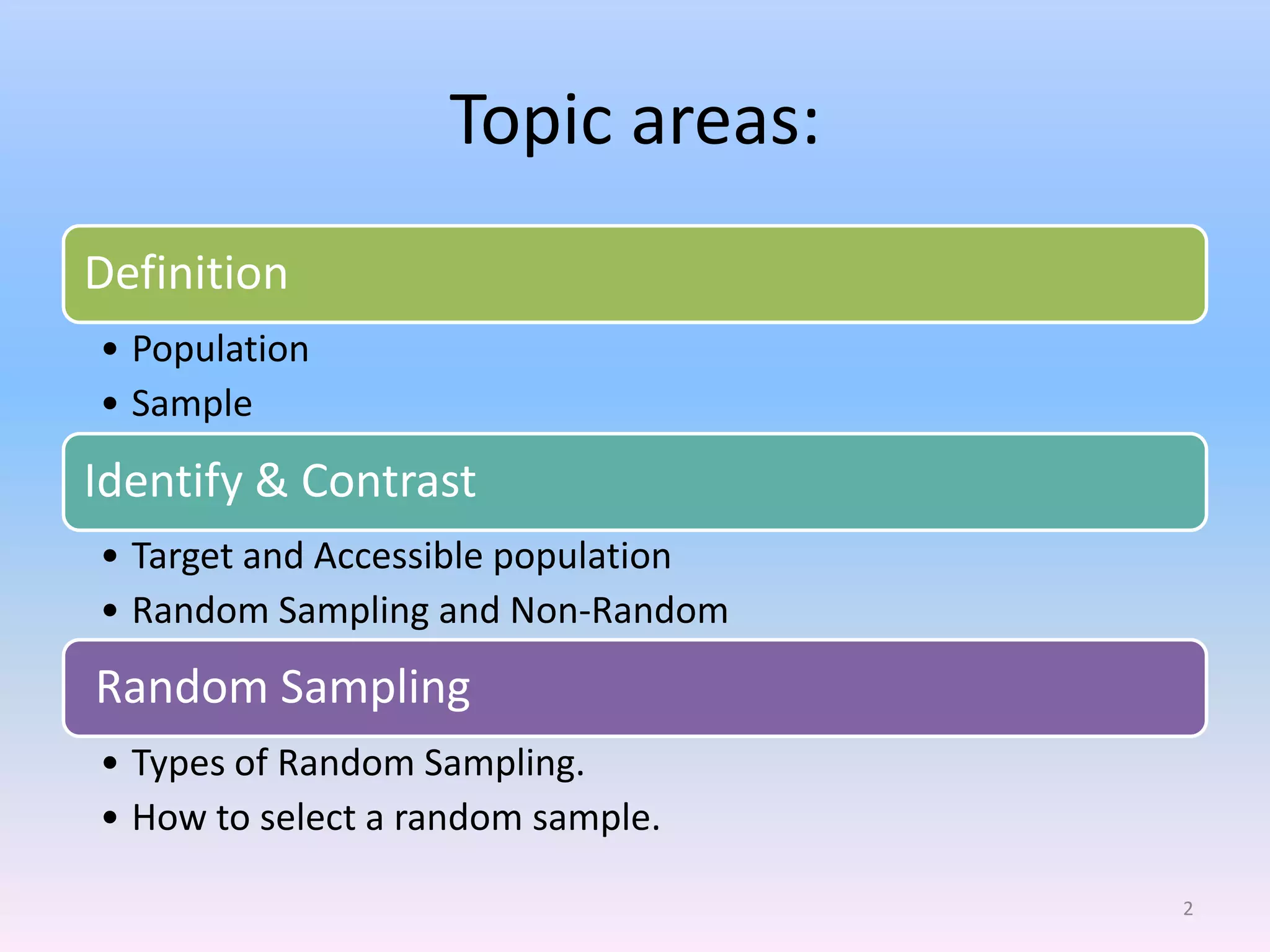
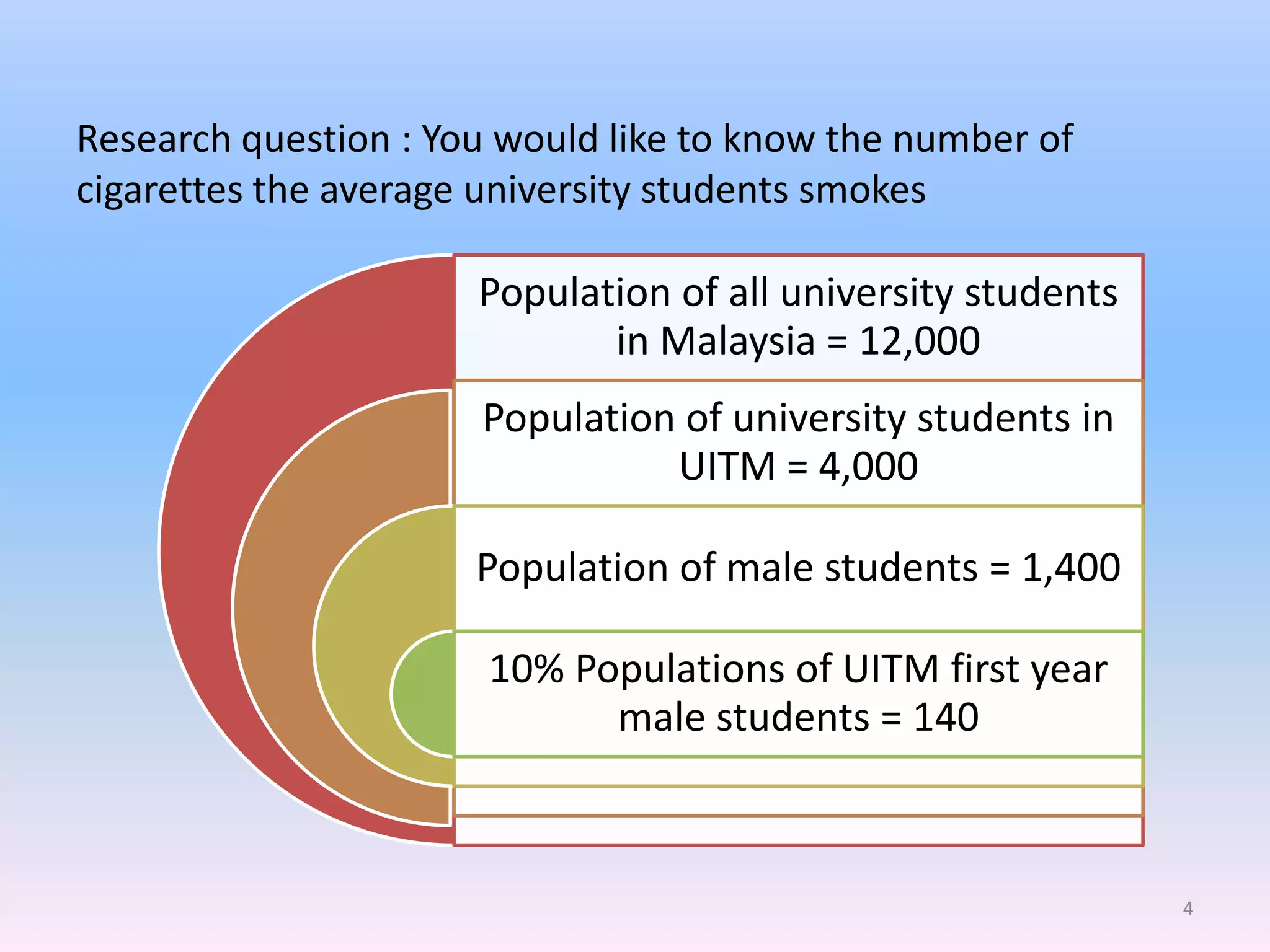
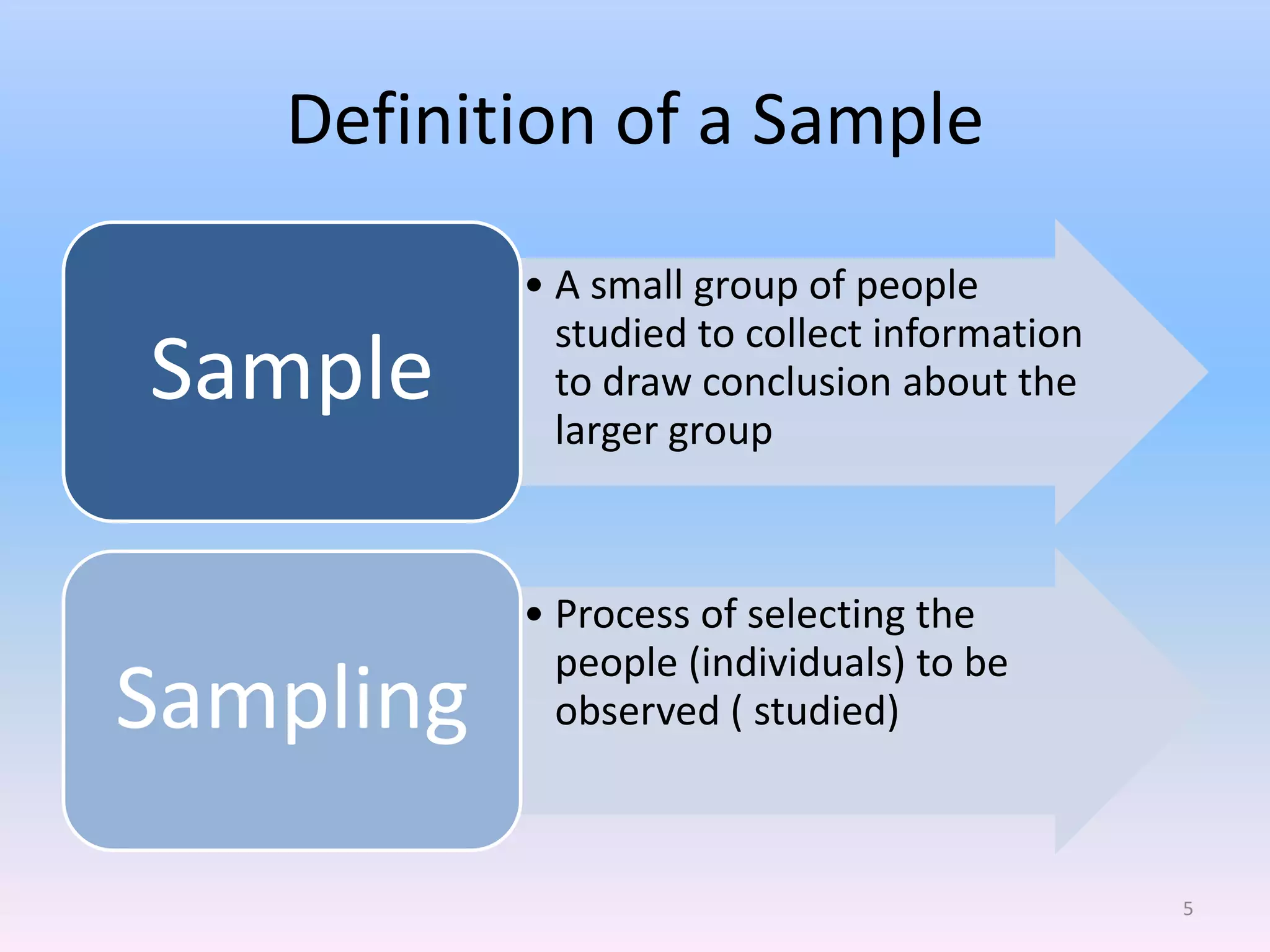
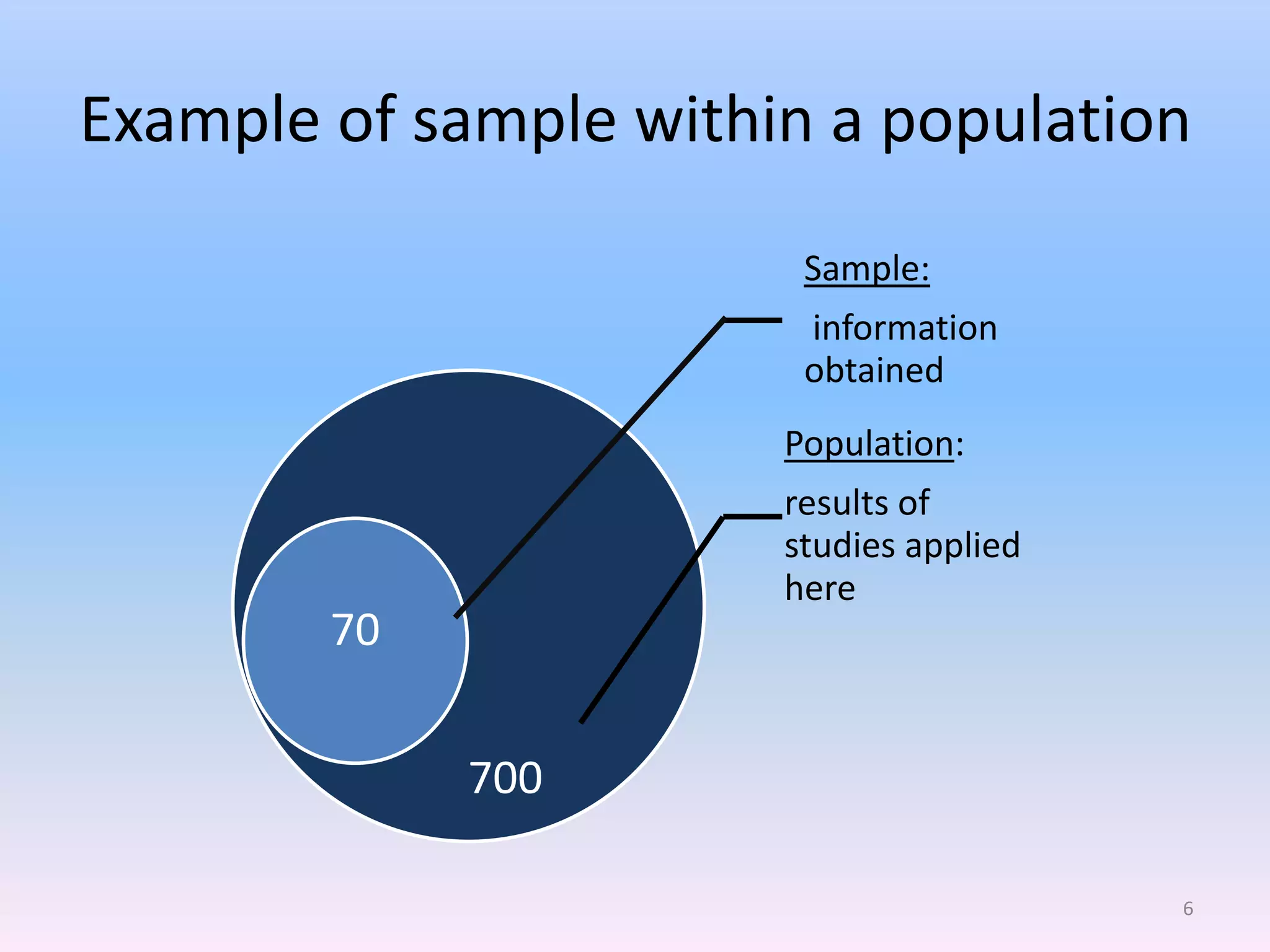
