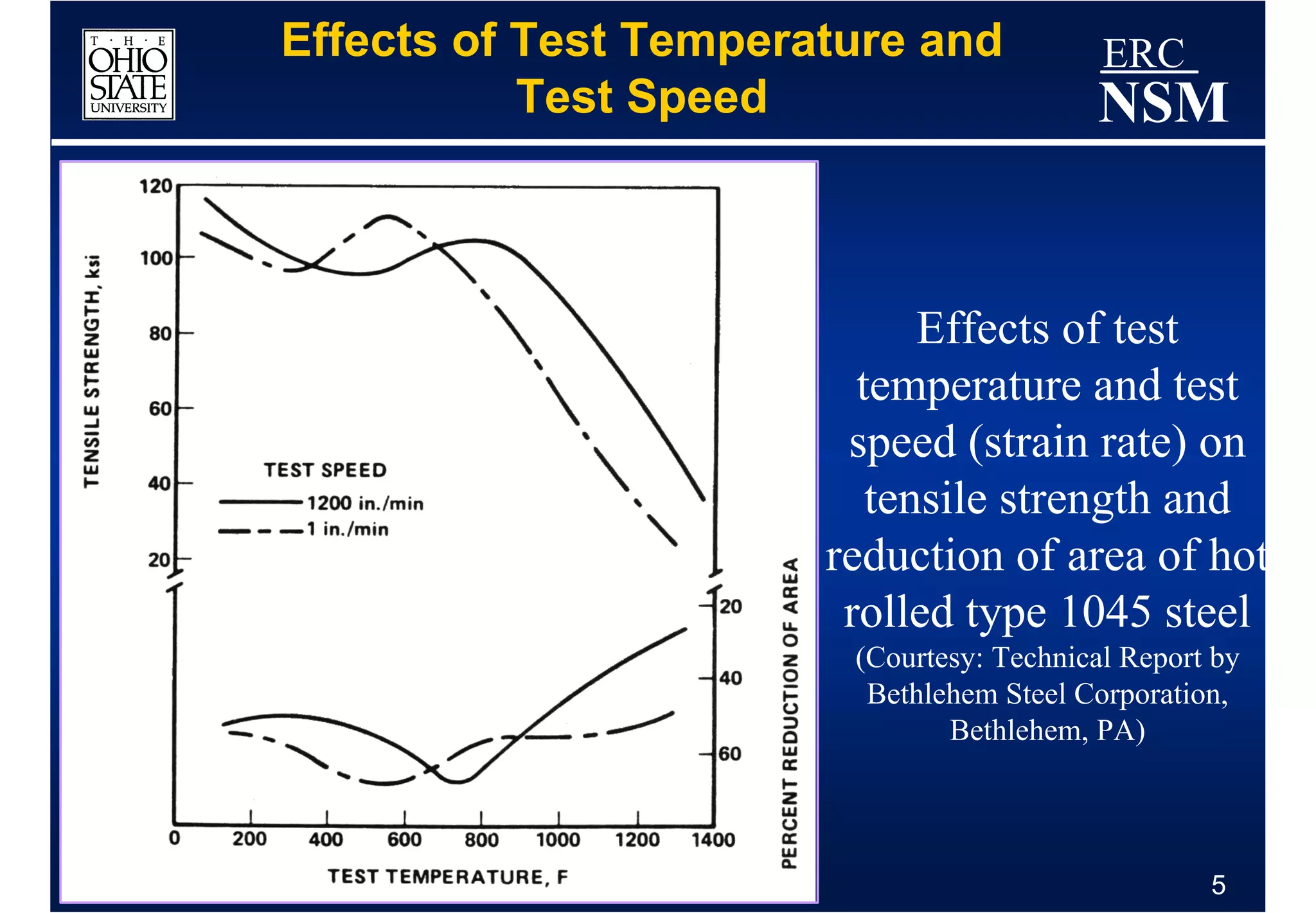
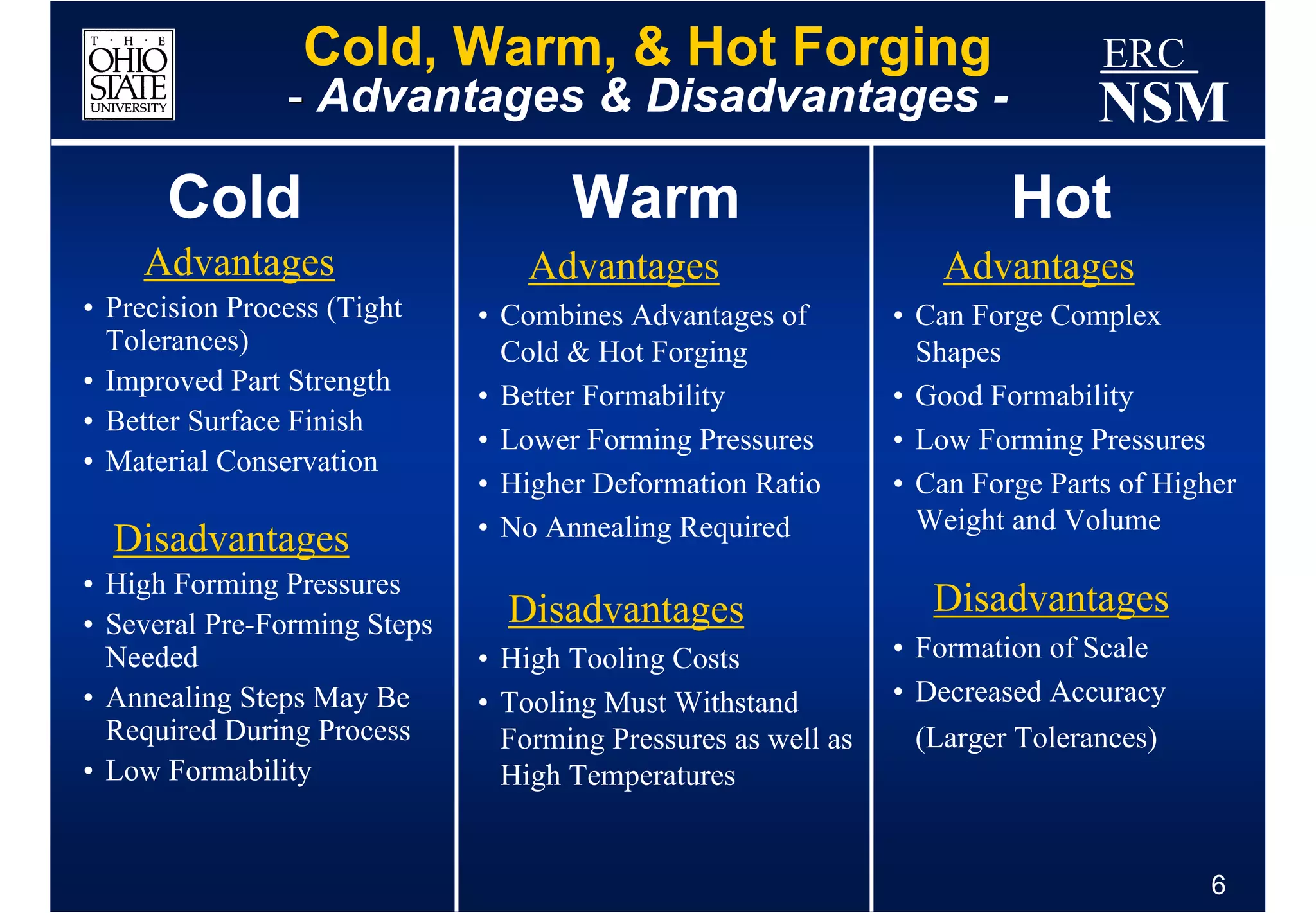
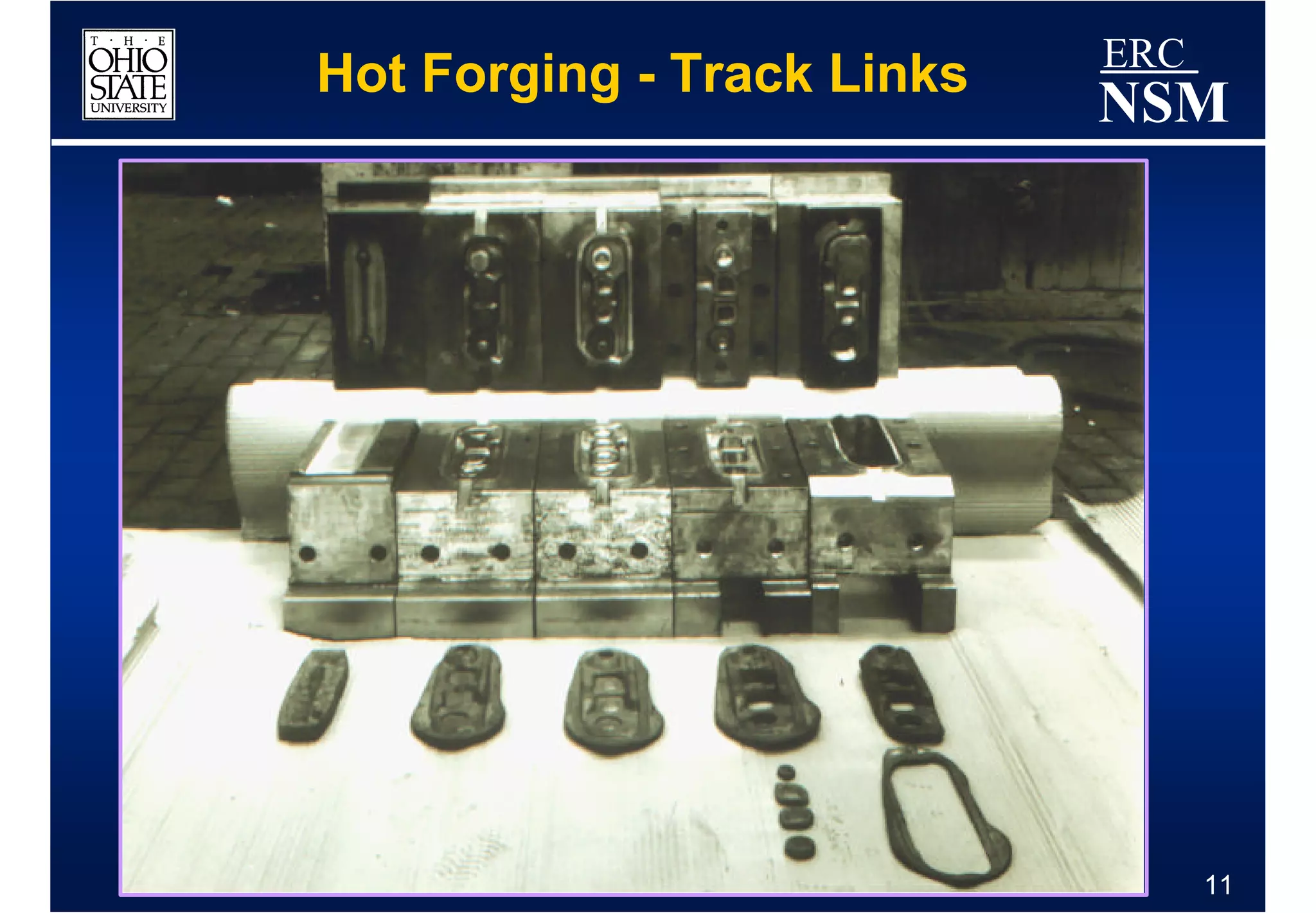
