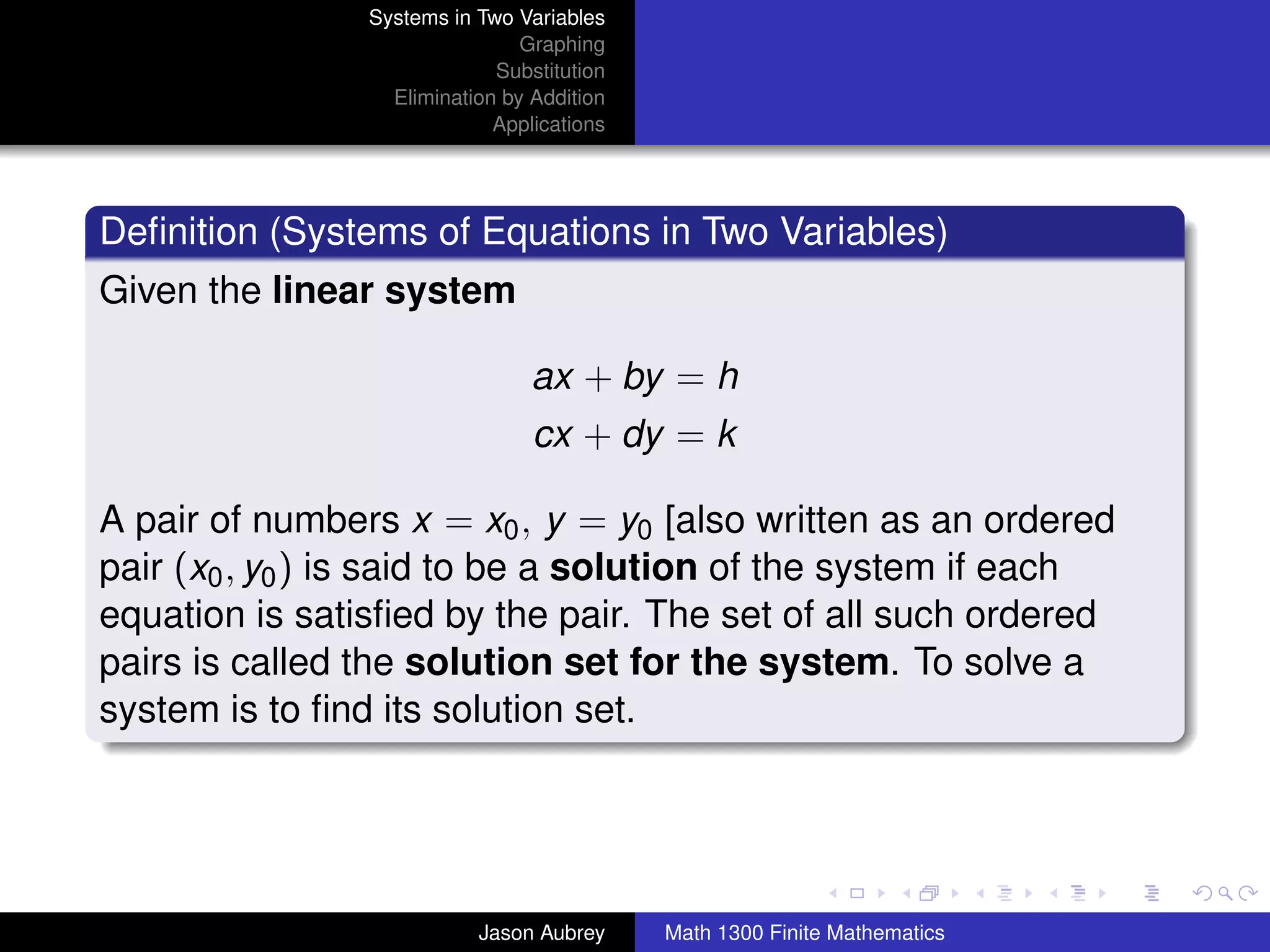
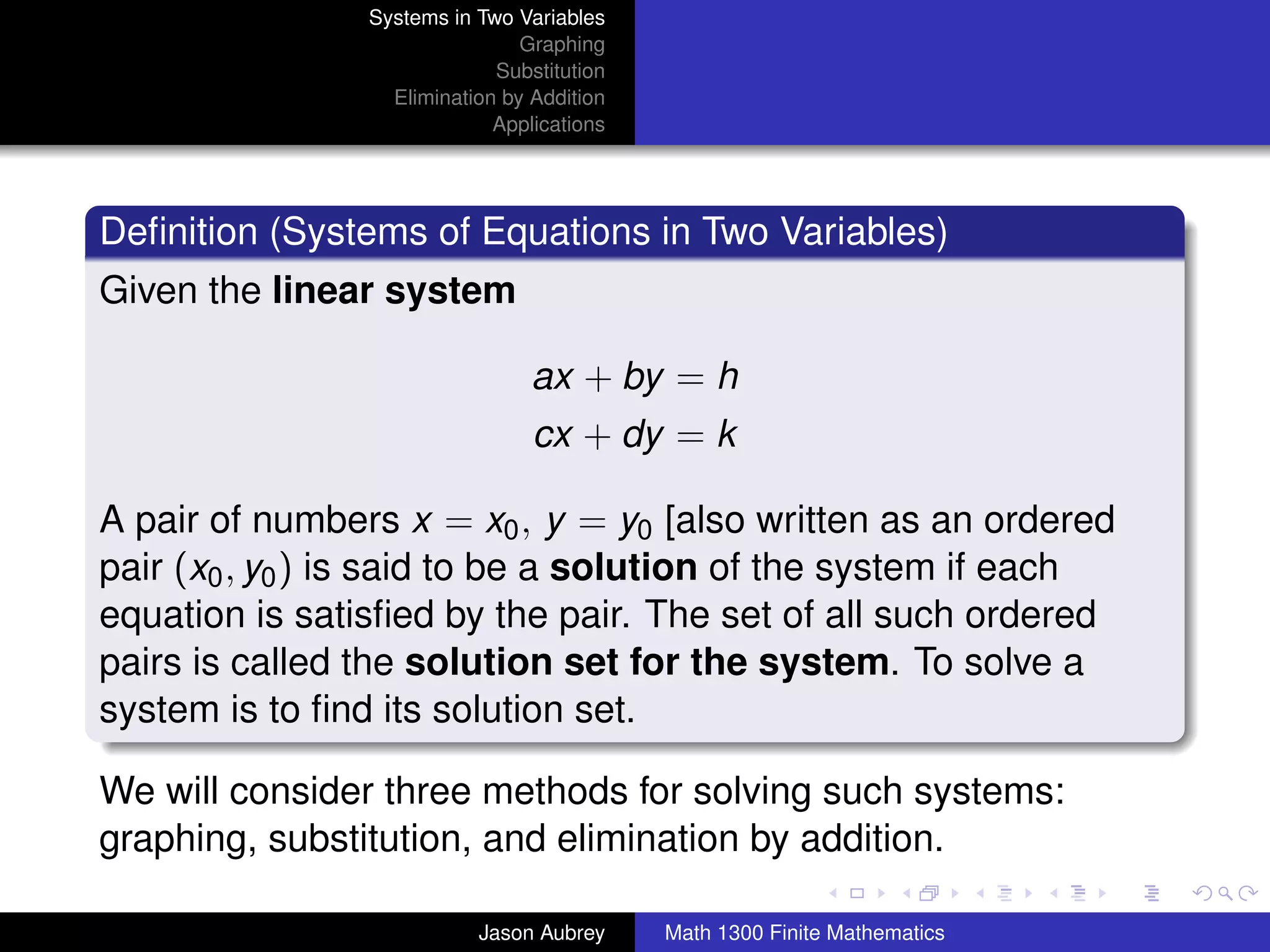
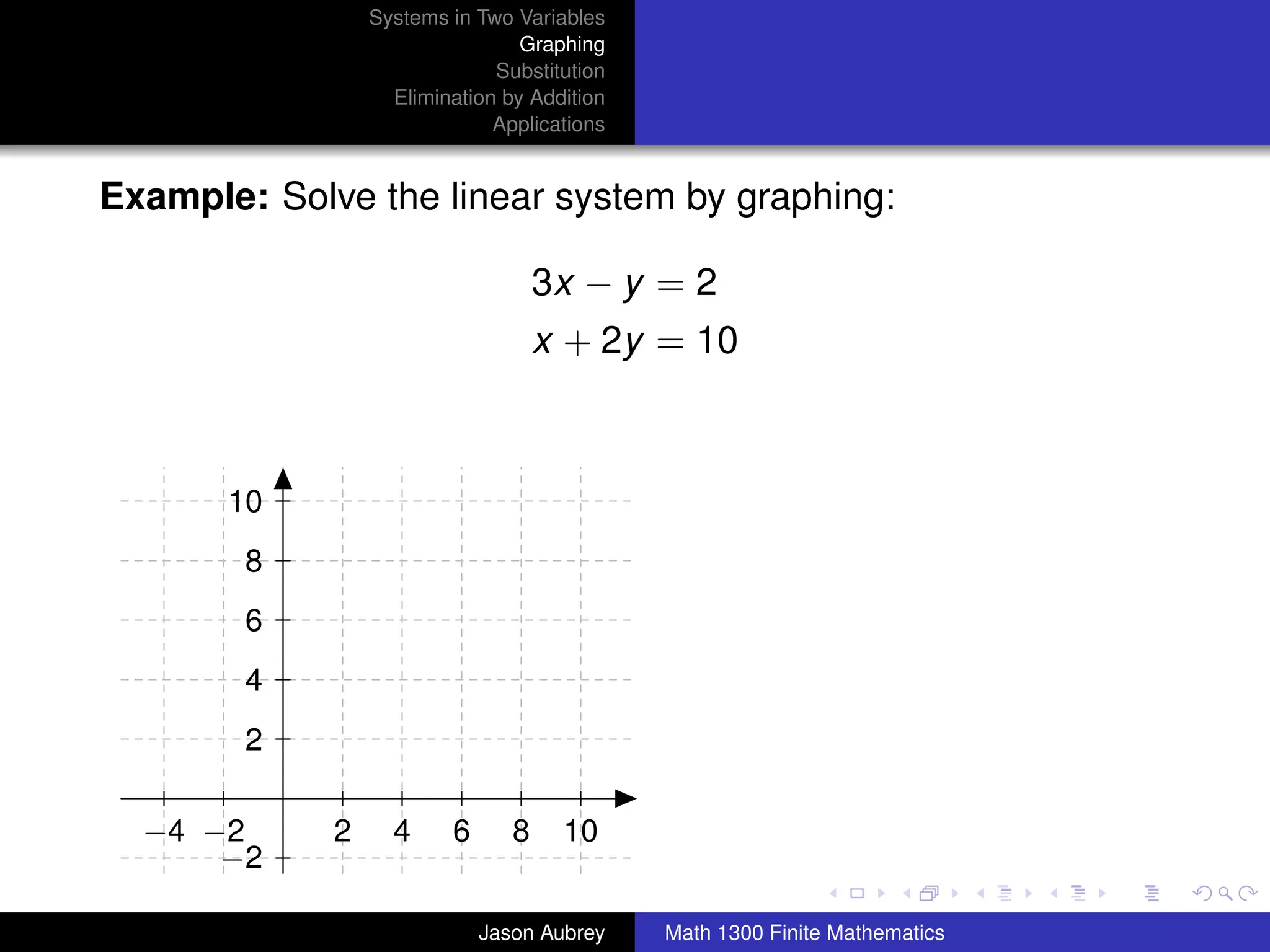
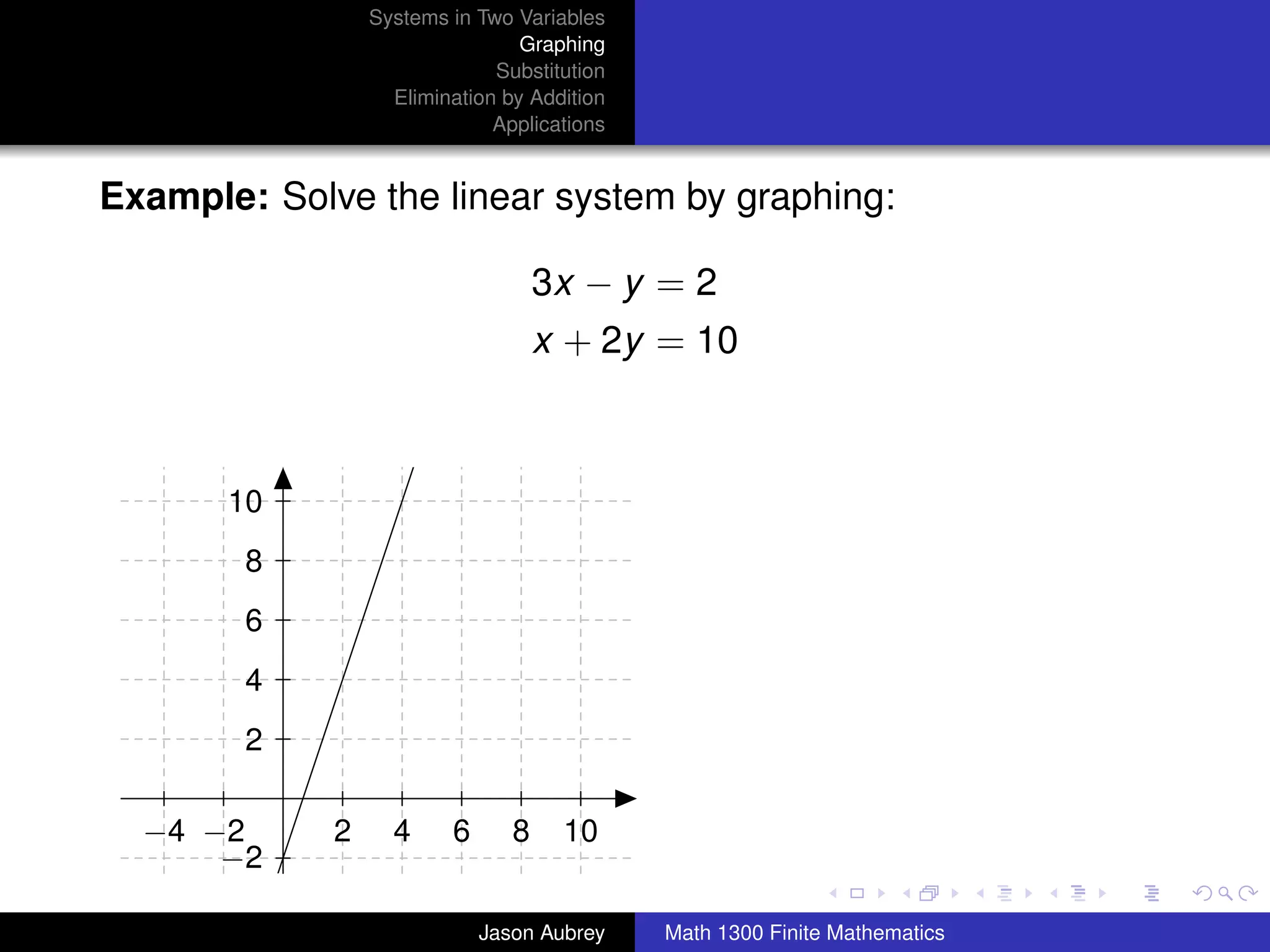
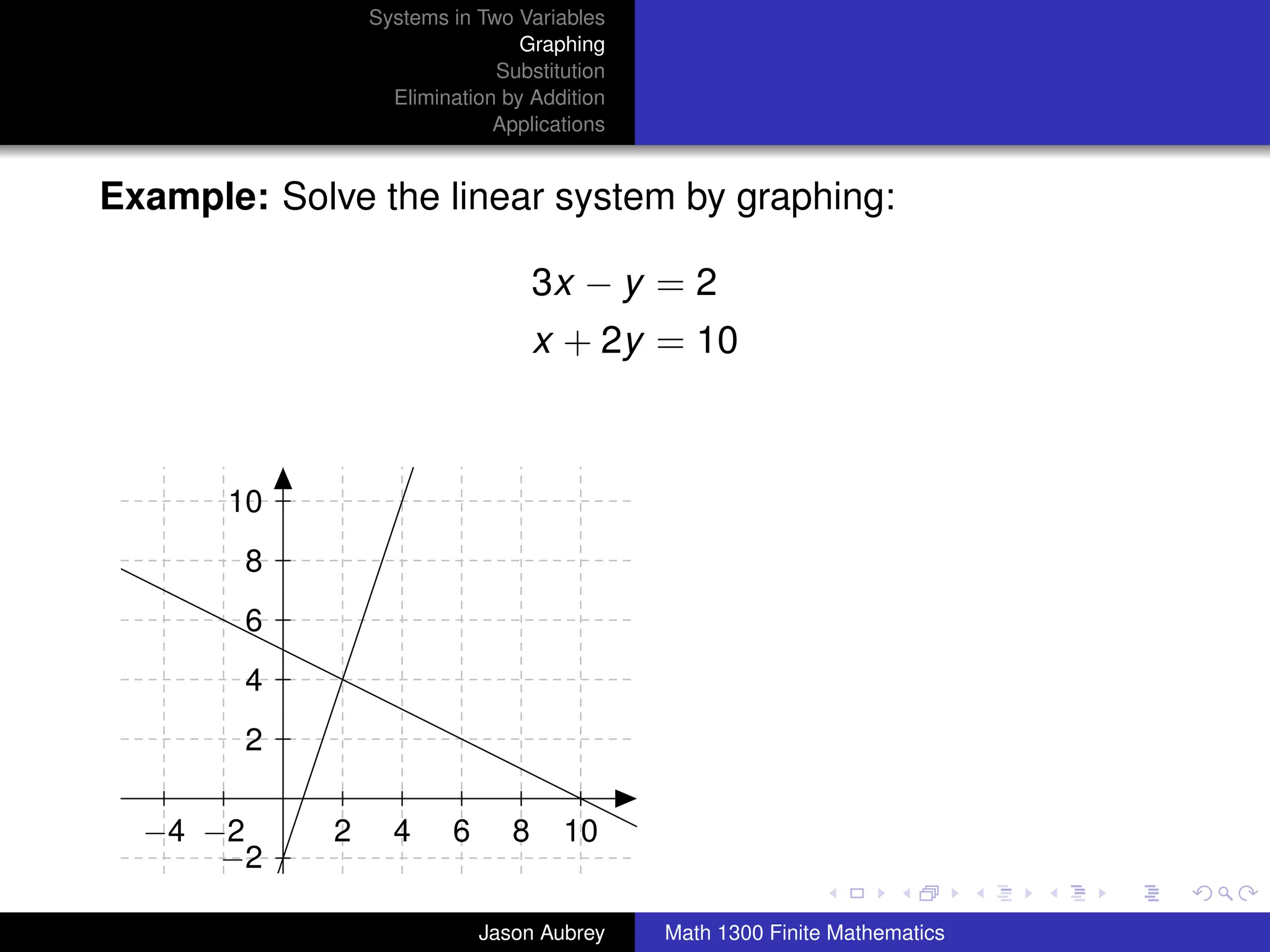
