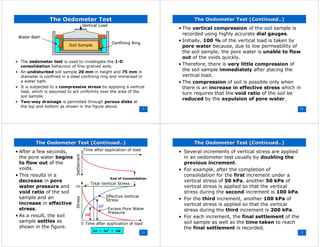
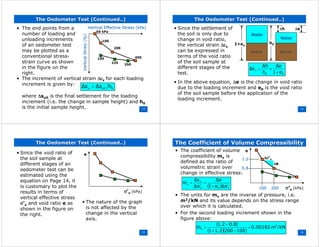
This document provides an overview of one-dimensional consolidation and oedometer tests. It discusses how consolidation leads to a reduction in soil volume through drainage of water from voids over time. An oedometer test subjects an undisturbed soil sample to incremental loads in a confined apparatus to measure consolidation settlement and determine coefficients of compressibility. Graphs of void ratio versus effective stress and their slopes yield information on soil compression and expansion behavior and overconsolidation ratio.