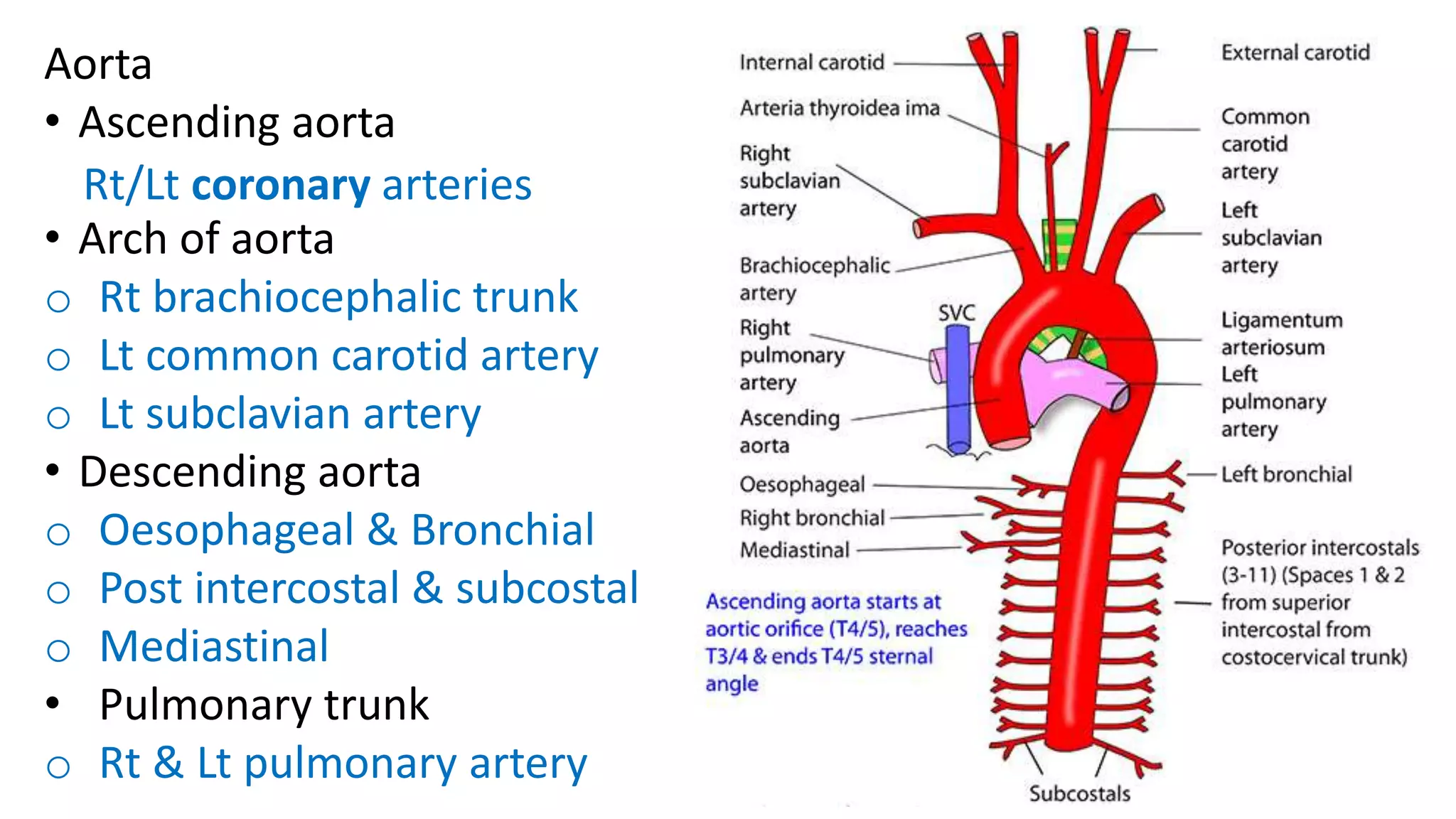
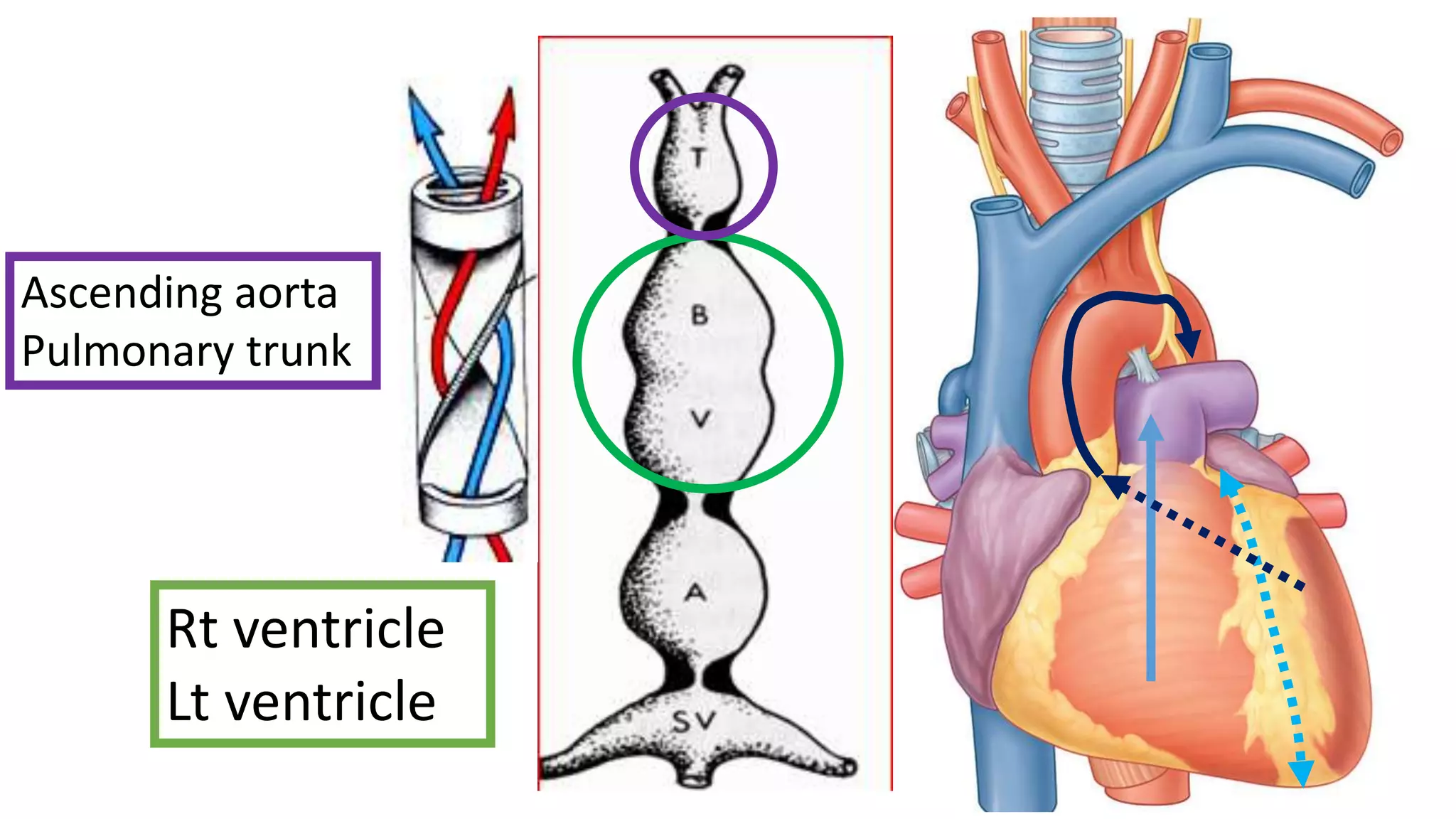
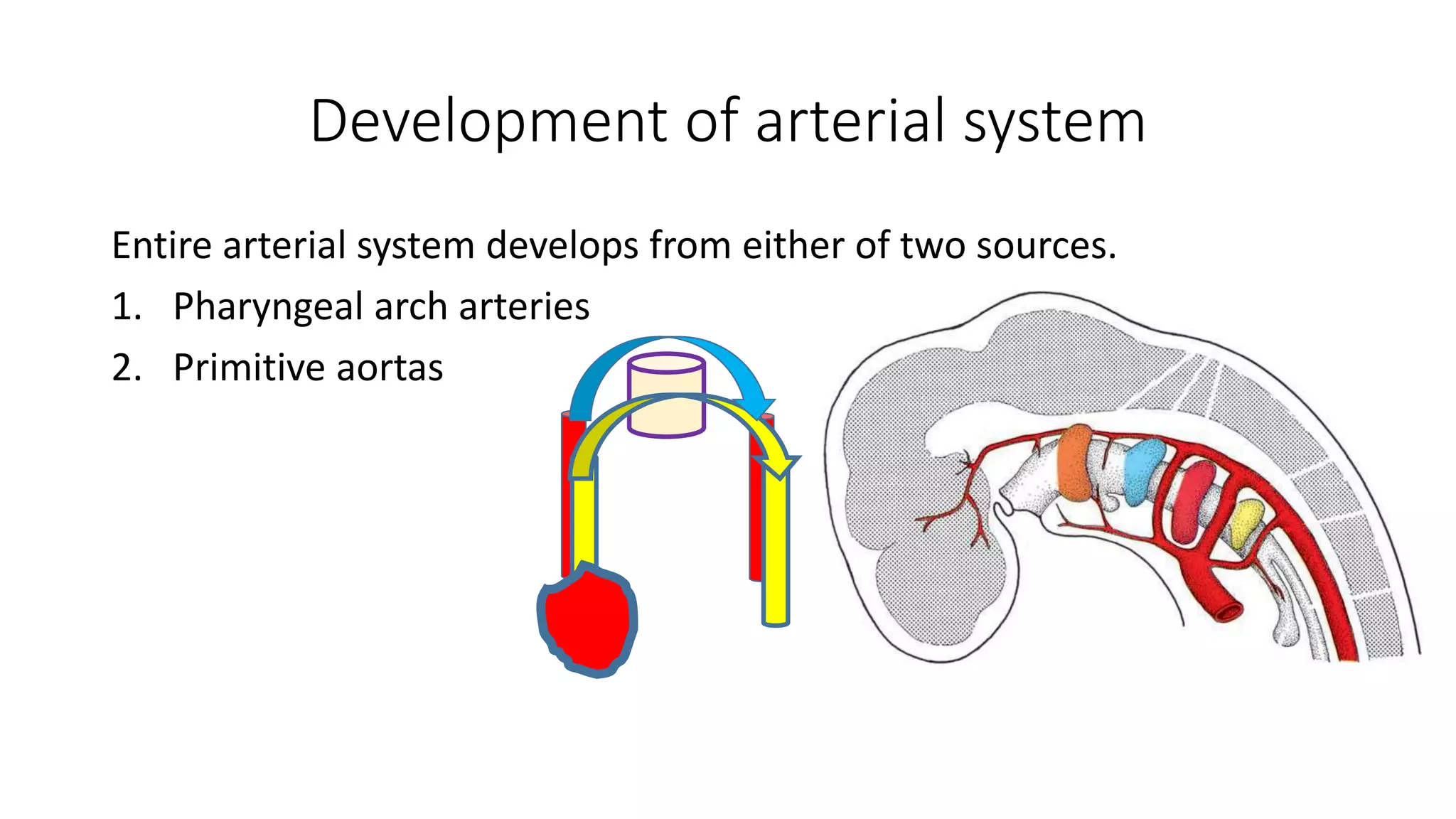
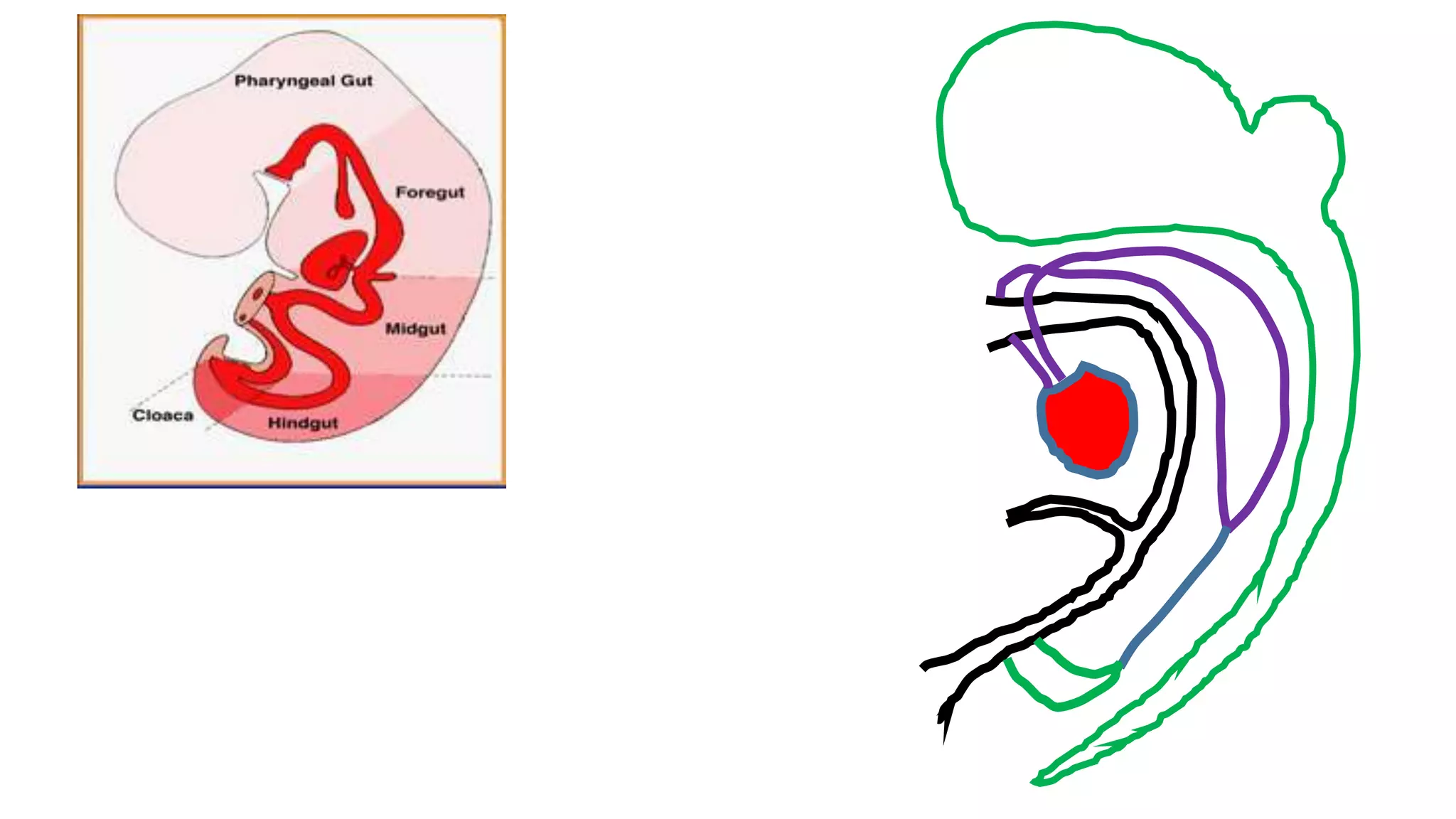
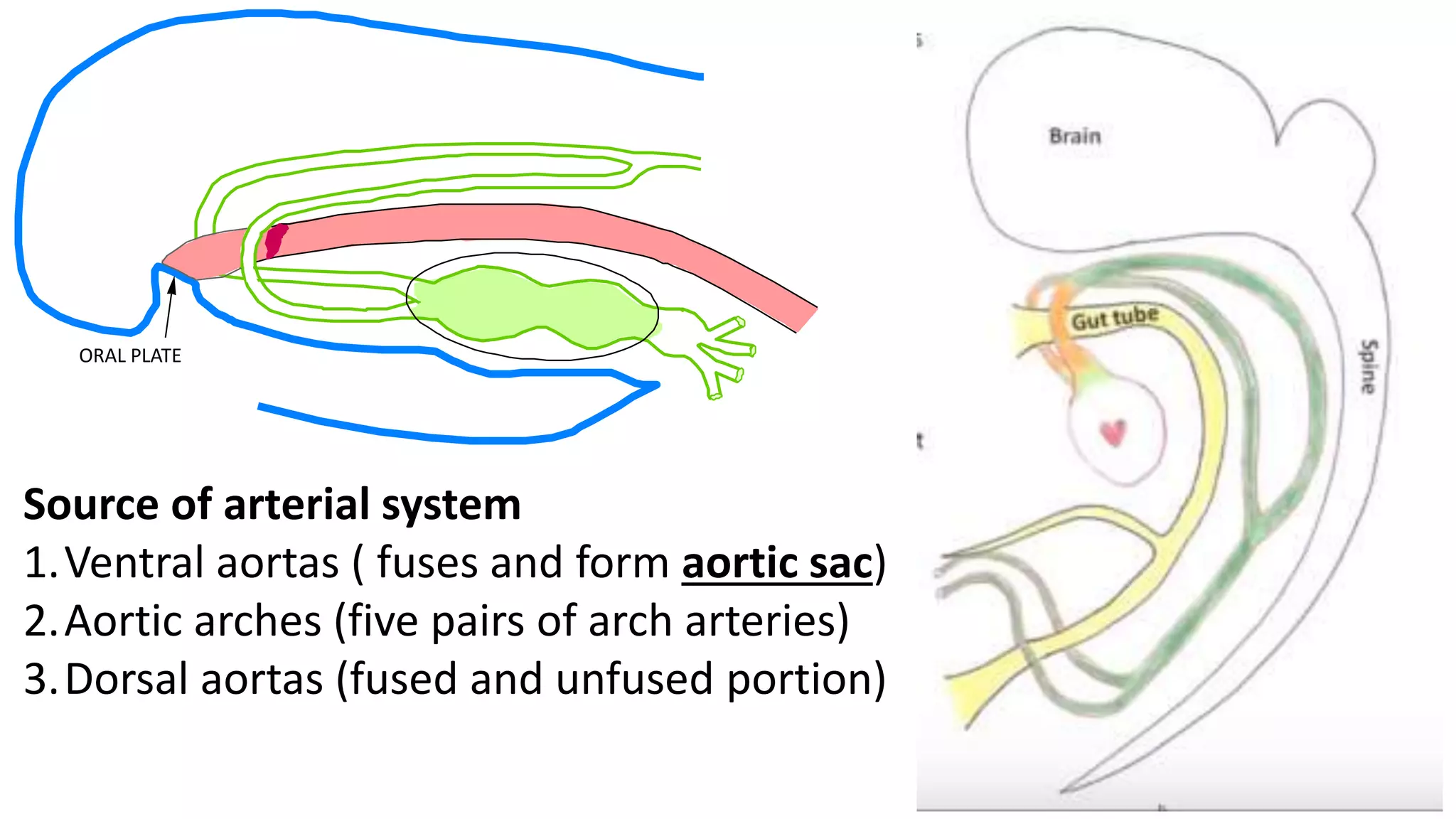
