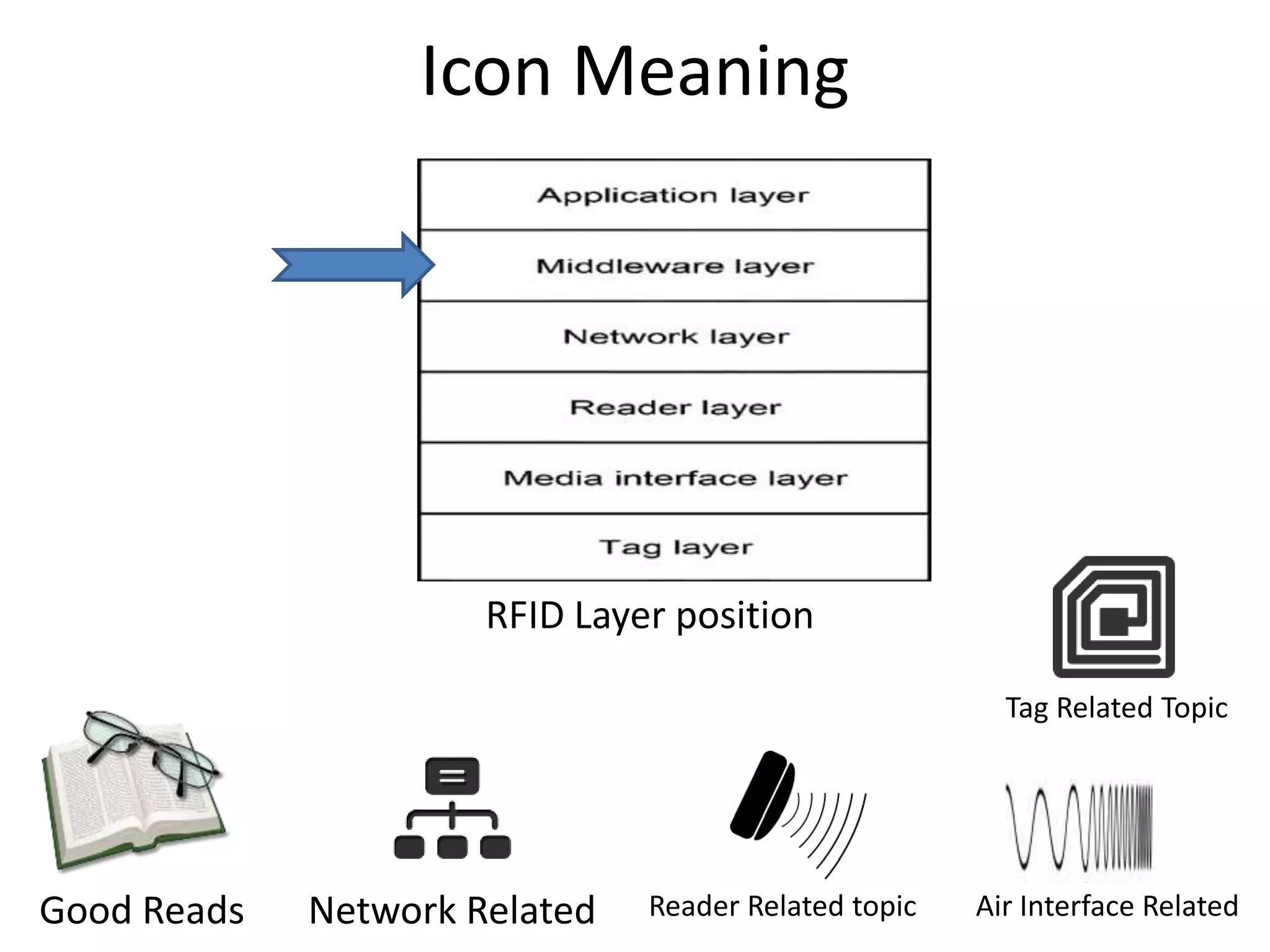
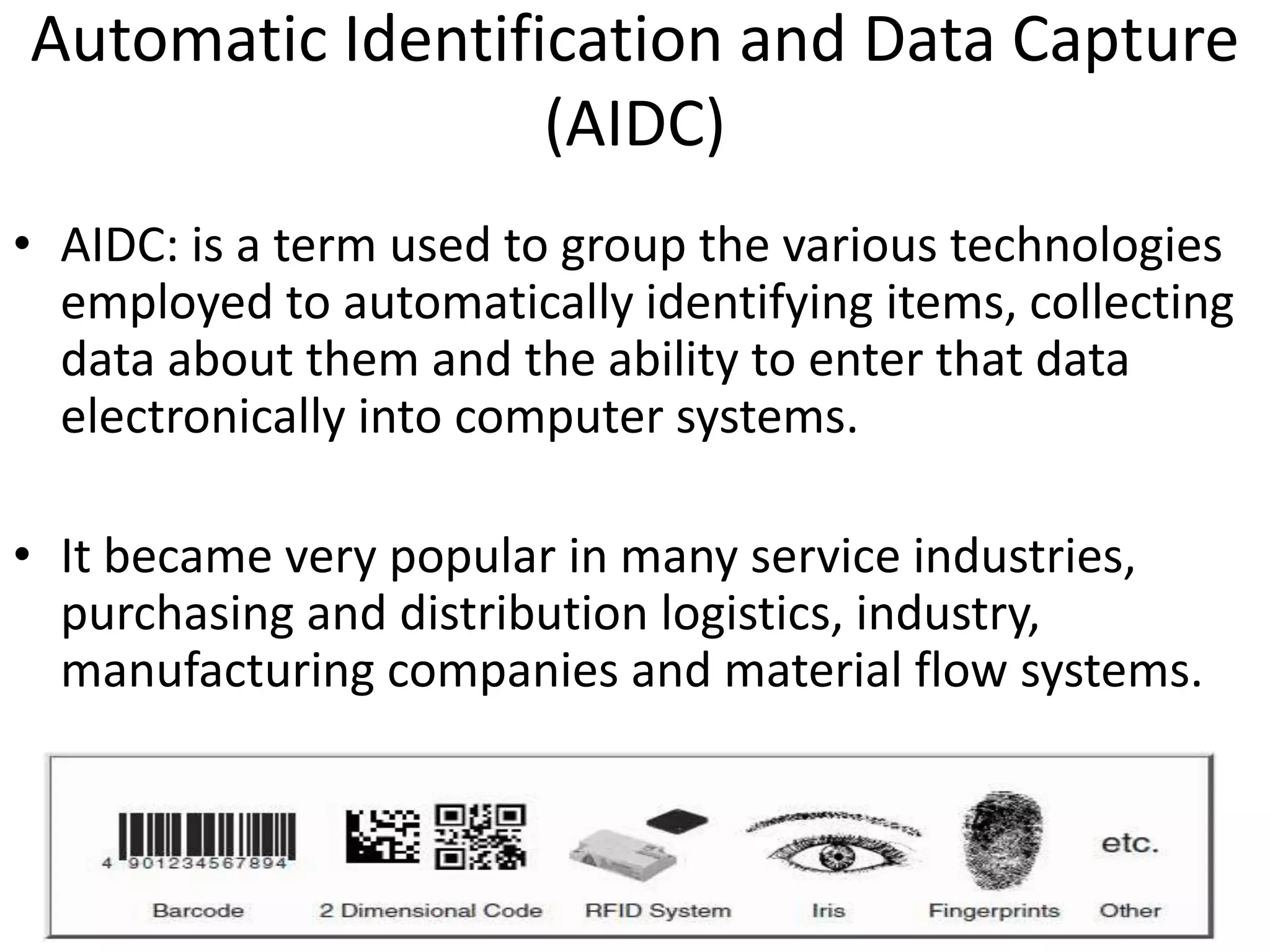
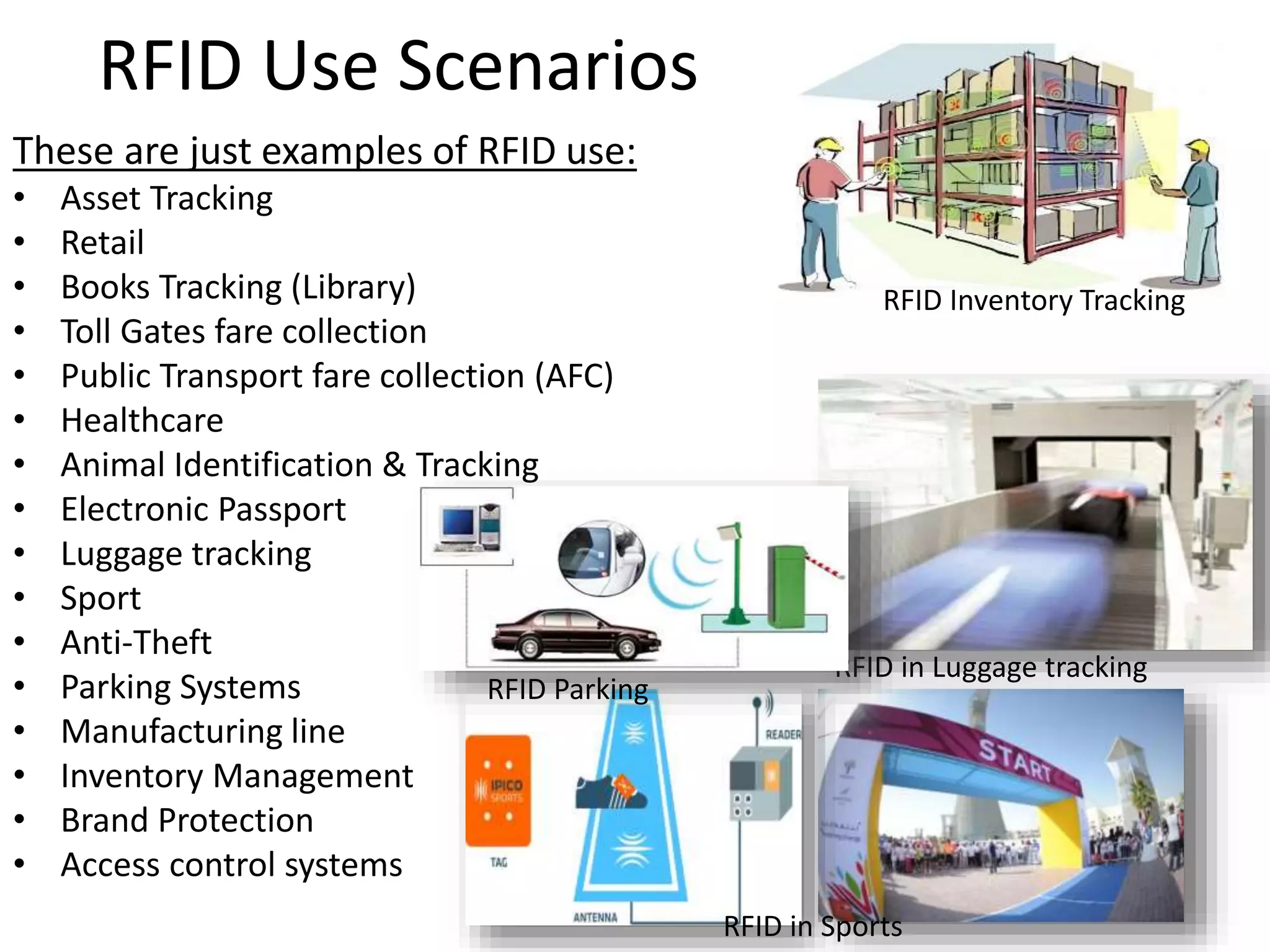