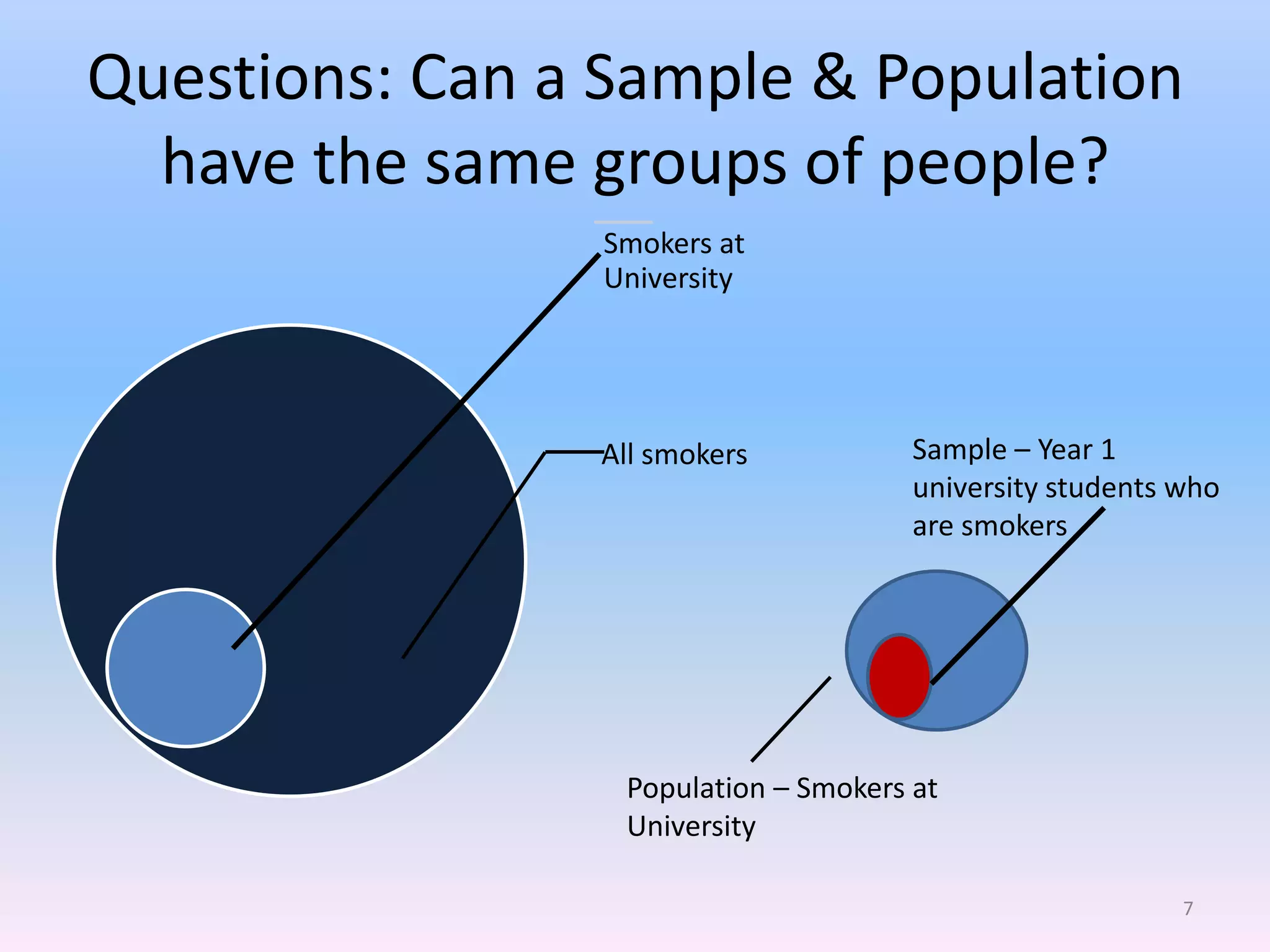
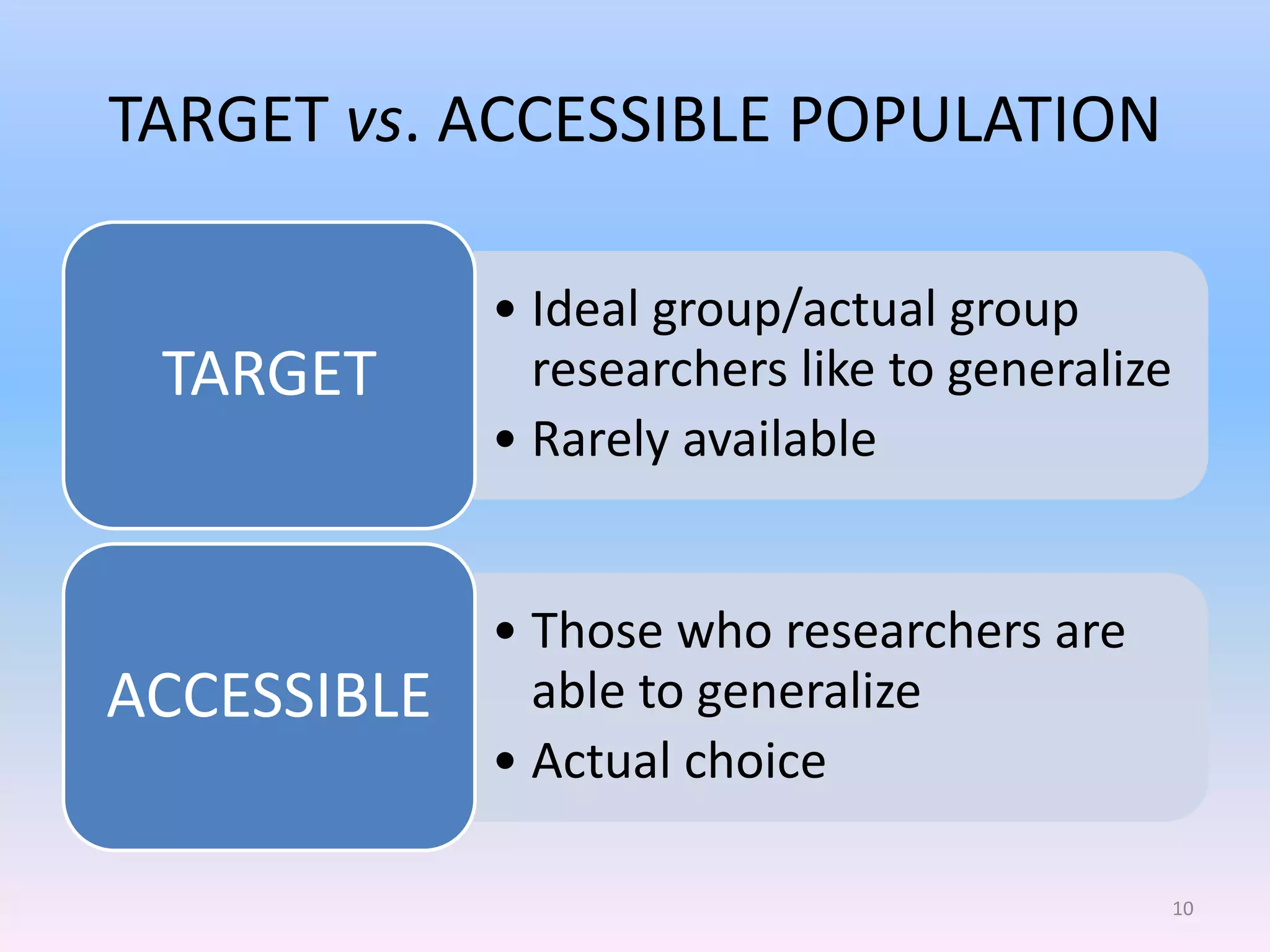
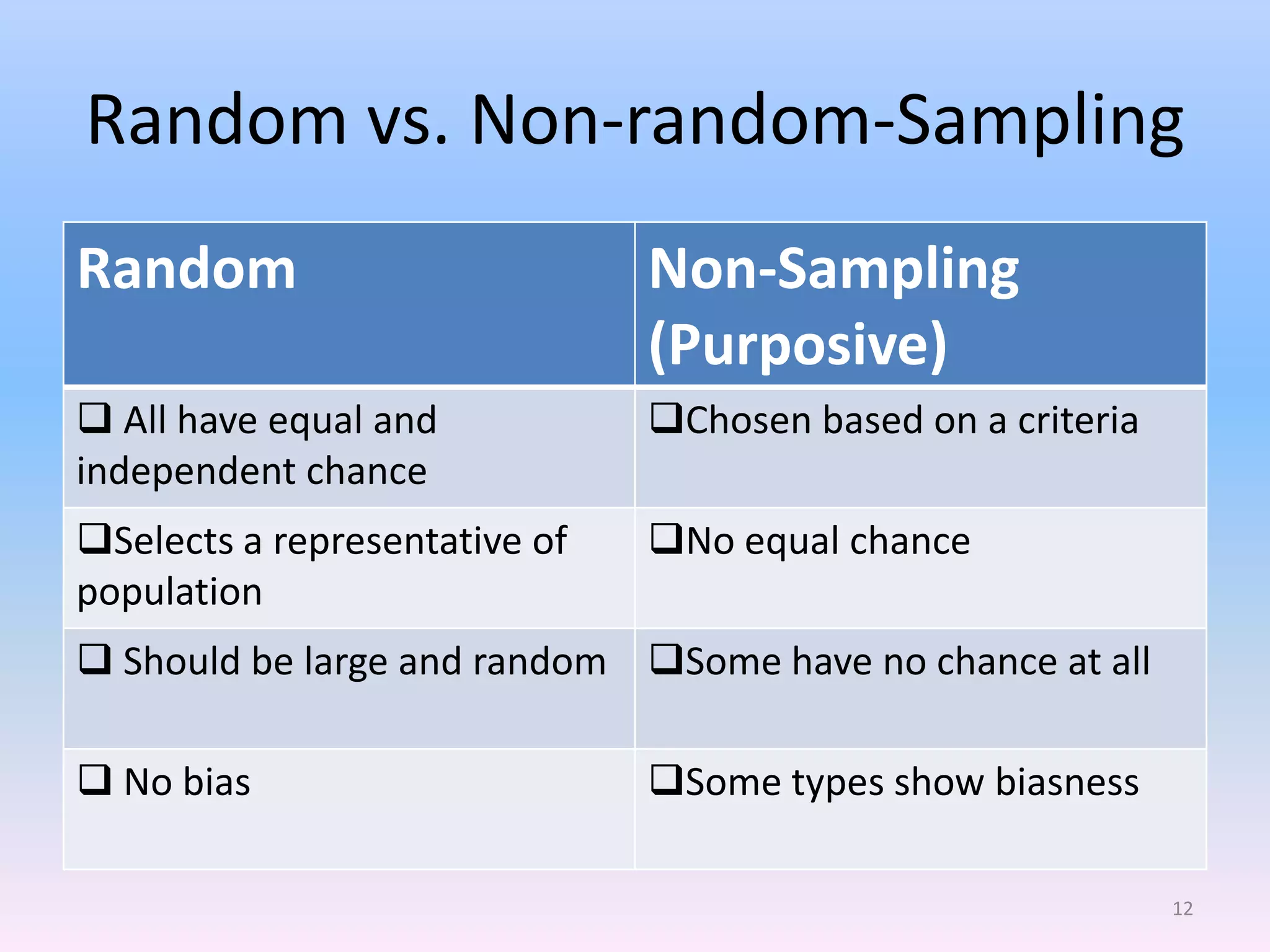
