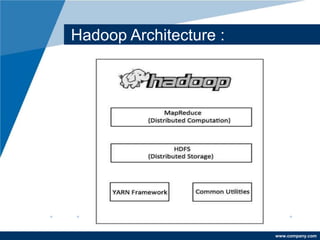
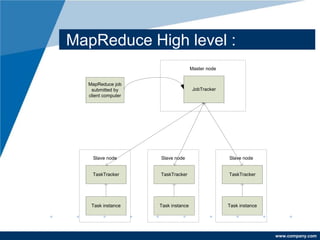
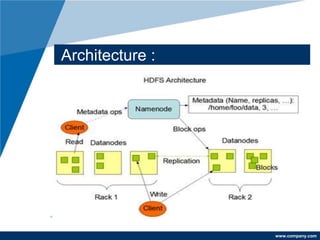
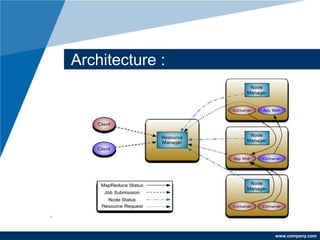
Apache Hadoop is a free, Java-based framework designed for processing large data sets in a distributed computing environment, using its MapReduce processing layer and Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for storage. The framework facilitates efficient data management, fault tolerance, and resource negotiation through YARN, supporting massive scalability and applicability across various enterprises like Amazon and Google. Its advantages include easy integration, rapid testing of distributed systems, and high compatibility across platforms.