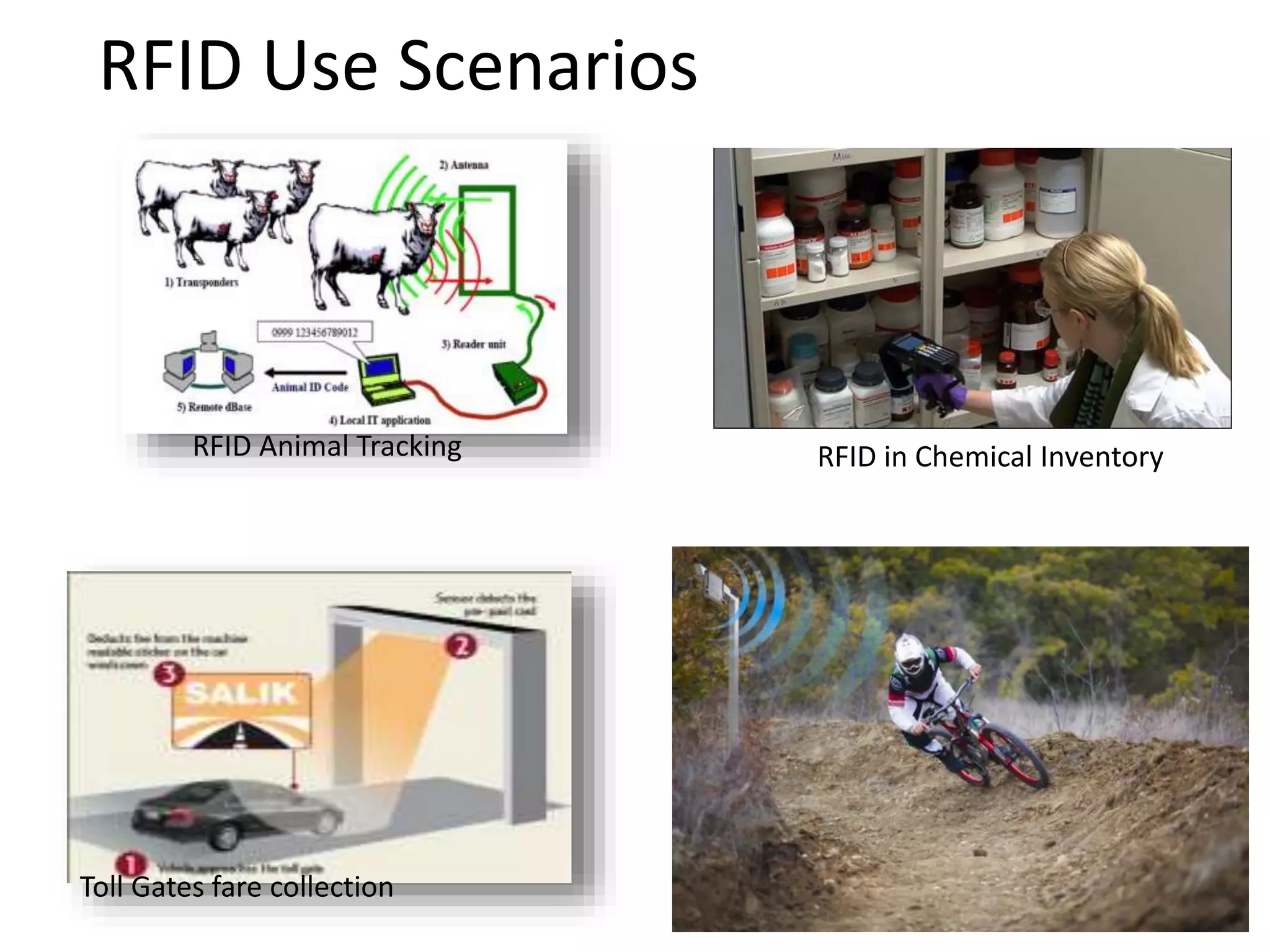
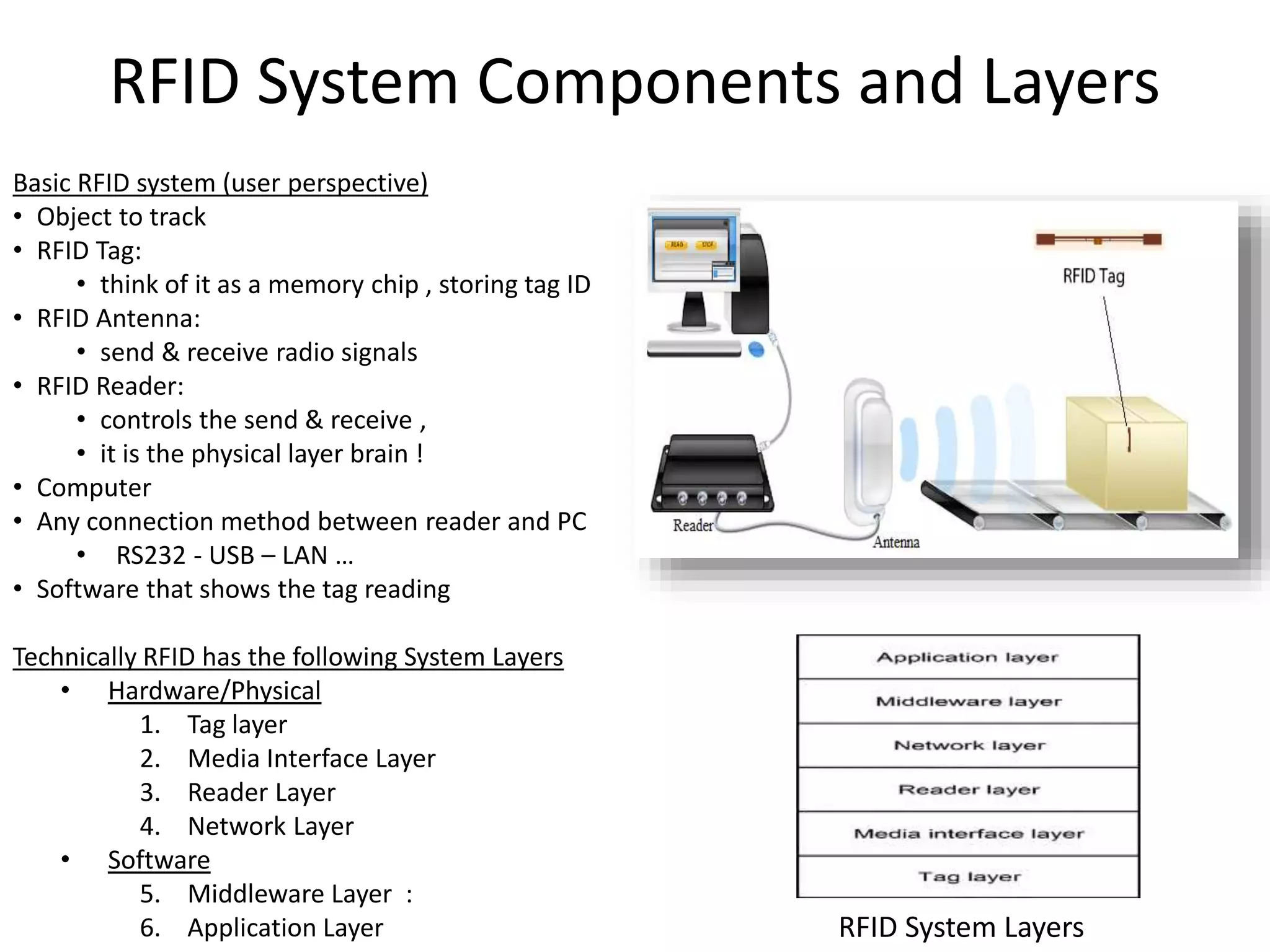
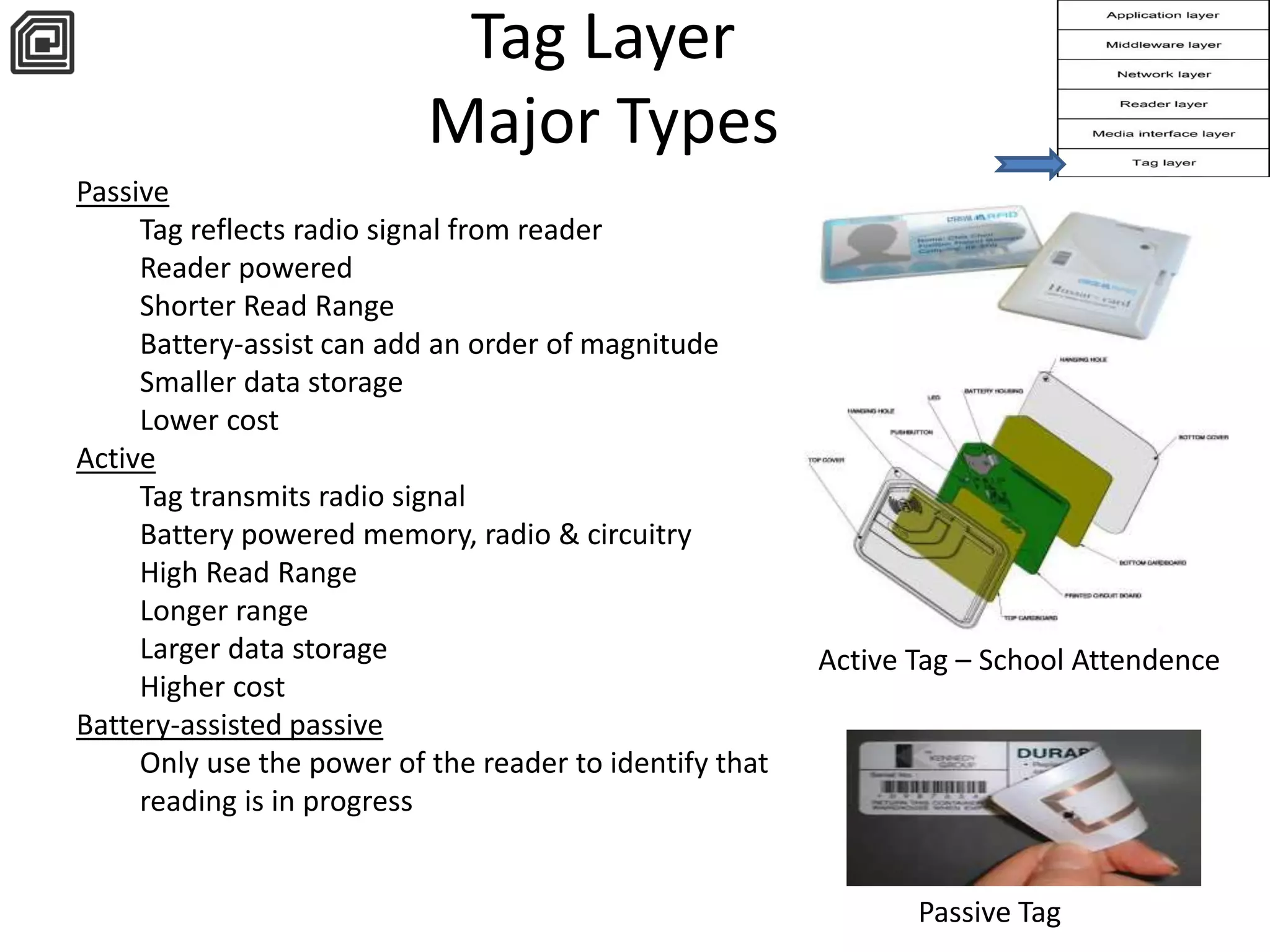