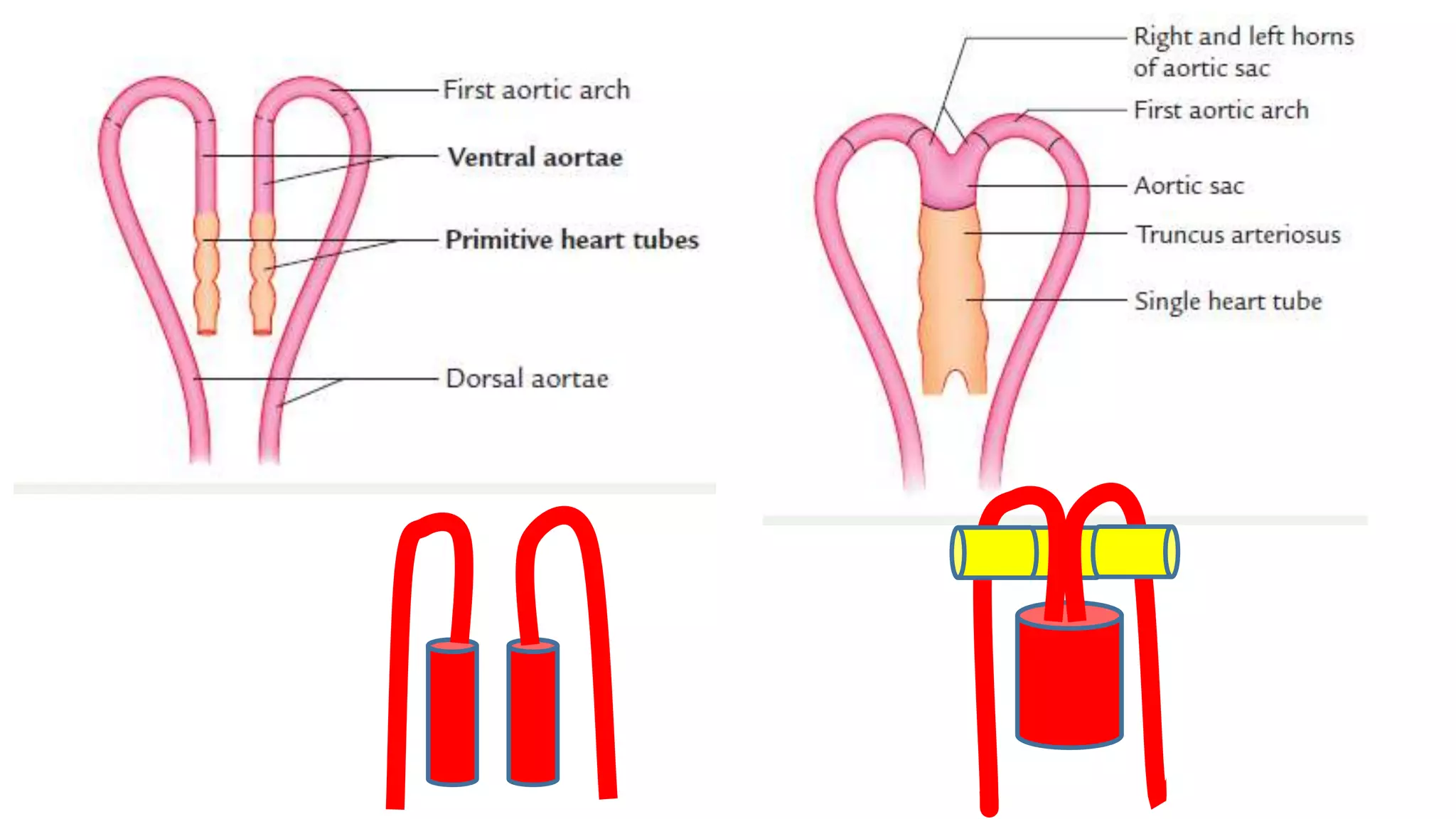
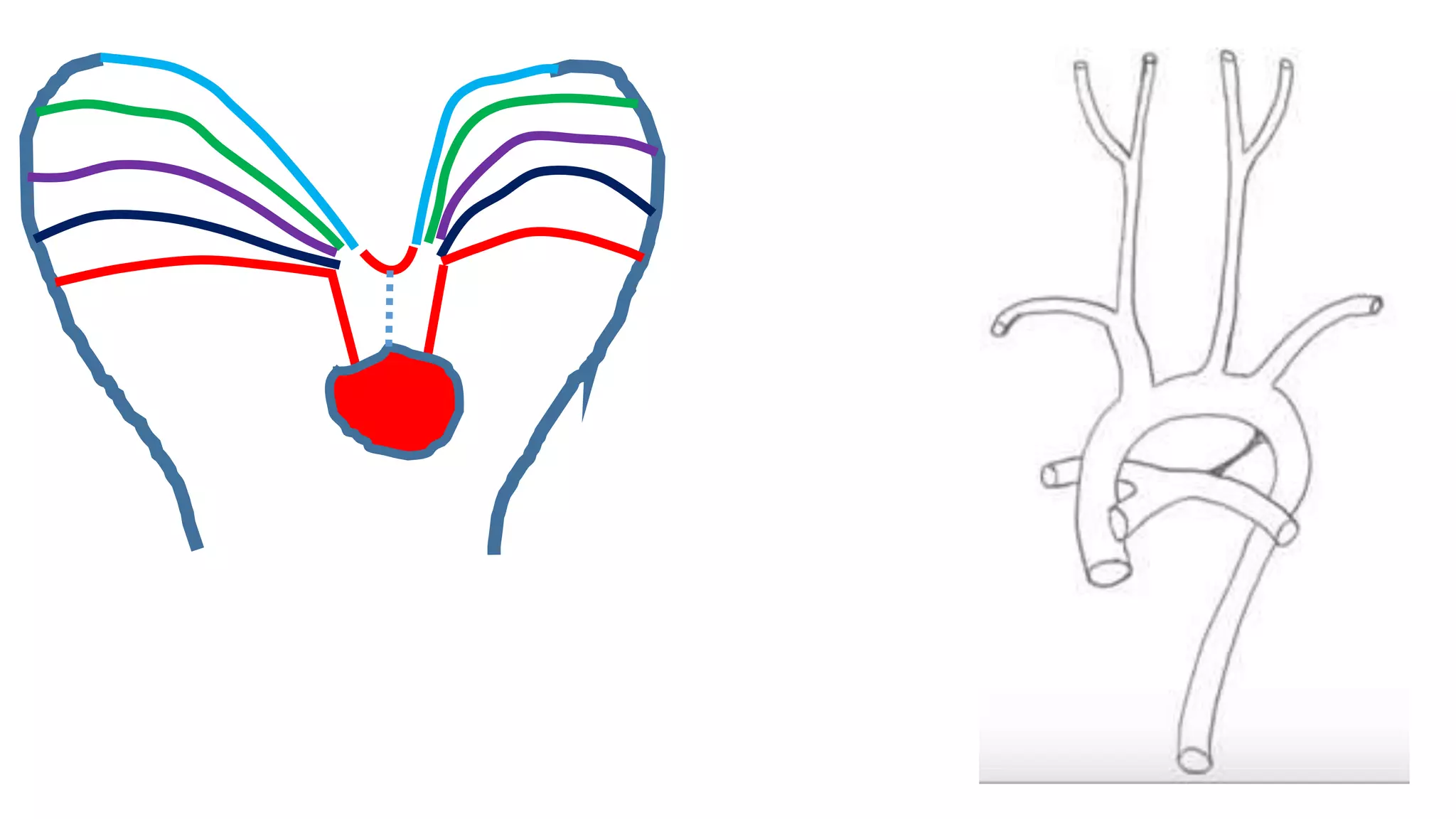
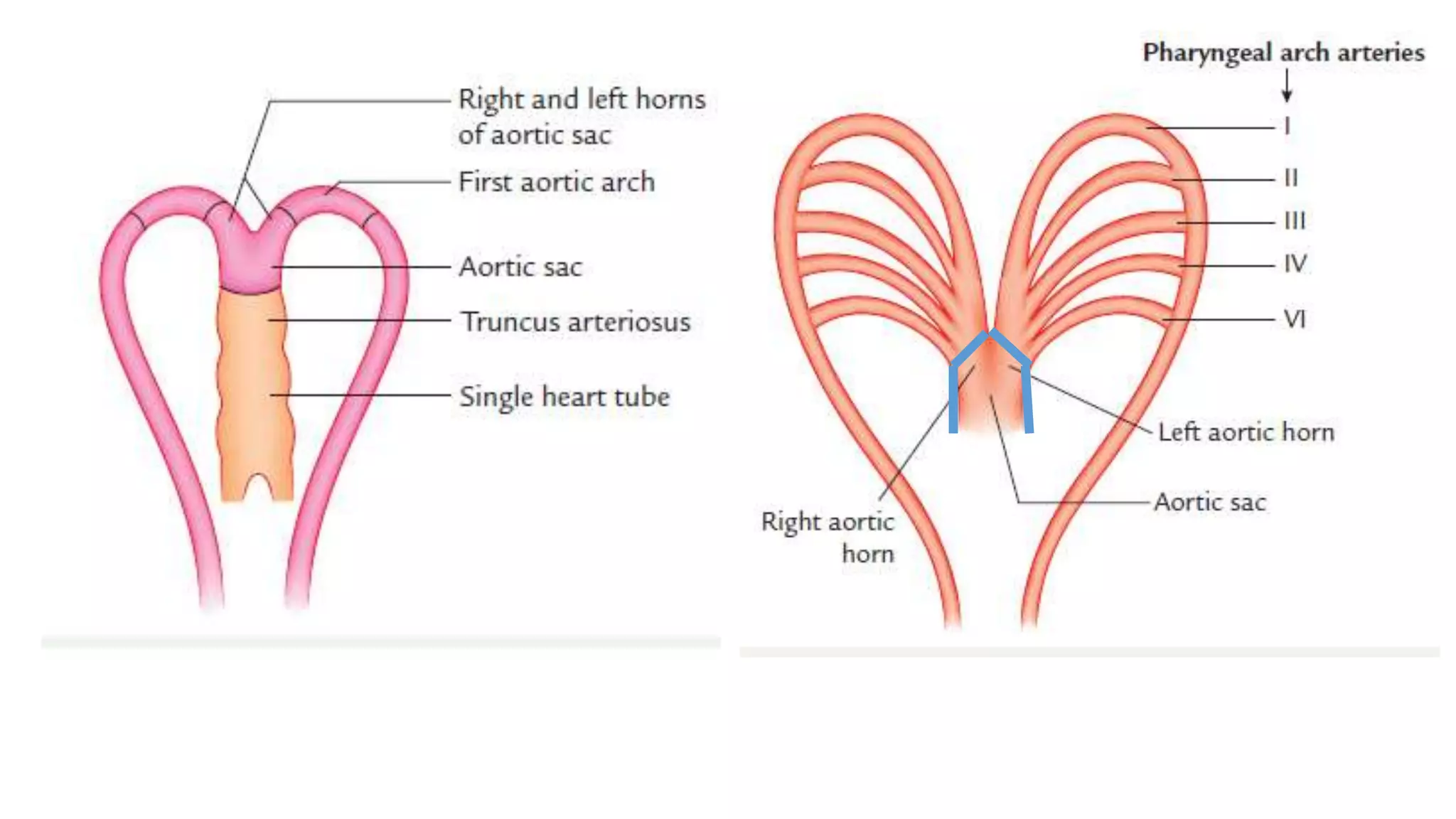
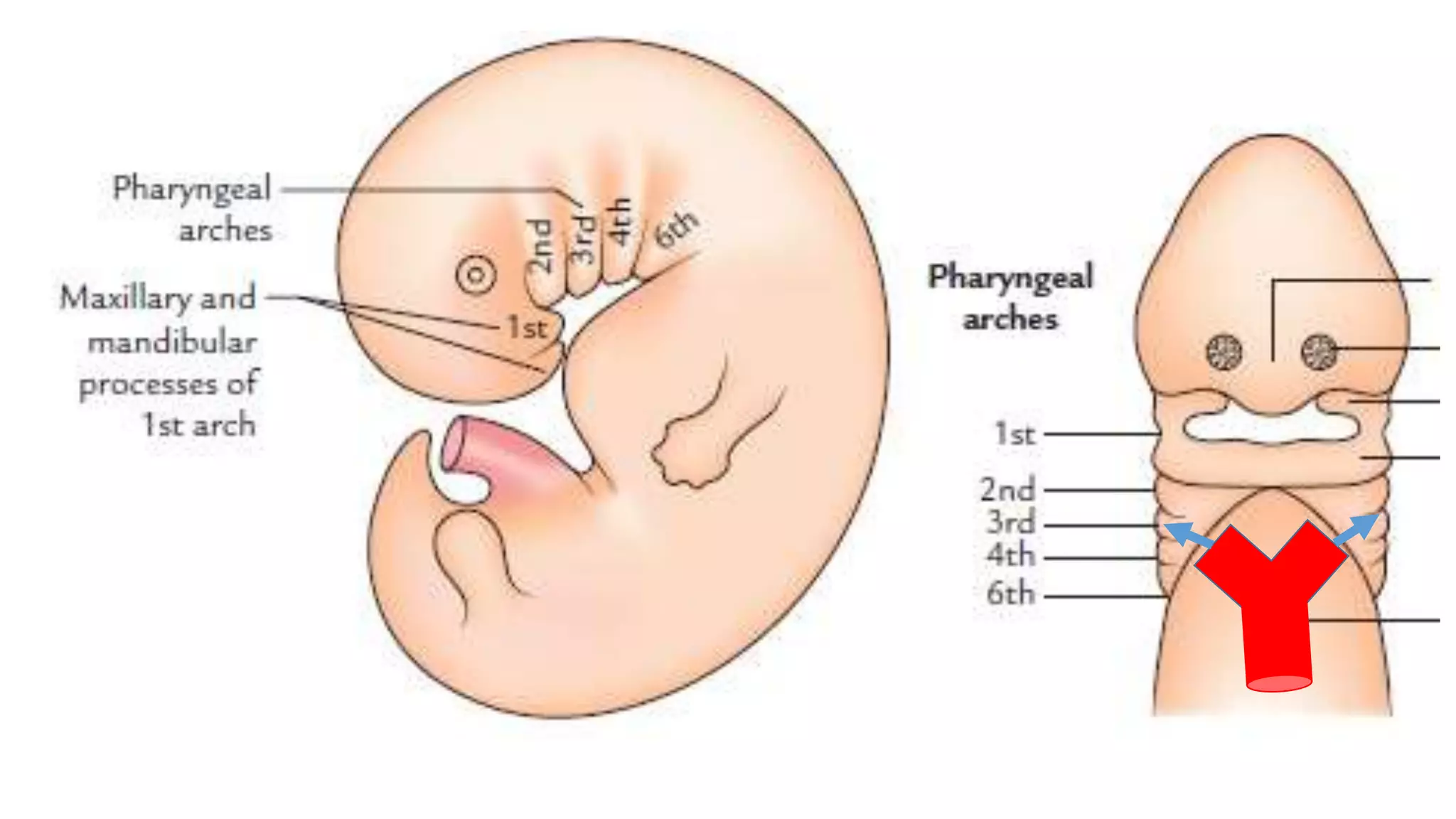
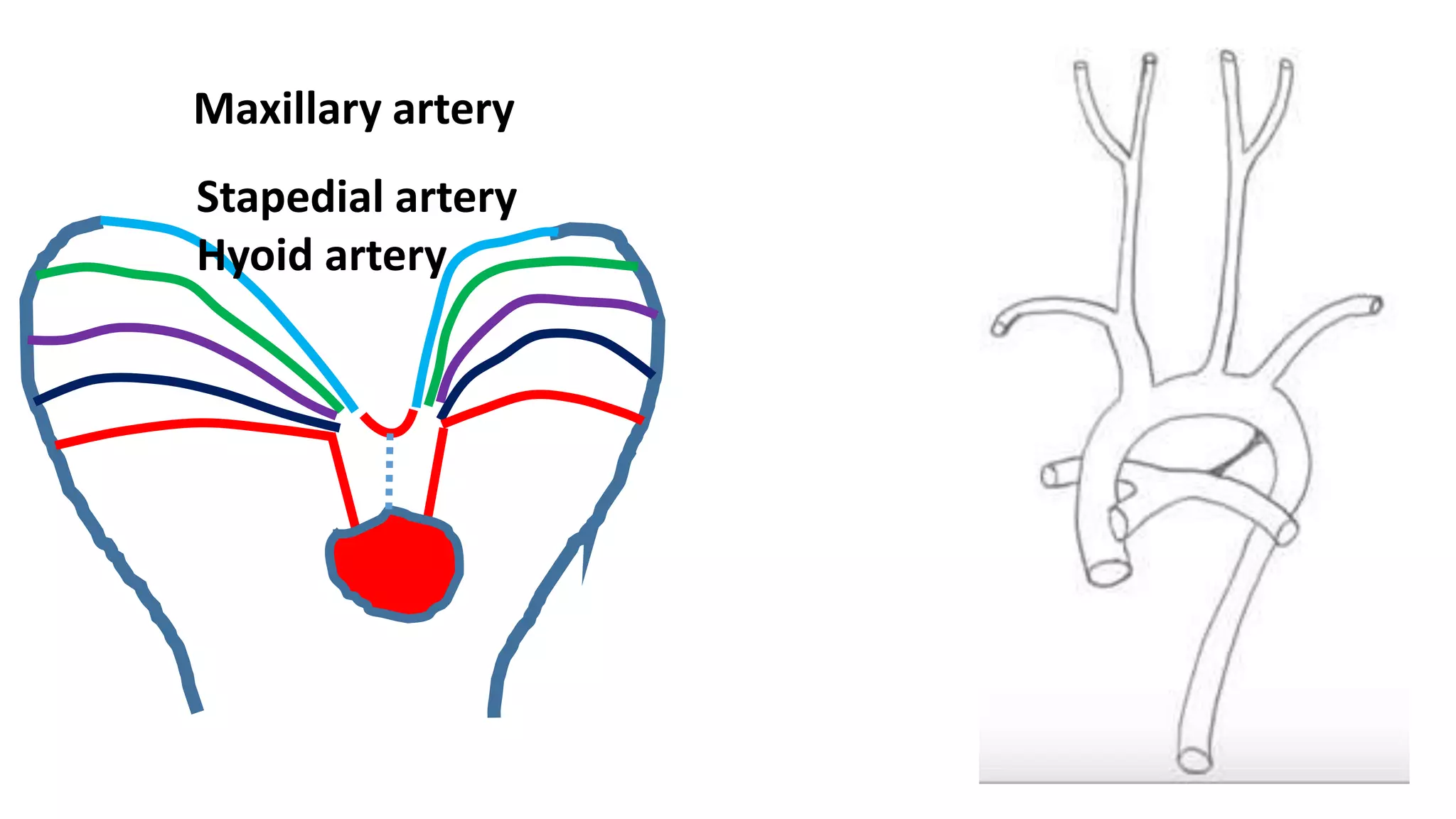