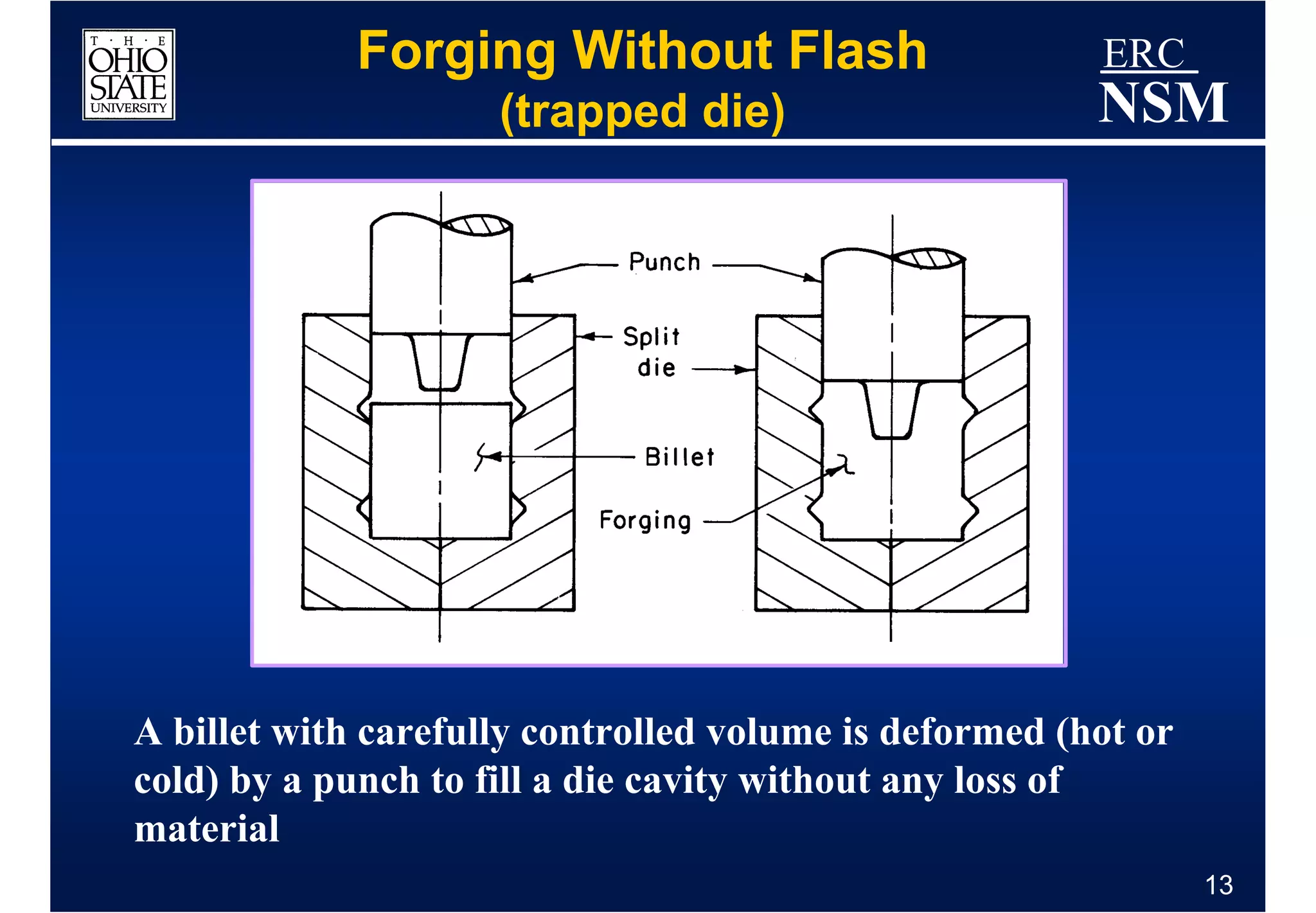
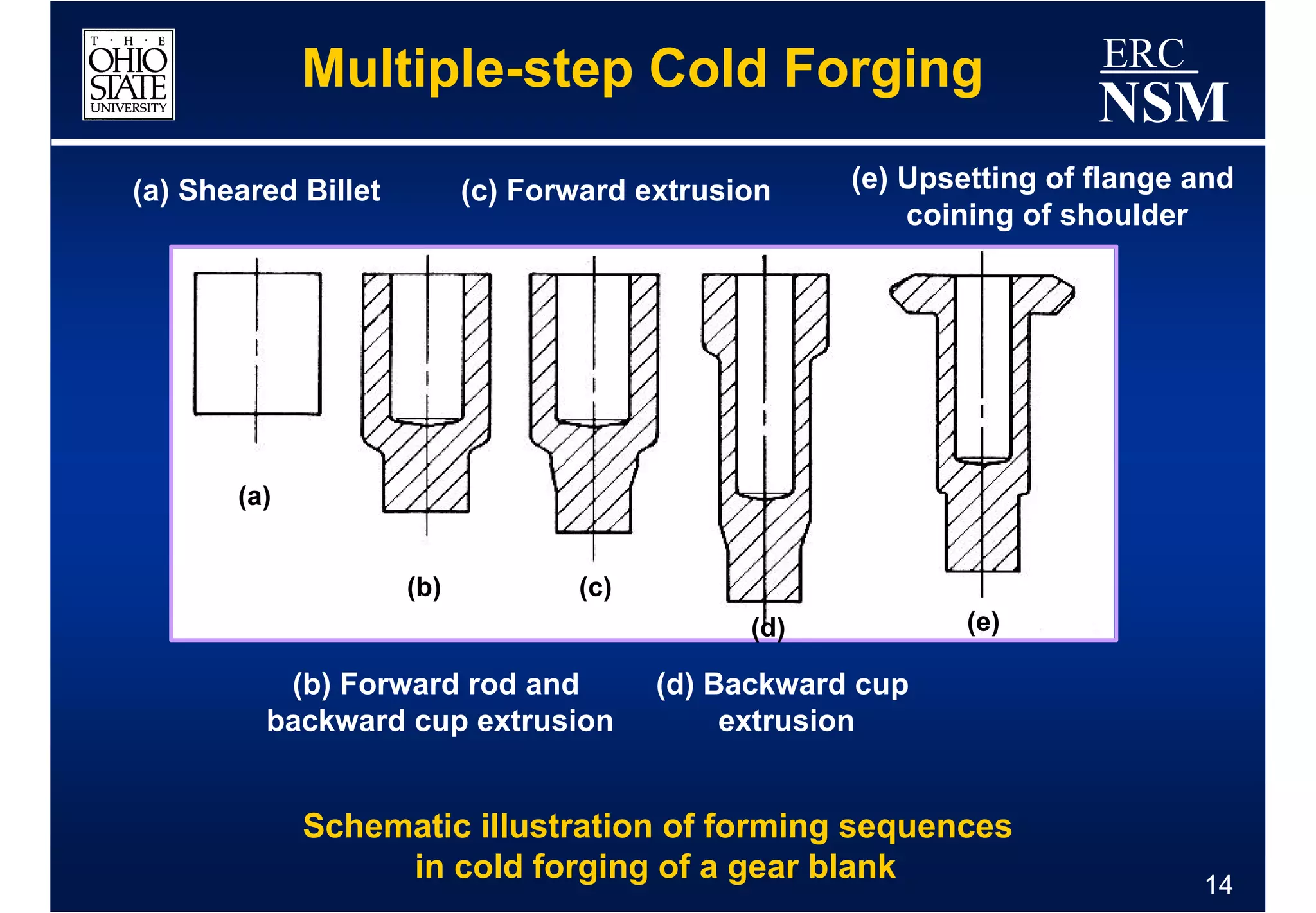
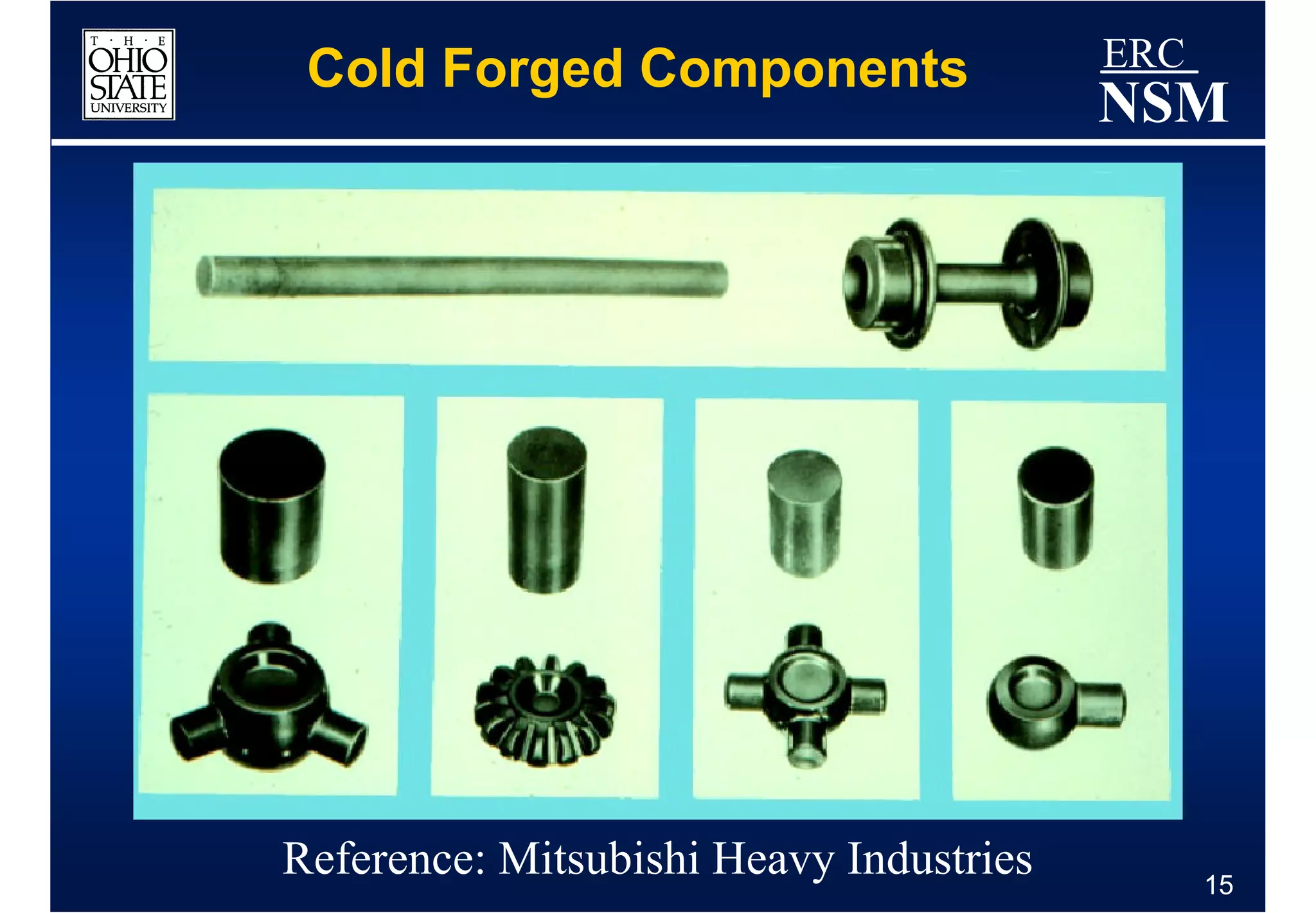
