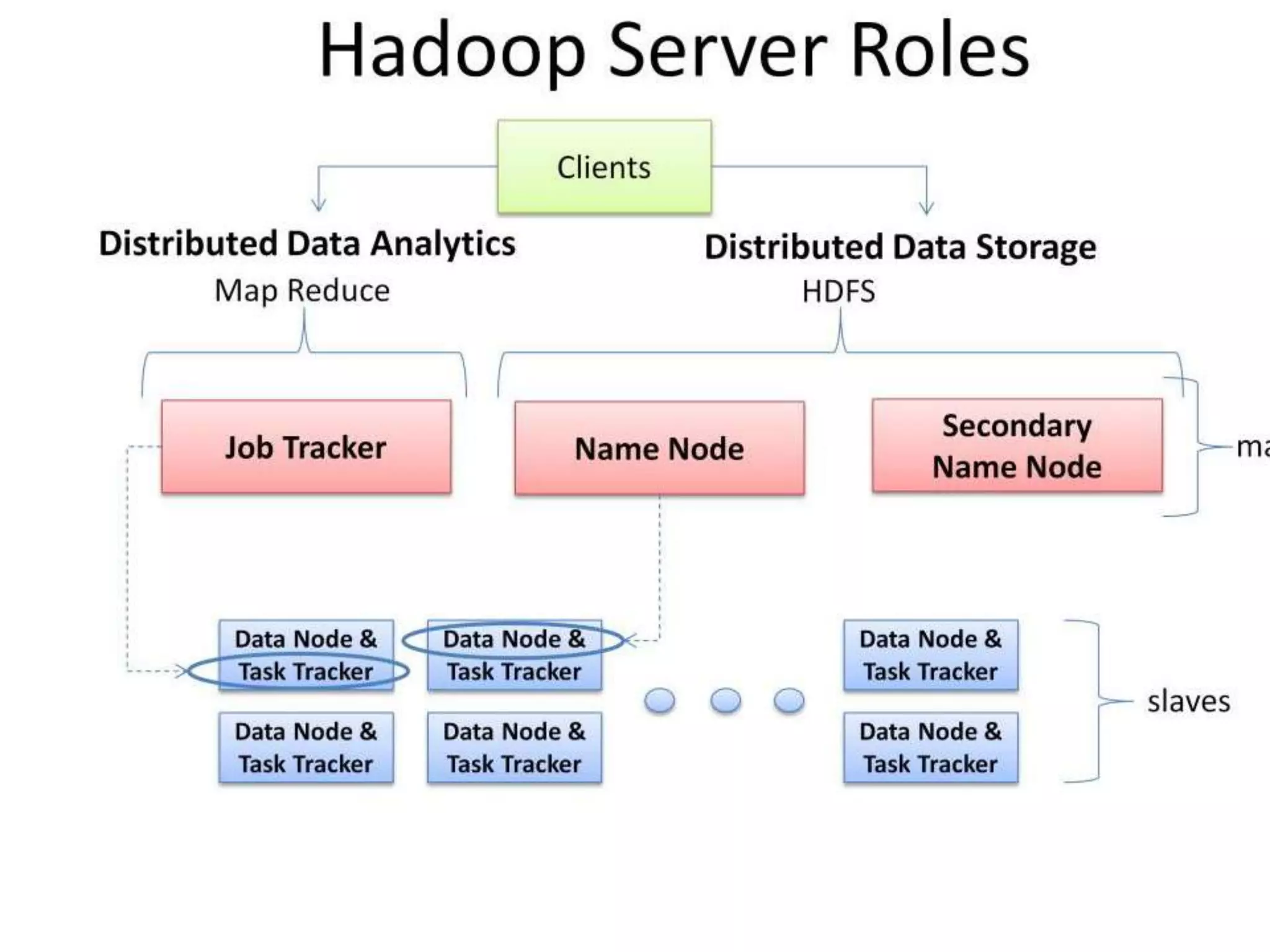
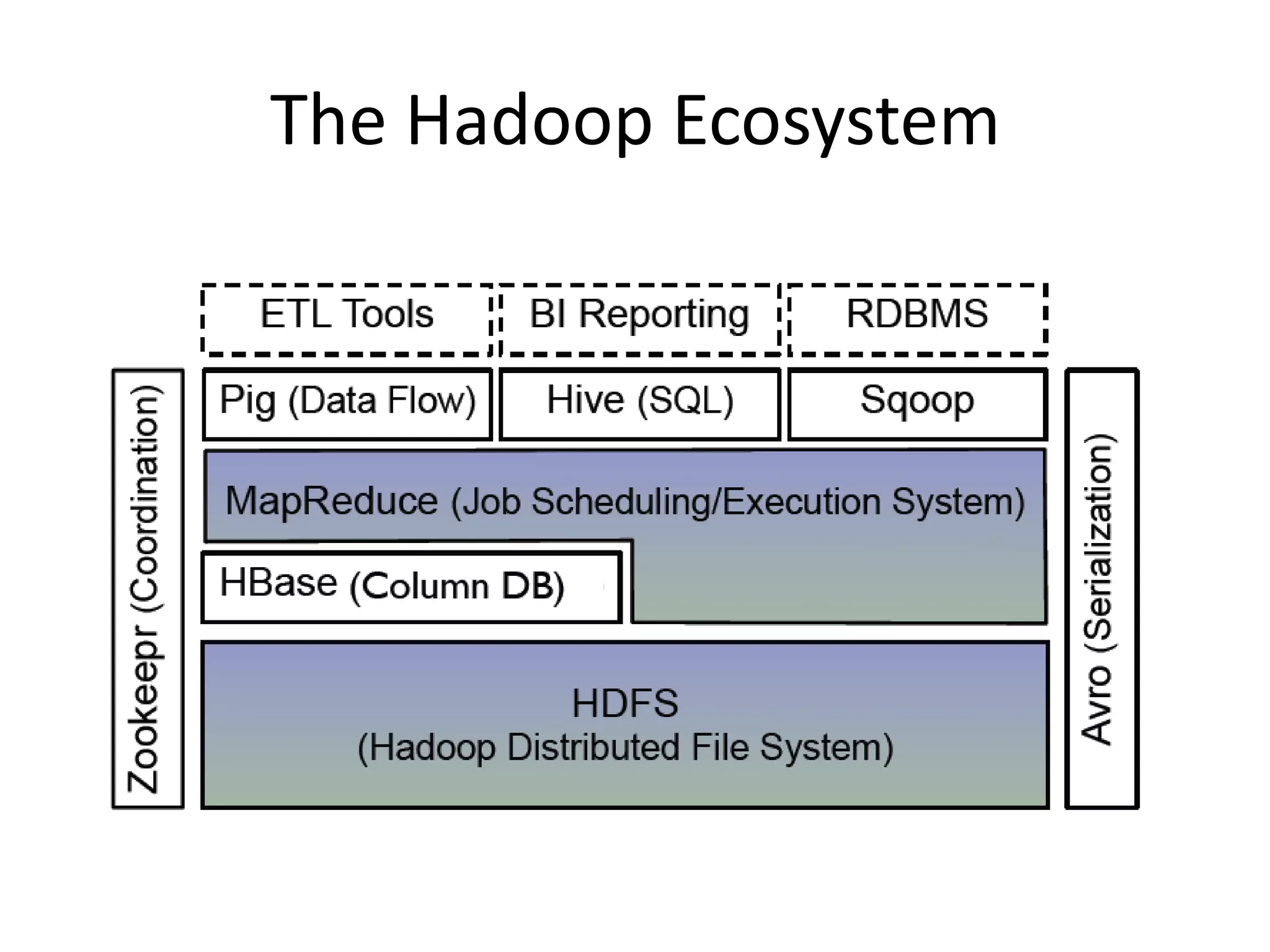
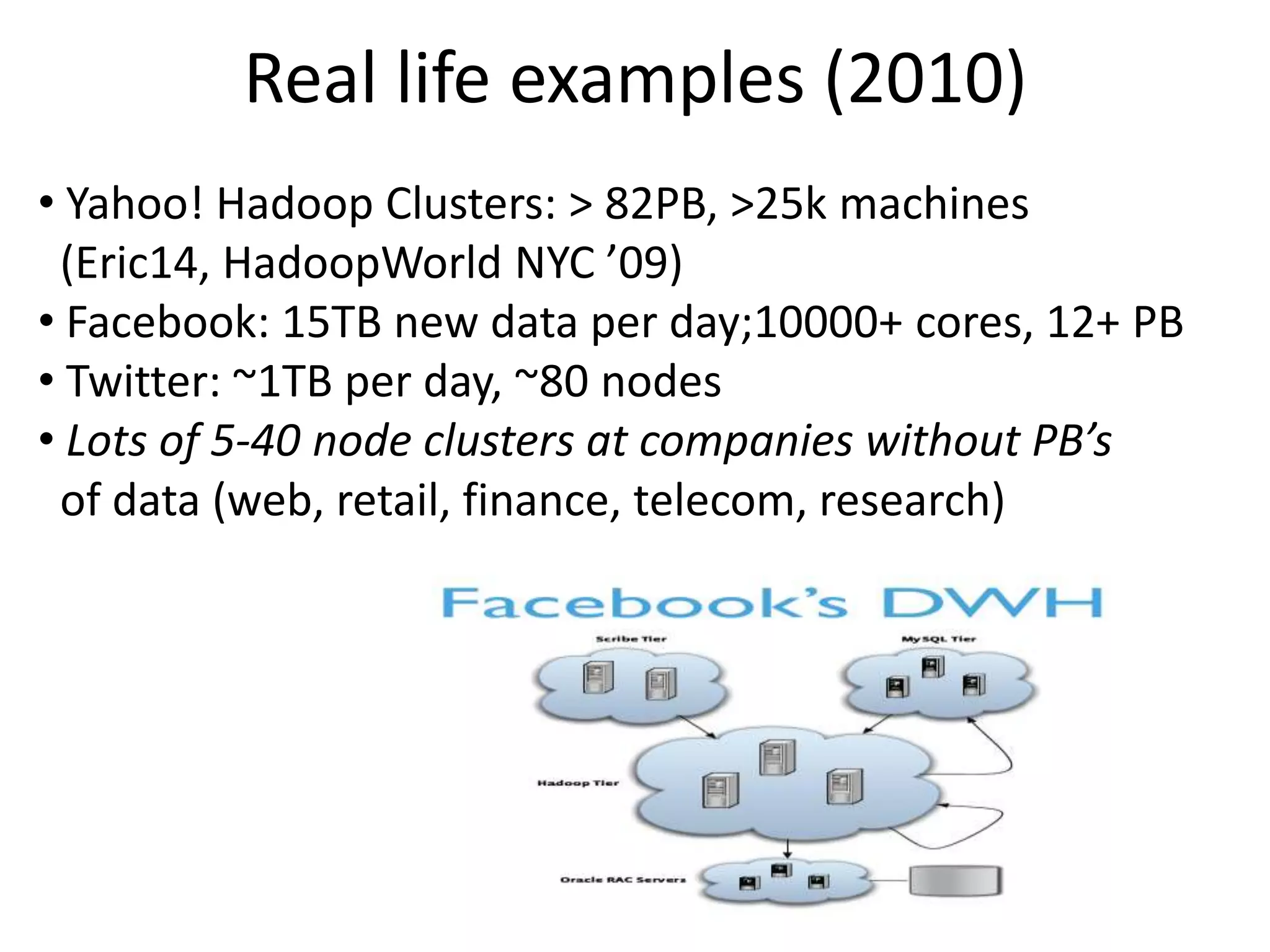
Hadoop is an open-source software framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers. It reliably stores and processes gobs of information across many commodity computers. Key components of Hadoop include the HDFS distributed file system for high-bandwidth storage, and MapReduce for parallel data processing. Hadoop can deliver data and run large-scale jobs reliably in spite of system changes or failures by detecting and compensating for hardware problems in the cluster.