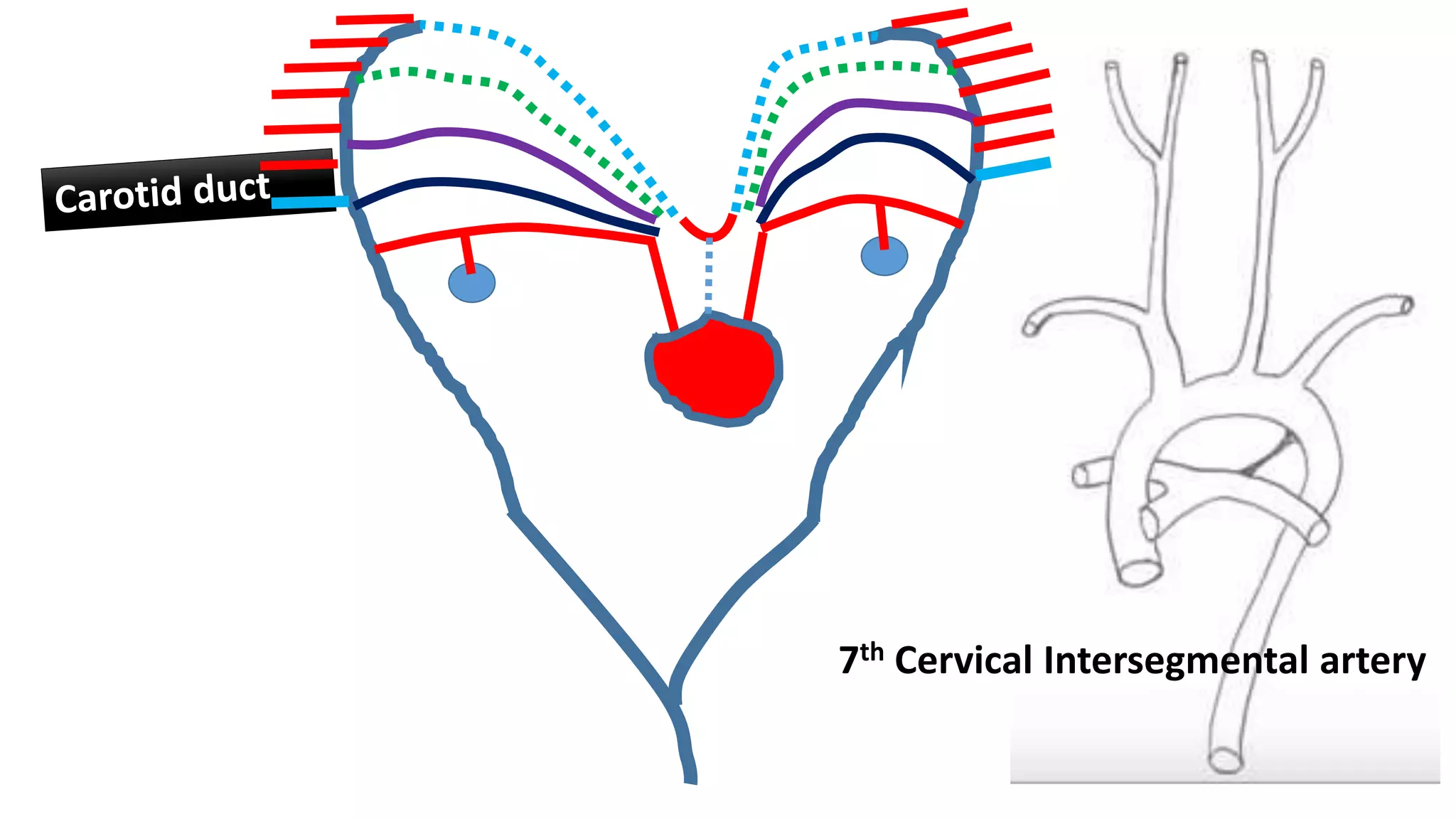
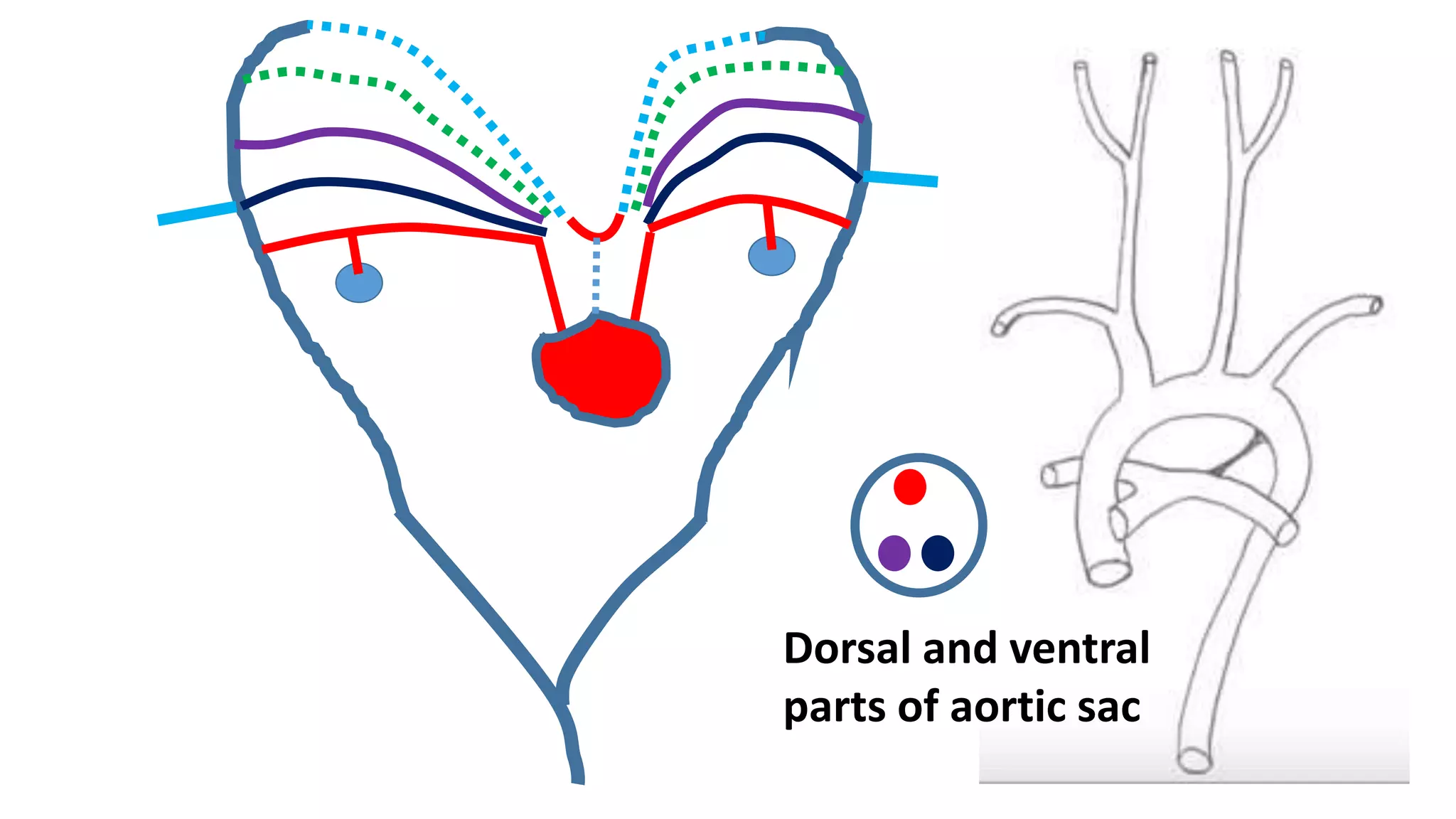
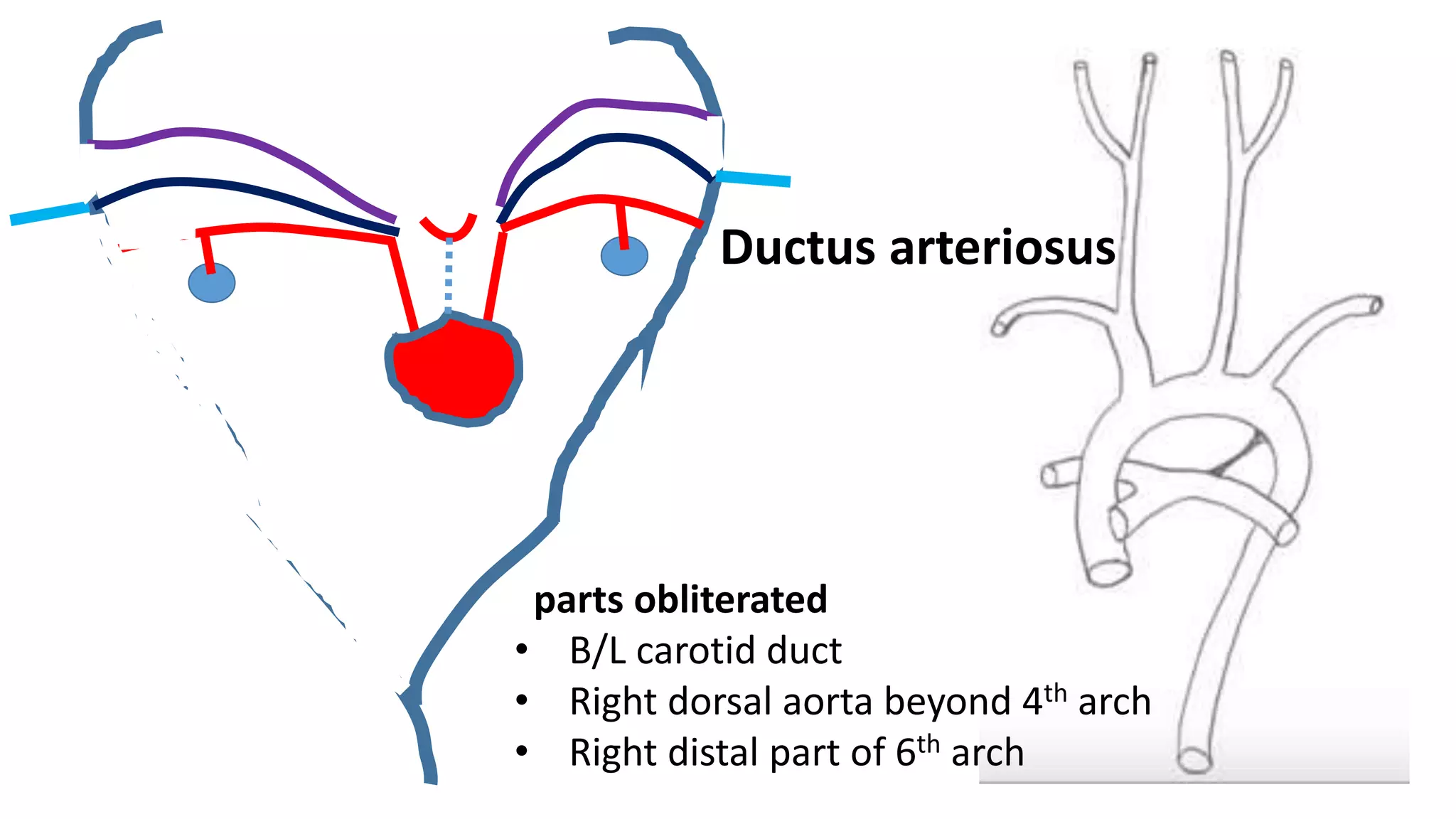
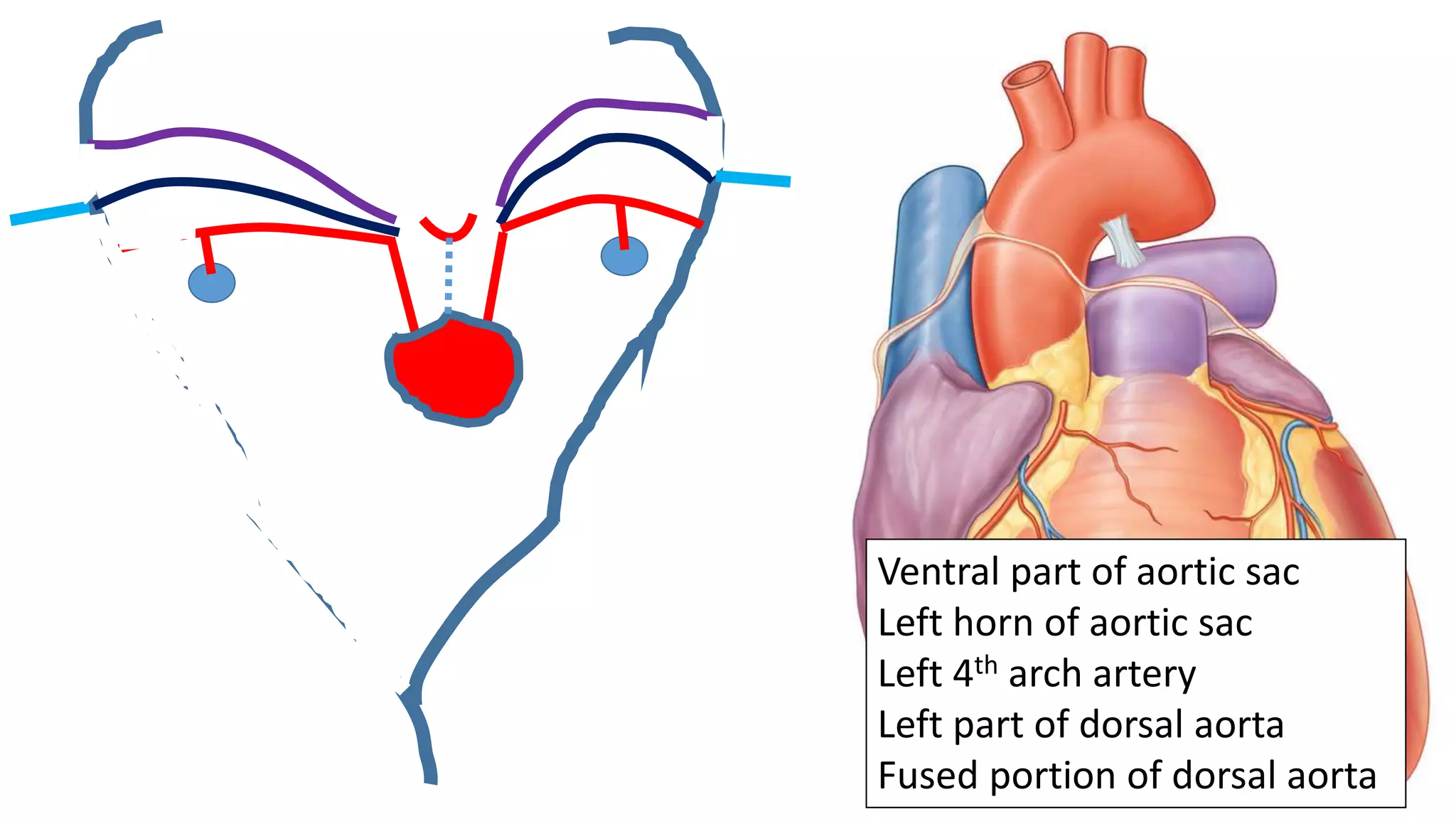
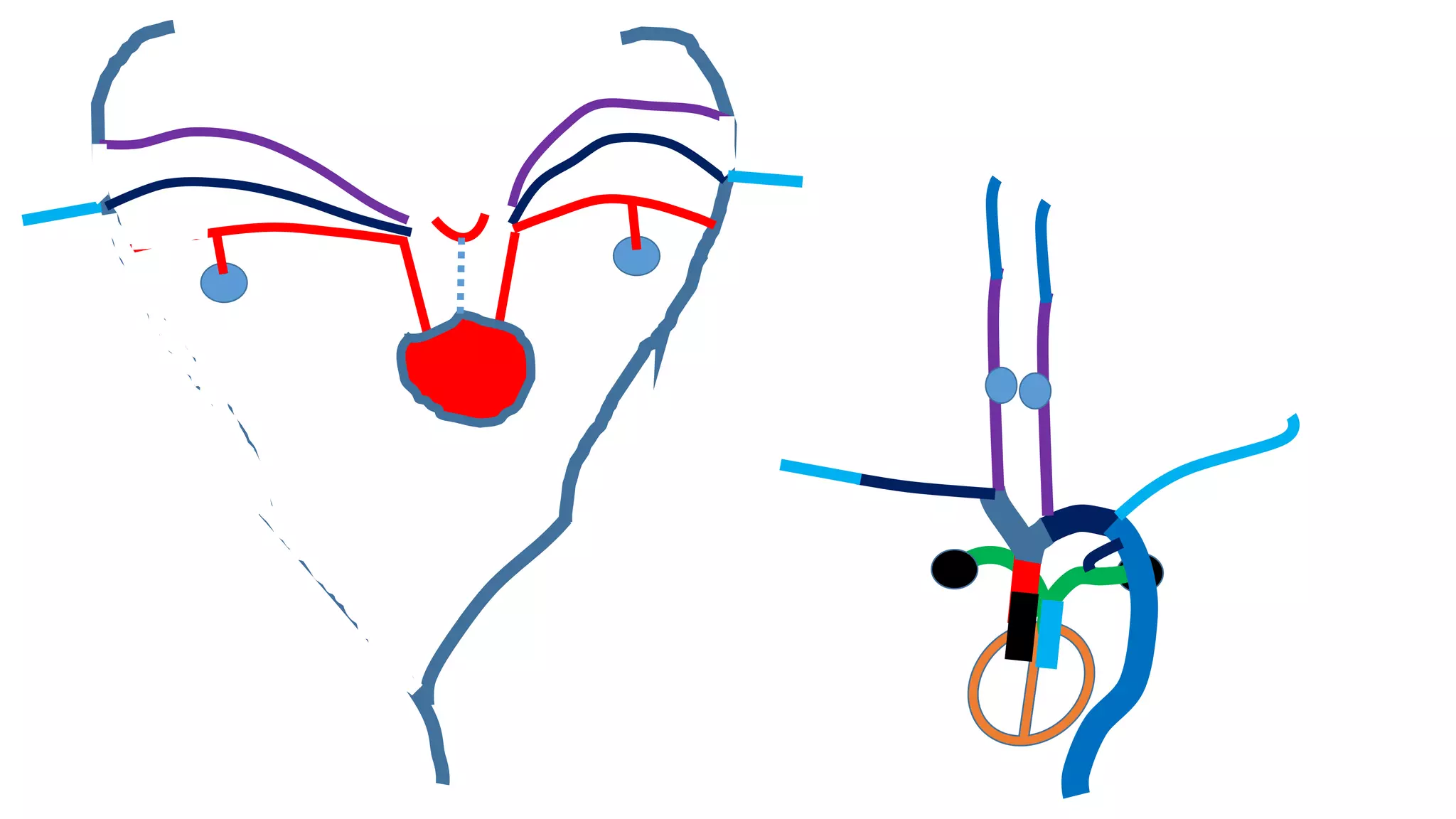
