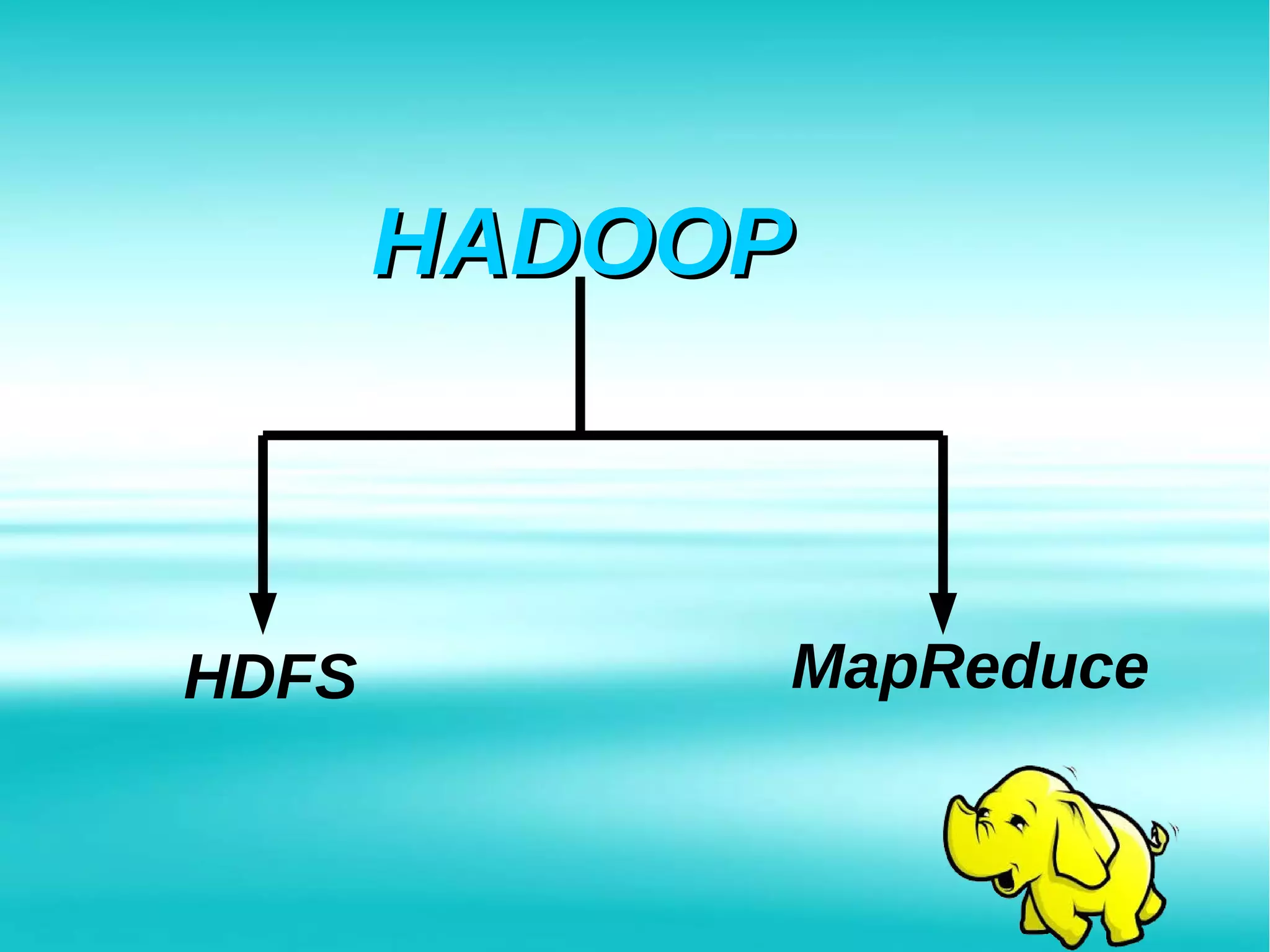
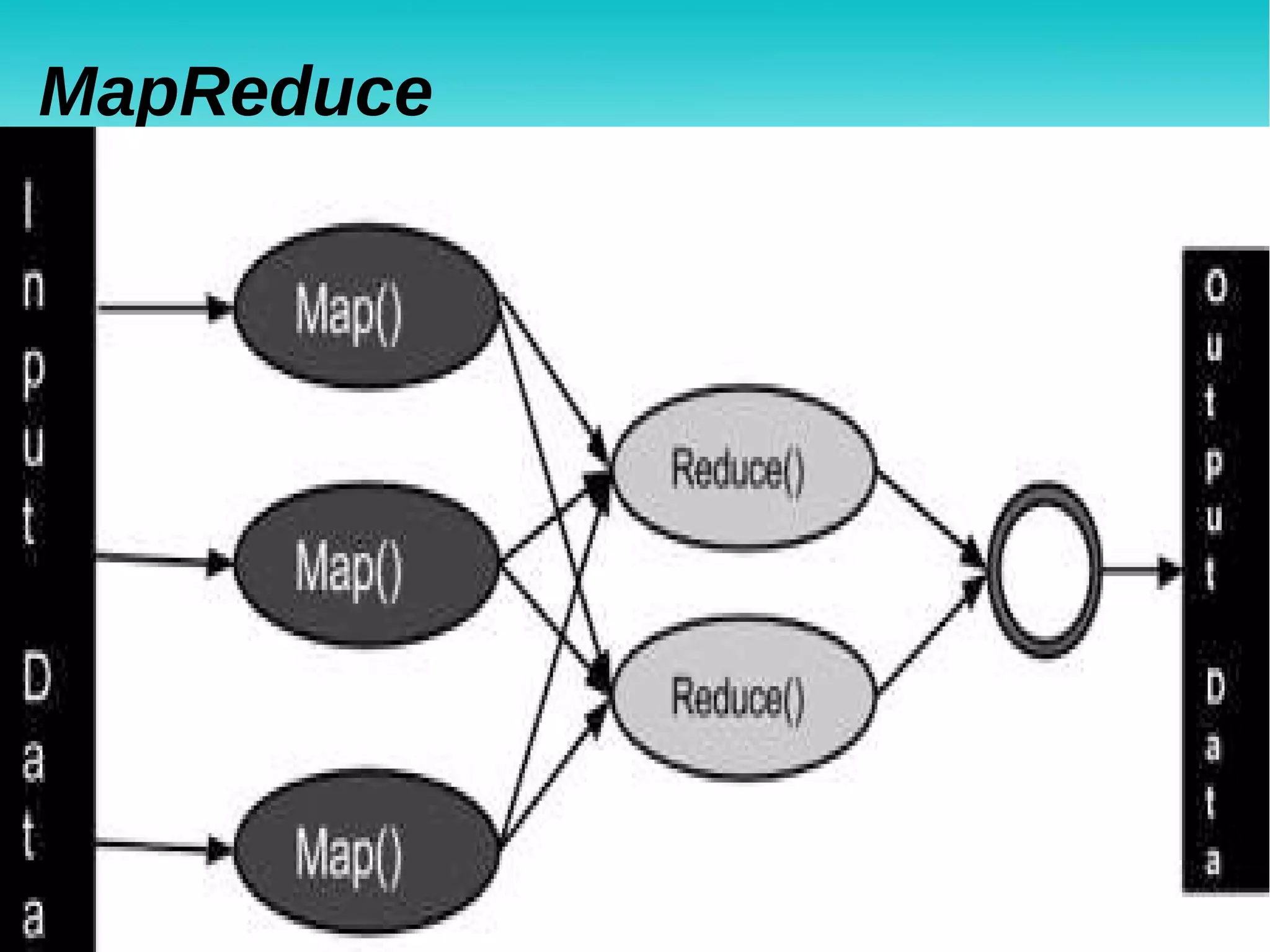
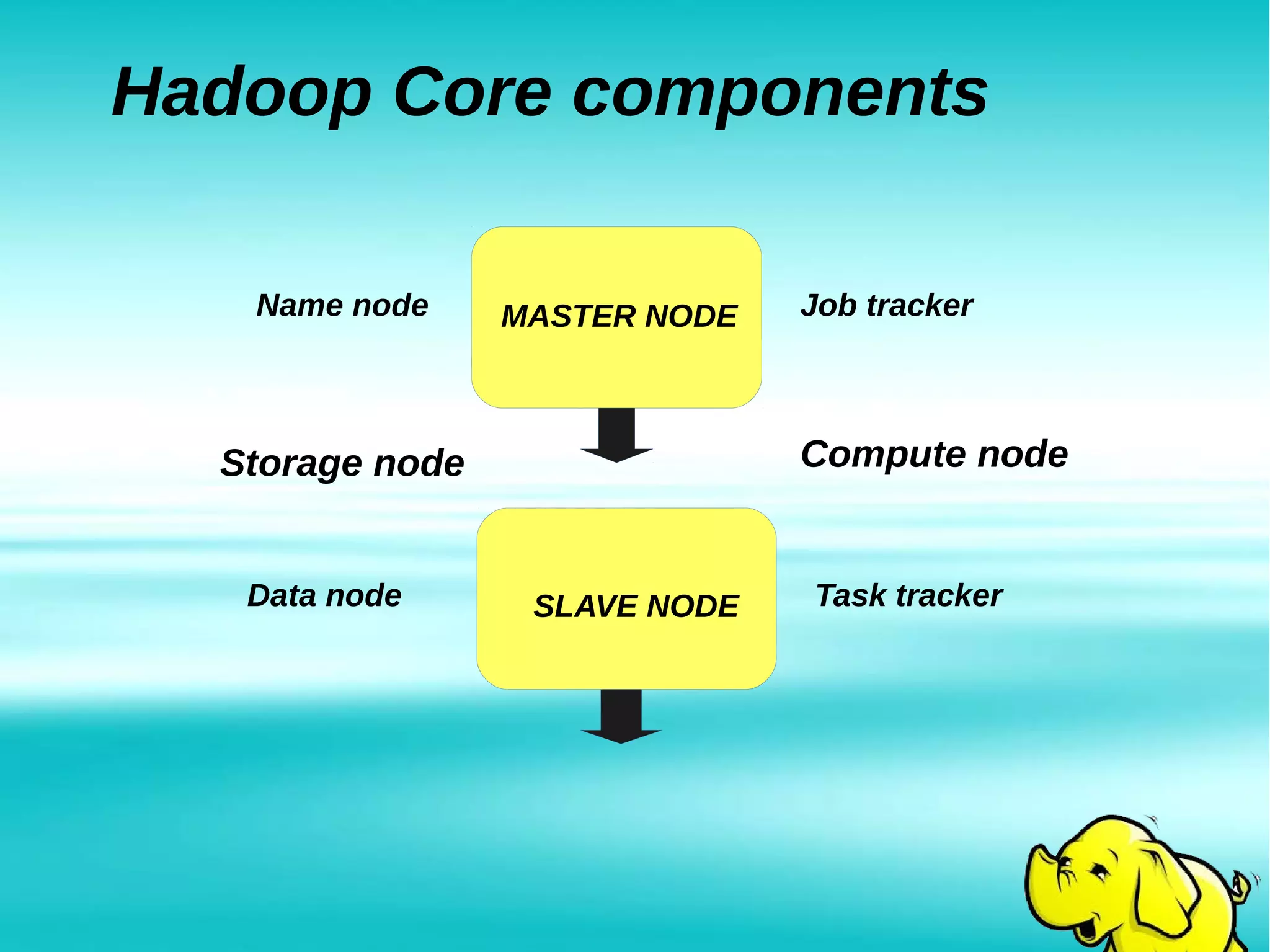
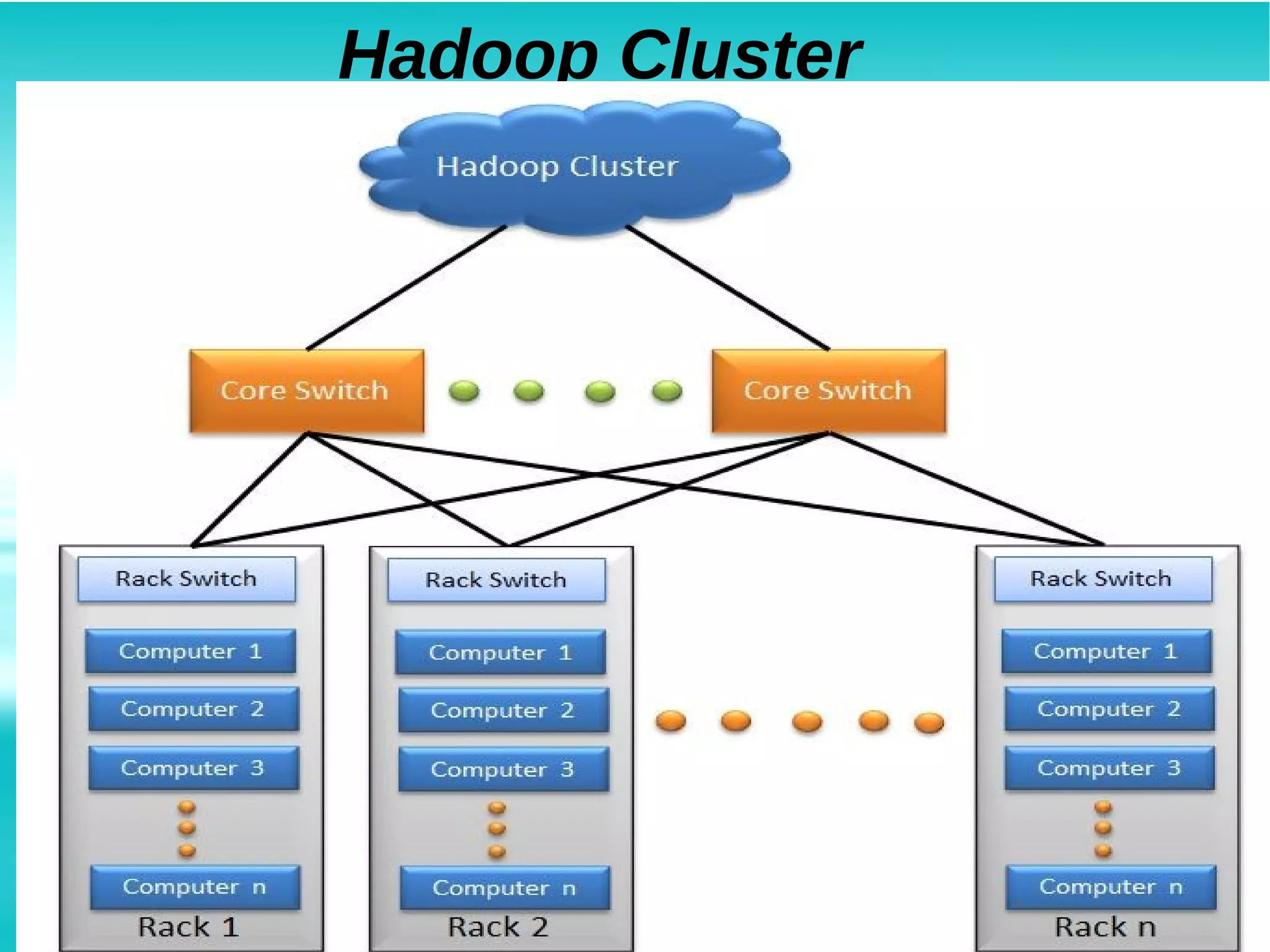
Hadoop is an open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of commodity hardware. It addresses problems posed by large and complex datasets that cannot be processed by traditional systems. Hadoop uses HDFS for storage and MapReduce for distributed processing of data in parallel. Hadoop clusters can scale to thousands of nodes and petabytes of data, providing low-cost and fault-tolerant solutions for big data problems faced by internet companies and other large organizations.