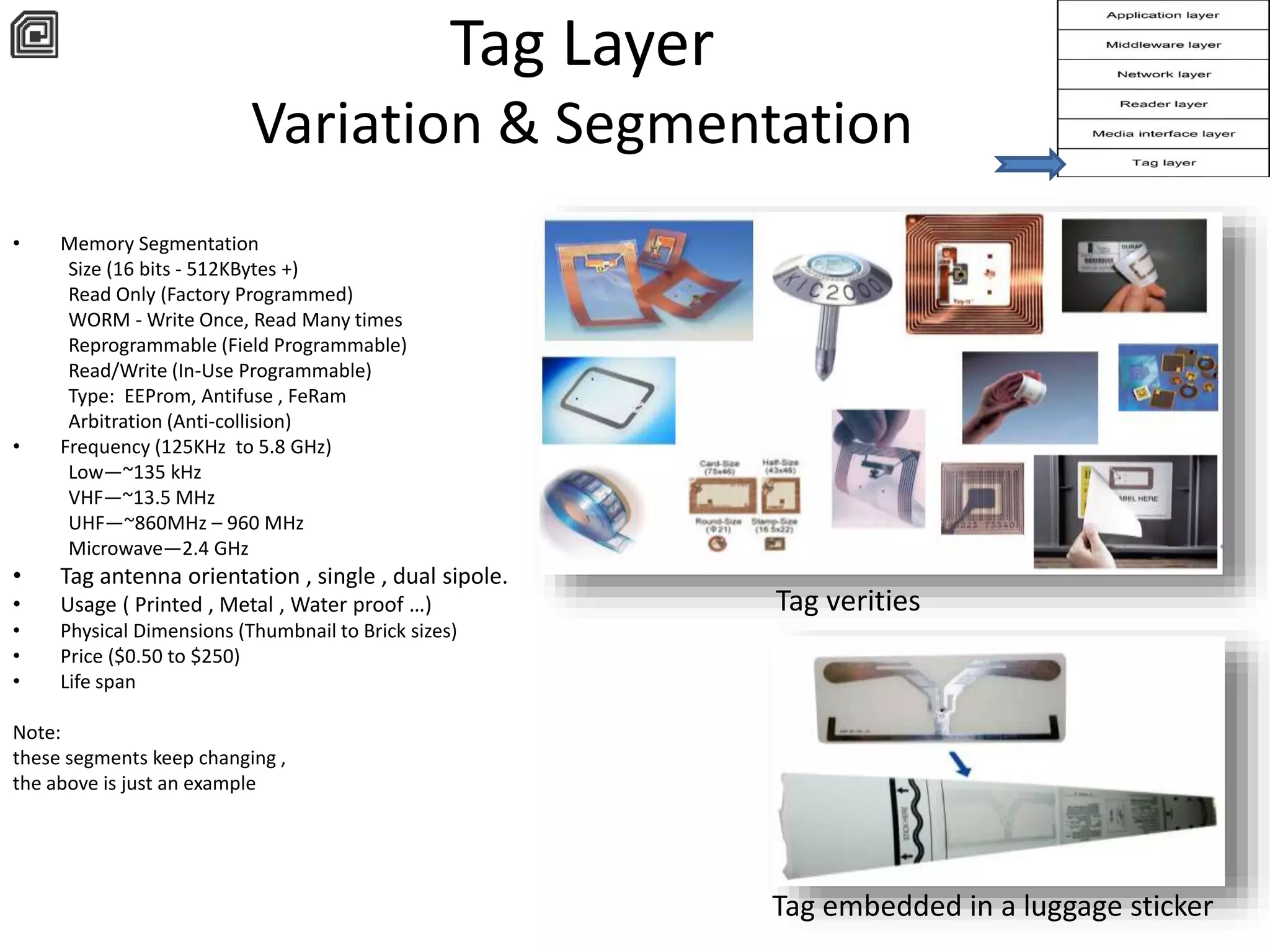
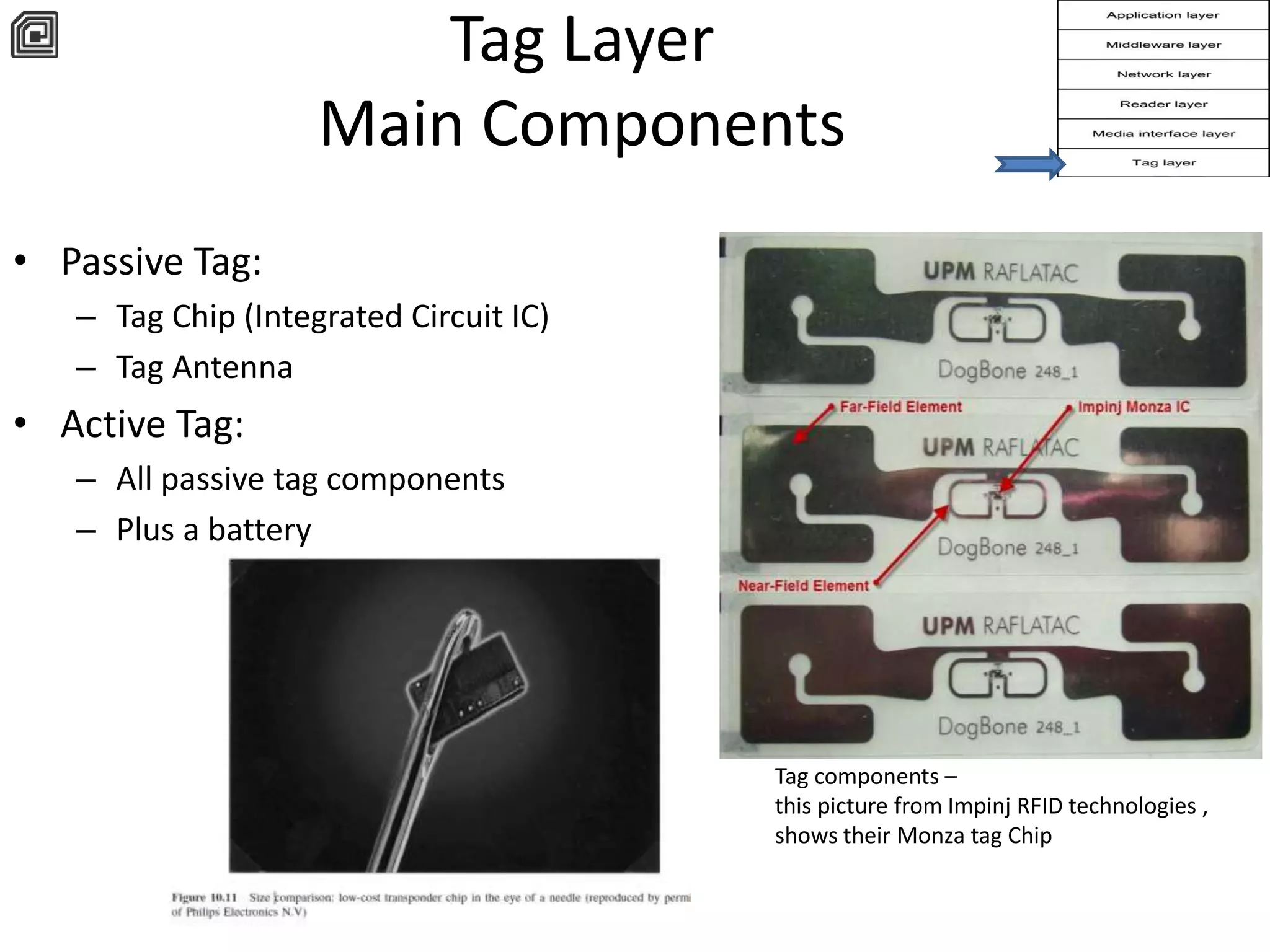
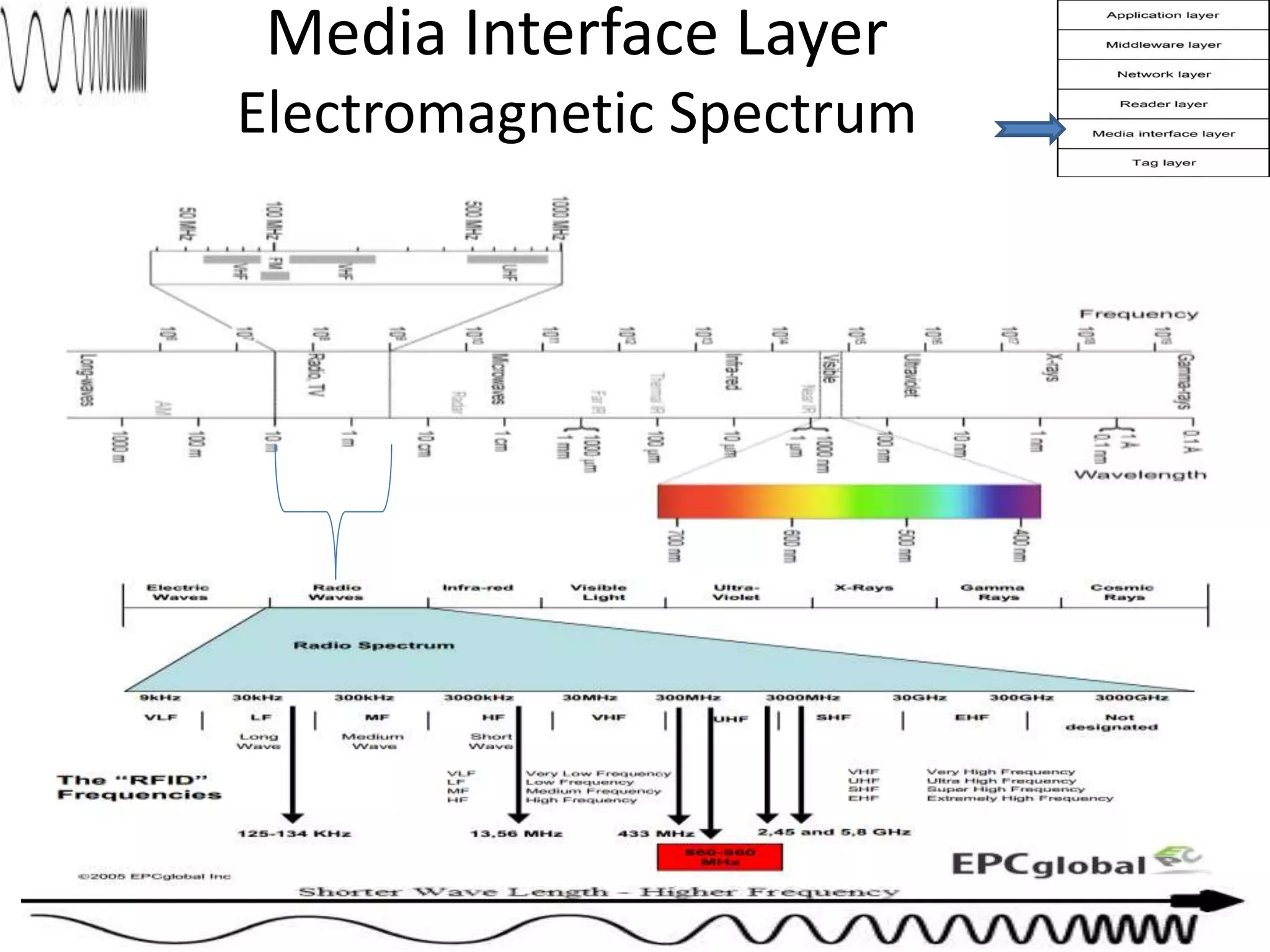
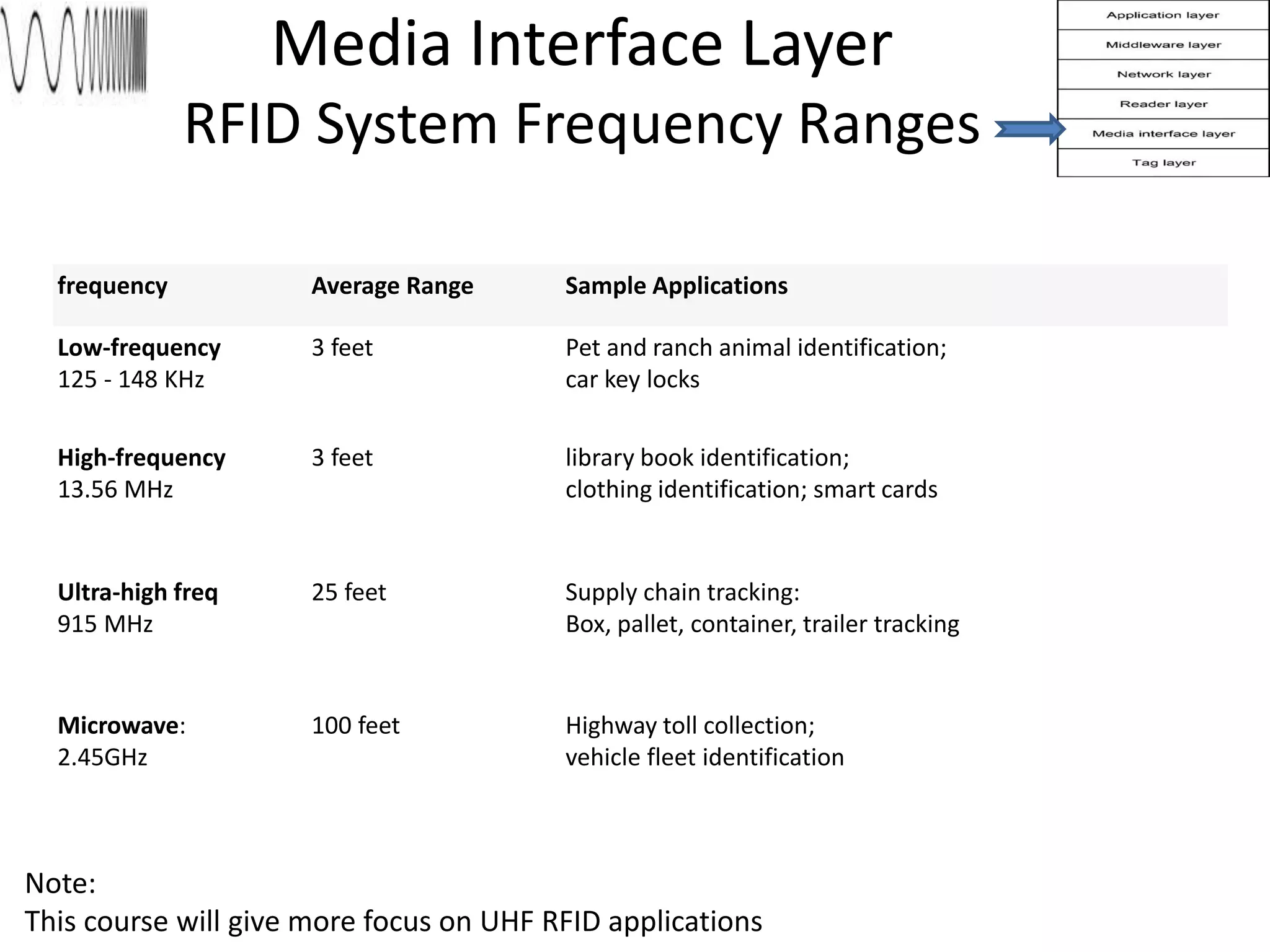