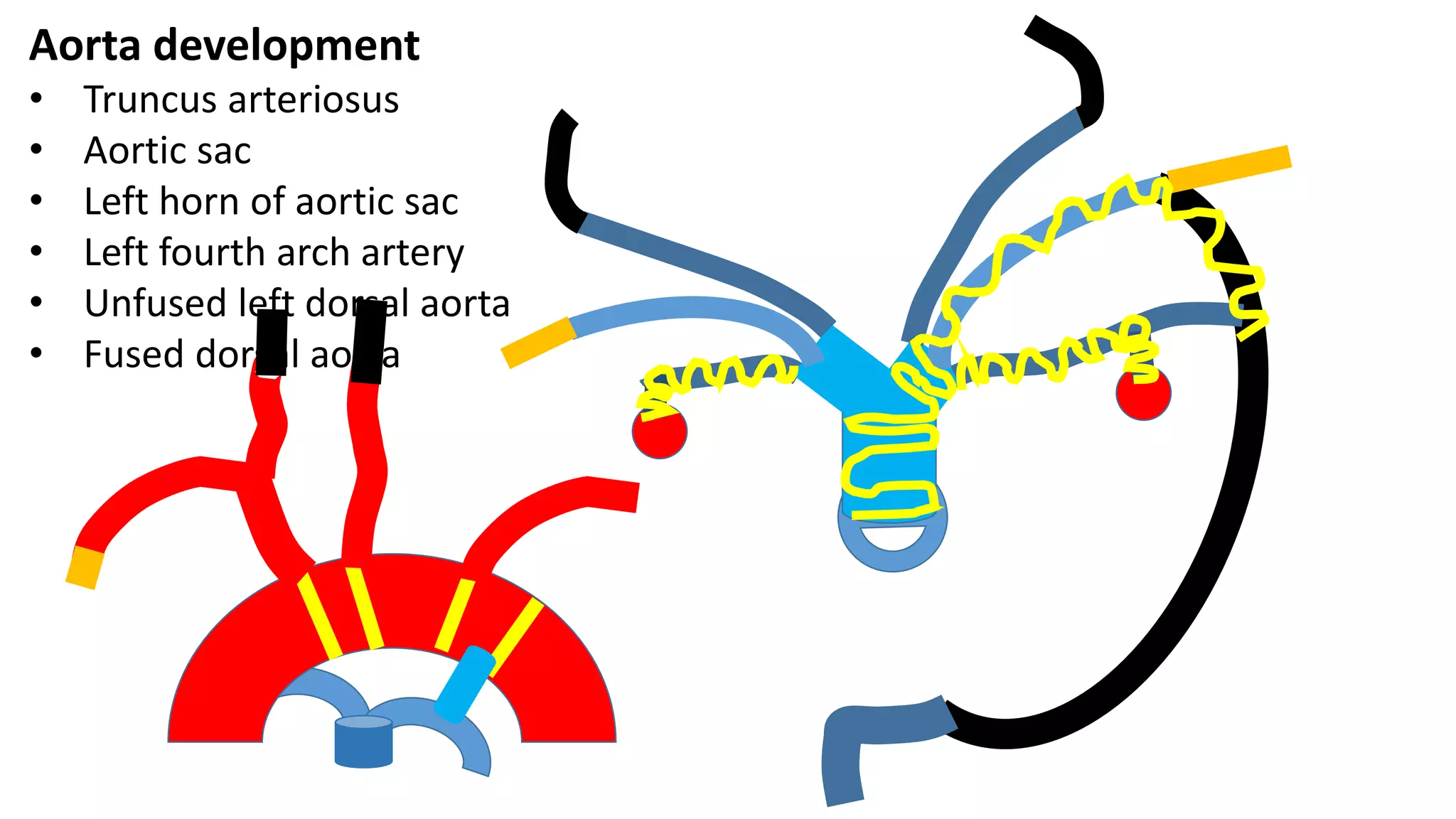
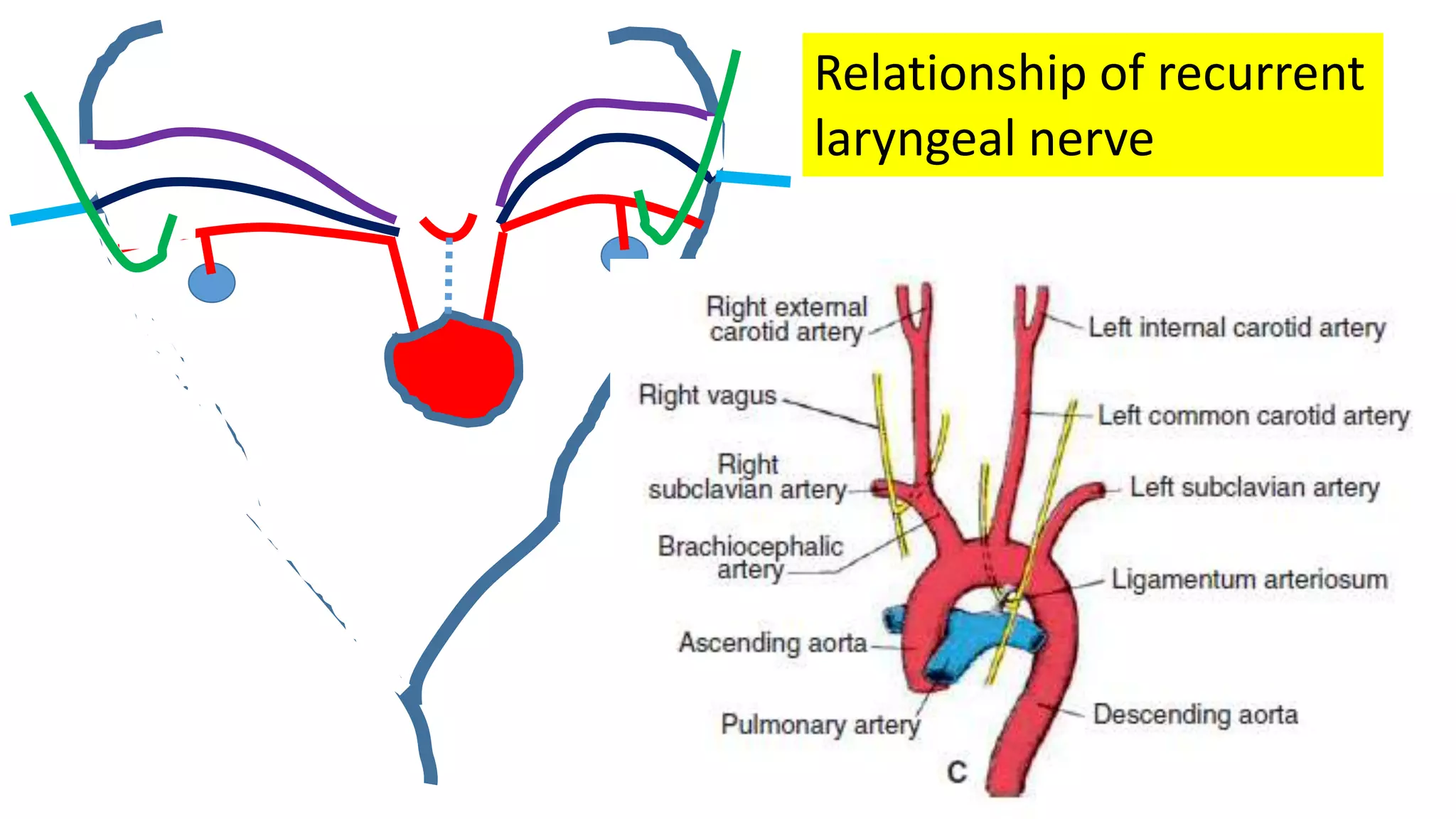
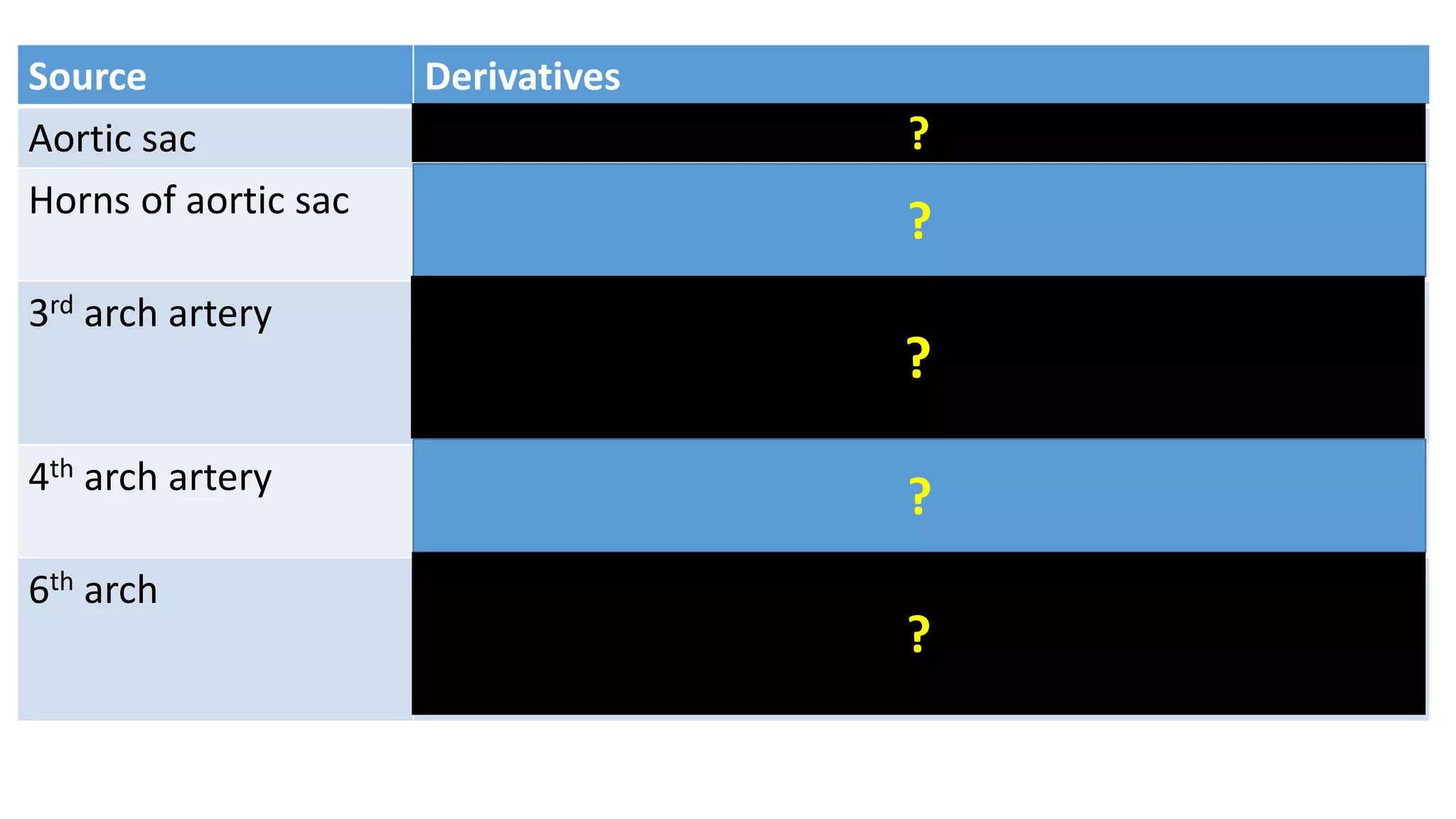
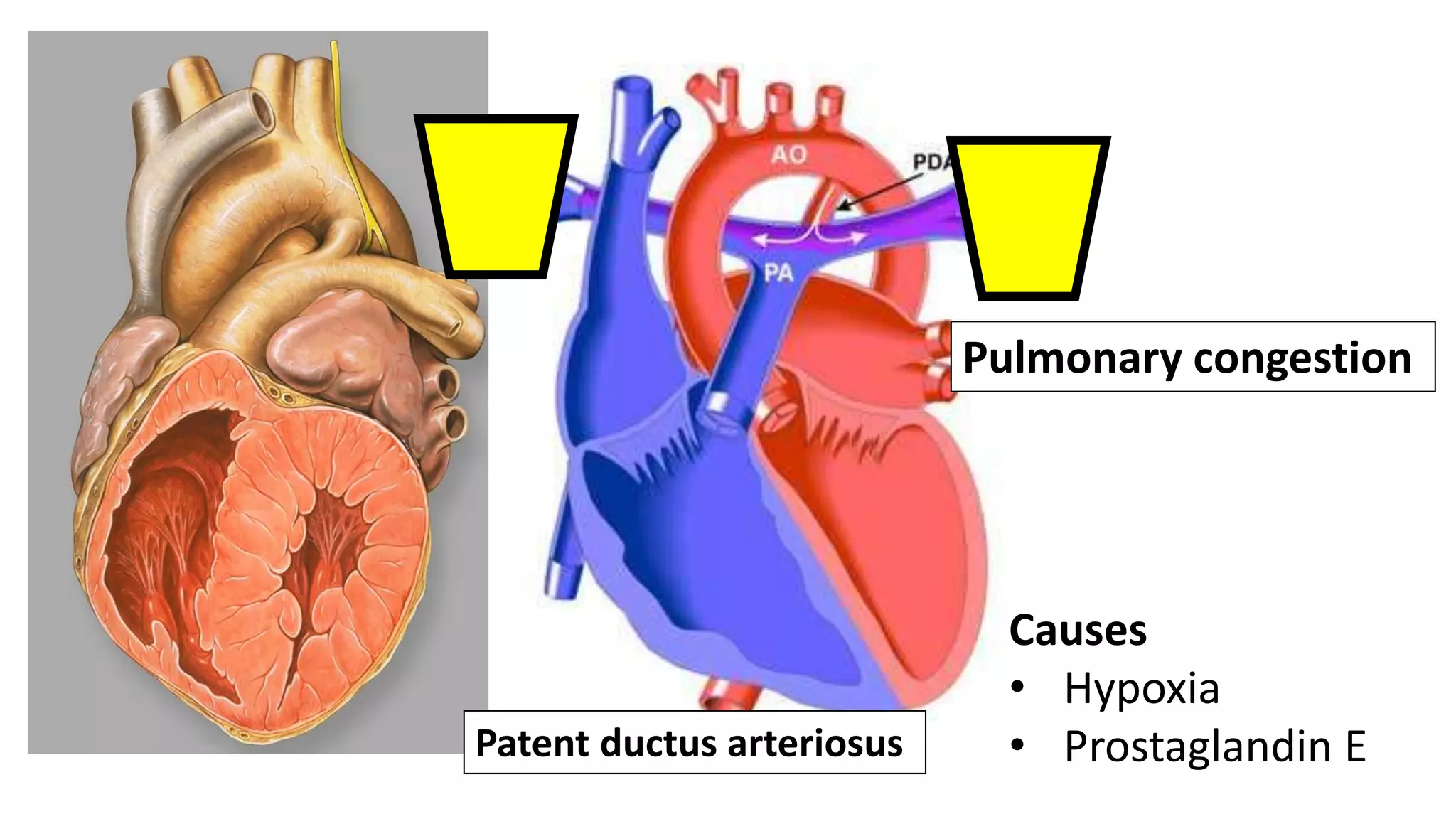