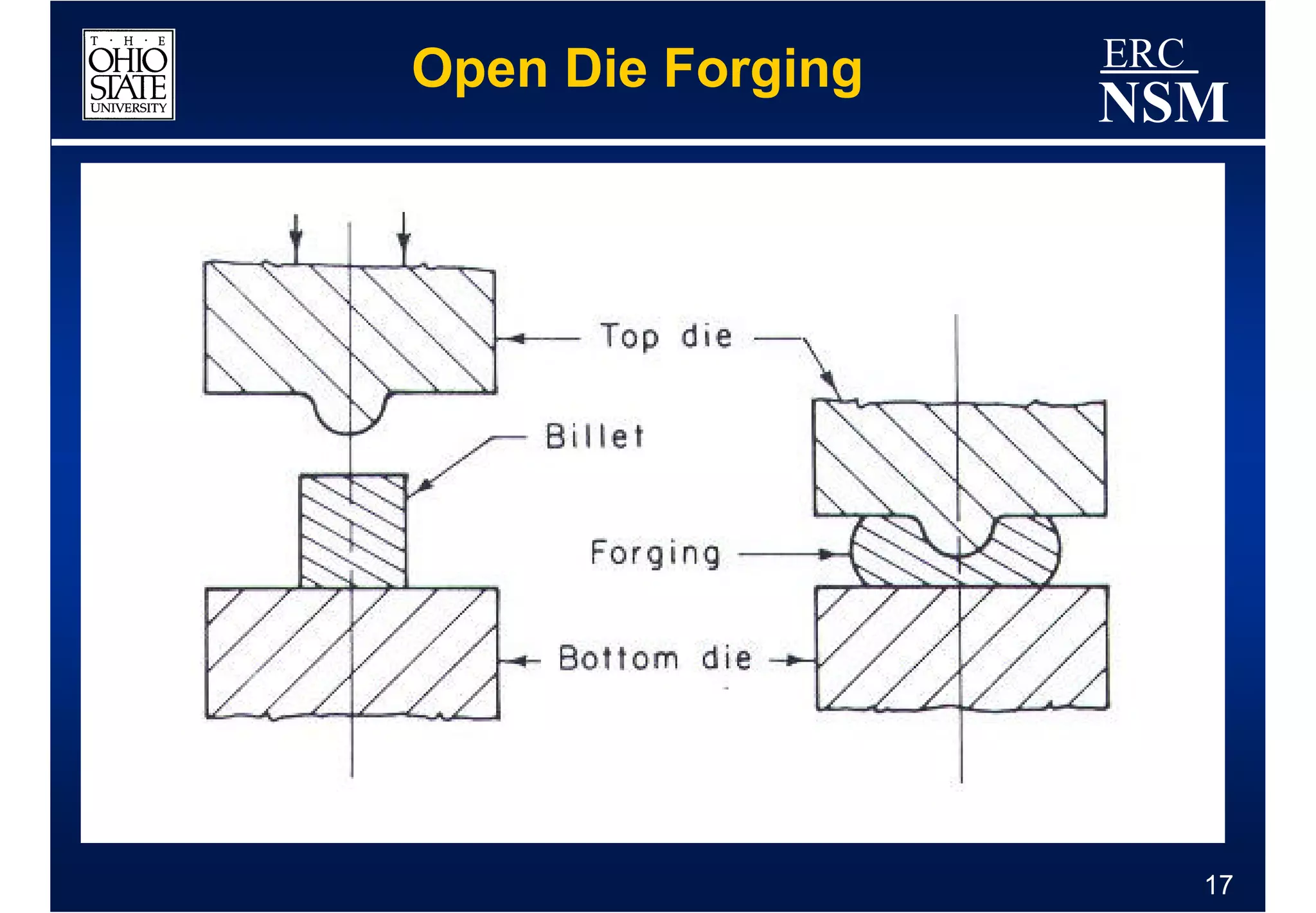
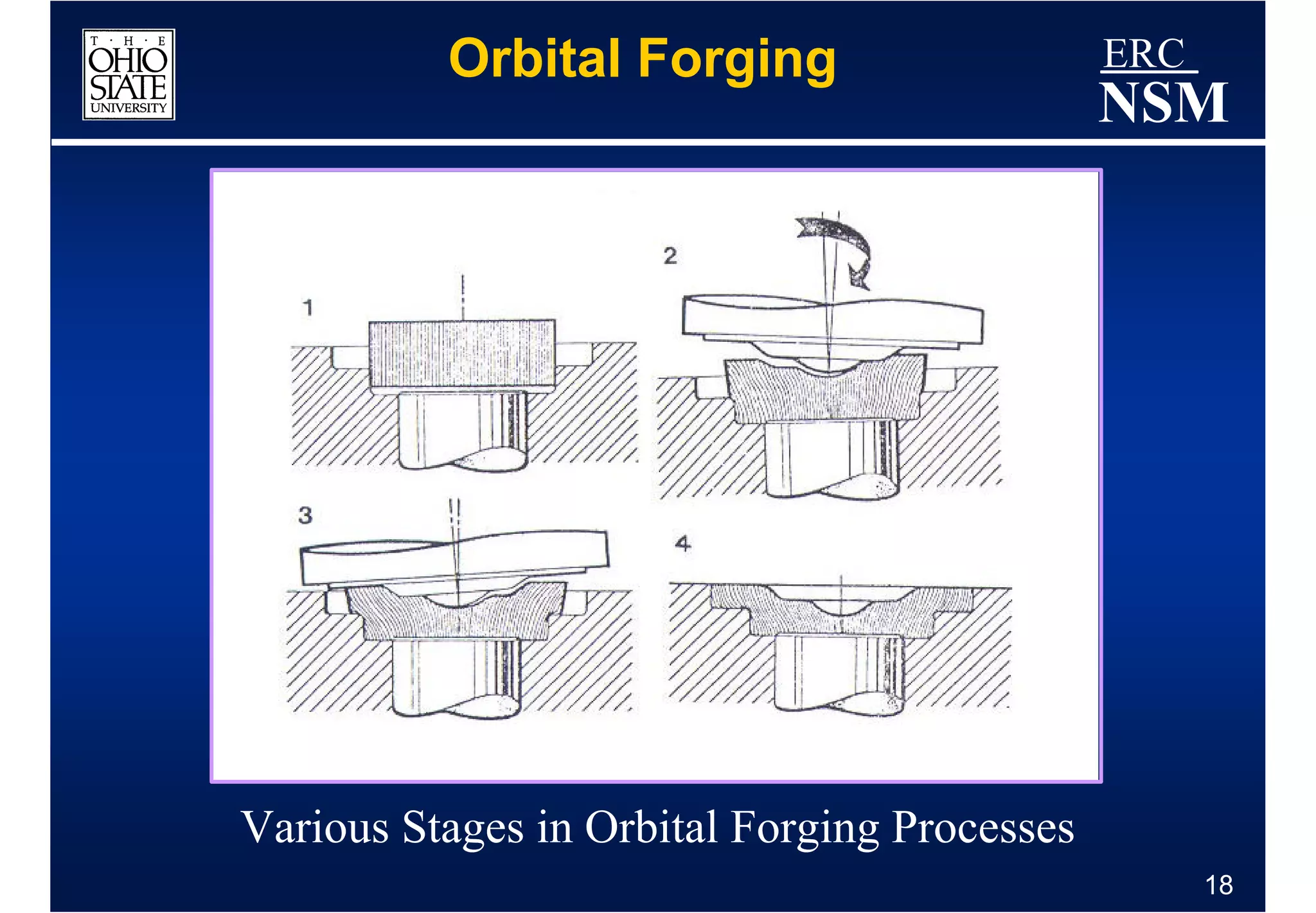
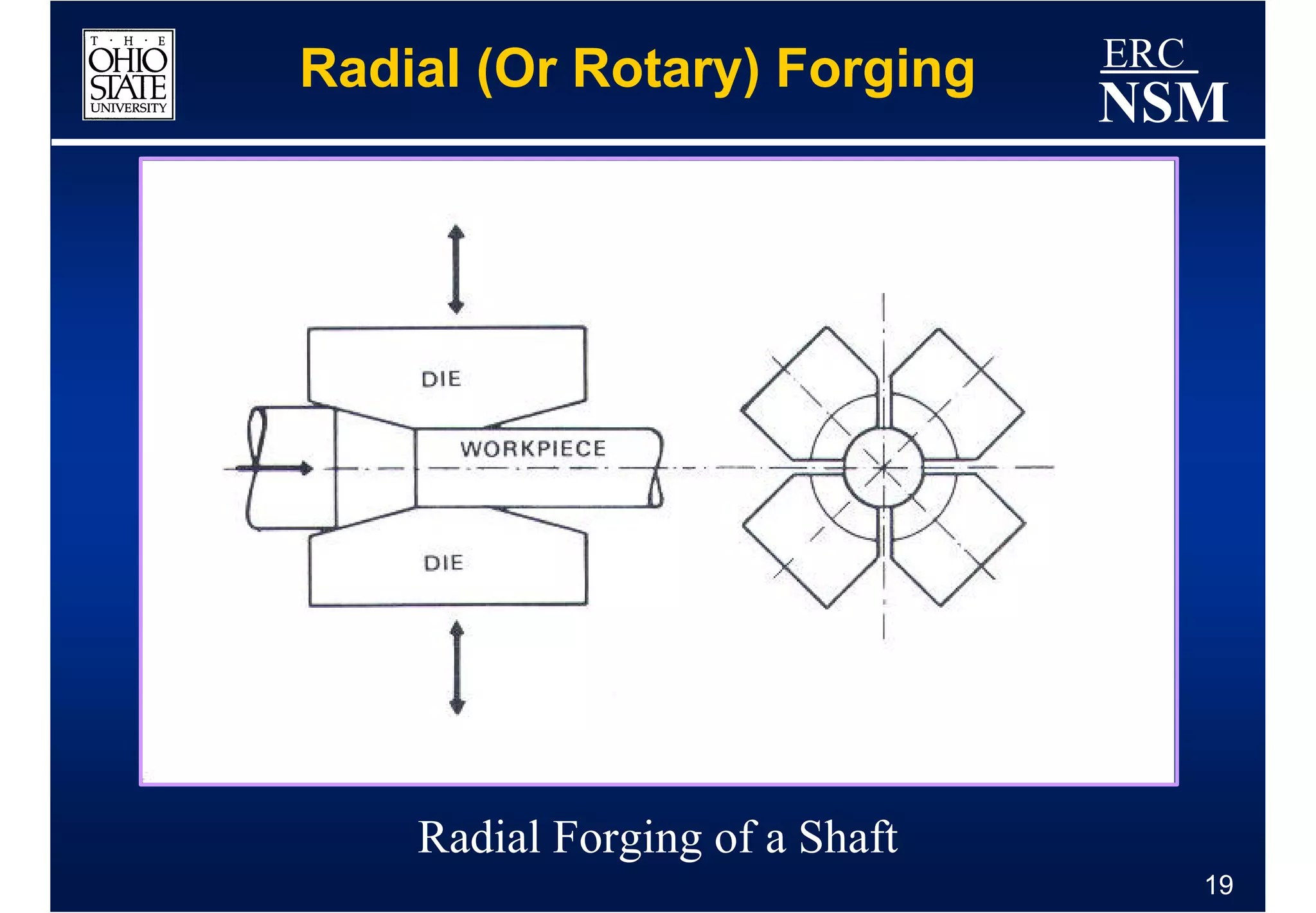
