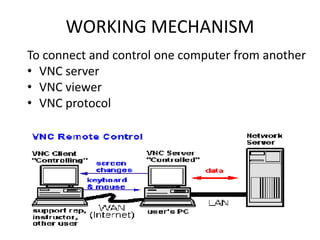
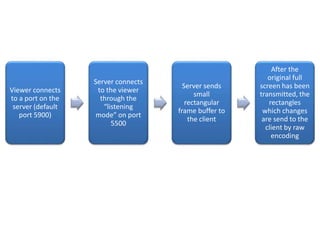
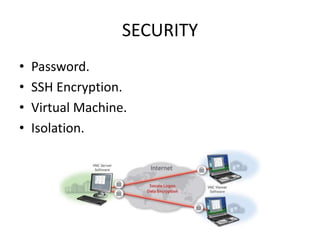
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) allows users to access and control a remote computer over a network. It works by having a VNC server on the remote computer and a VNC viewer on the local computer. The viewer connects to the server's port and the server sends rectangular frames of the desktop buffer to the viewer. VNC offers advantages like eliminating distance constraints and enabling remote troubleshooting, but has disadvantages like using bandwidth and only allowing one-way communication on cellular networks. It provides graphical desktop sharing across platforms with AES encryption and is widely used with servers like RealVNC, TightVNC, and UltraVNC.