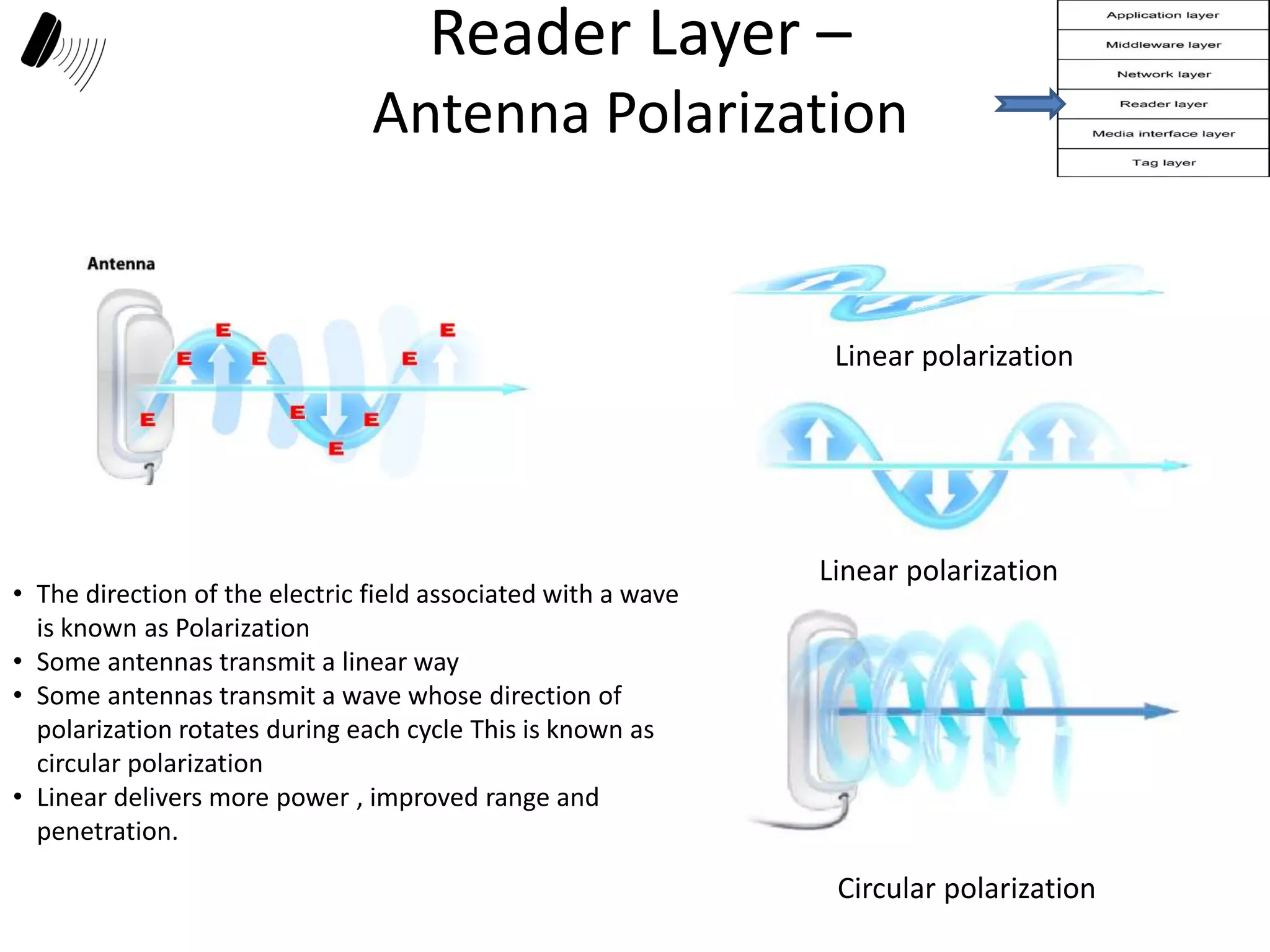
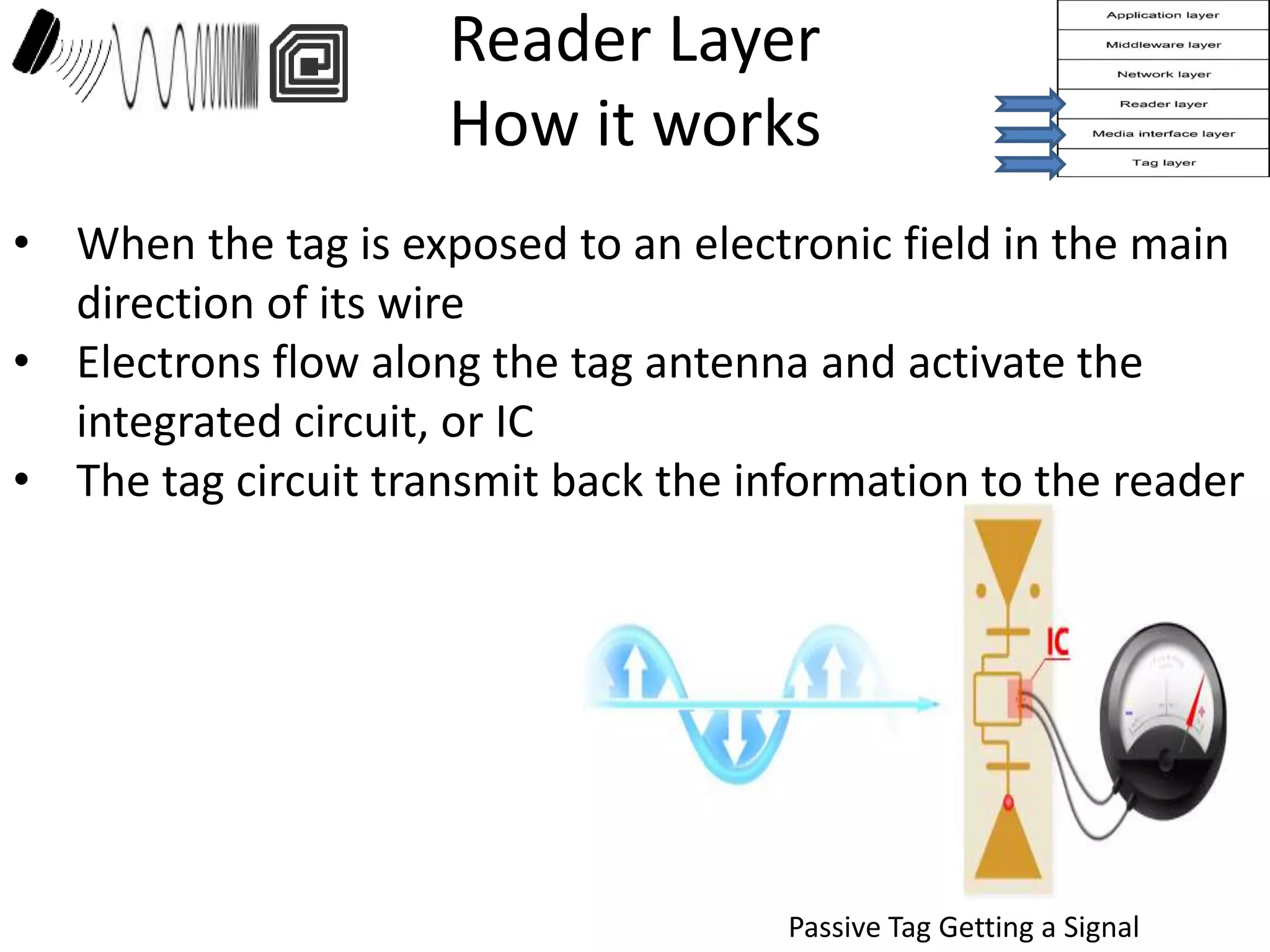
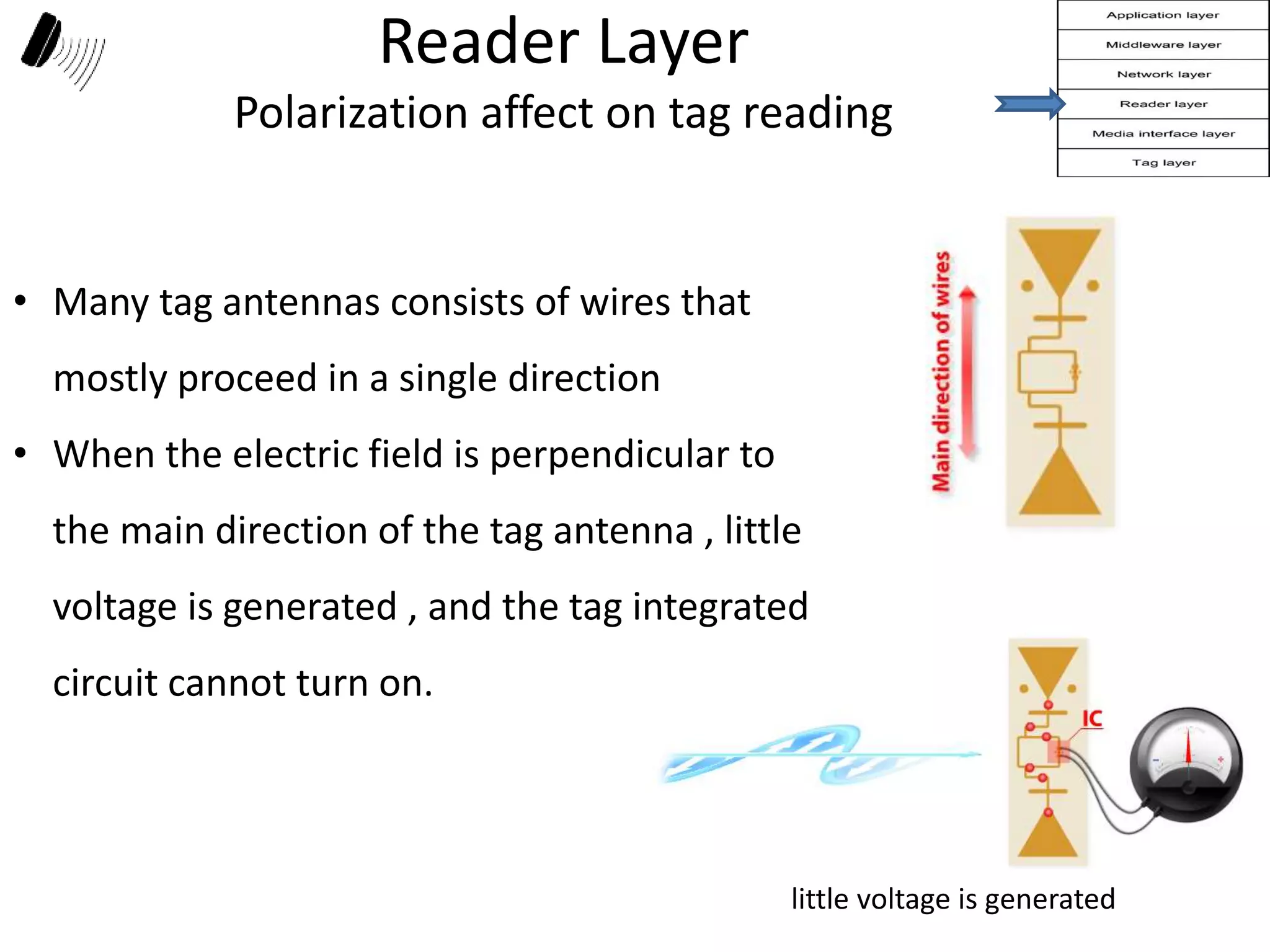