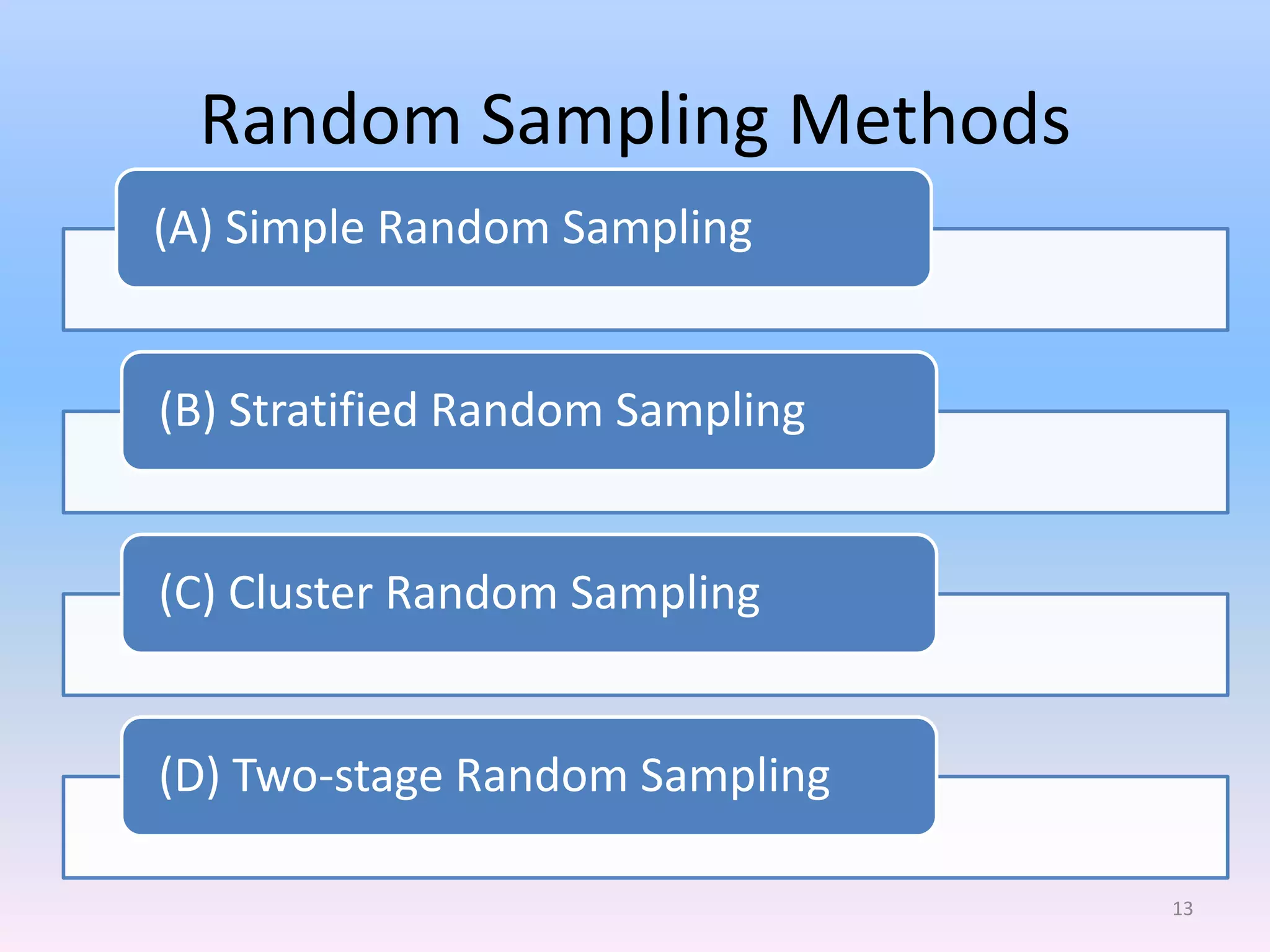
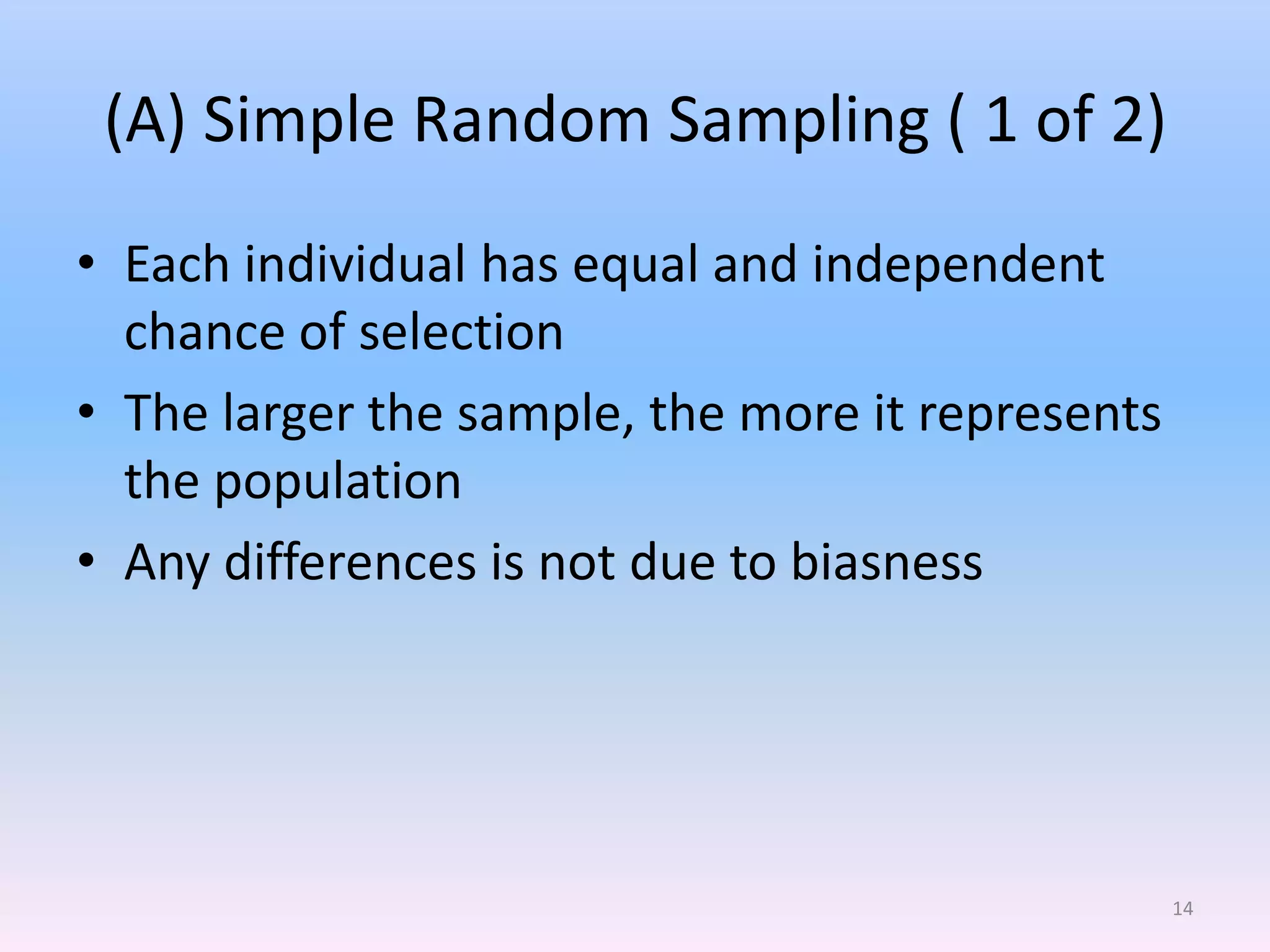
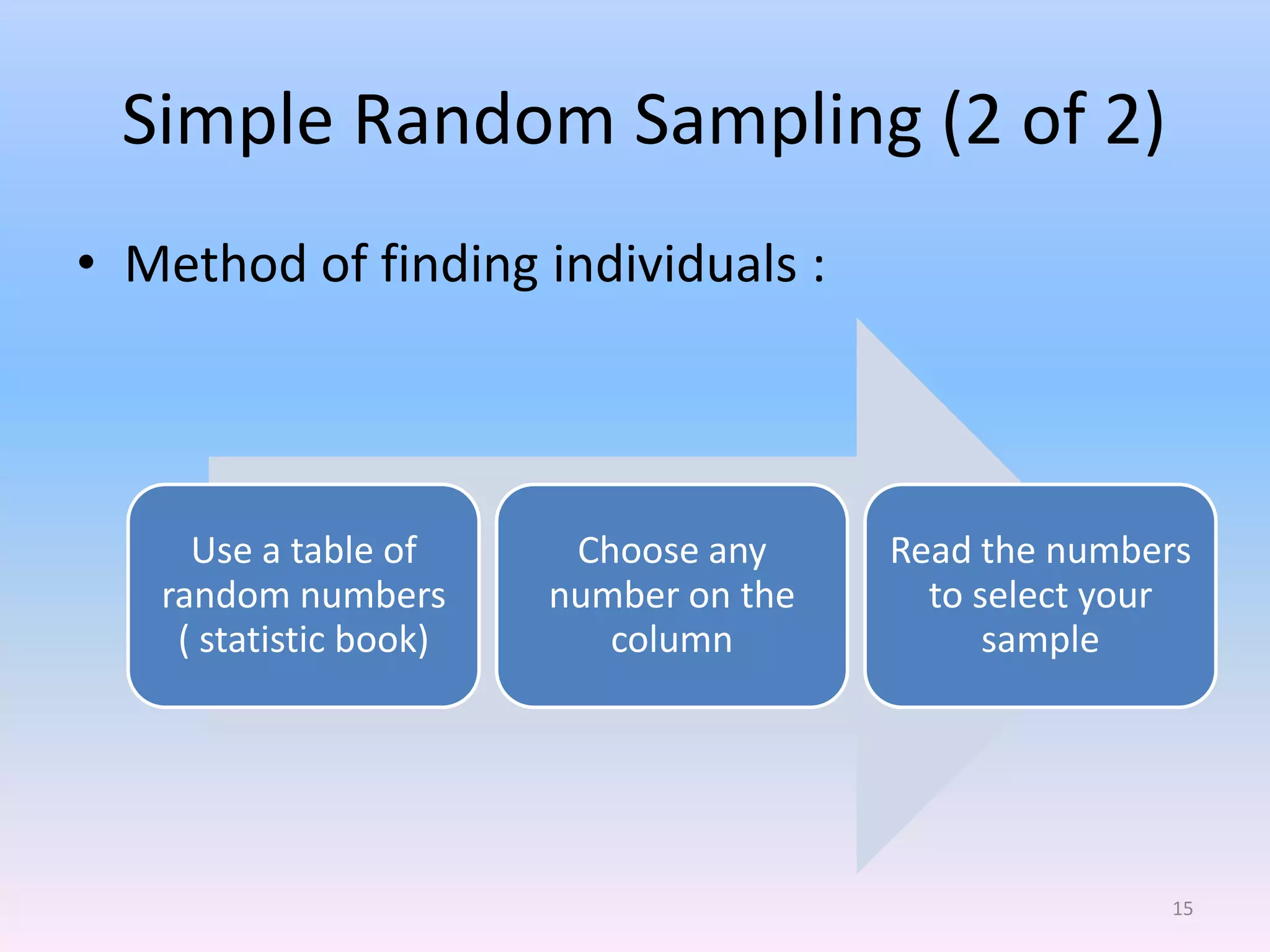
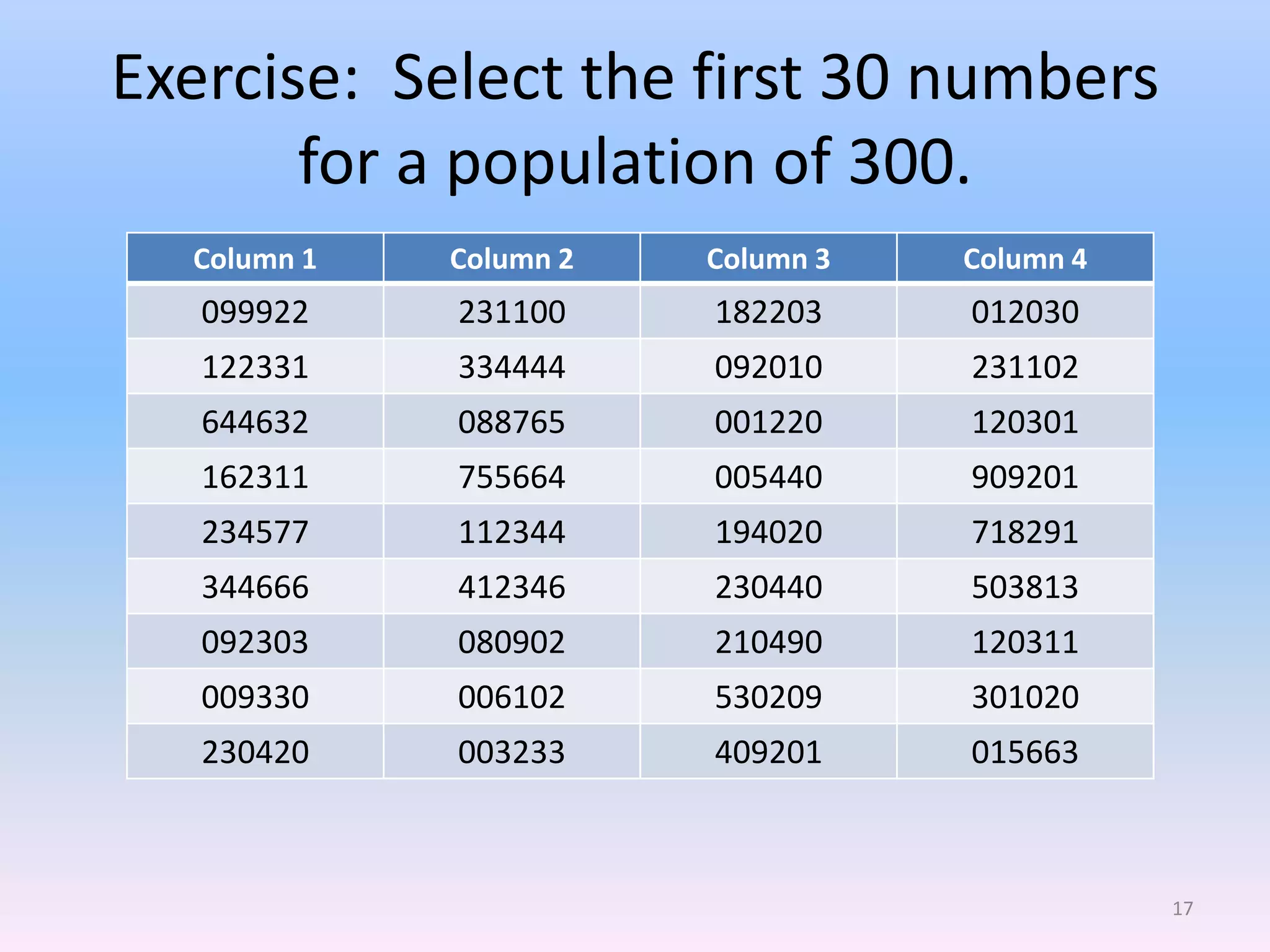
