Embed presentation
Downloaded 33 times

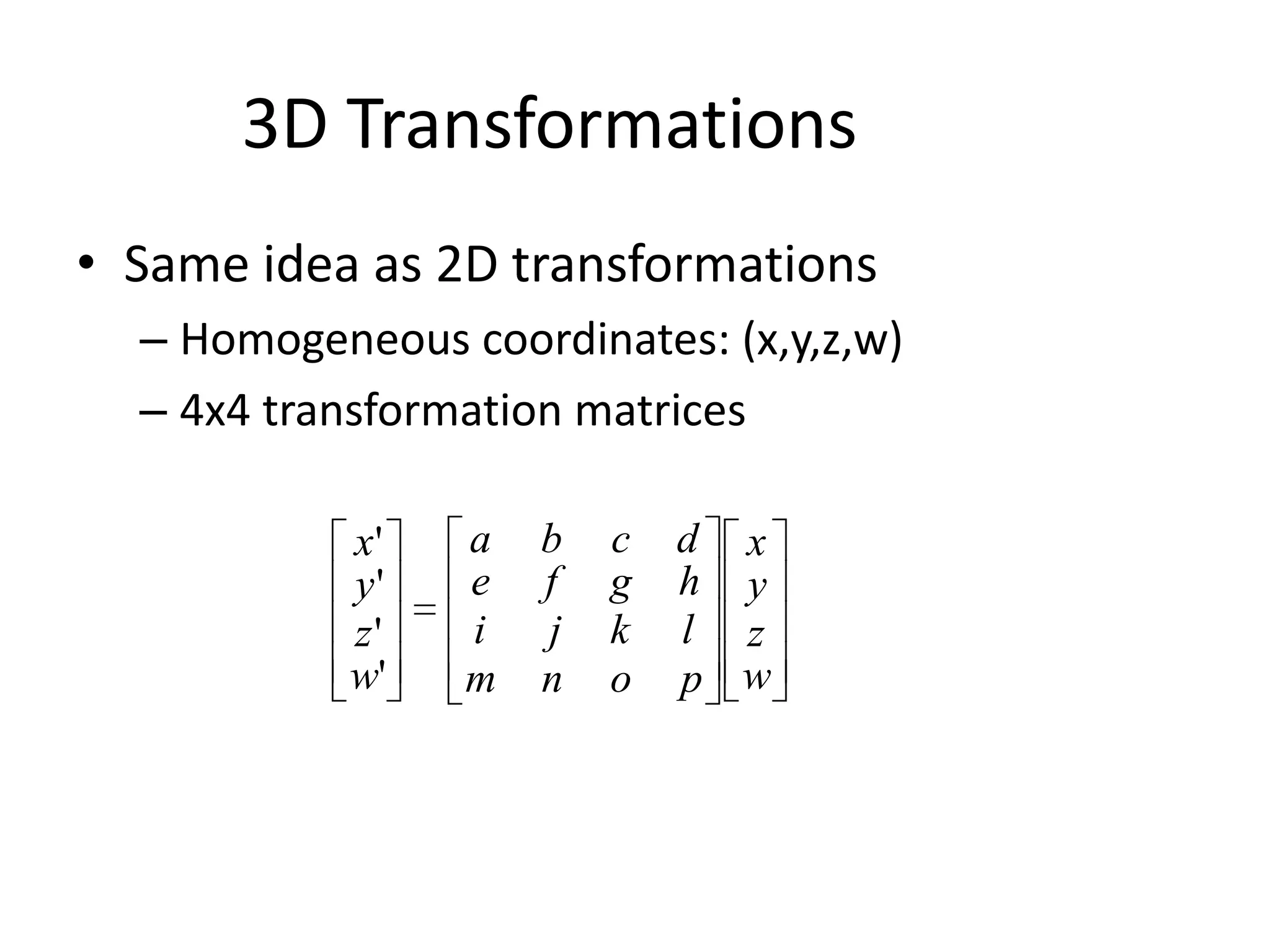
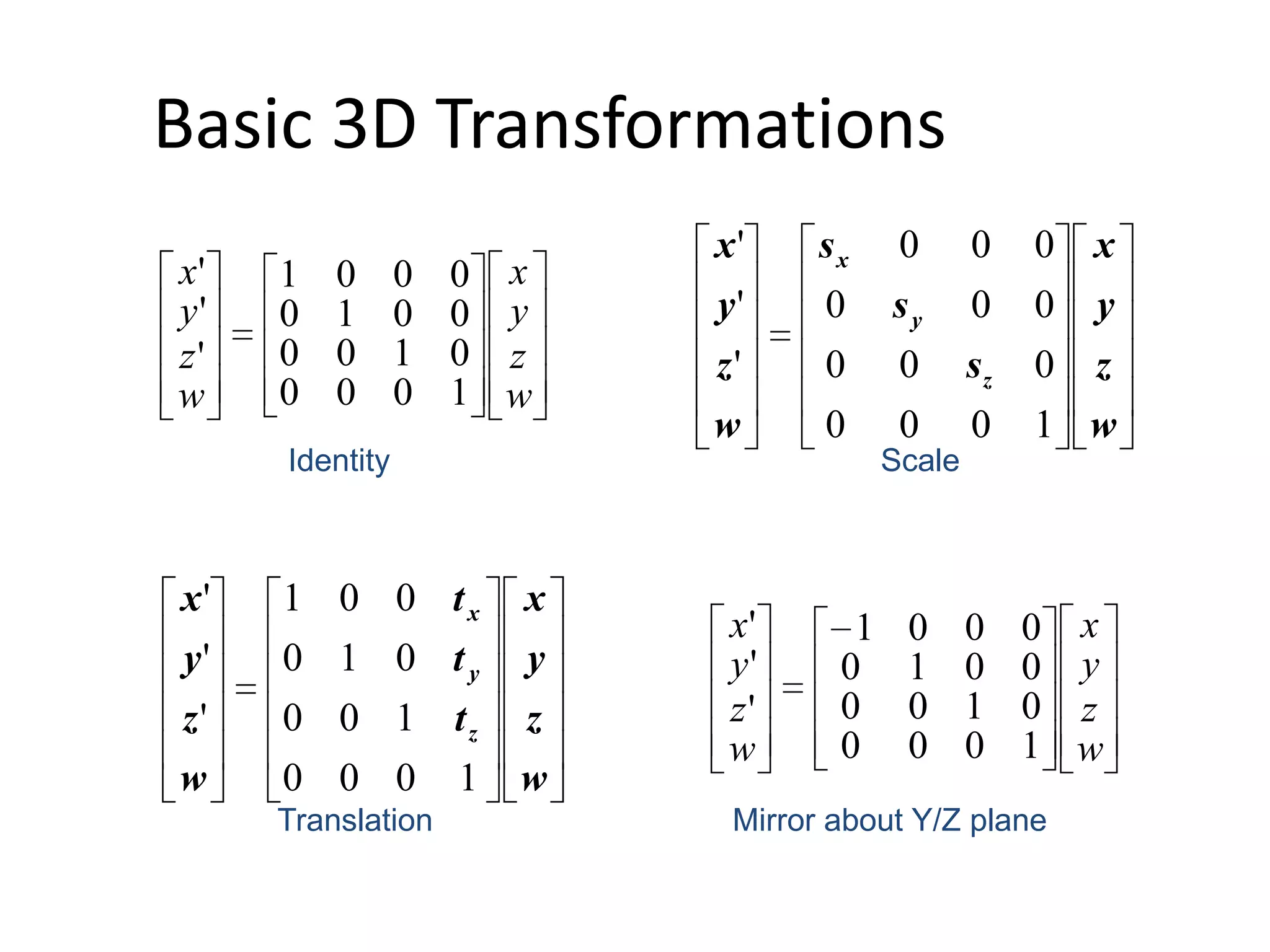
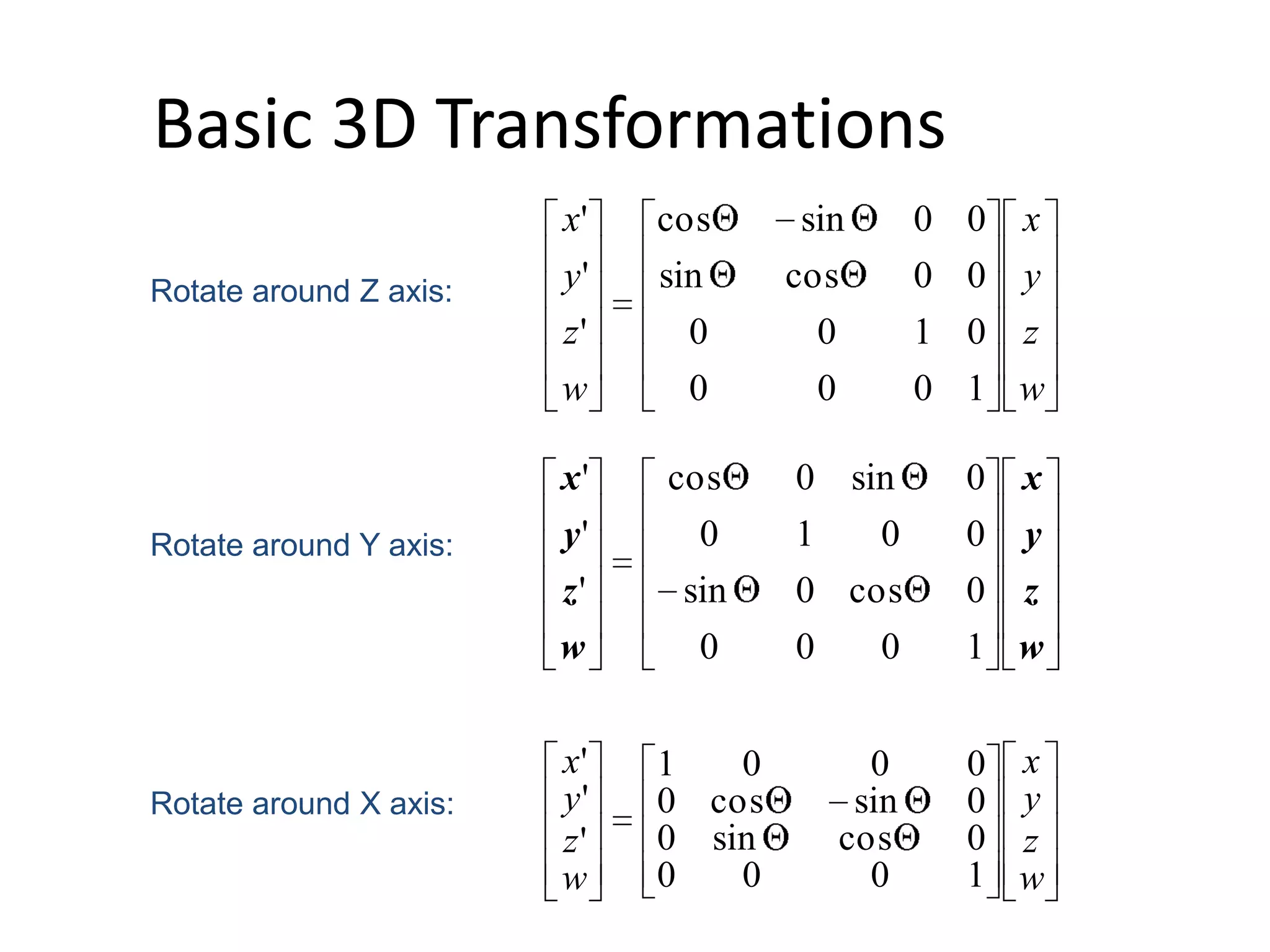