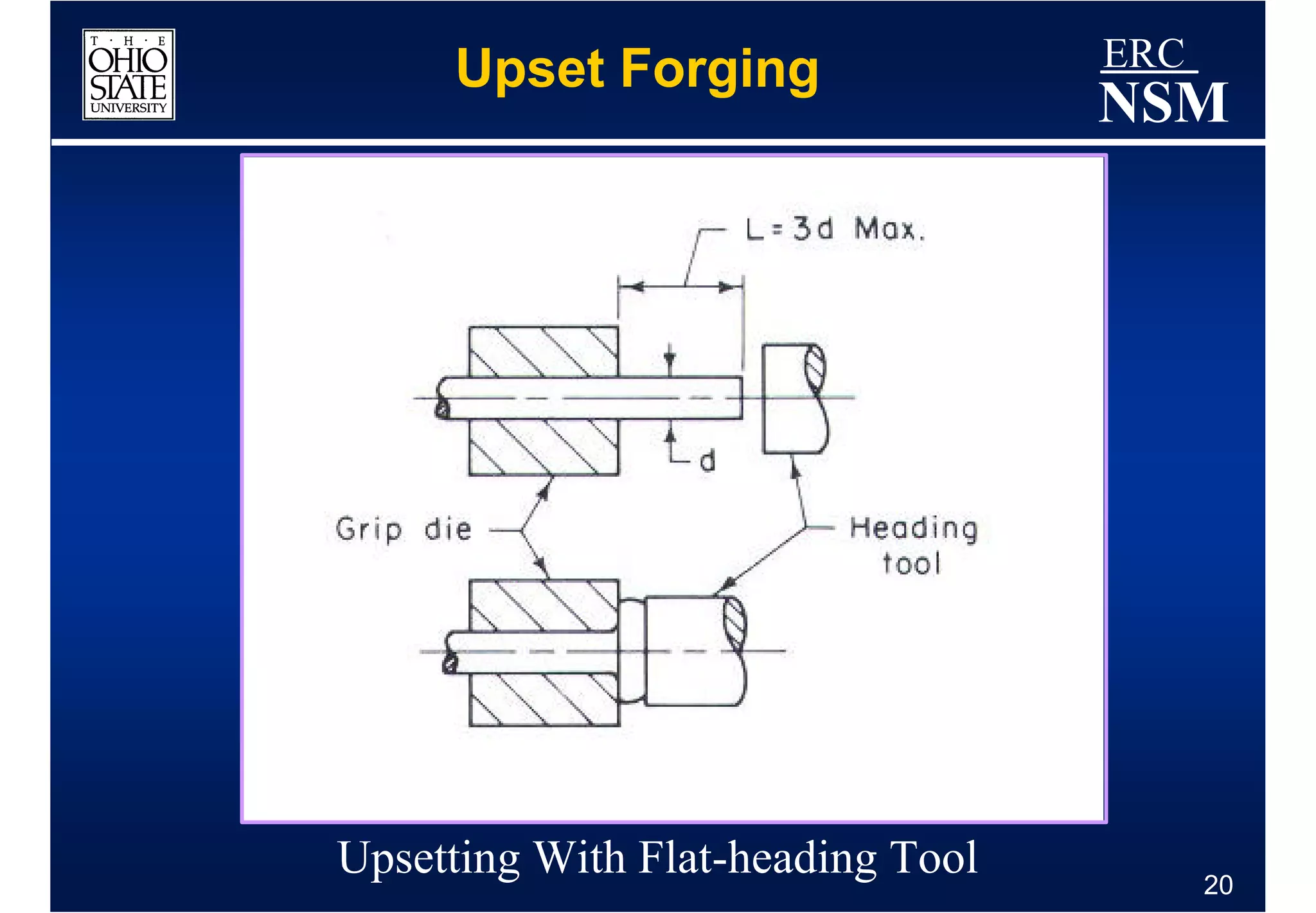
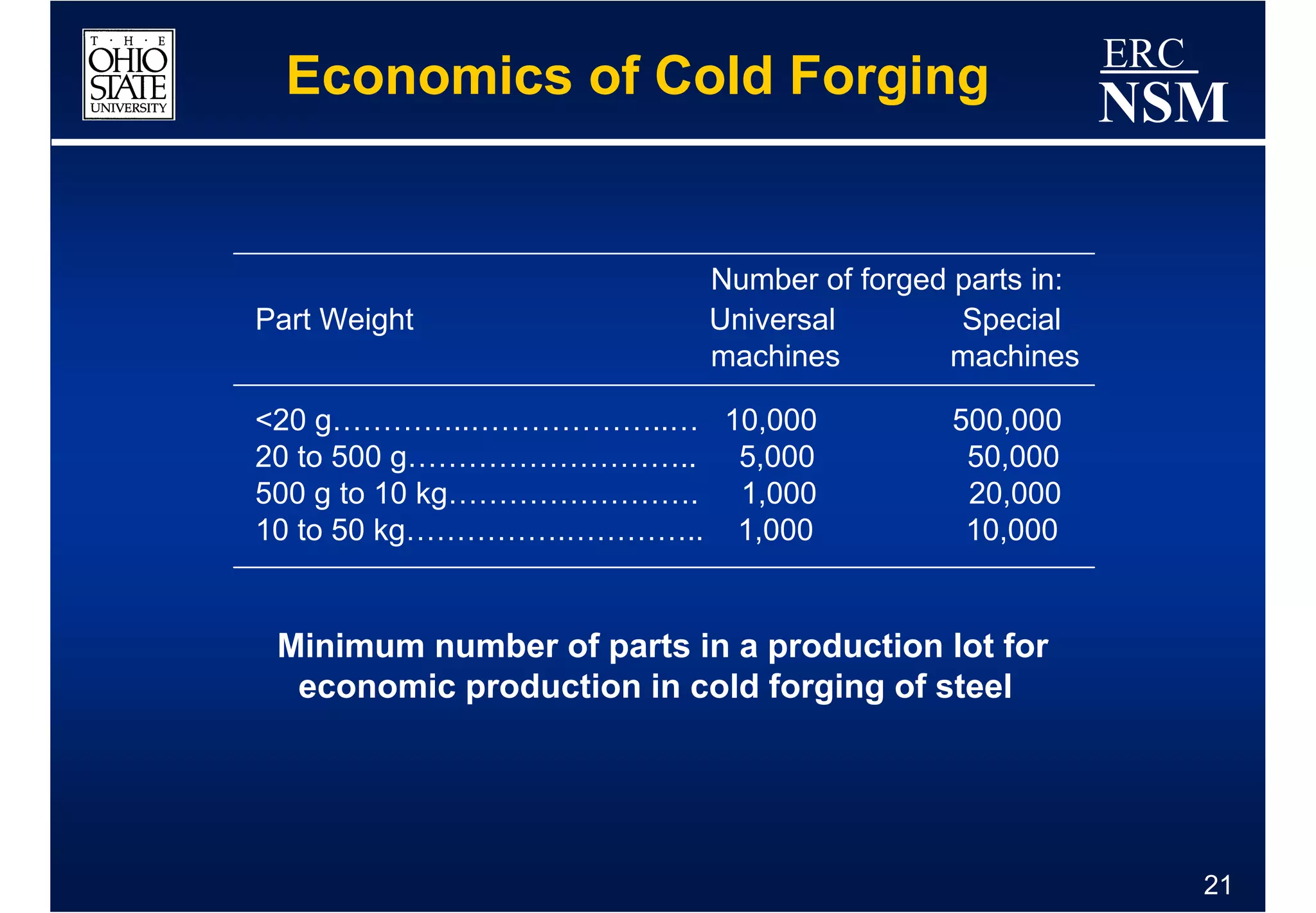
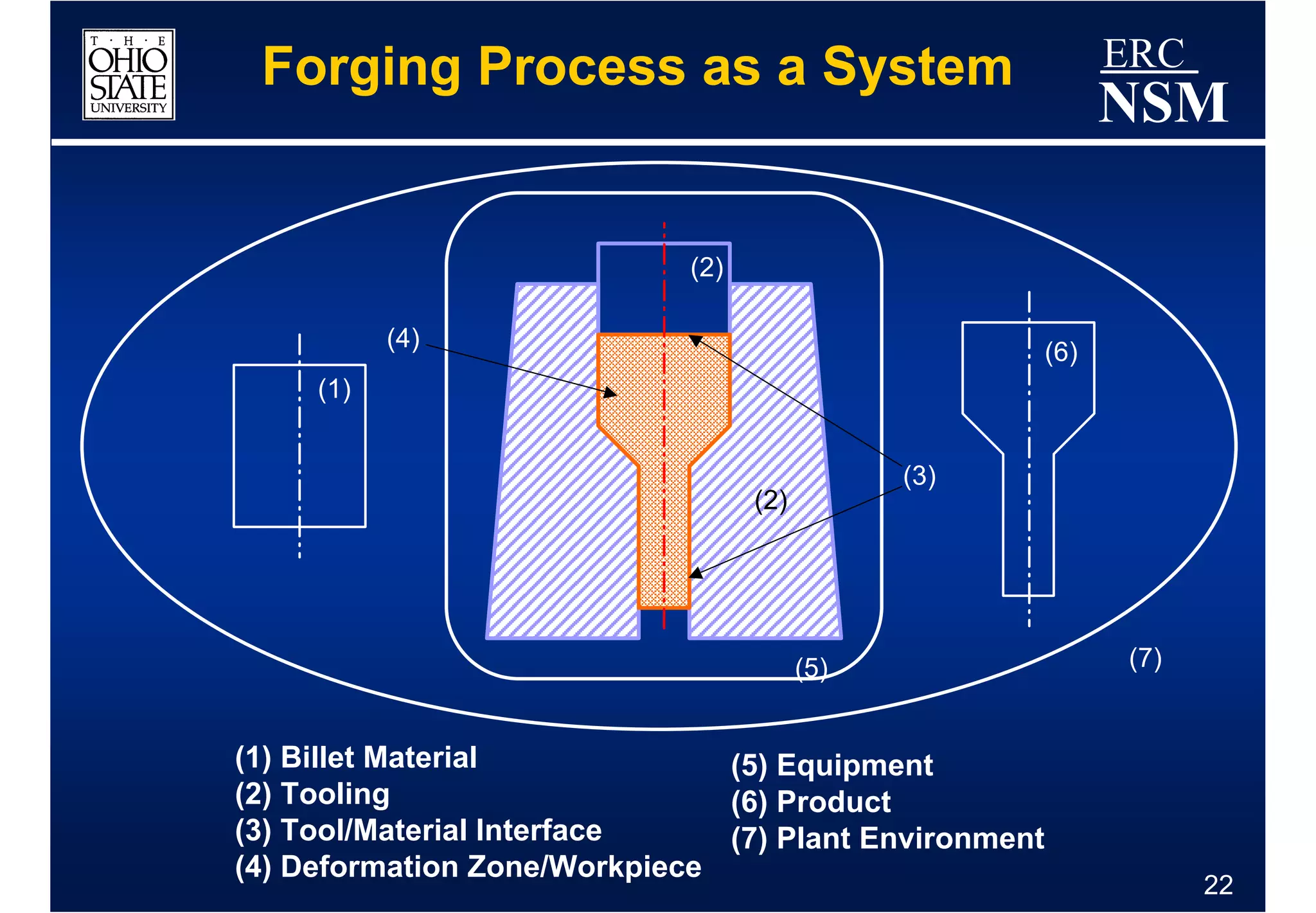