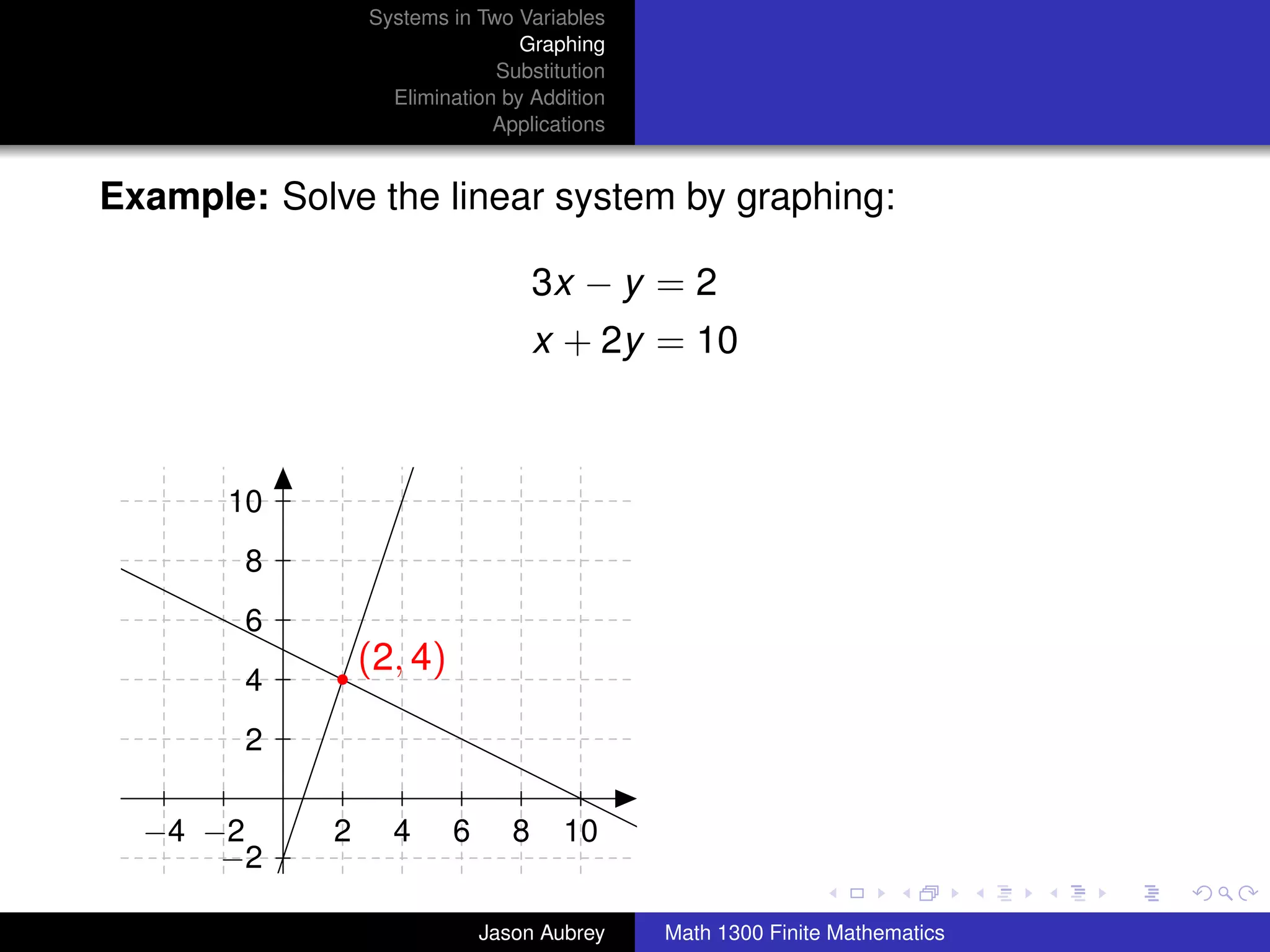
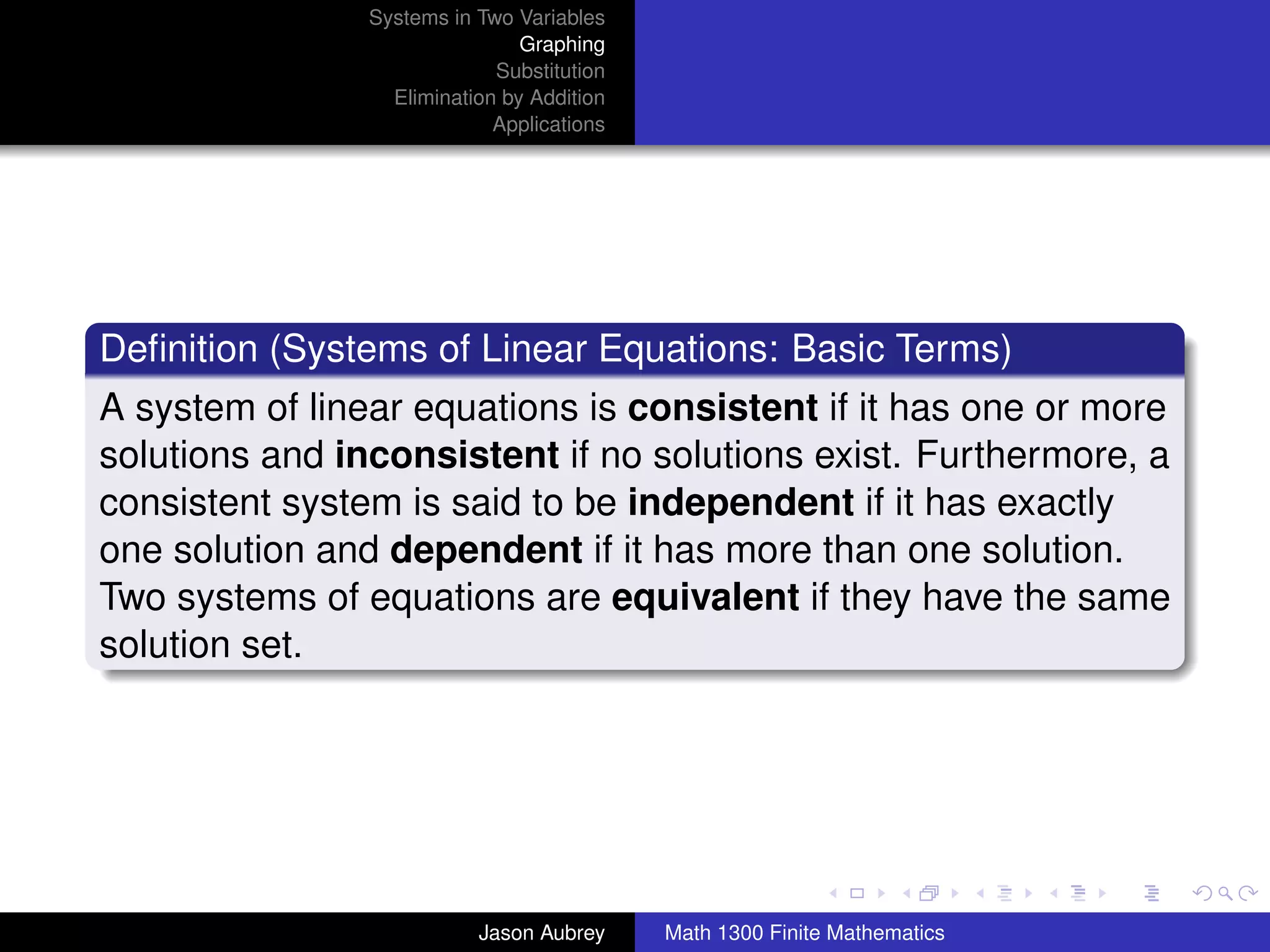
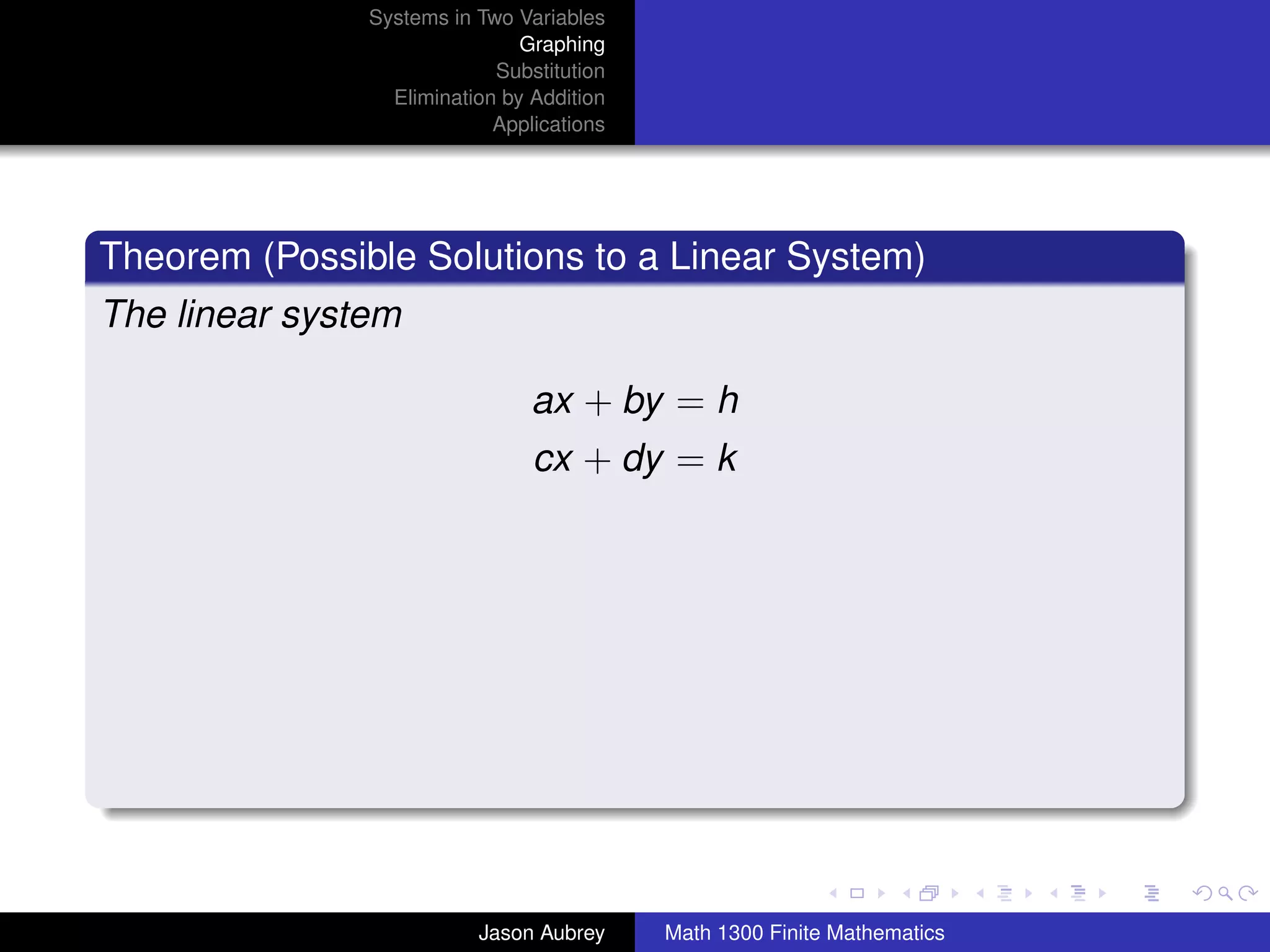
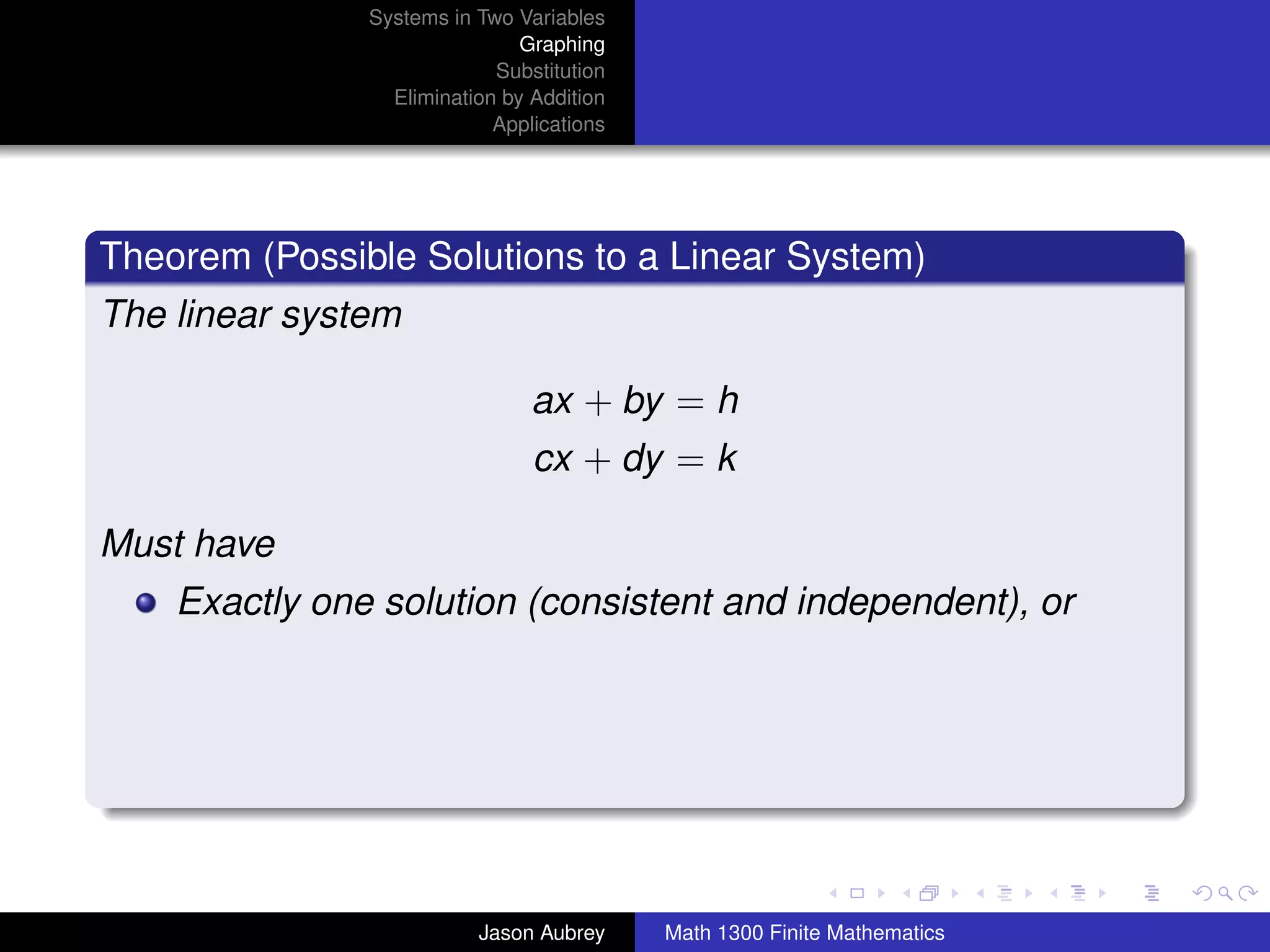
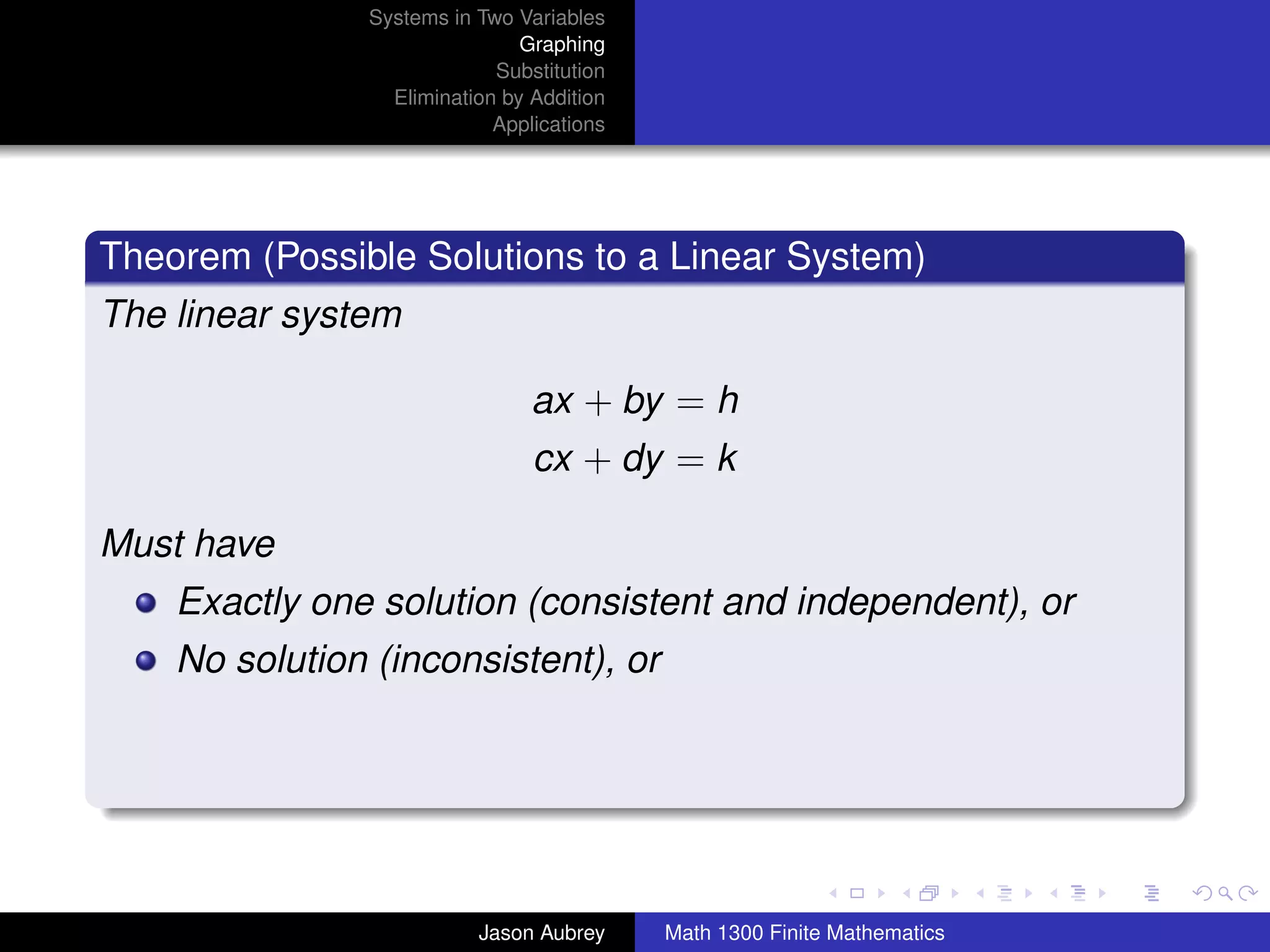
