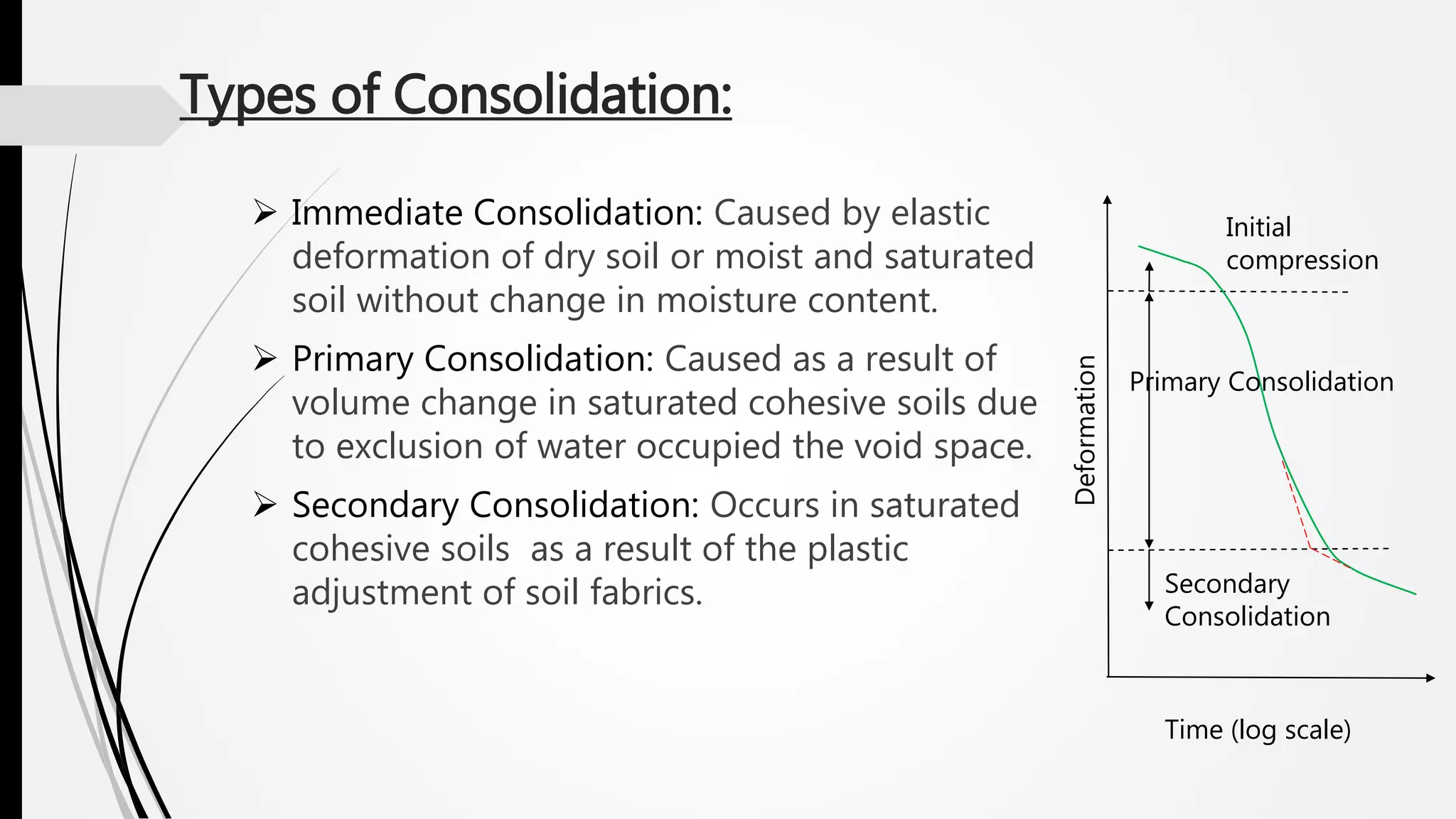
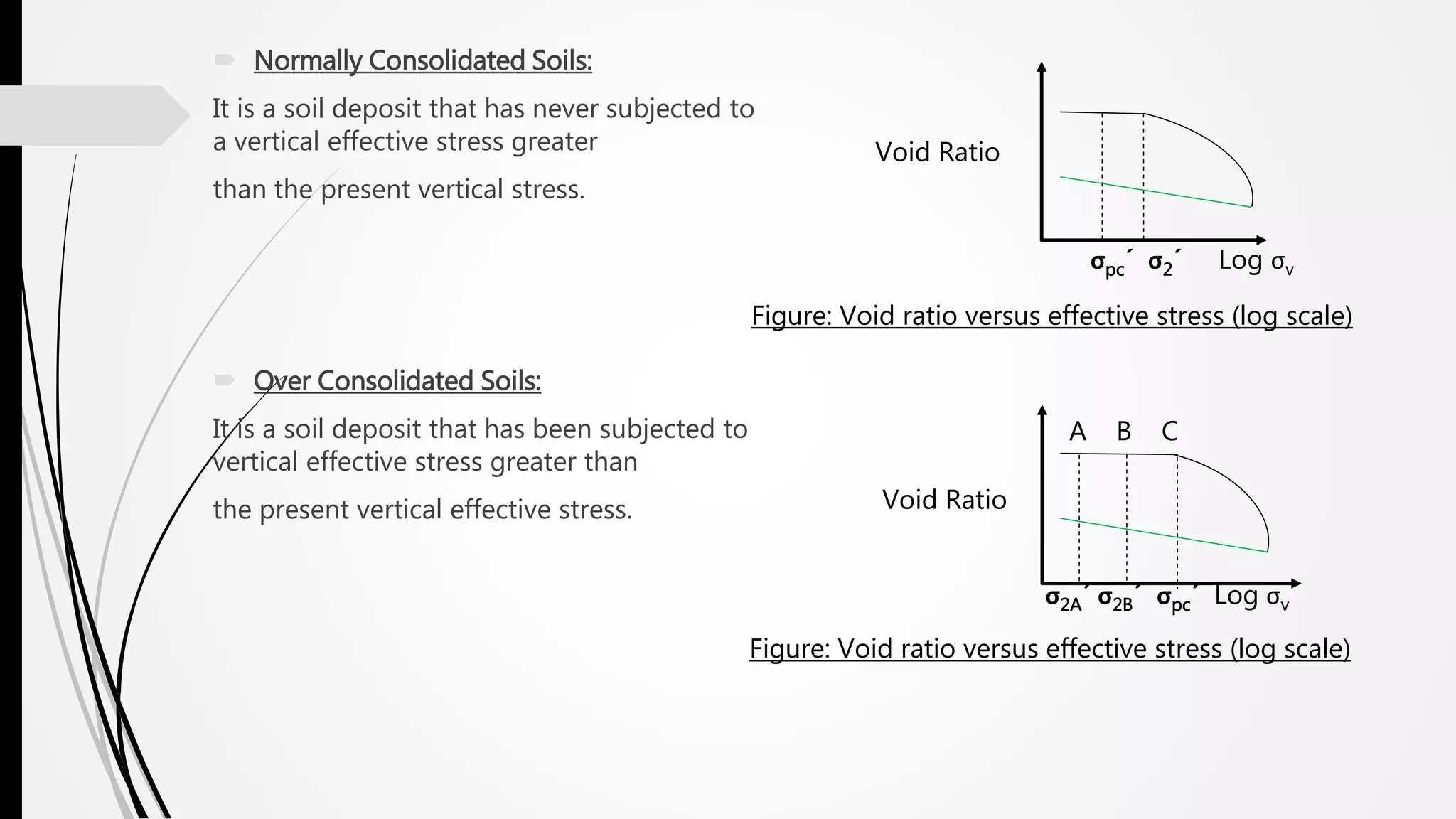
Consolidation is the process where water drains from saturated soil pores, transferring the load from water to soil particles and causing volume change. There are three types of consolidation: immediate, primary, and secondary. One-dimensional consolidation assumes vertical drainage, making the process primarily vertical. Terzaghi's theory of one-dimensional consolidation models this using parameters like permeability, compressibility, and effective stress. The coefficient of consolidation describes the rate of compression, while compression and swelling indices characterize the void ratio-effective stress relationship. The oedometer test experimentally determines consolidation properties from soil specimen compression under incremental loads.