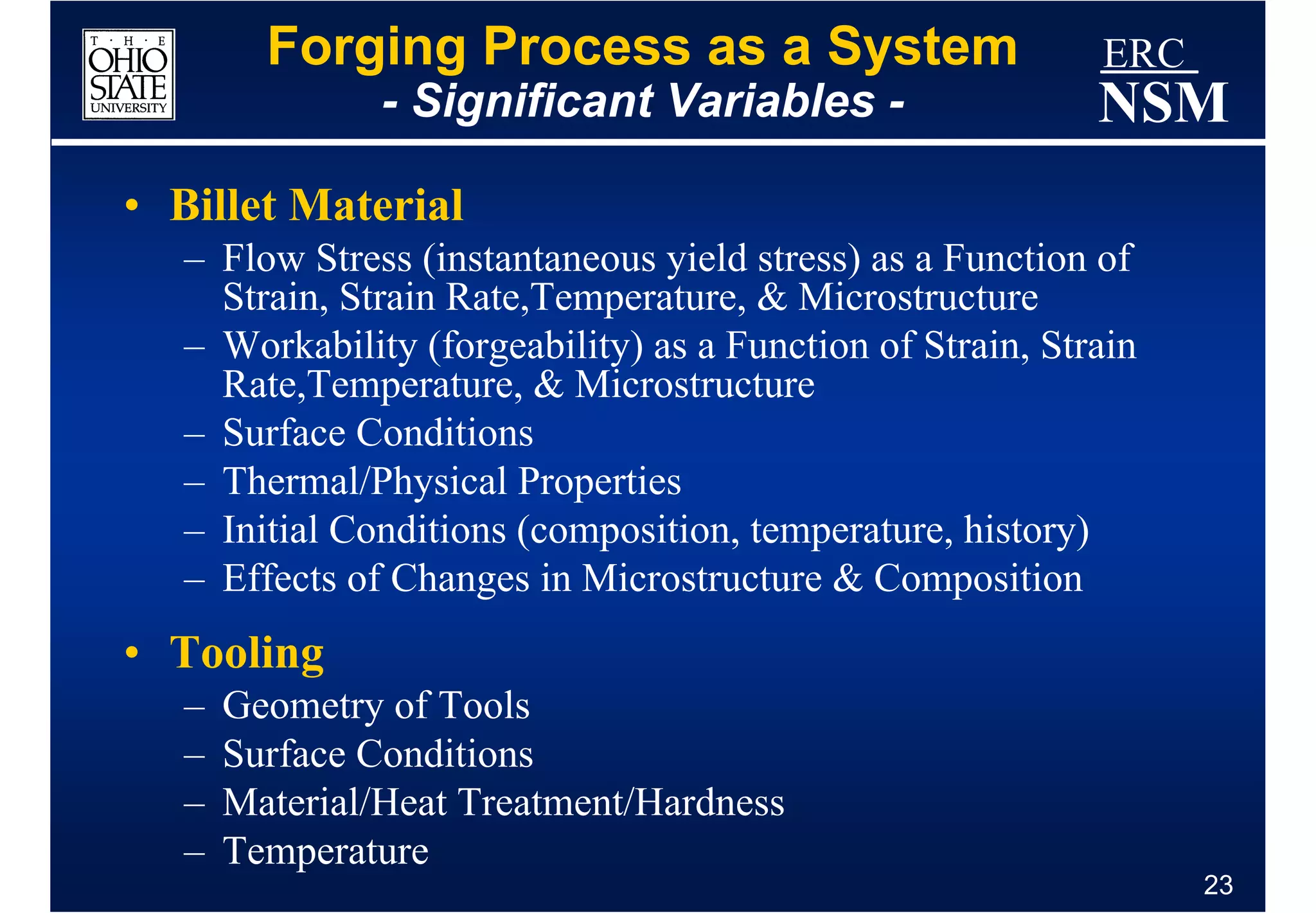
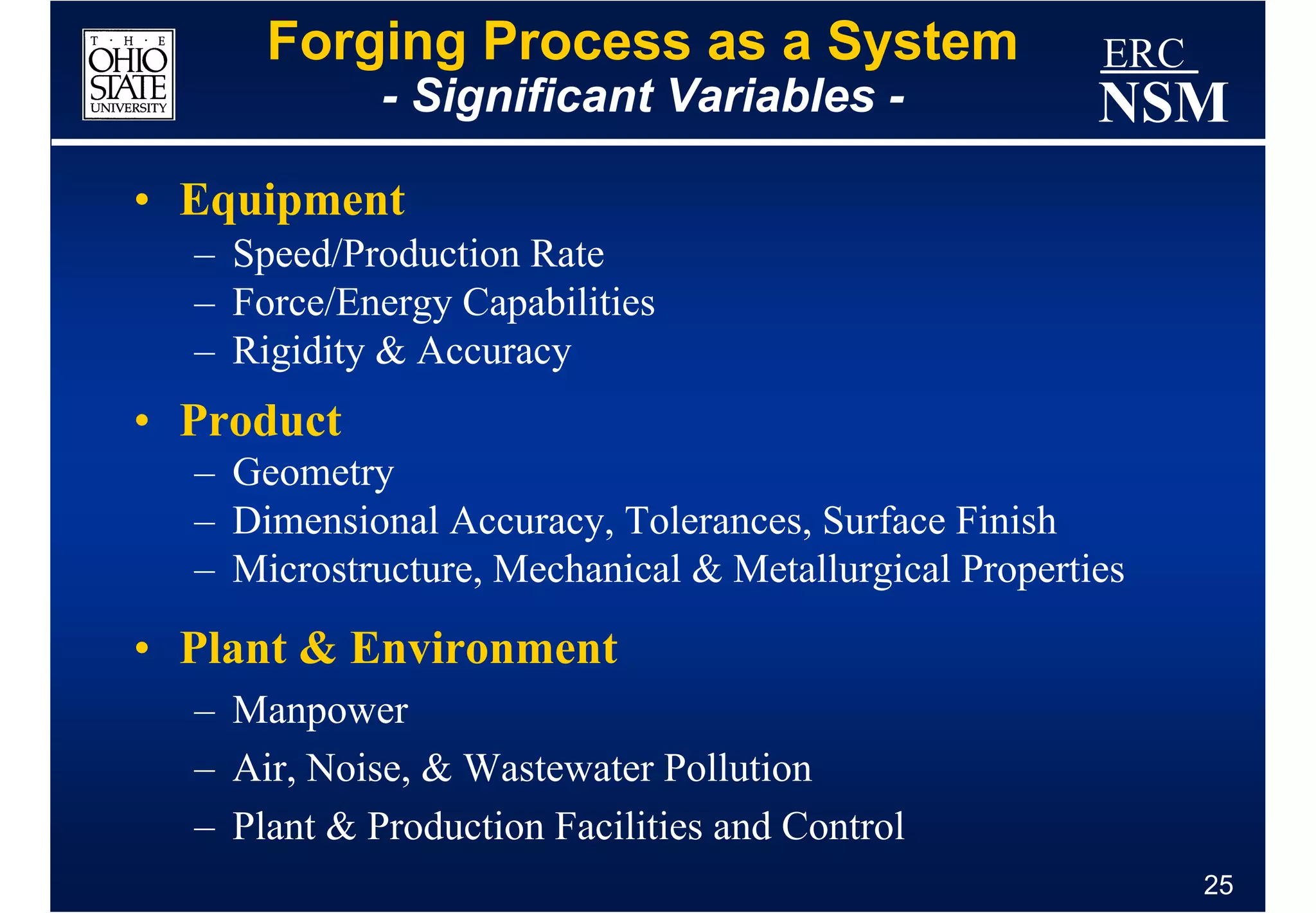