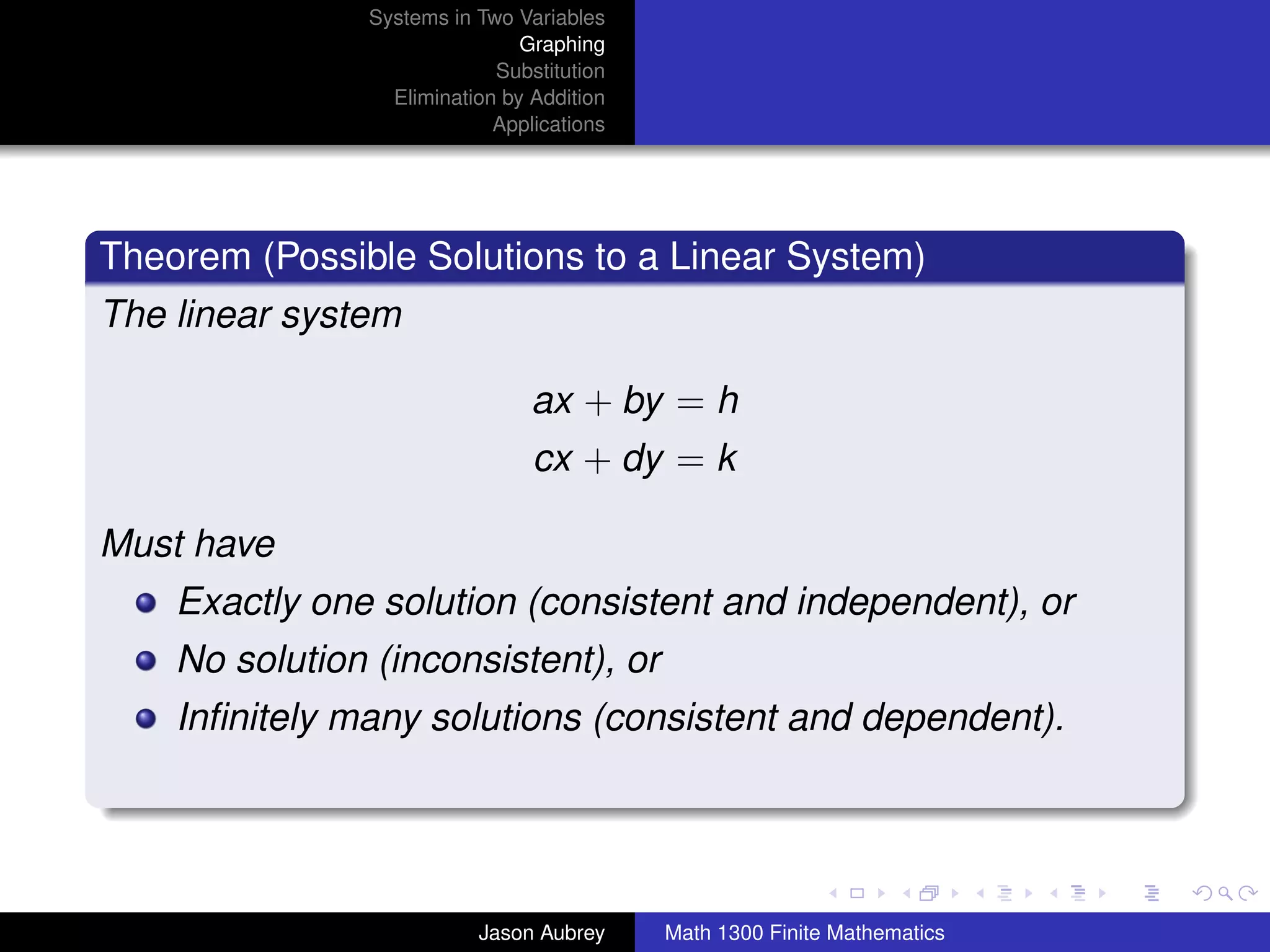
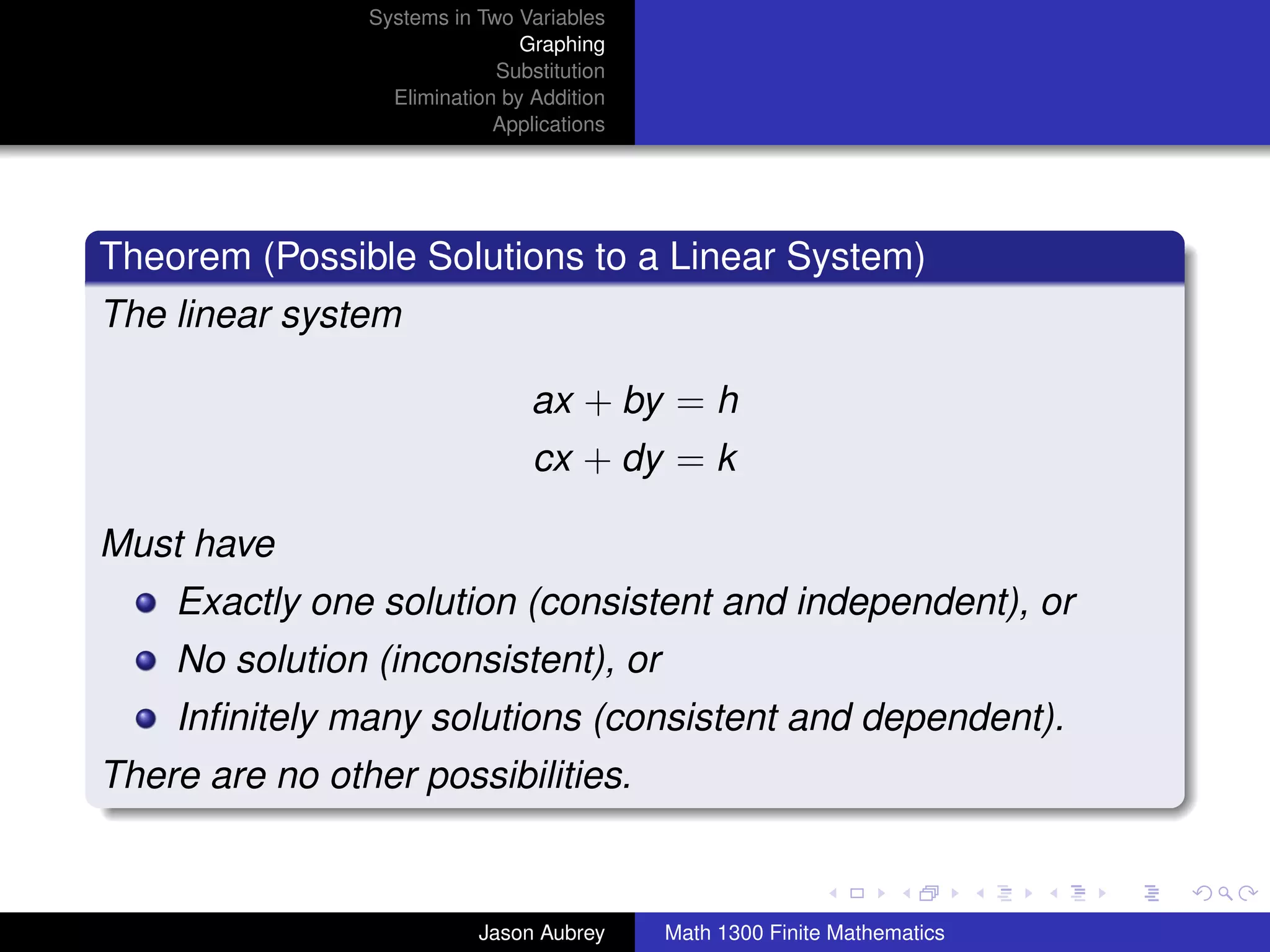
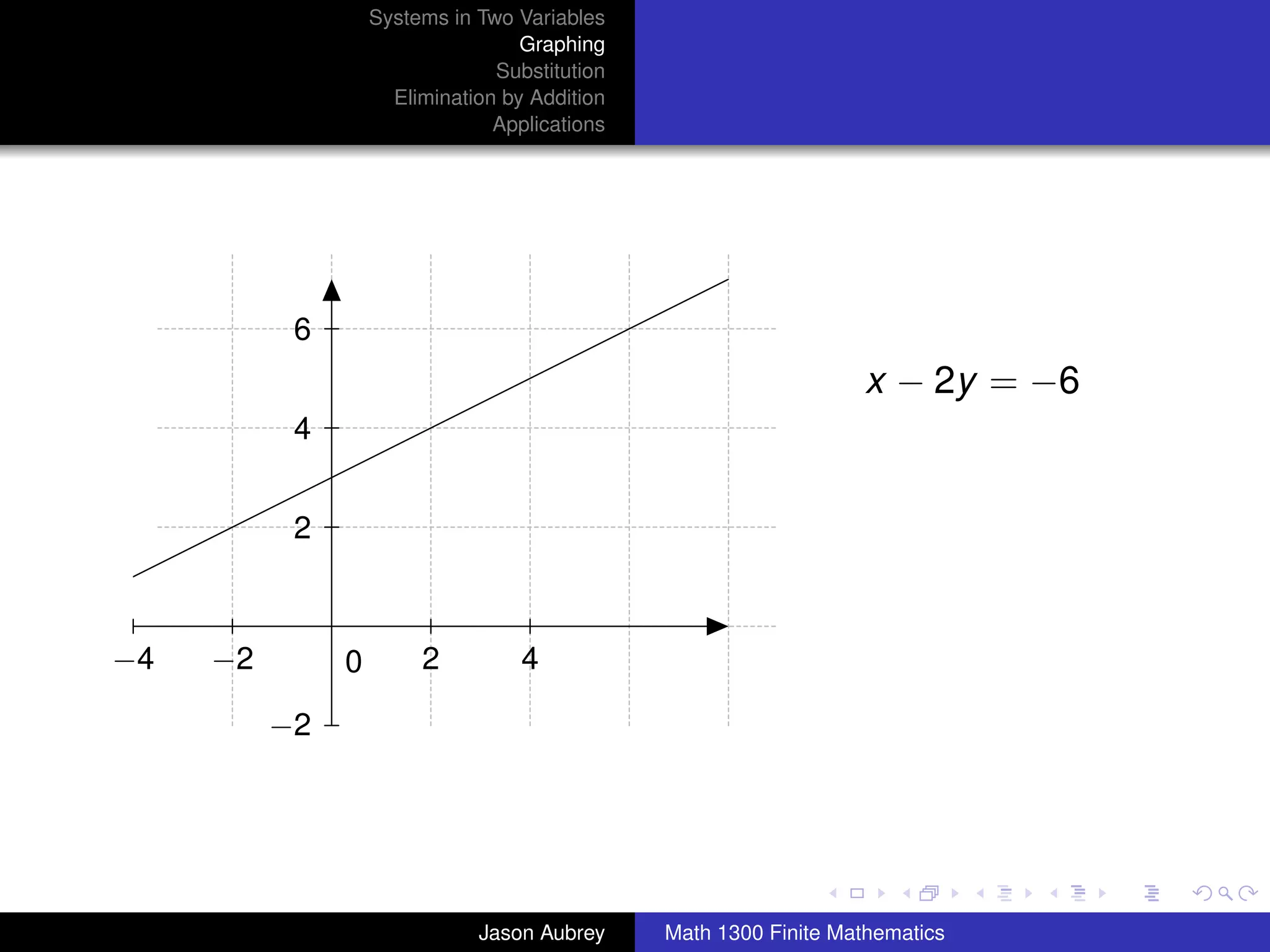
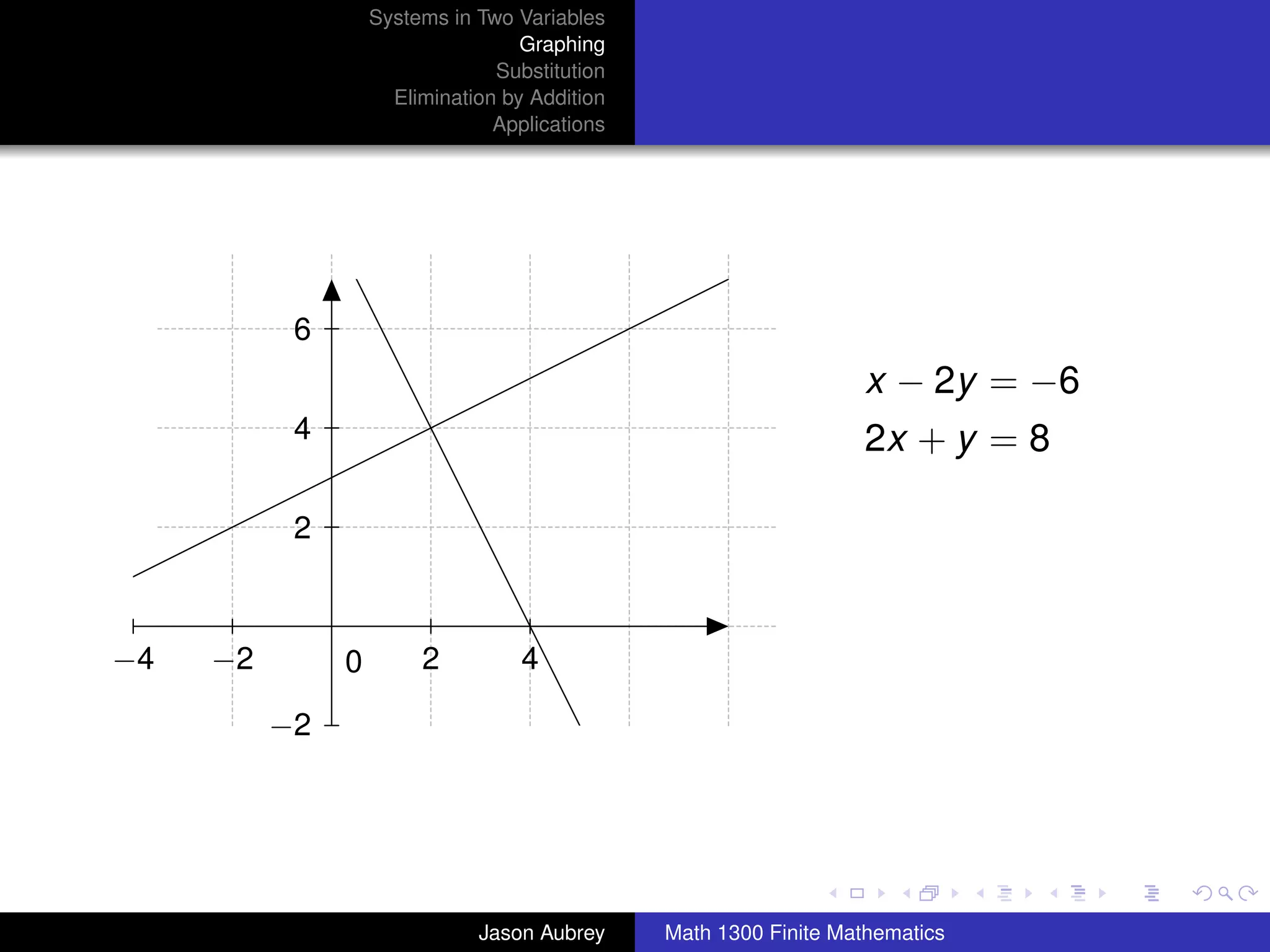
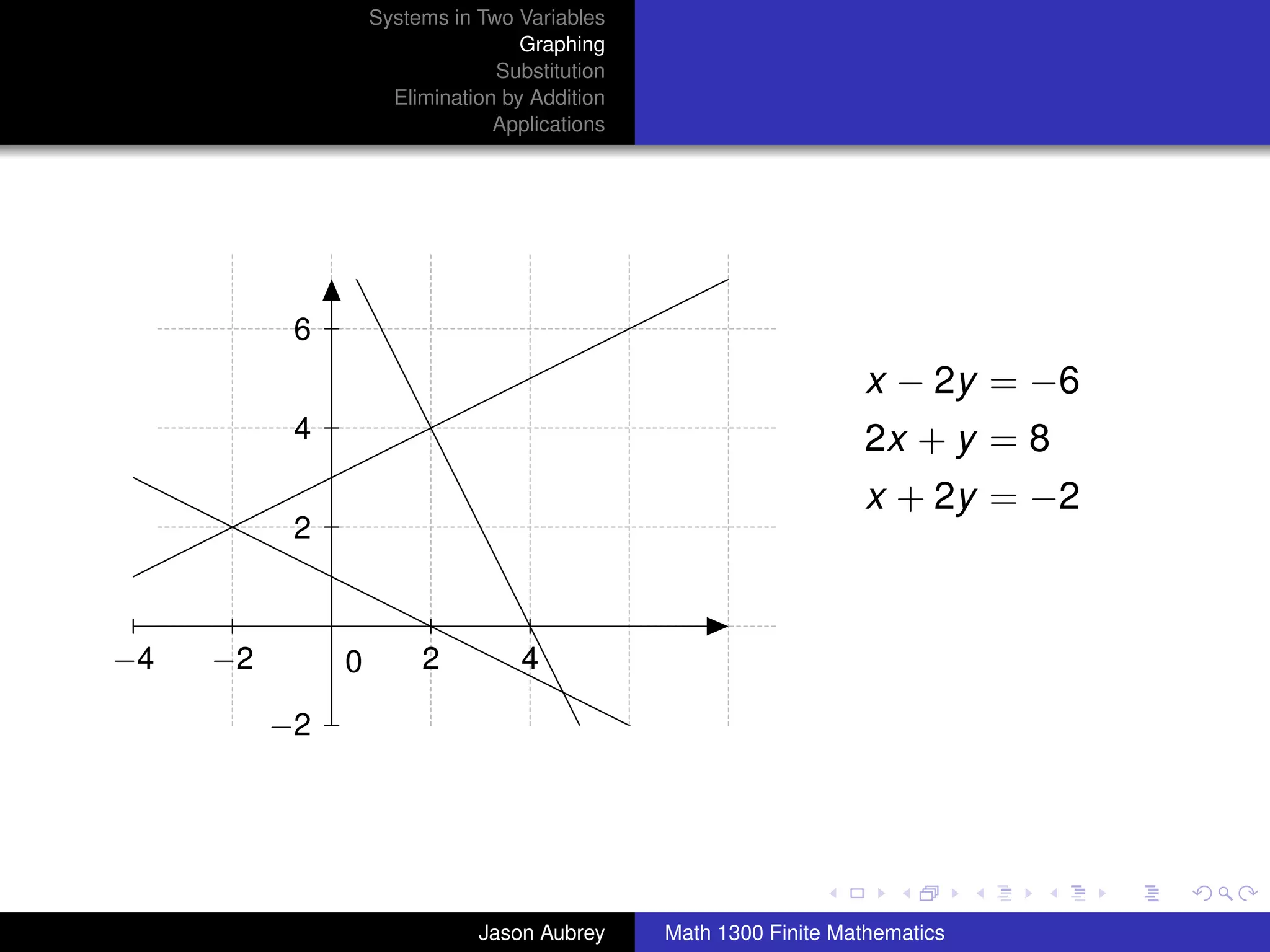