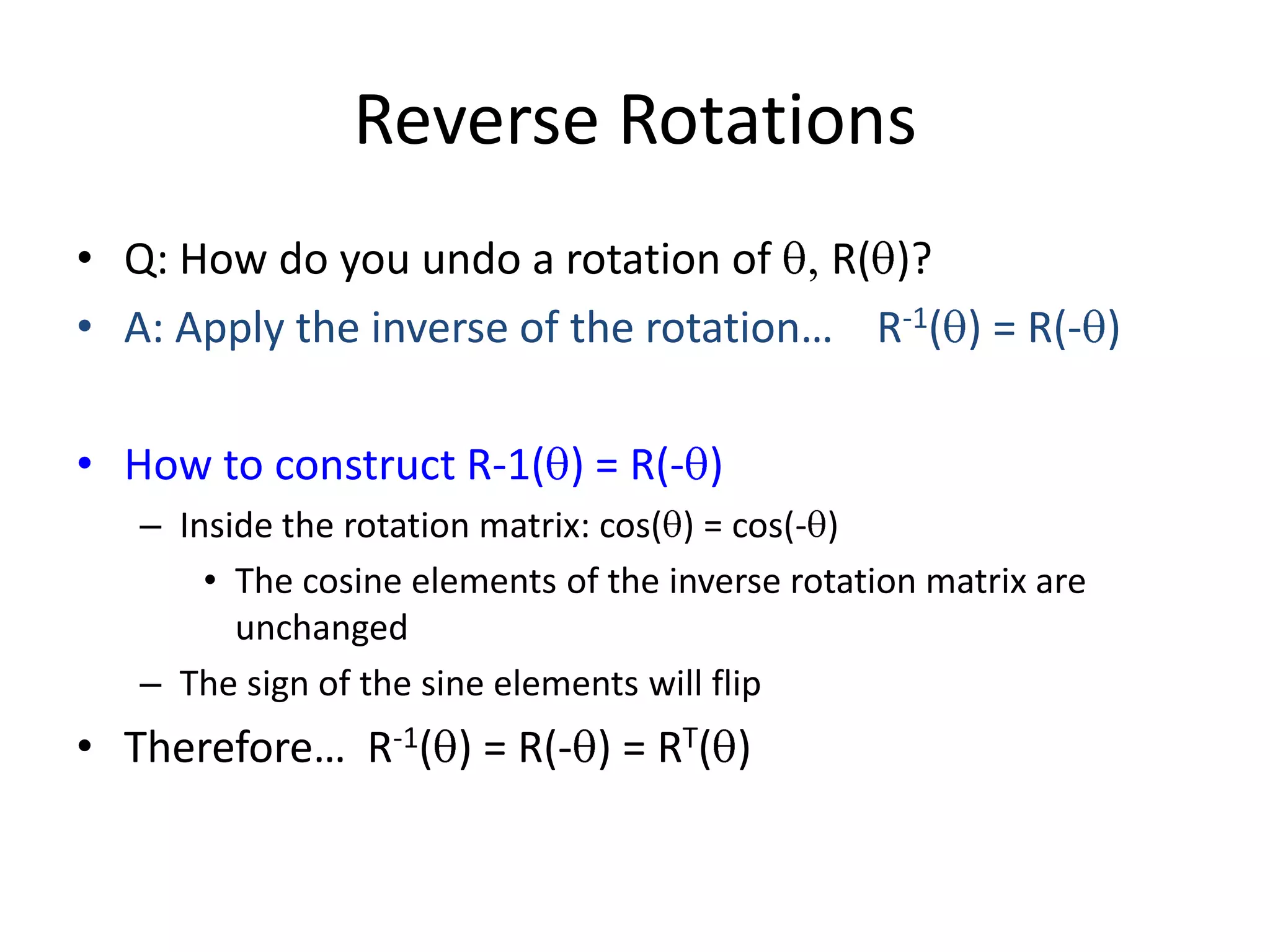

3D transformations use homogeneous coordinates and 4x4 matrices similarly to 2D transformations. There are basic transformations like identity, scale, translation, and mirroring as well as rotations around the X, Y, and Z axes represented by matrices. To reverse a rotation of q degrees, apply the inverse rotation R(-q) which has the same cosine elements but flipped sine elements, making it the transpose of the original rotation matrix.