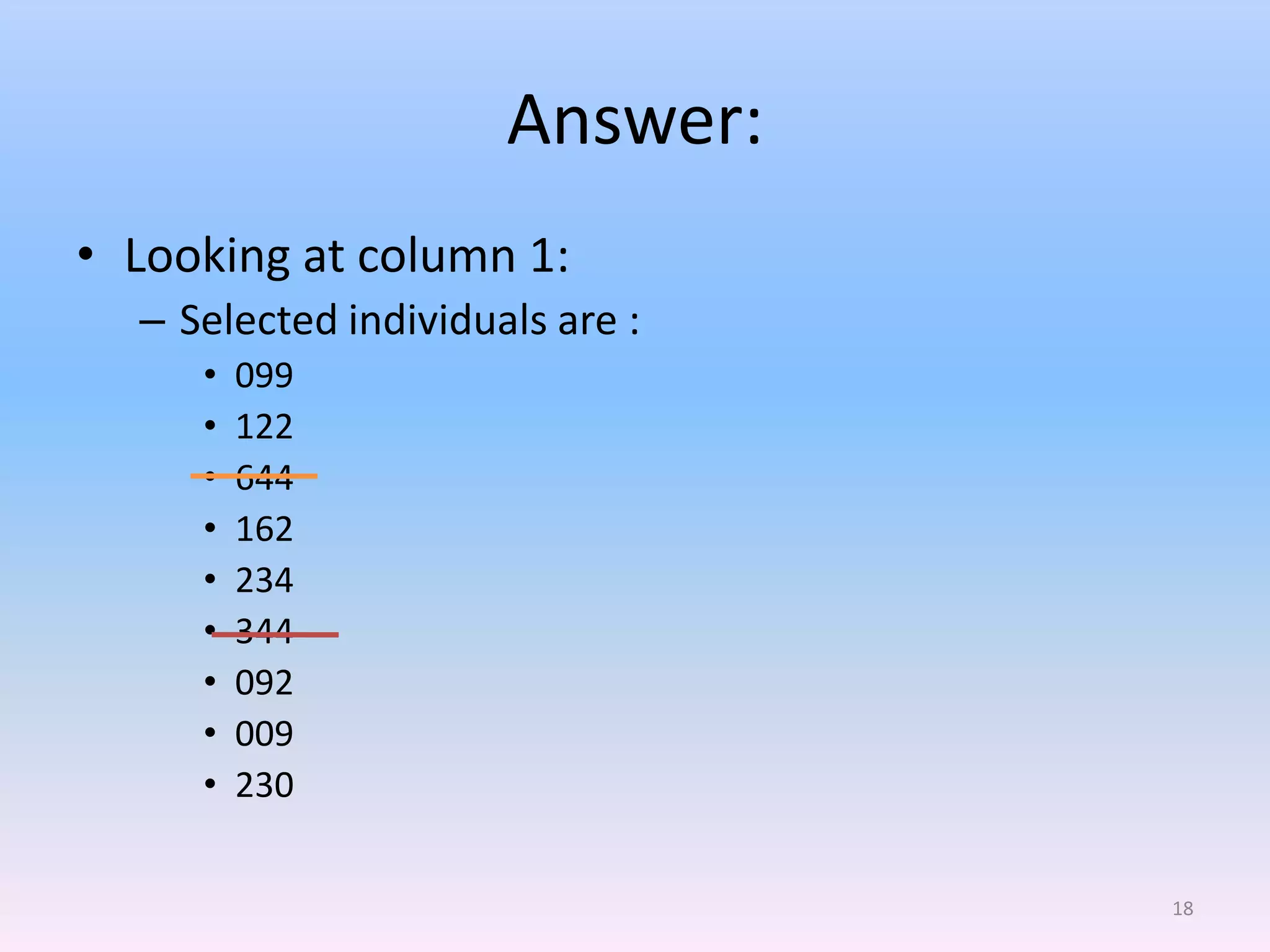
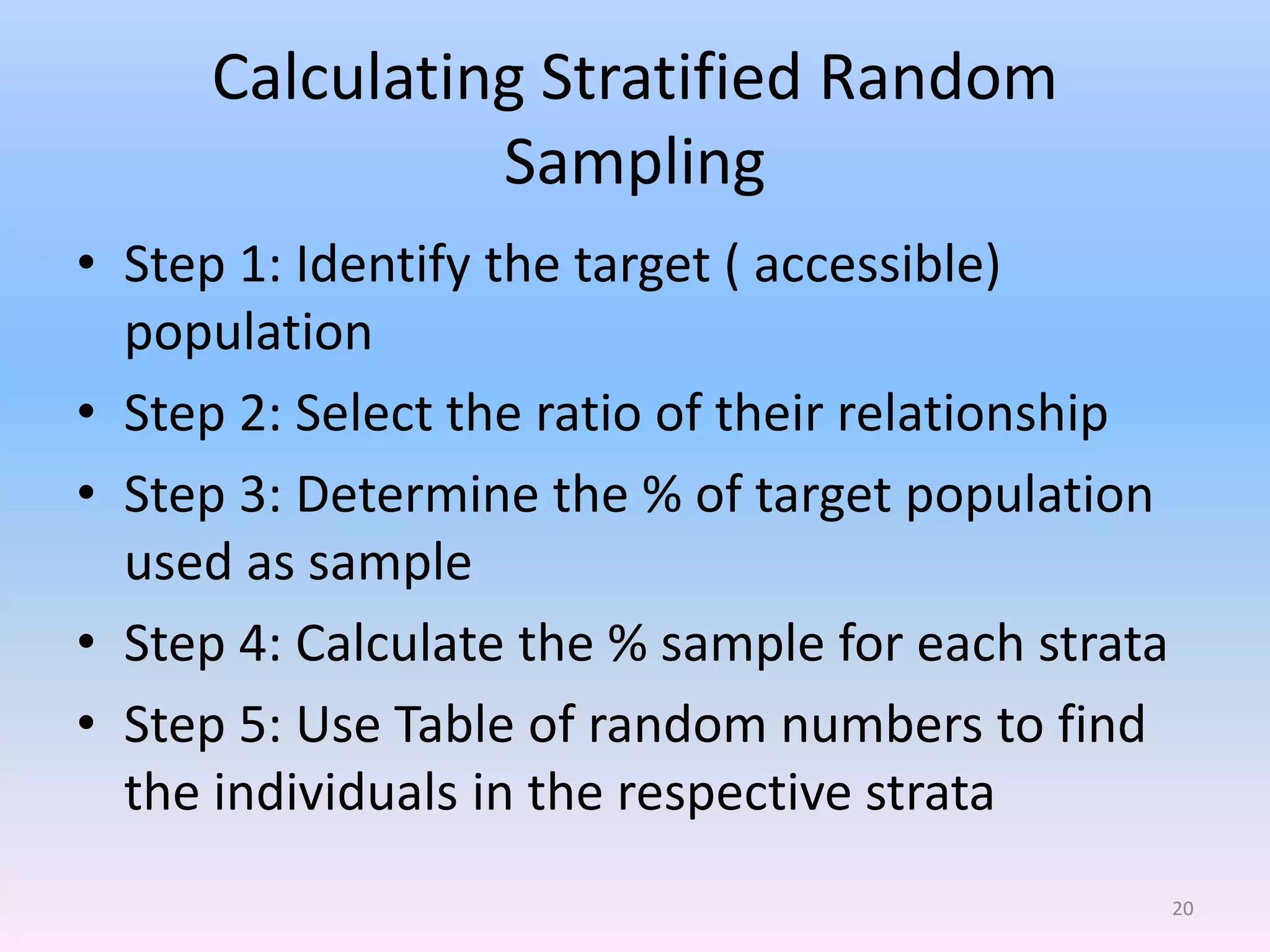
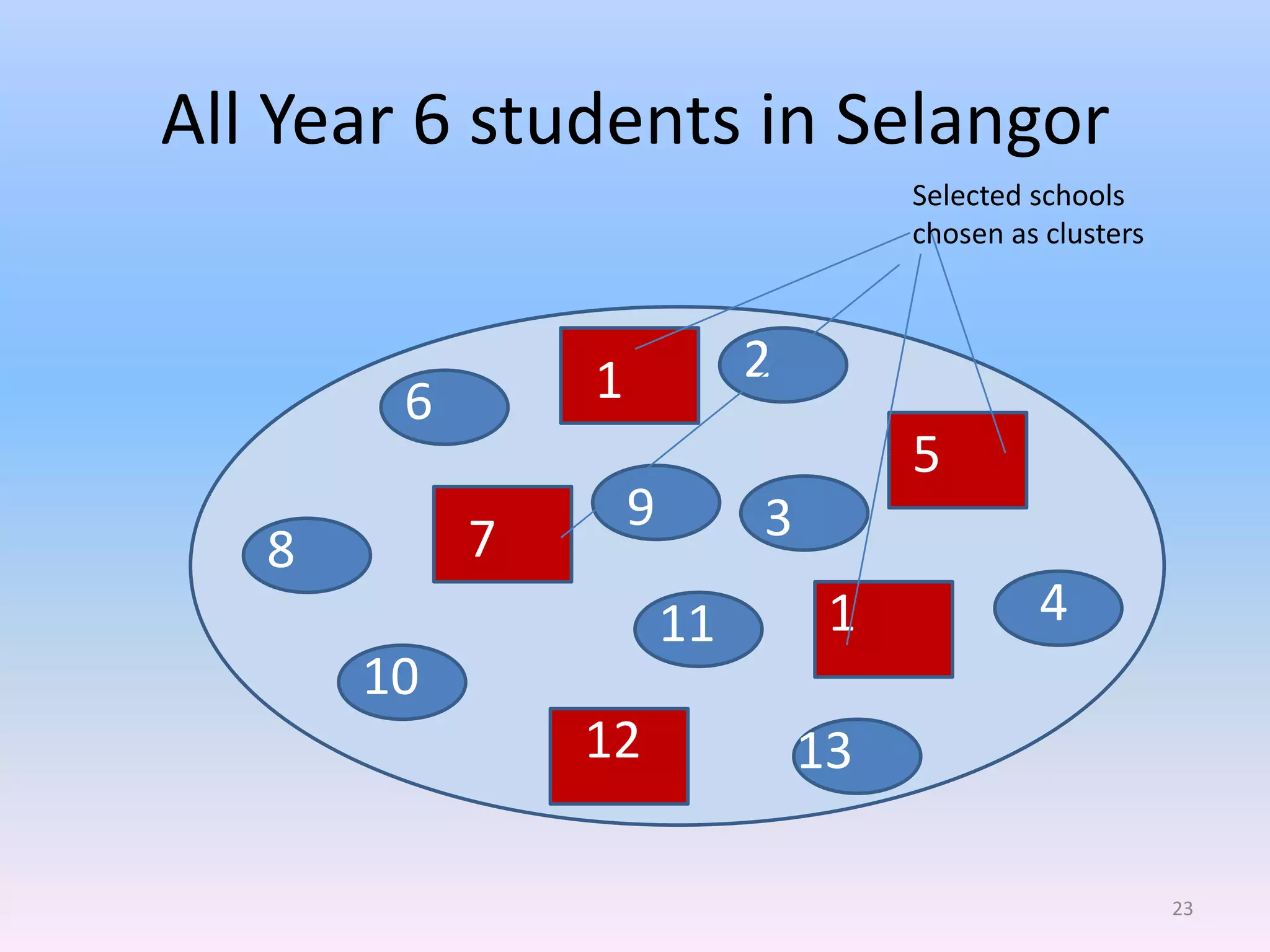
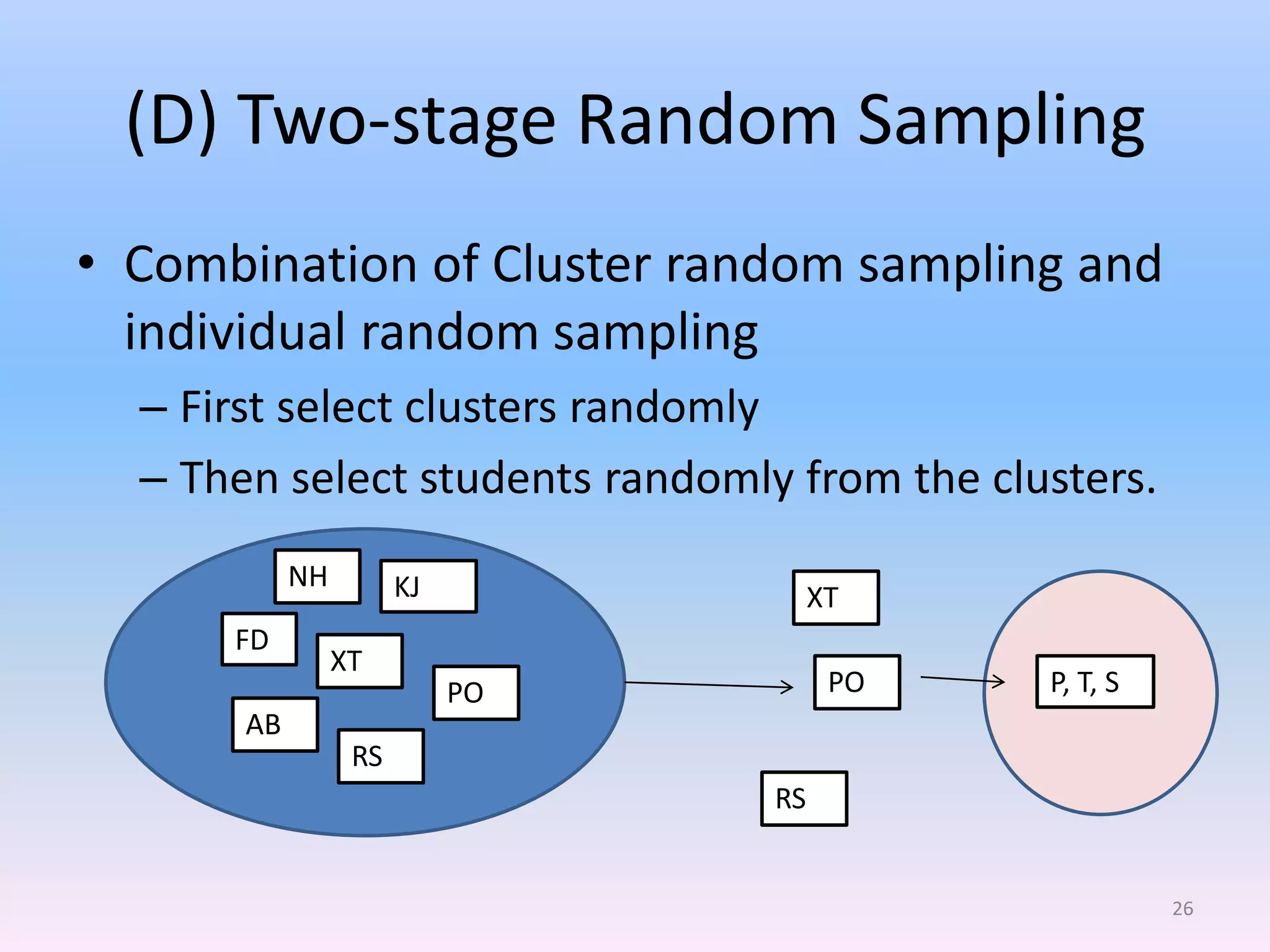
This document discusses different types of sampling methods used in research. It defines key terms like population, sample, target population and accessible population. It identifies and contrasts random sampling and non-random sampling. It then explains different types of random sampling techniques in detail, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, cluster random sampling, and two-stage random sampling. Examples are provided for each method to illustrate how to select random samples from populations. Common mistakes to avoid with cluster random sampling are also highlighted.