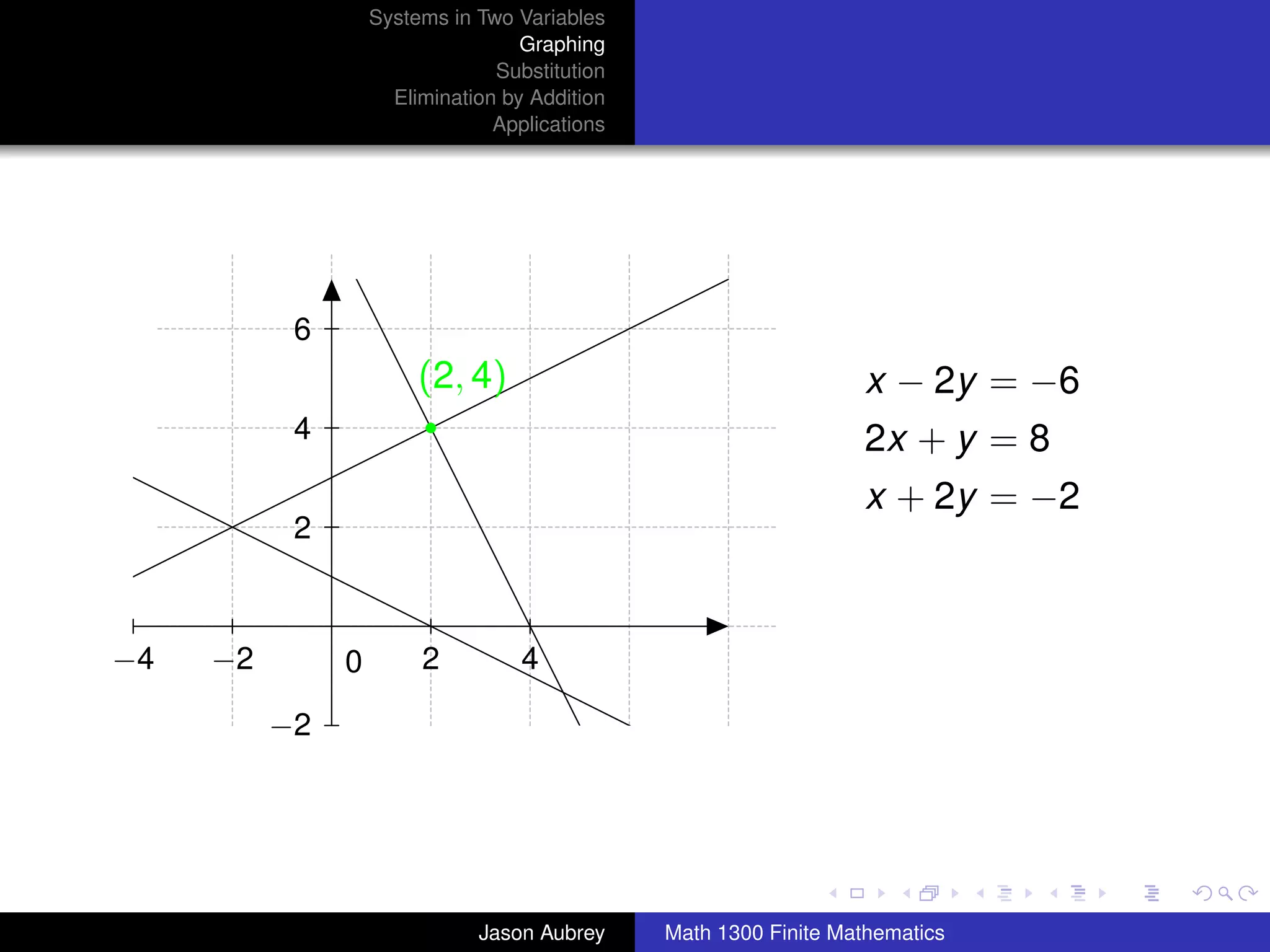
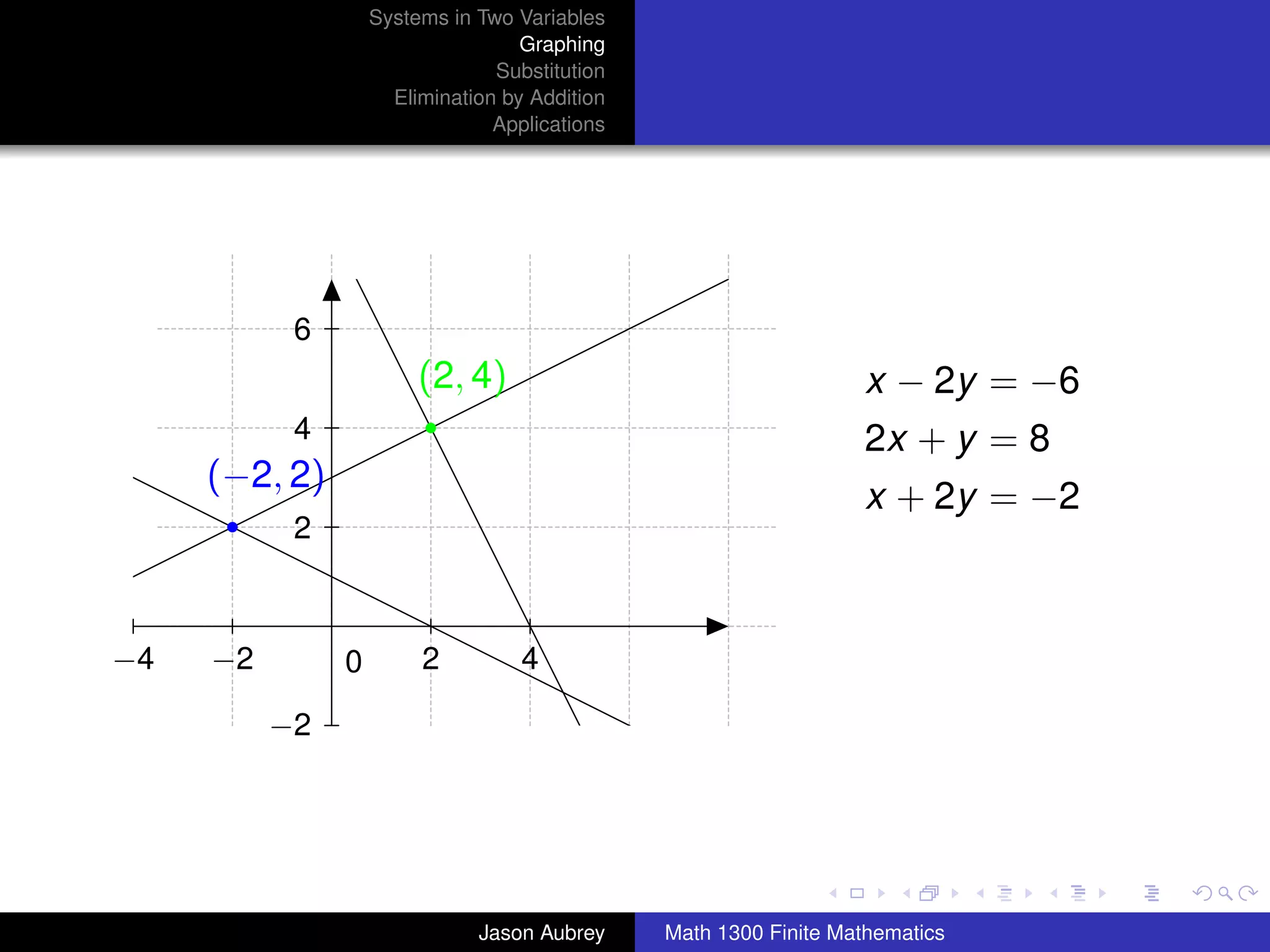
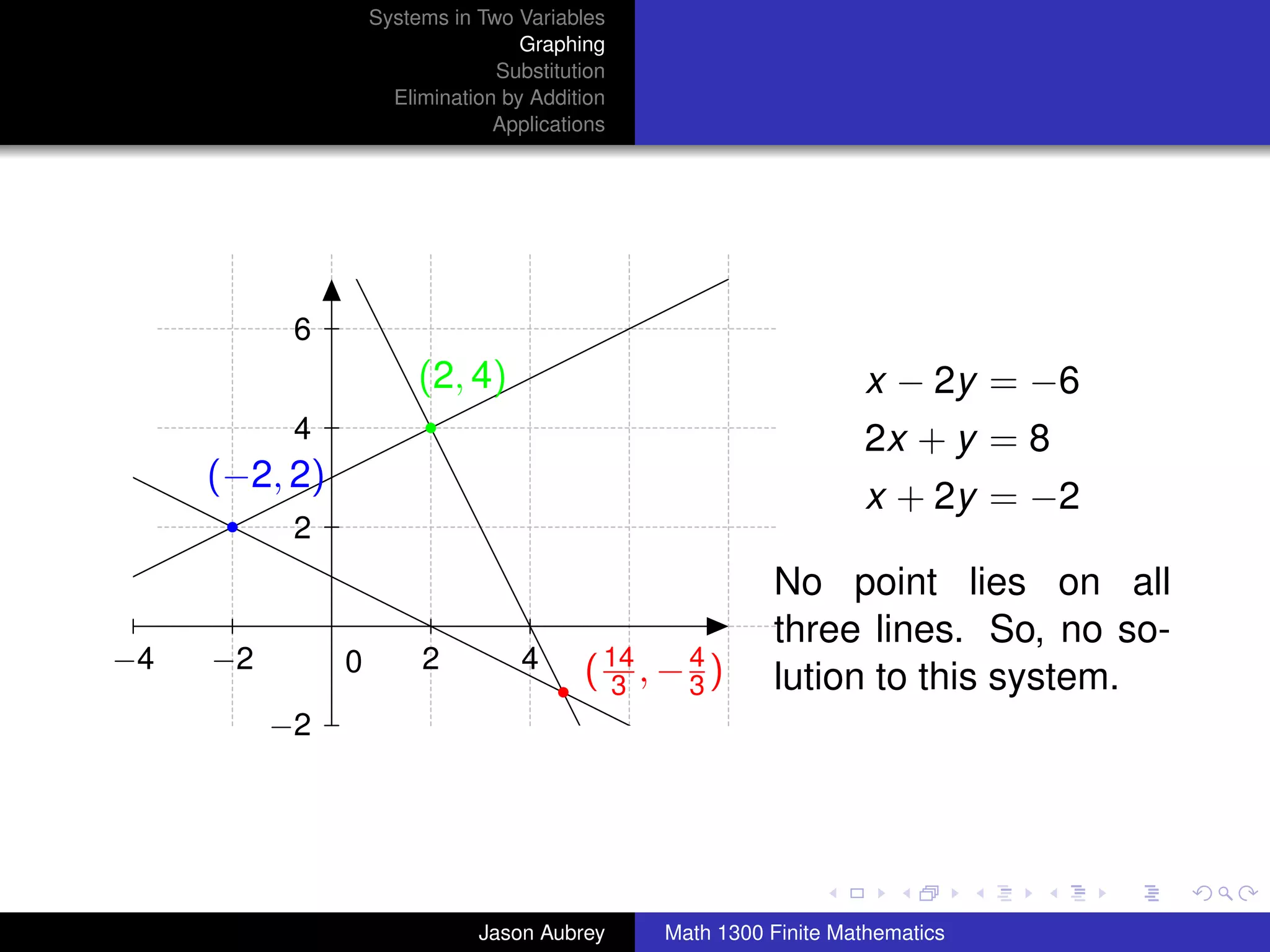
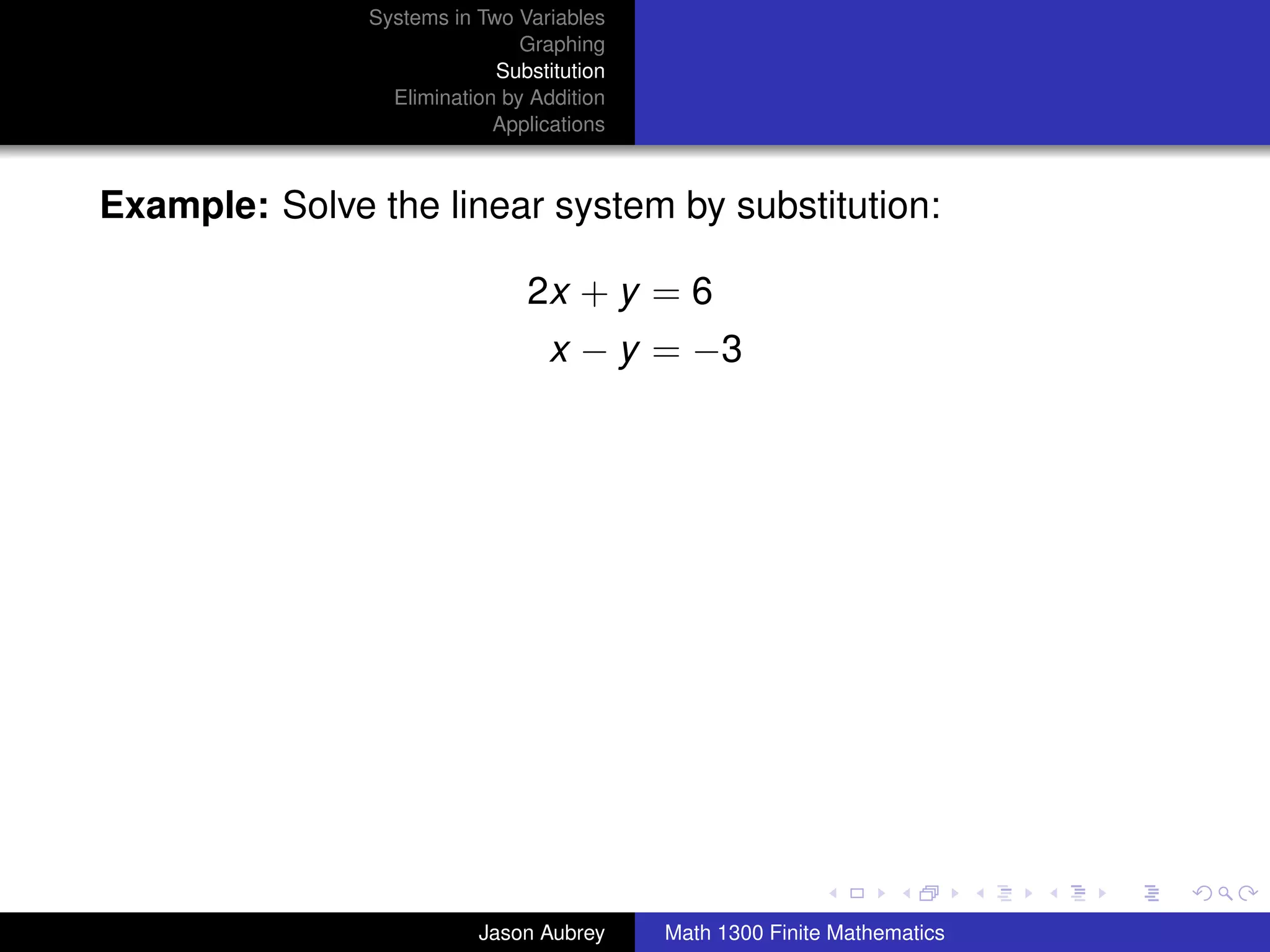
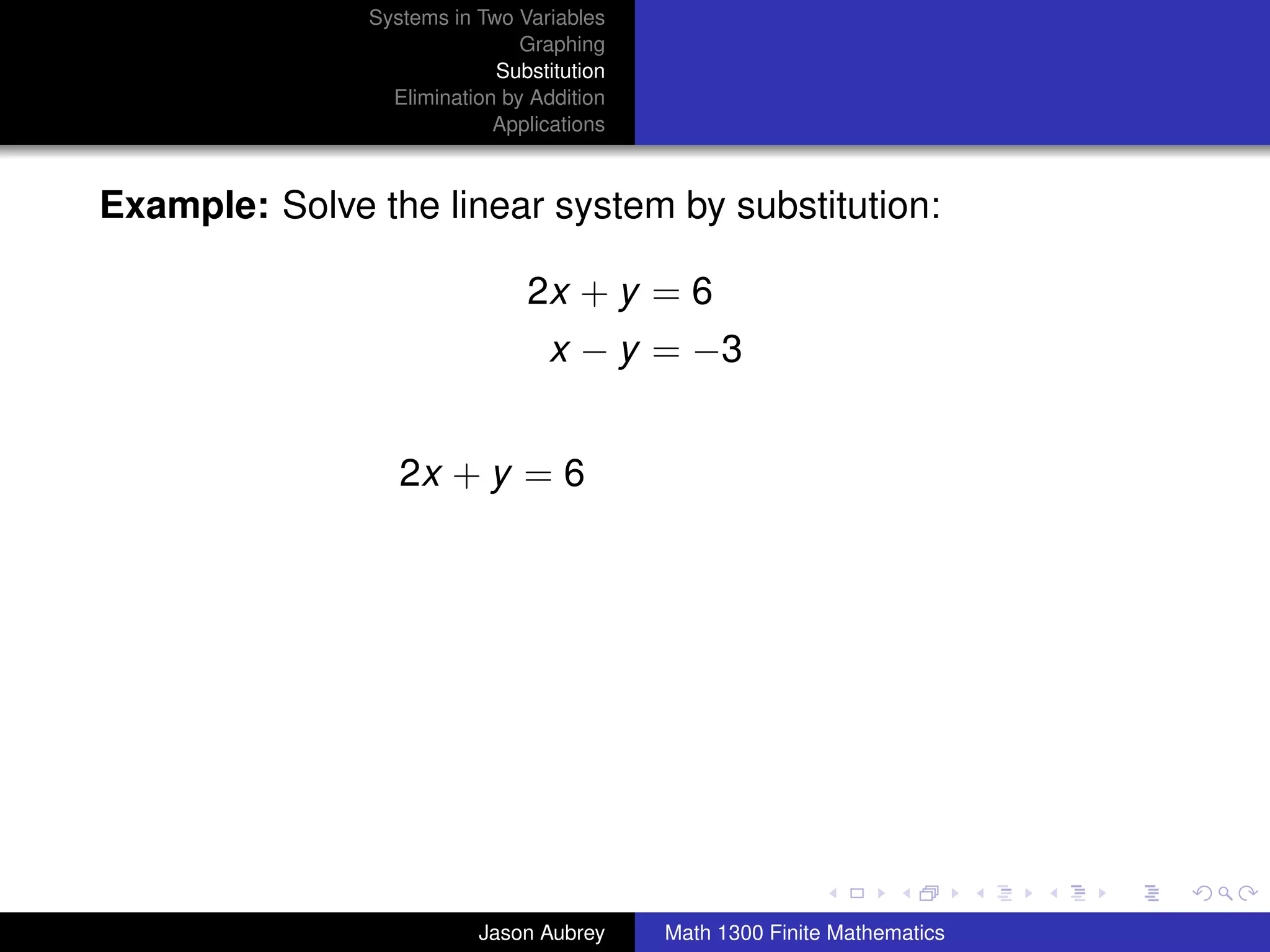
