This document summarizes the development of various veins in the human body, including:
- Vitelline veins arise from capillary plexuses around the yolk sac and form parts of the portal vein system.
- Umbilical veins carry oxygenated blood from the placenta, with the left vein joining the portal vein.
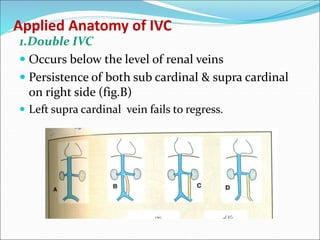
- Cardinal veins drain the body wall and form parts of the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Vitelline and umbilical veins within the developing liver break down and contribute to hepatic sinusoids.
- The cardinal veins give rise to major veins including the azygos vein, inferior vena cava, and major thoracic veins.