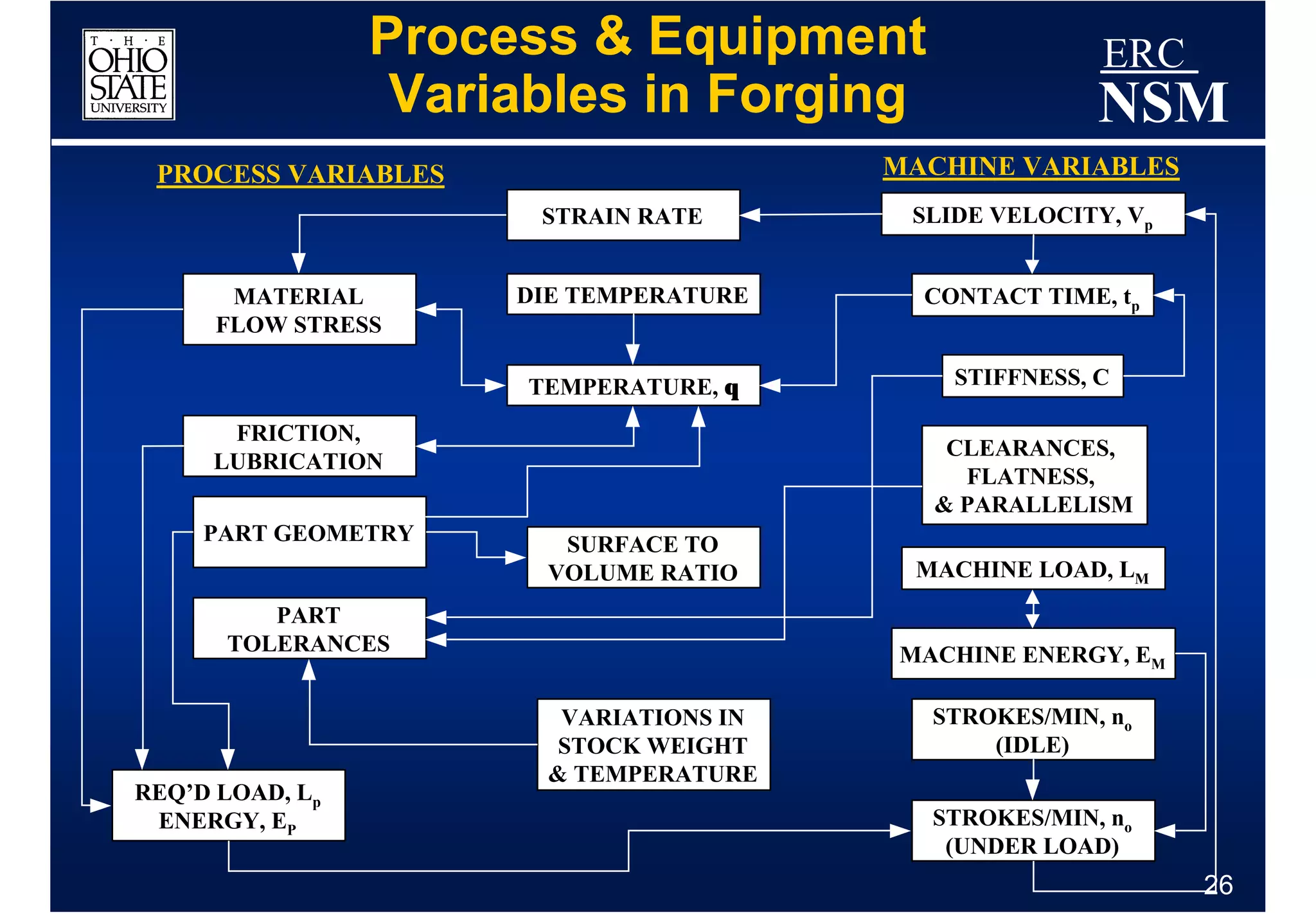
1) Properties of the billet material and how it deforms under different conditions of strain, strain