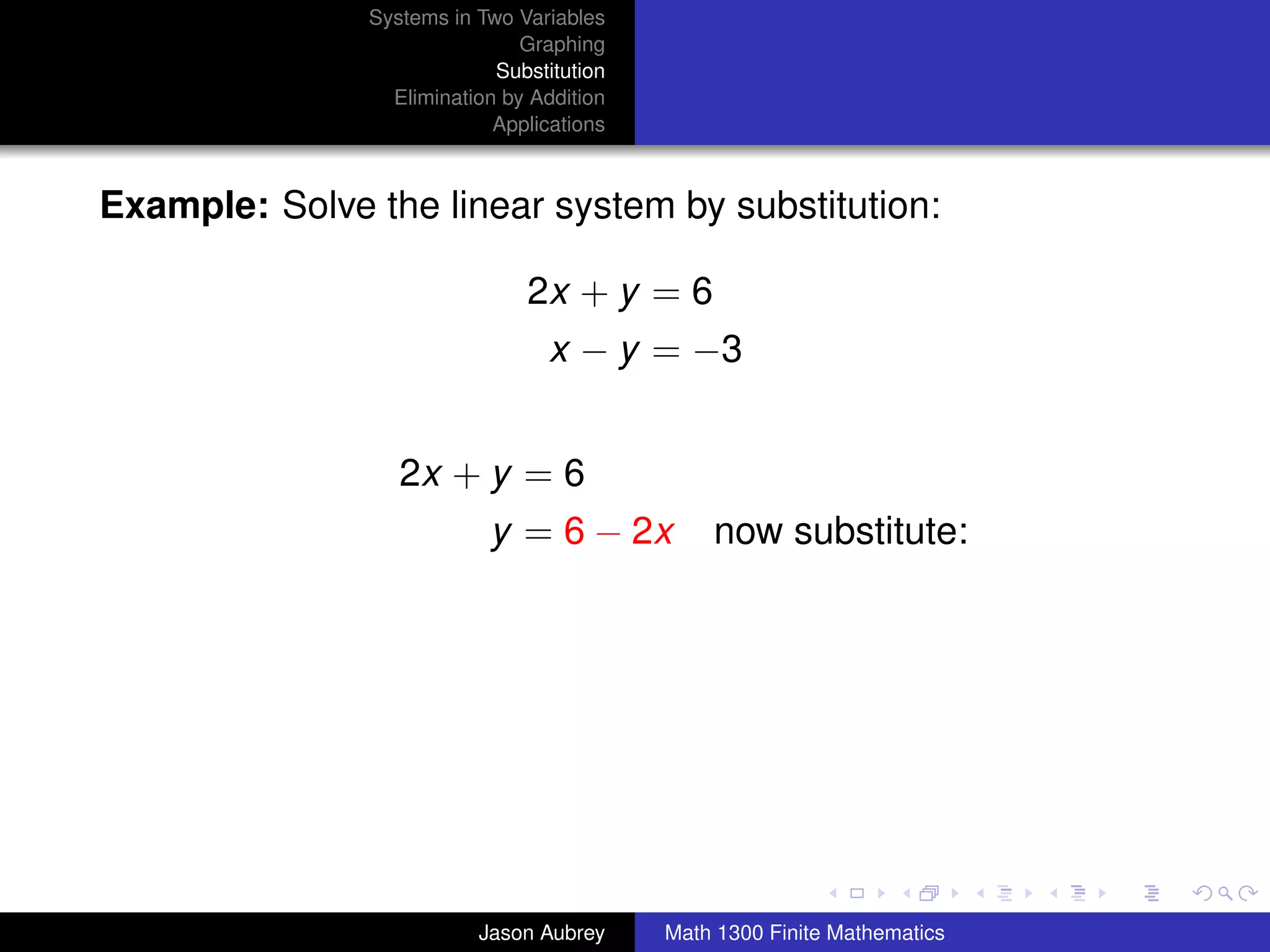
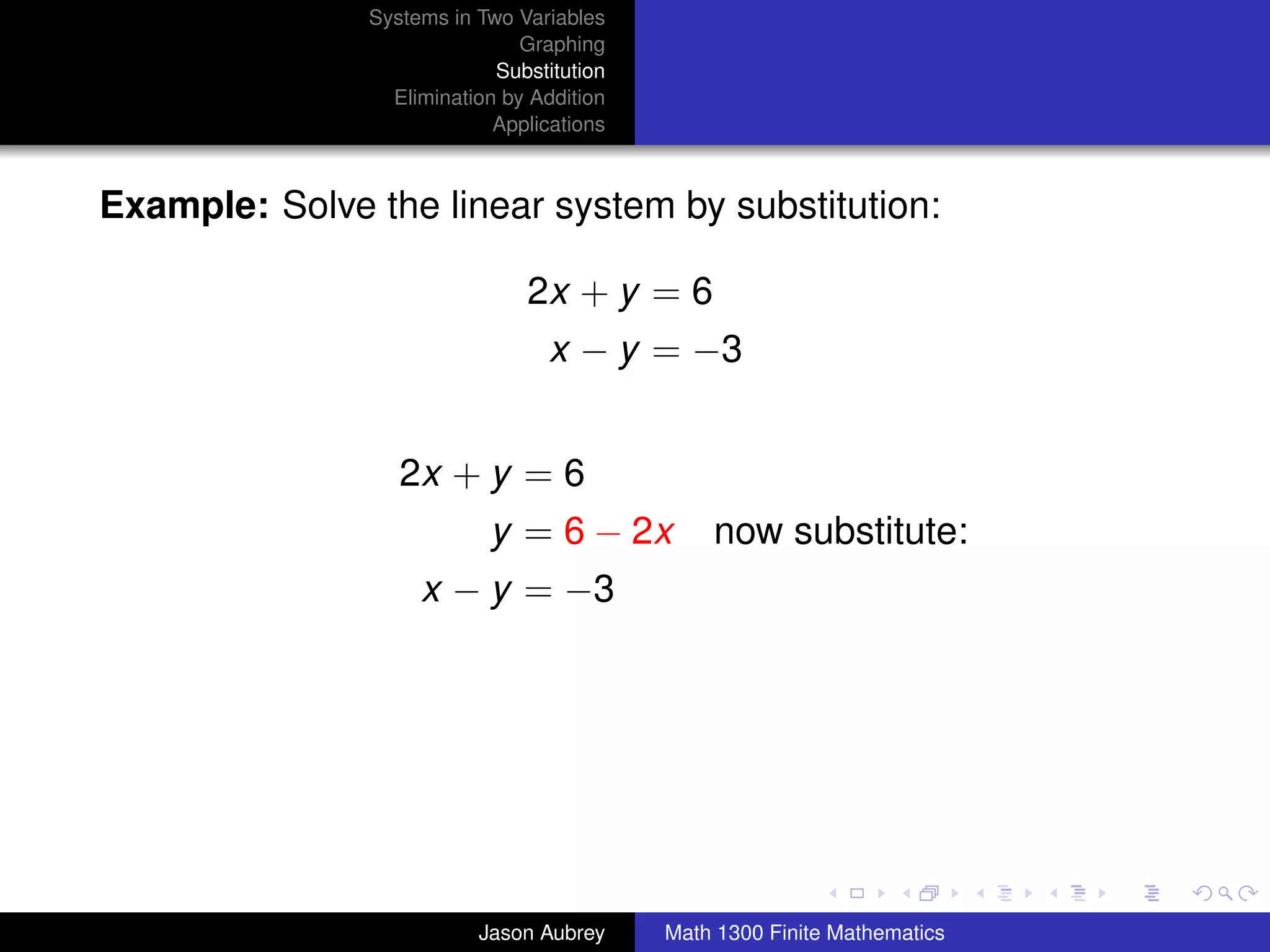
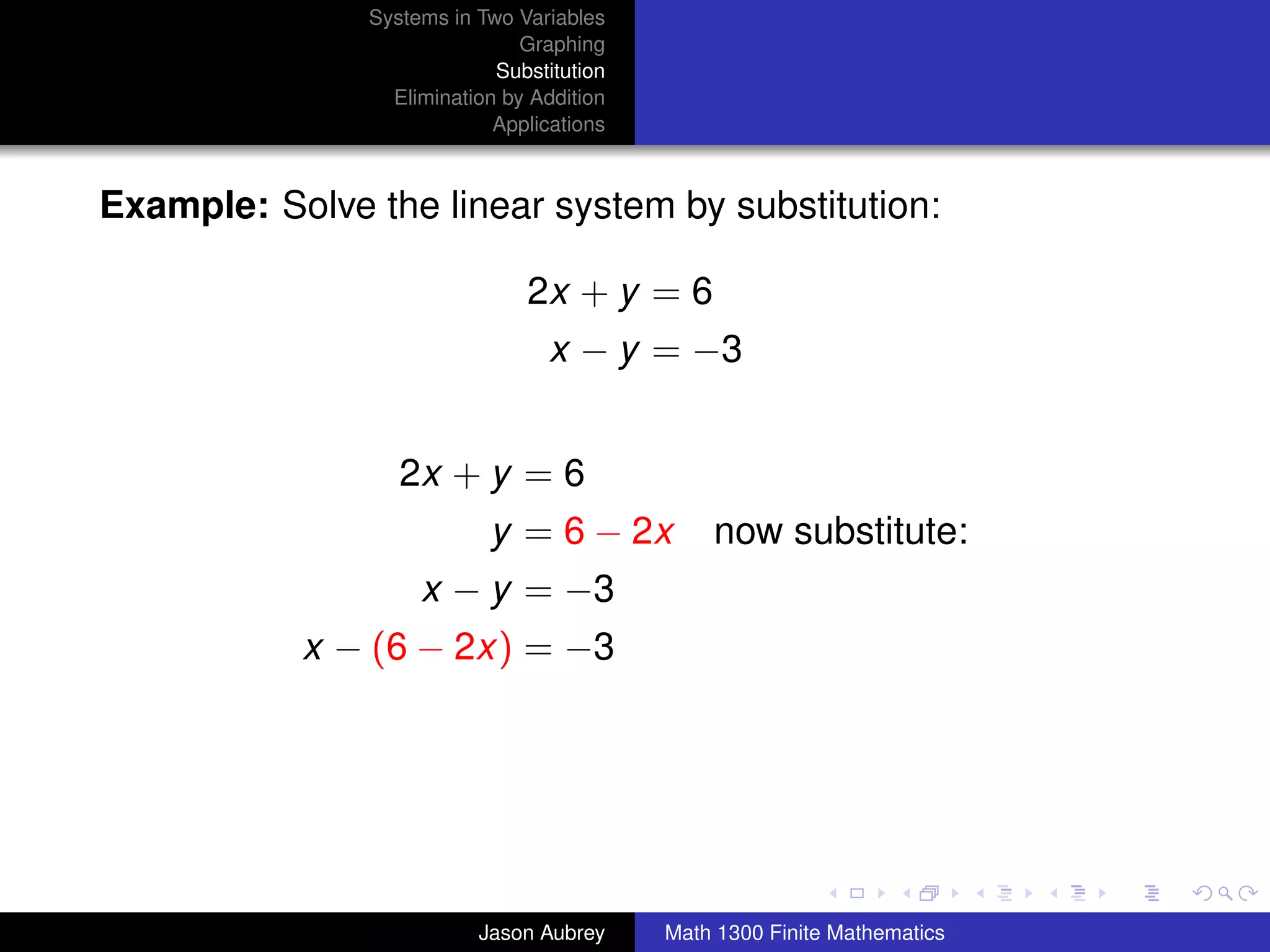
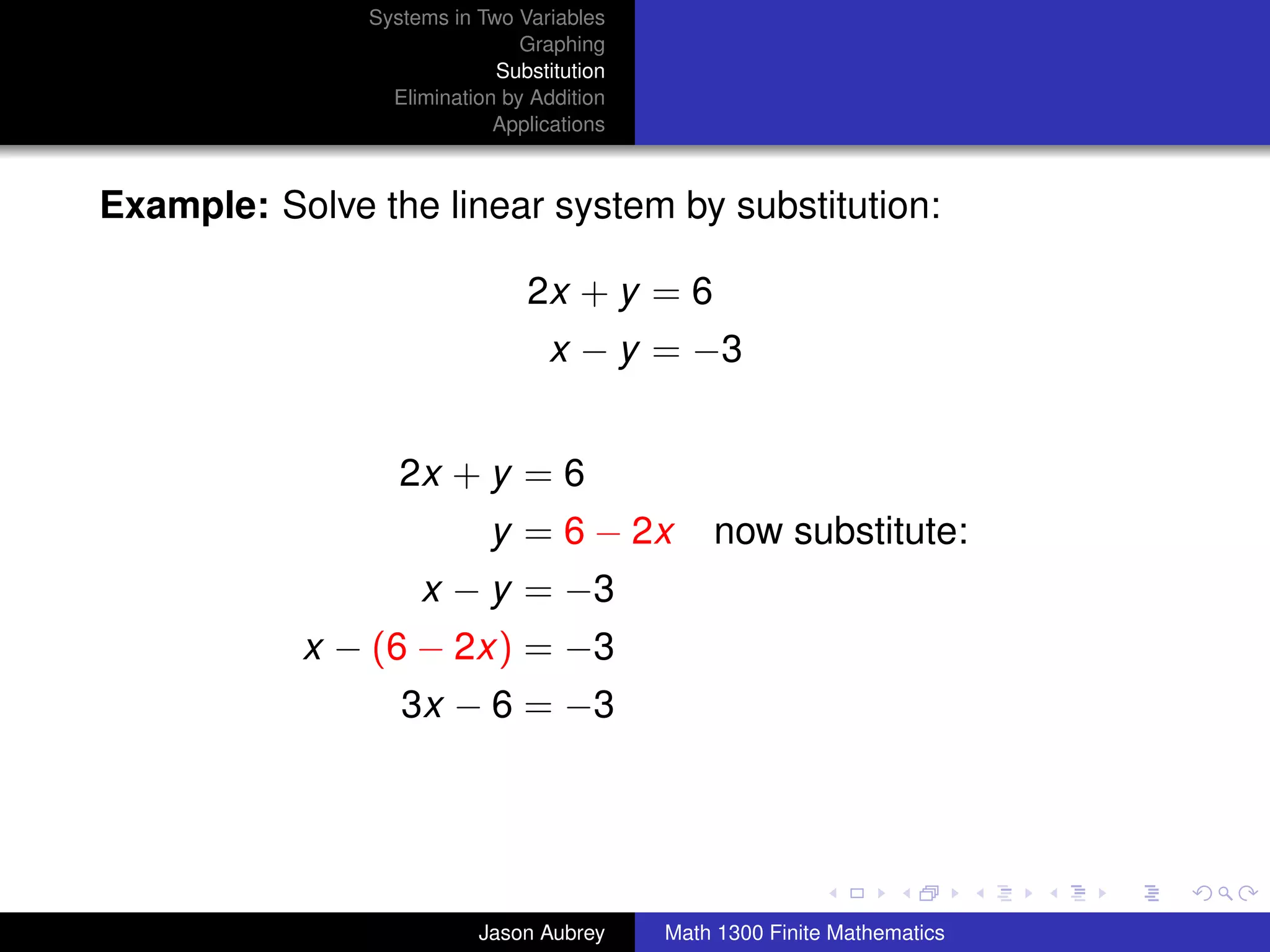
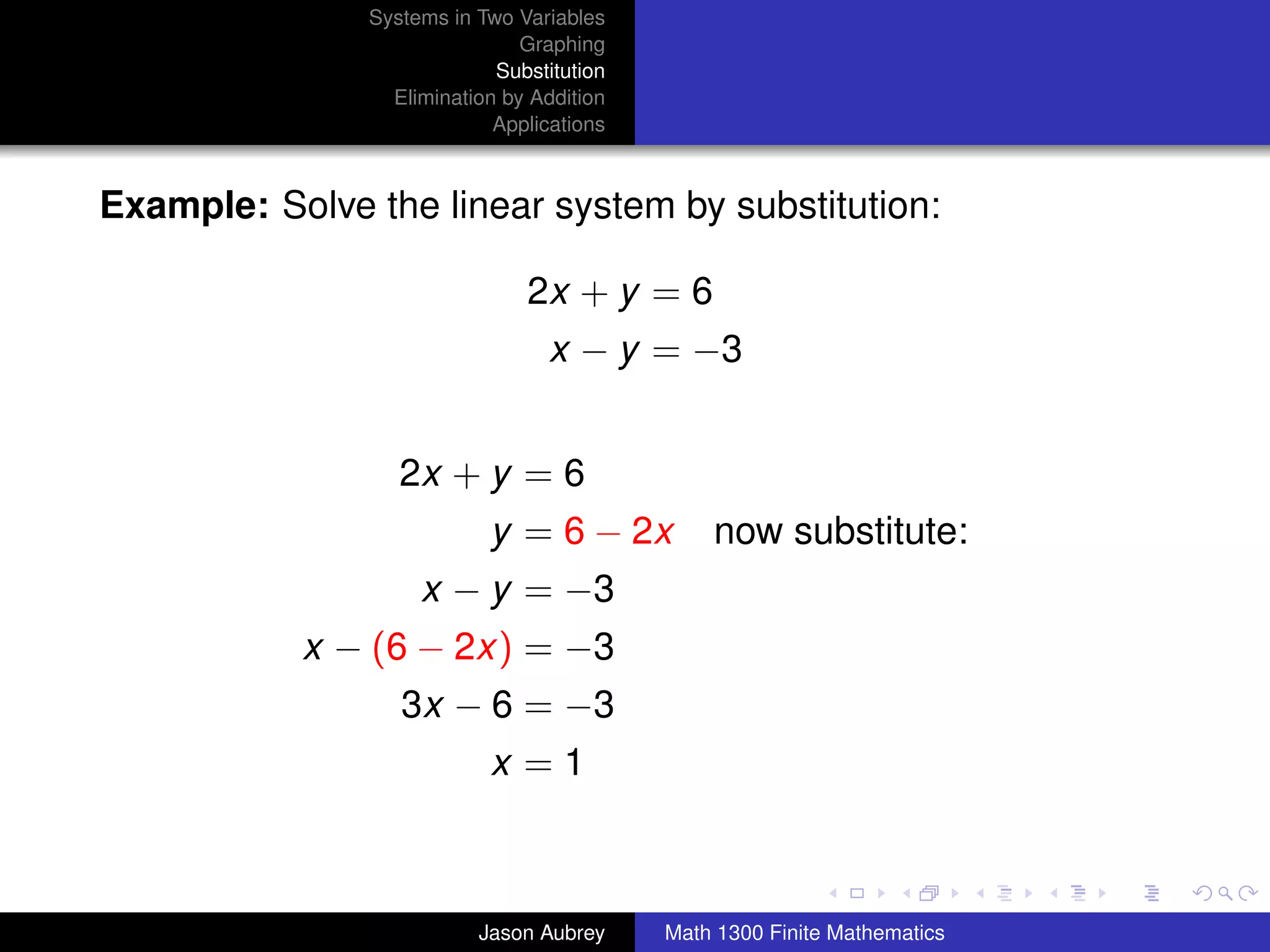