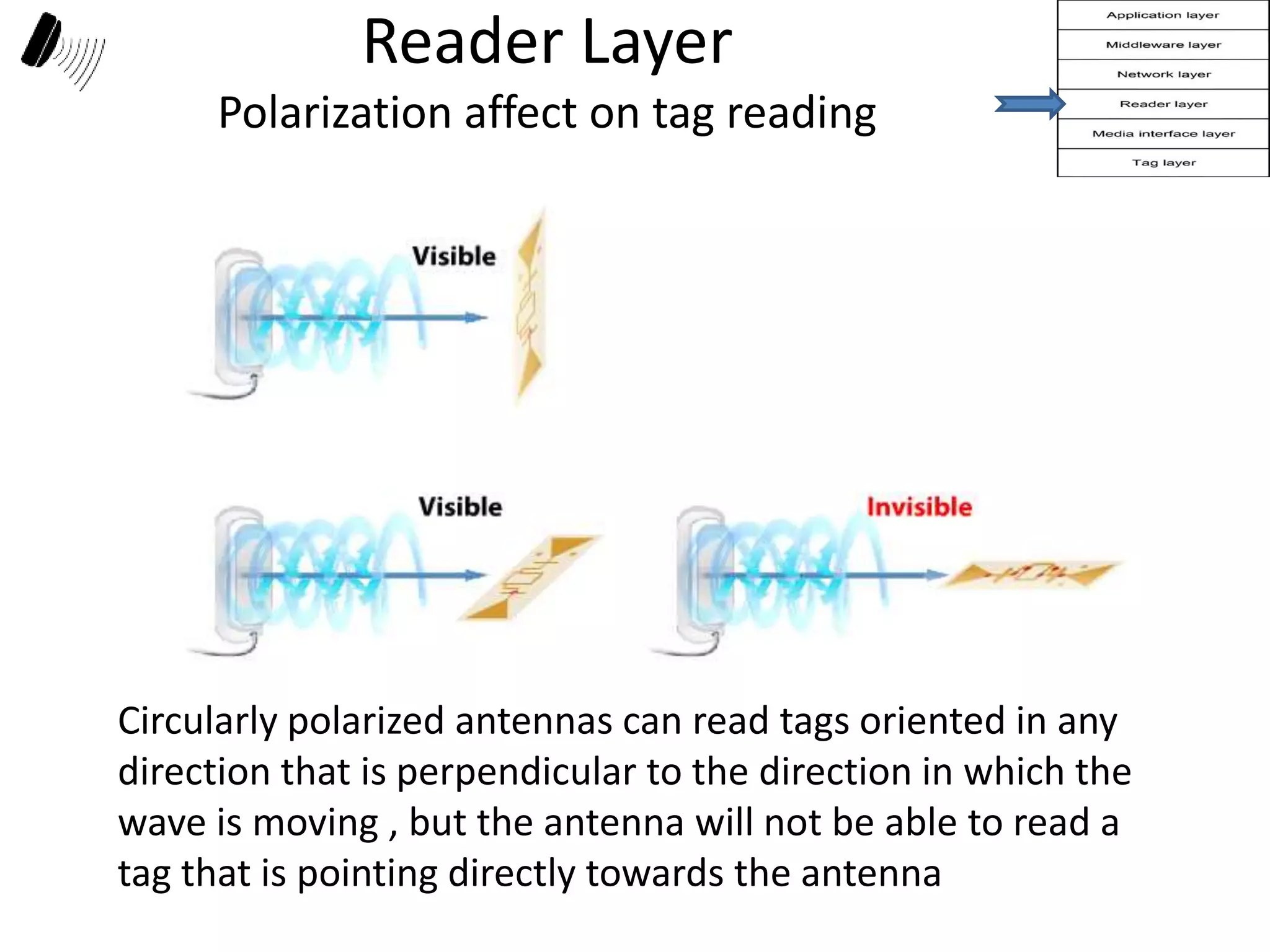
The document provides a comprehensive overview of RFID applications, including system components, layers, and use cases across various industries such as retail, healthcare, and logistics. It details the different types of RFID tags, their functionalities, the reader layer, and the middleware that interfaces with business software. Key topics include tag orientation, frequency ranges, and examples of RFID in practical scenarios like luggage tracking and inventory management.