rate, and temperature
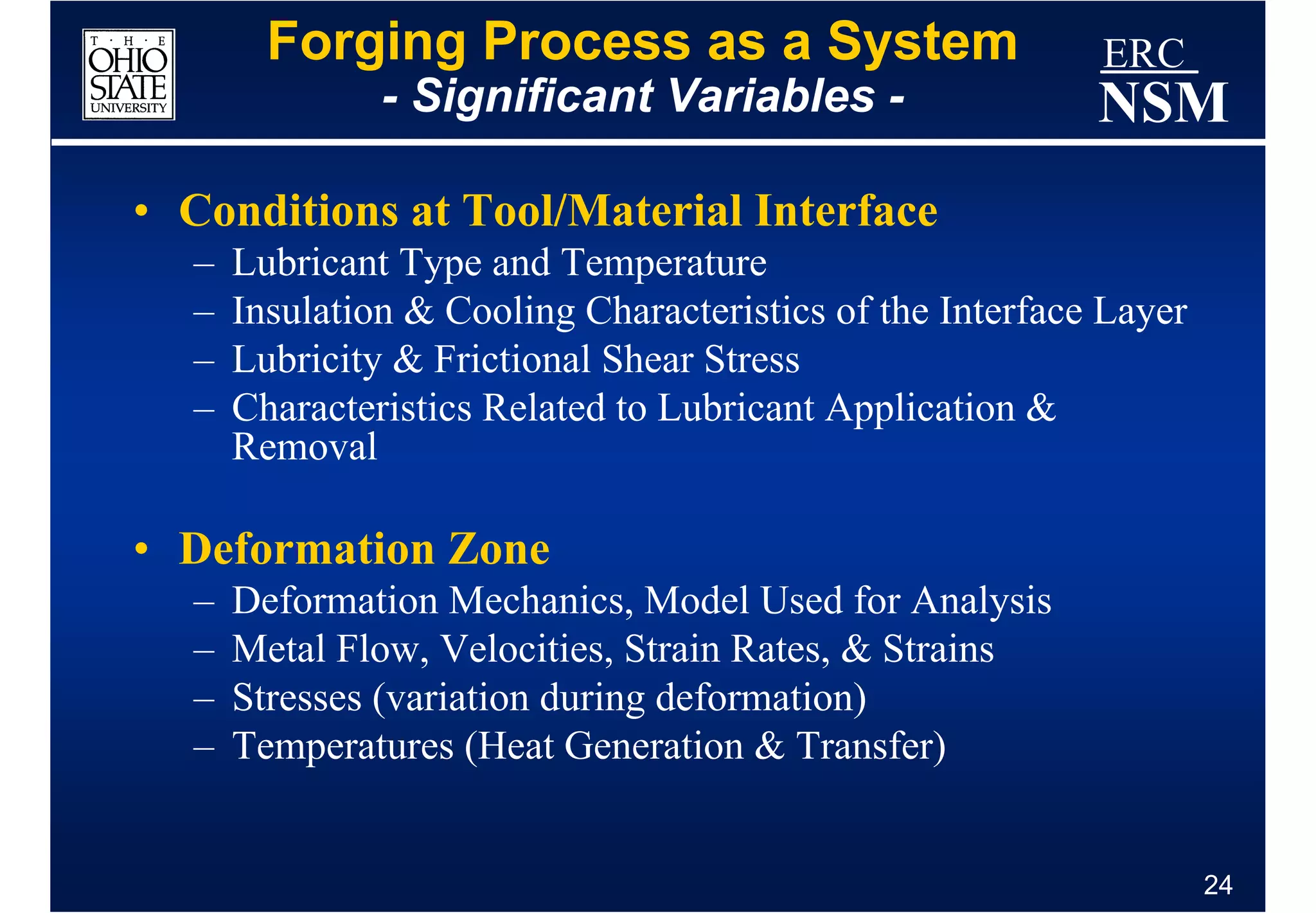
2) Geometry and properties of the forging tools and die interface
3) Conditions within the deformation zone such as metal flow, stresses, and temperatures during forming