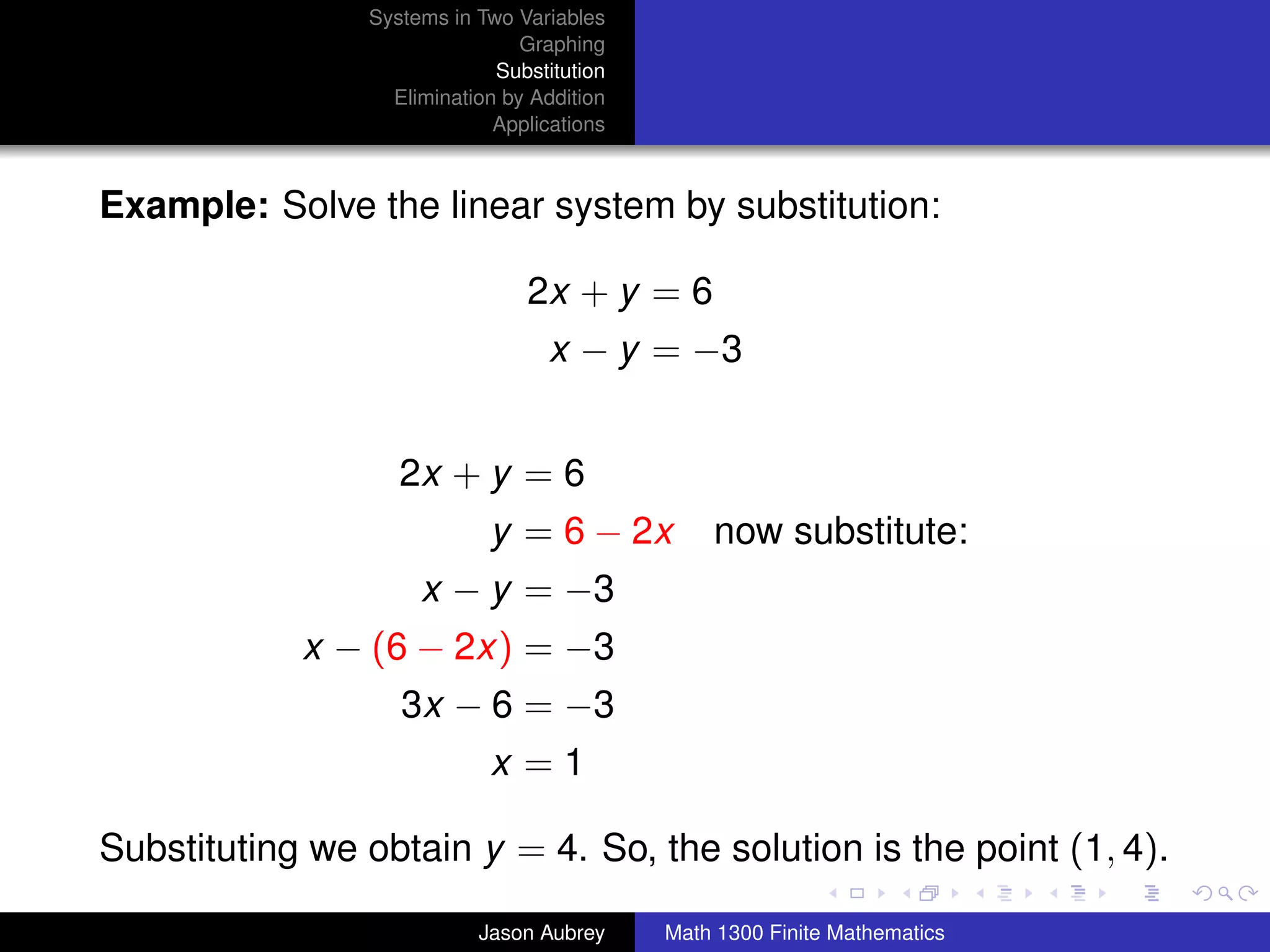
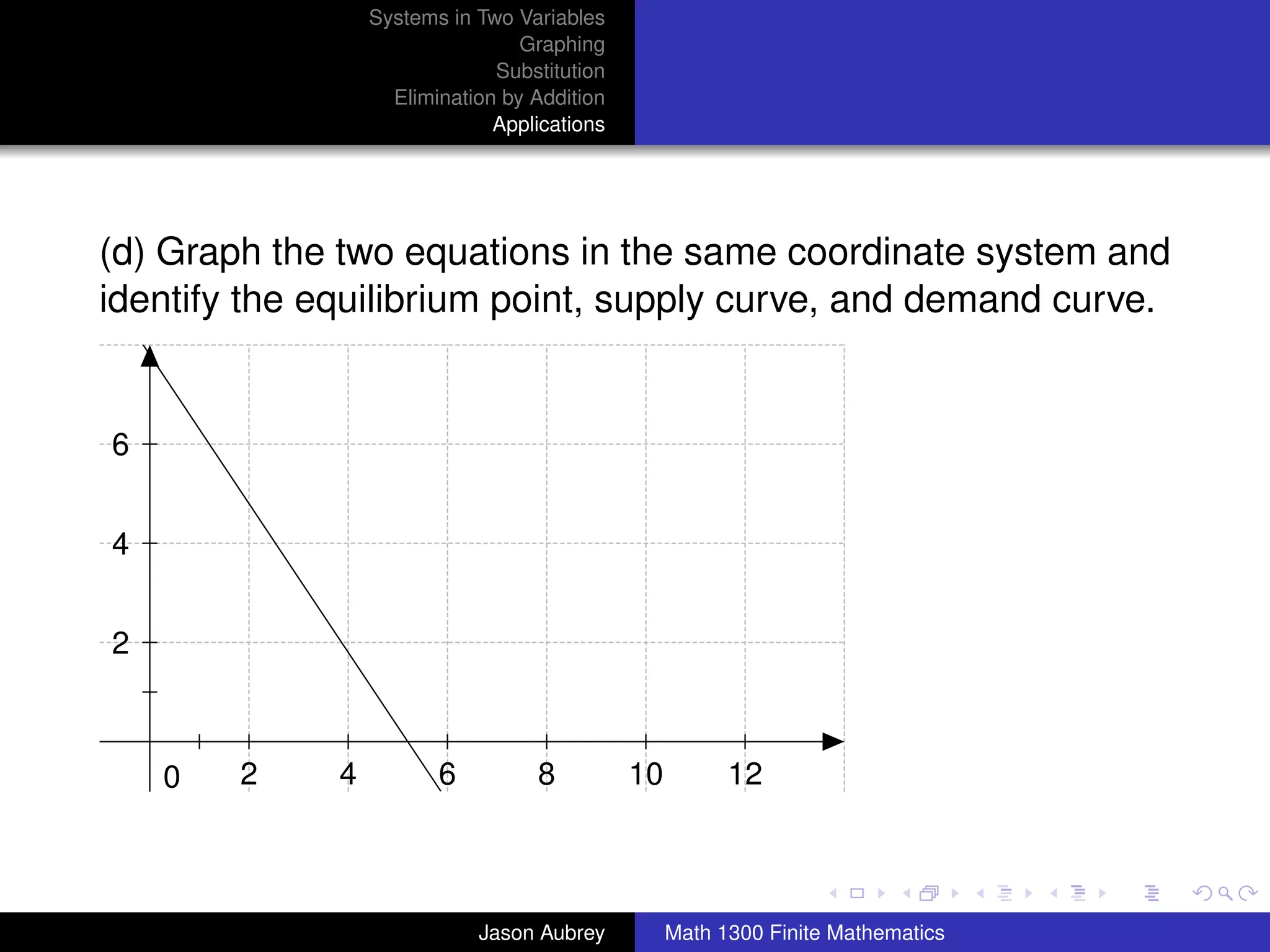
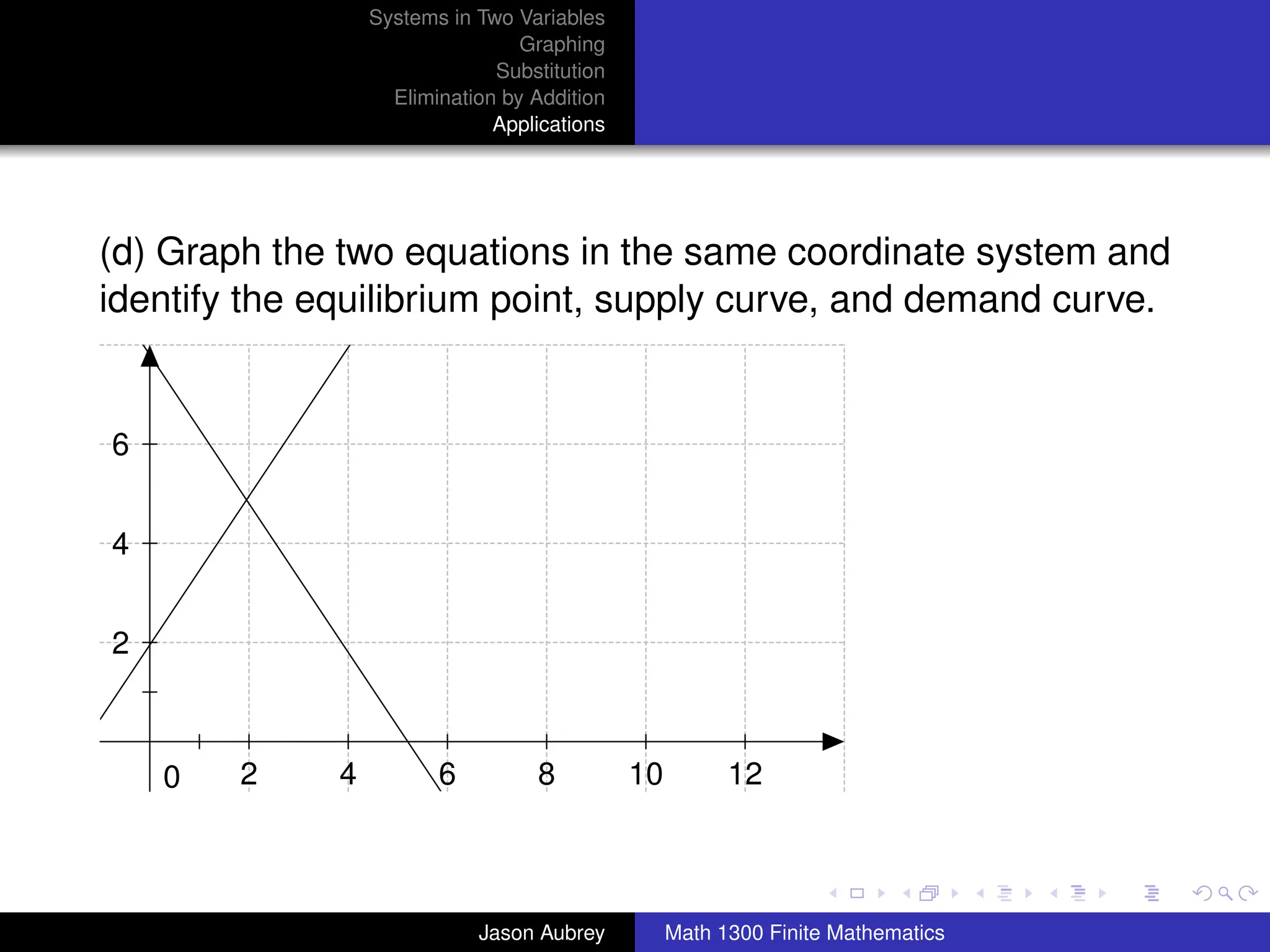
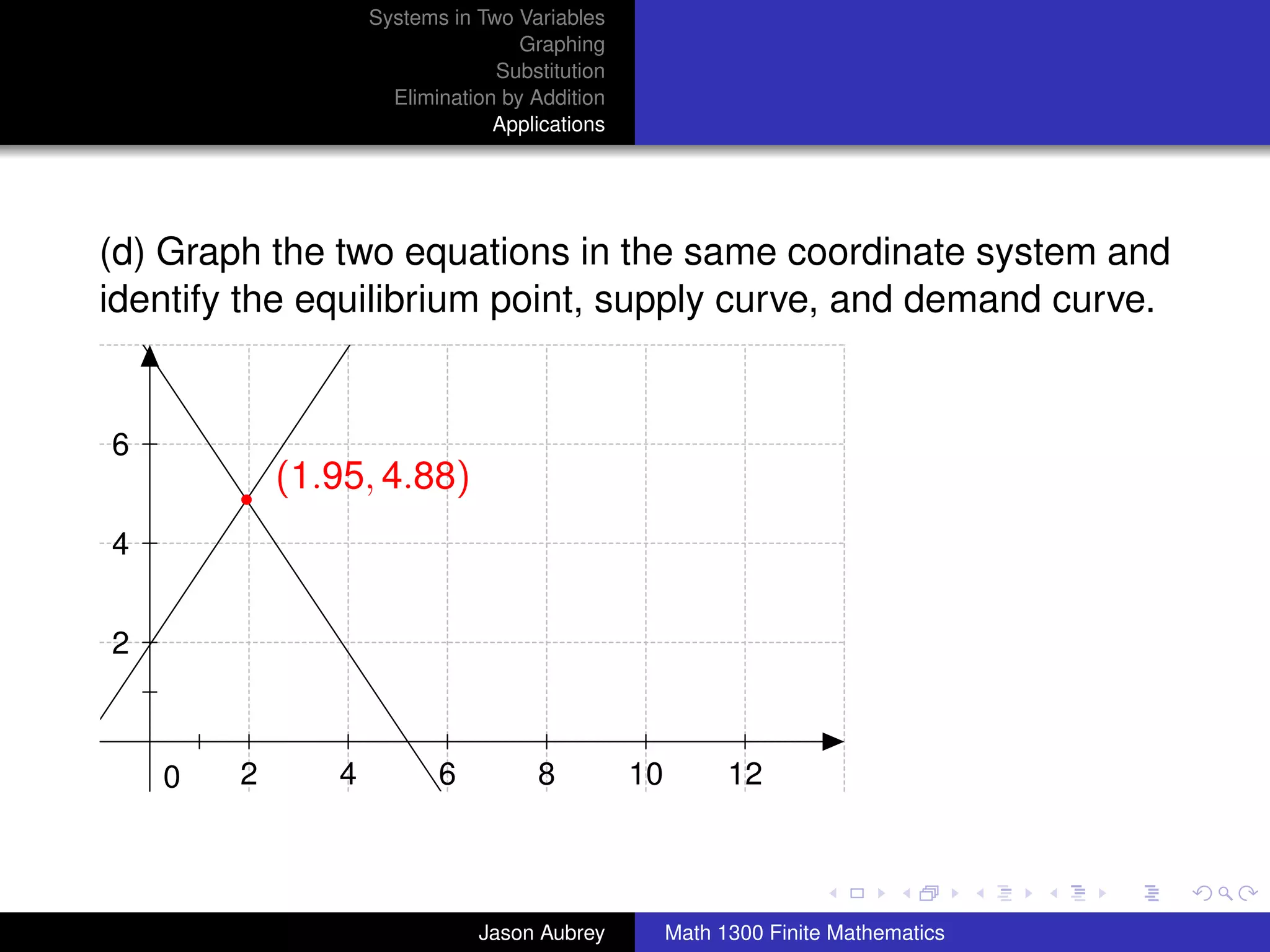
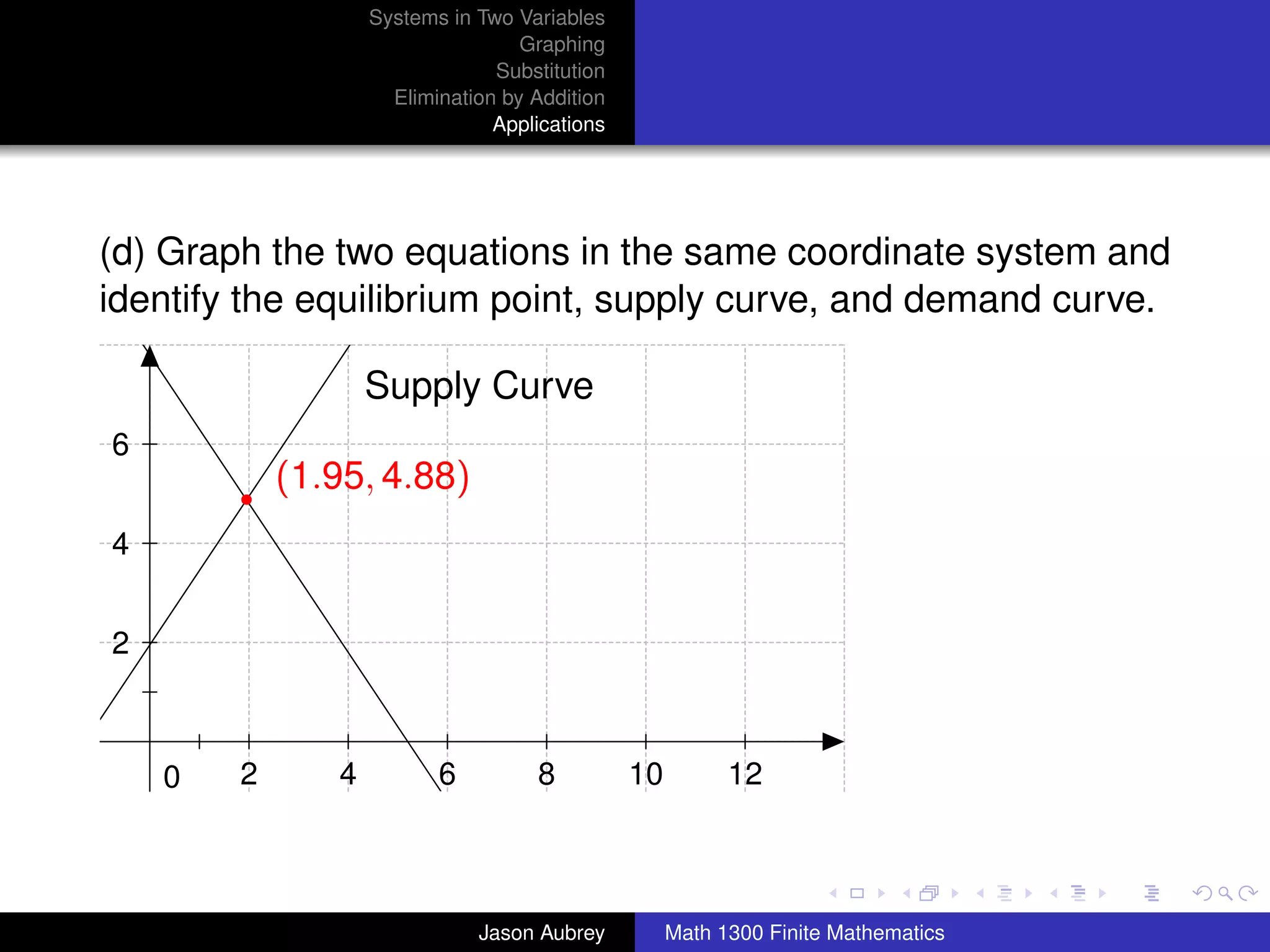
This document discusses solving systems of linear equations in two variables through three methods: graphing, substitution, and elimination. It defines key terms like consistent, independent, and dependent when describing systems of linear equations. The document also presents a theorem stating the possible solutions a linear system can have and provides an example of graphing a system to find the solution set.