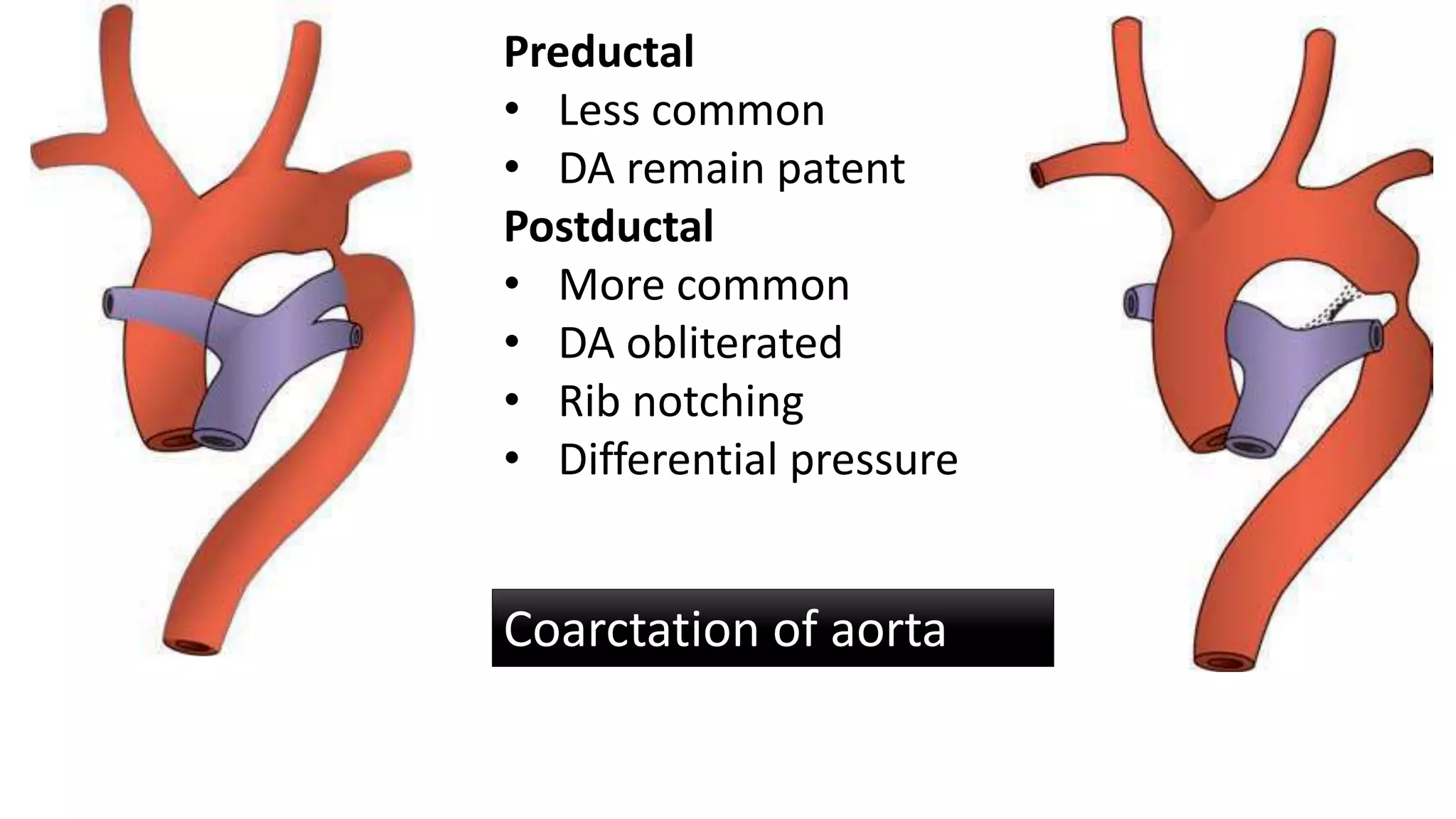
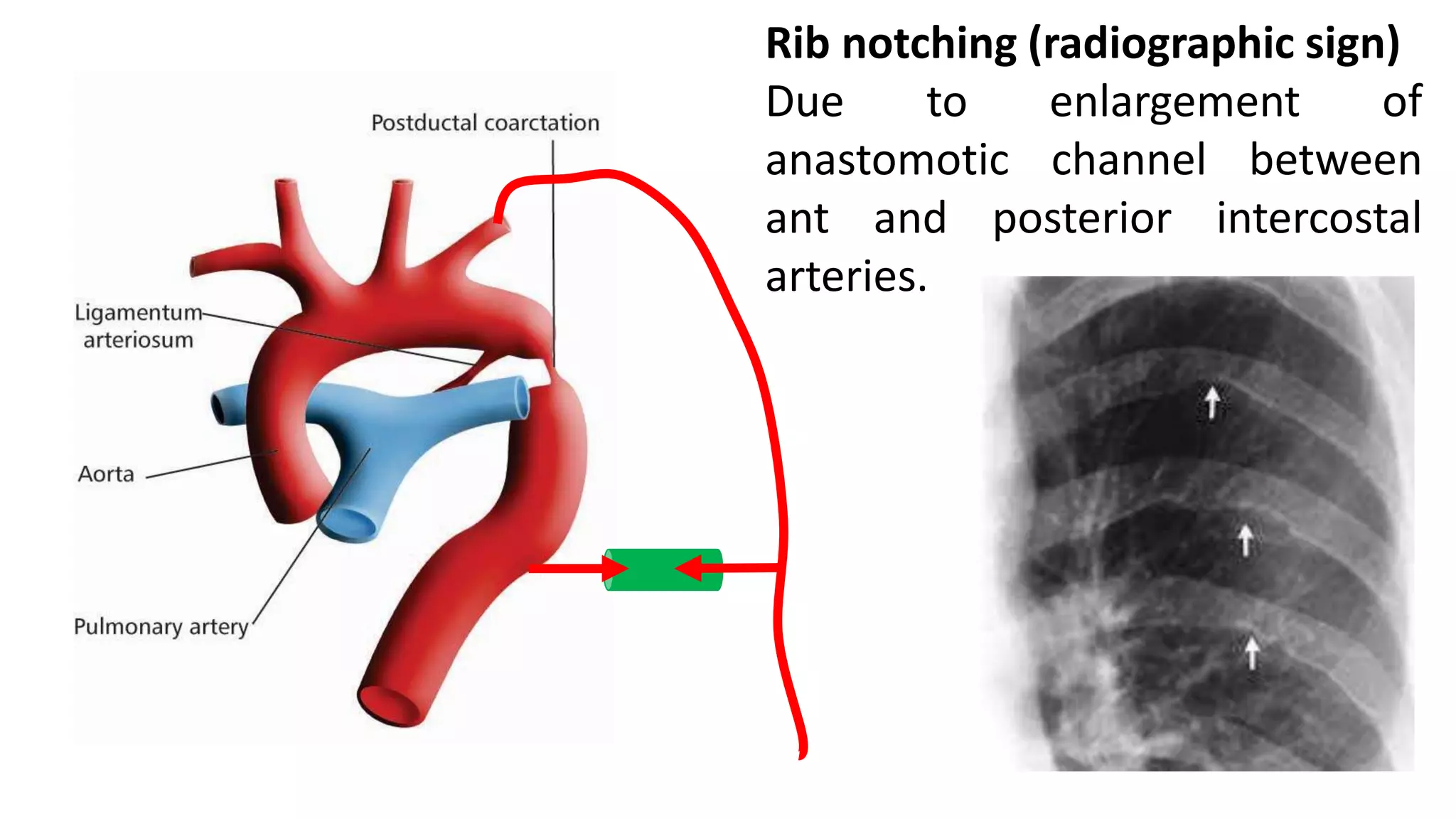
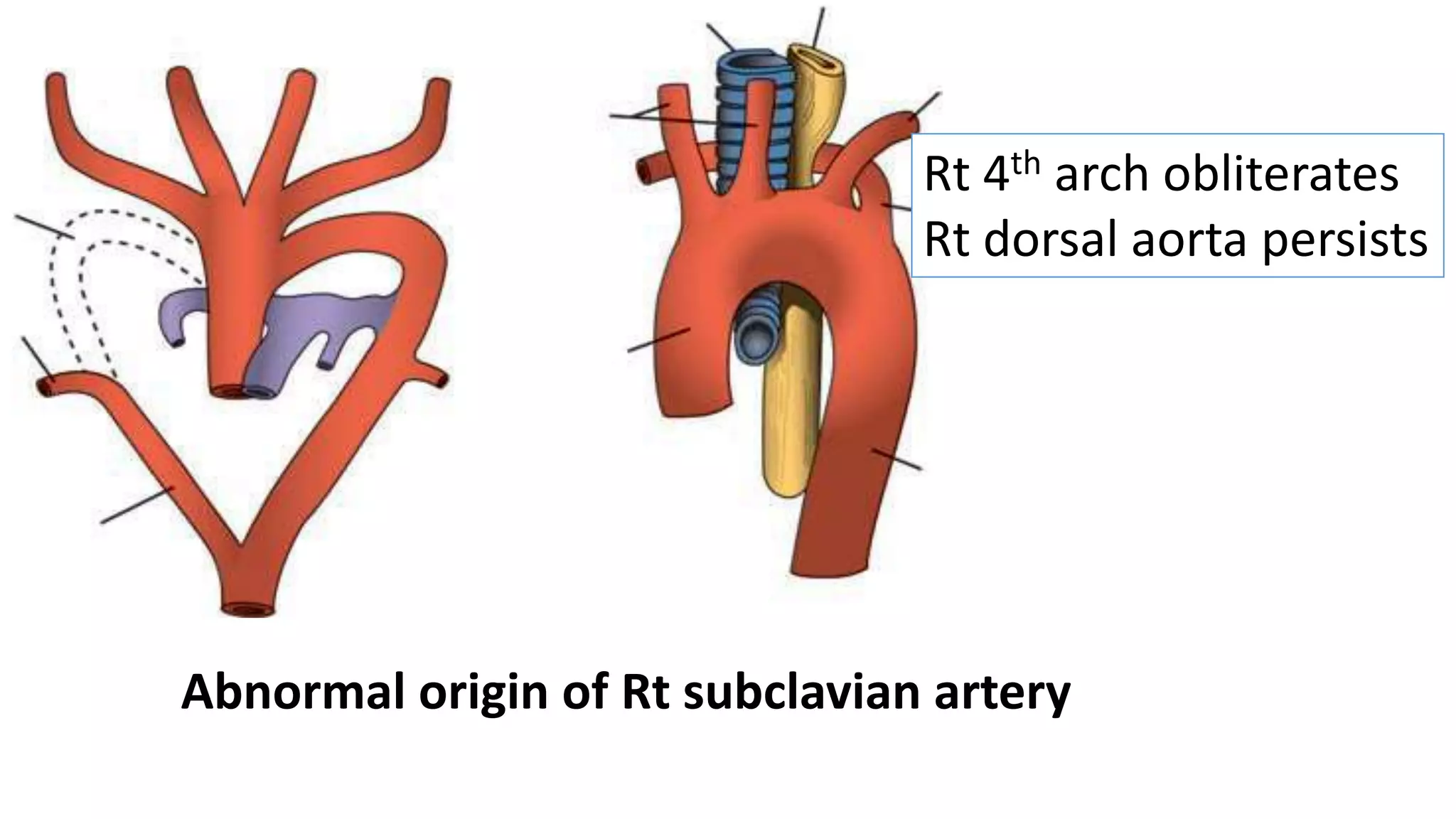
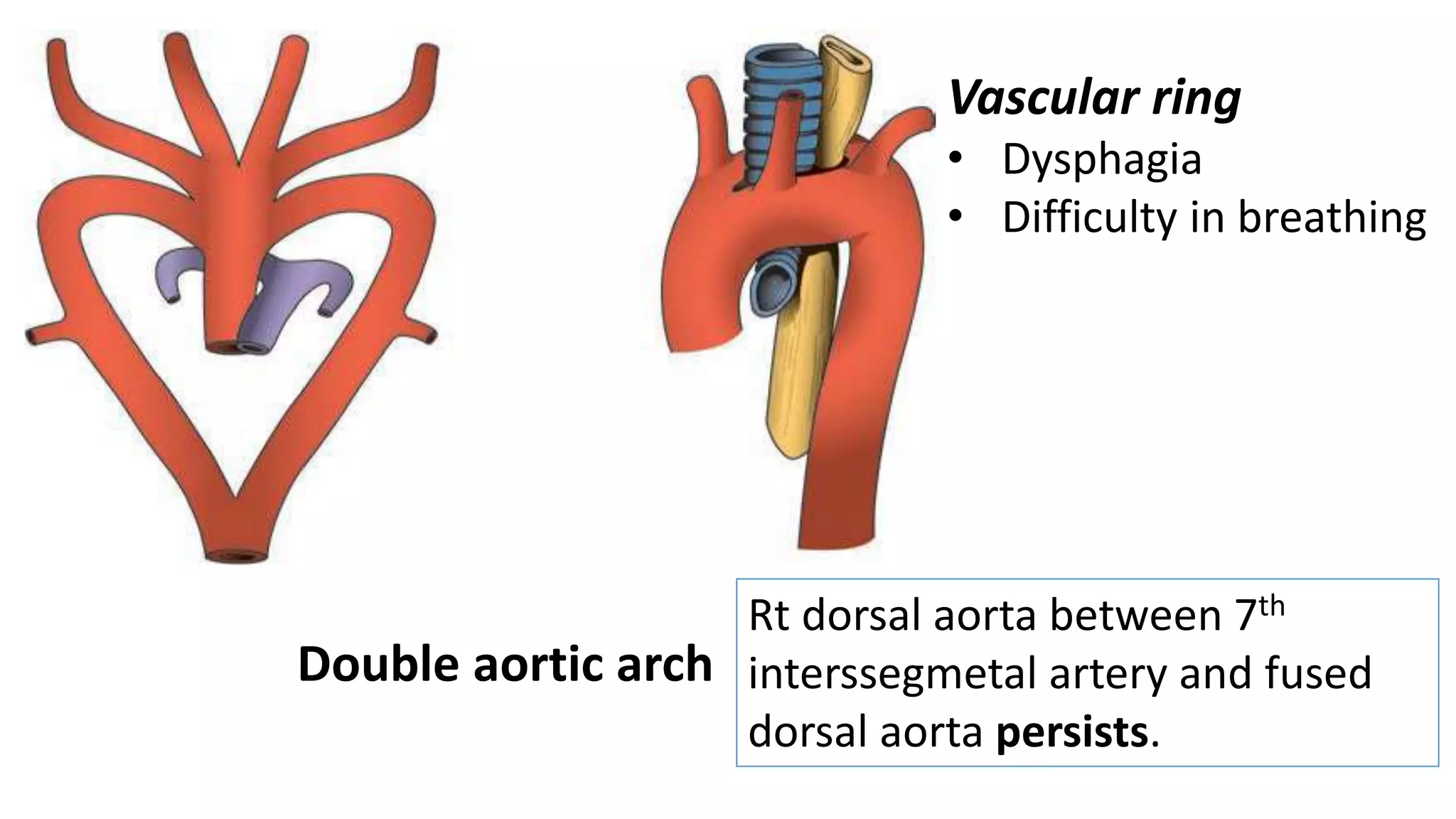
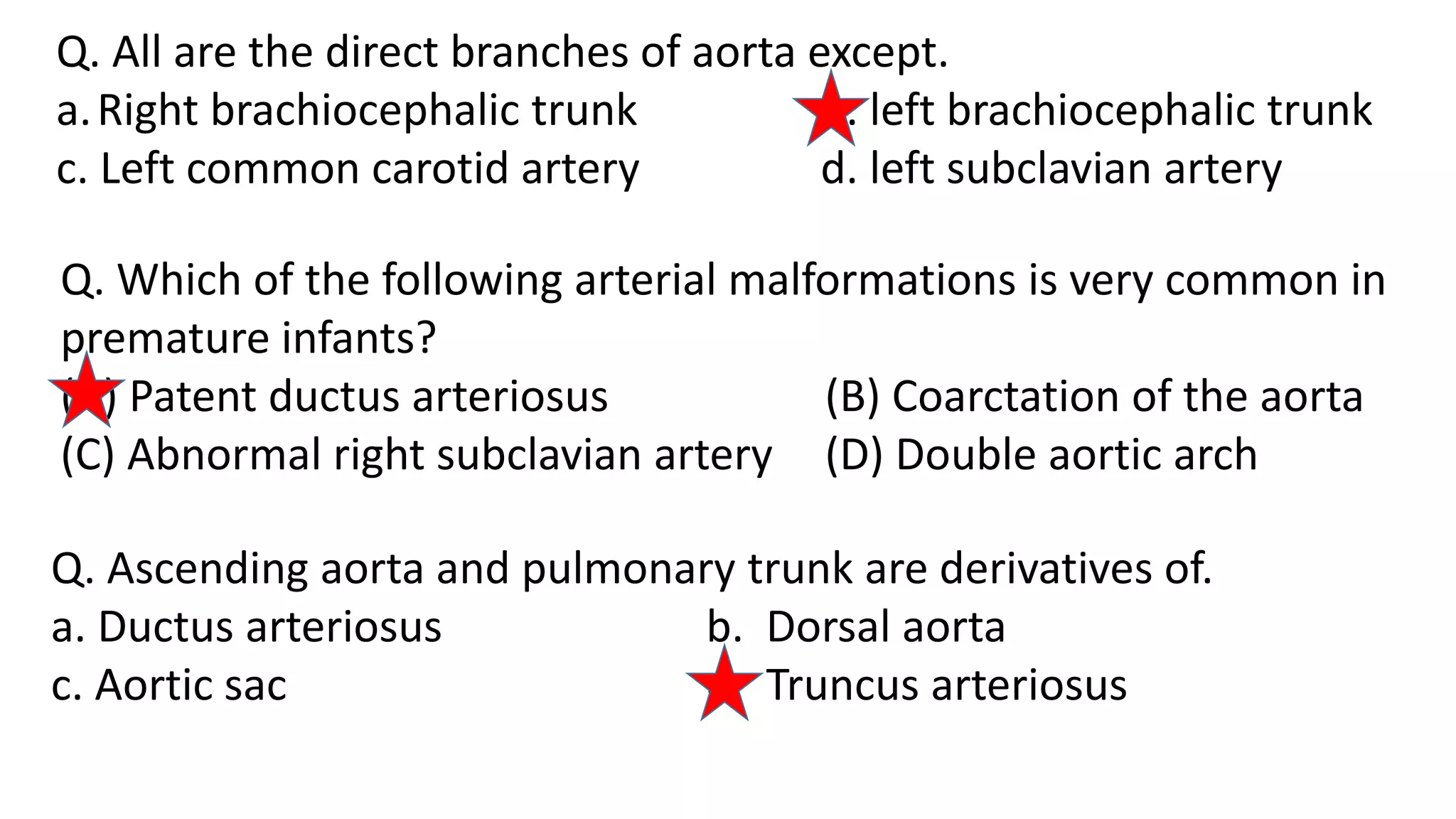
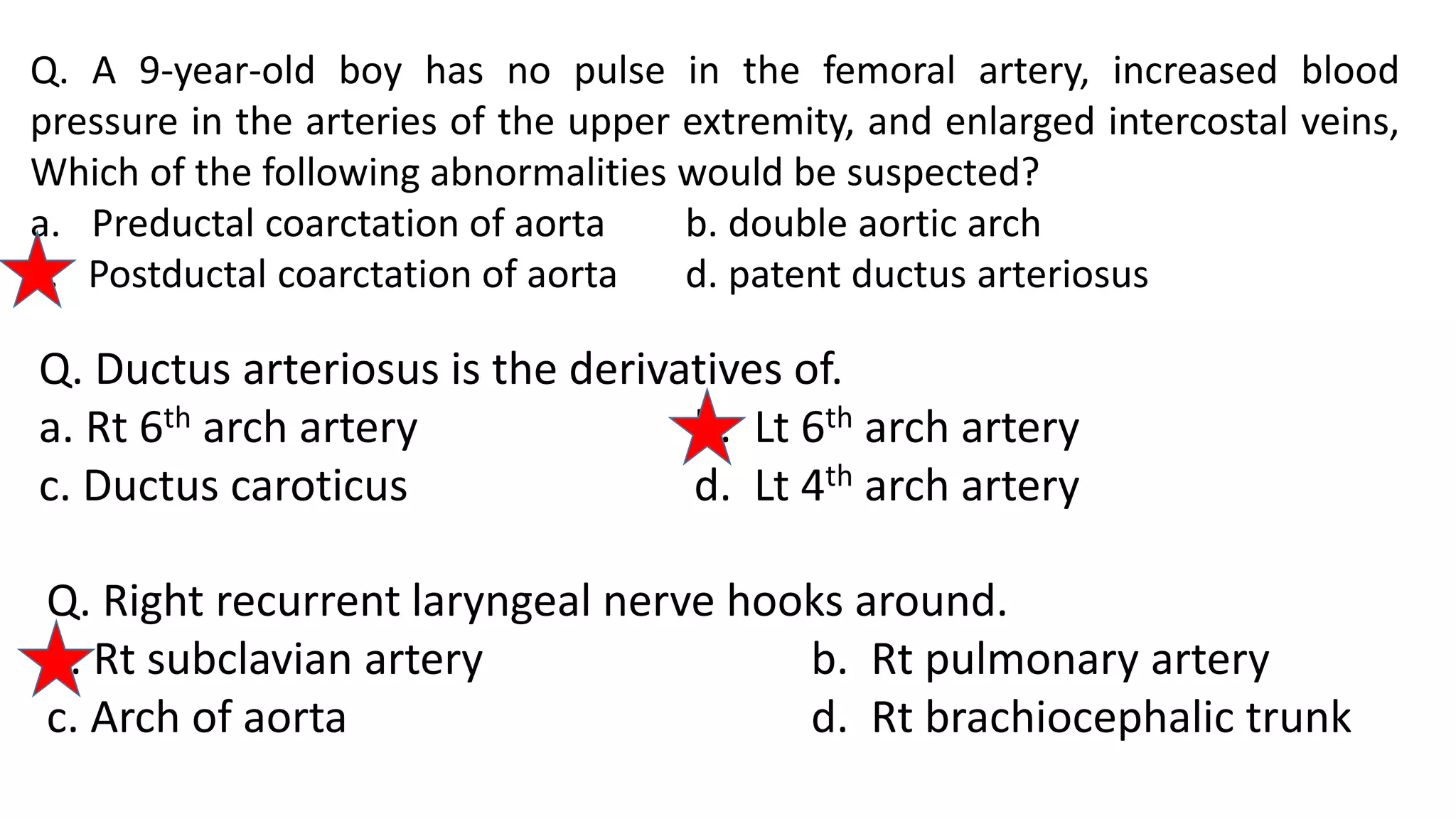
The document discusses the development of the aorta and pulmonary trunk from embryonic structures. It notes that the arterial system develops from the pharyngeal arch arteries and primitive aortas. Specifically, it outlines that the aortic sac, left horn of the aortic sac, left fourth arch artery, and unfused left dorsal aorta develop into parts of the aorta. The right and left sixth arch arteries develop into the pulmonary trunk and ductus arteriosus. It provides details on derivatives of the pharyngeal arches and common congenital anomalies that can occur.