Parkinson Plus Syndrome - Multiple System Atrophy: Case Report
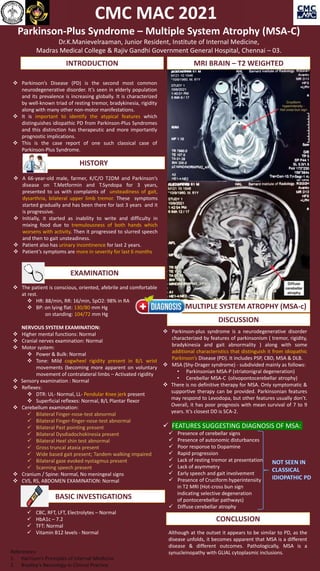
Parkinson Plus Syndrome - Multiple System Atrophy: Case Report. Poster used in CMC MAC 2021. ABSTRACT A 61yr/Male, K/C/O T2DM & Parkinson’s disease(PD) on T.Metformin and T.Syndopa for 3 years, presented to us with complaints of unsteadiness of gait, dysarthria, bilateral upper limb tremor. These symptoms started gradually and has been there for last 3 years and it is progressive. Initially, it started as inability to write and difficulty in mixing food due to tremulousness of both hands which worsens with activity. Then it progressed to slurred speech and then to gait unsteadiness. Patient also has urinary incontinence for last 2 years. Patient’s symptoms are more in severity for last 6 months. On examination, patient was having orthostatic hypotension, cogwheel rigidity on bilateral wrist movement and pendular knee jerks. All cerebellar signs were present bilaterally including finger nose test abnormality, past pointing, dysdiadochokinesia, heel shin test abnormality, gross truncal ataxia, wide based gait, impaired tandem walking, gaze evoked nystagmus, scanning speech. Presence of cerebellar signs, autonomic disturbances, poor response to syndopa, rapid progression, lack of resting tremor at presentation, symmetrical involvement, early speech and gait involvement - are usually NOT seen in PD. So, evaluated further. MRI Brain T2 showed classical cruciform hyperintensity in pons (Hot cross bun sign) & diffuse cerebellar atrophy. Hence the diagnosis MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY (MSA-C) - Shy Drager Syndrome. This shows the importance of identifying atypical features in PD.
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Parkinson Plus Syndrome - Multiple System Atrophy: Case Report
Similar to Parkinson Plus Syndrome - Multiple System Atrophy: Case Report (20)
More from Manievelraaman Kannan
More from Manievelraaman Kannan (11)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Parkinson Plus Syndrome - Multiple System Atrophy: Case Report
- 1. GERONTOCON 2021 Parkinson-Plus Syndrome – Multiple System Atrophy (MSA-C) Dr.K.Manievelraaman, Junior Resident, Institute of Internal Medicine, Madras Medical College & Rajiv Gandhi Government General Hospital, Chennai – 03. Parkinson-plus syndrome is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by features of parkinsonism ( tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and gait abnormality ) along with some additional characteristics that distinguish it from idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease (PD). It includes PSP, CBD, MSA & DLB. MSA (Shy-Drager syndrome) - subdivided mainly as follows: • Parkinsonian MSA-P (striatonigral degeneration) • Cerebellar MSA-C (olivopontocerebellar atrophy) There is no definitive therapy for MSA. Only symptomatic & supportive therapy can be provided. Parkinsonian features may respond to Levodopa, but other features usually don’t. Overall, it has poor prognosis with mean survival of 7 to 9 years. It’s closest DD is SCA-2. FEATURES SUGGESTING DIAGNOSIS OF MSA: Presence of cerebellar signs Presence of autonomic disturbances Poor response to Dopamine Rapid progression Lack of resting tremor at presentation Lack of asymmetry Early speech and gait involvement Presence of Cruciform hyperintensity in T2 MRI (Hot-cross bun sign indicating selective degeneration of pontocerebellar pathways) Diffuse cerebellar atrophy A 66-year-old male, farmer, K/C/O T2DM and Parkinson’s disease on T.Metformin and T.Syndopa for 3 years, presented to us with complaints of unsteadiness of gait, dysarthria, bilateral upper limb tremor. These symptoms started gradually and has been there for last 3 years and it is progressive. Initially, it started as inability to write and difficulty in mixing food due to tremulousness of both hands which worsens with activity. Then it progressed to slurred speech and then to gait unsteadiness. Patient also has urinary incontinence for last 2 years. Patient’s symptoms are more in severity for last 6 months The patient is conscious, oriented, afebrile and comfortable at rest. HR: 88/min, RR: 16/min, SpO2: 98% in RA BP: on lying flat: 130/80 mm Hg on standing: 104/72 mm Hg NERVOUS SYSTEM EXAMINATION: Higher mental functions: Normal Cranial nerves examination: Normal Motor system: Power & Bulk: Normal Tone: Mild cogwheel rigidity present in B/L wrist movements (becoming more apparent on voluntary movement of contralateral limbs – Activated rigidity Sensory examination : Normal Reflexes: DTR: UL- Normal, LL- Pendular Knee jerk present Superficial reflexes: Normal, B/L Plantar flexor Cerebellum examination: Bilateral Finger-nose-test abnormal Bilateral Finger-finger-nose-test abnormal Bilateral Past pointing present Bilateral Dysdiadochokinesia present Bilateral Heel shin test abnormal Gross truncal ataxia present Wide based gait present; Tandem walking impaired Bilateral gaze evoked nystagmus present Scanning speech present Cranium / Spine: Normal, No meningeal signs CVS, RS, ABDOMEN EXAMINATION: Normal INTRODUCTION Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder. It’s seen in elderly population and its prevalence is increasing globally. It is characterized by well-known triad of resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity along with many other non-motor manifestations. It is important to identify the atypical features which distinguishes idiopathic PD from Parkinson-Plus Syndromes and this distinction has therapeutic and more importantly prognostic implications. This is the case report of one such classical case of Parkinson-Plus Syndrome. HISTORY EXAMINATION CBC, RFT, LFT, Electrolytes – Normal HbA1c – 7.2 TFT: Normal Vitamin B12 levels - Normal BASIC INVESTIGATIONS MRI BRAIN – T2 WEIGHTED DISCUSSION DIAGNOSIS:MULTIPLE SYSTEM ATROPHY (MSA-c) CONCLUSION Although at the outset it appears to be similar to PD, as the disease unfolds, it becomes apparent that MSA is a different disease & different outcomes. Pathologically, MSA is a synucleinopathy with GLIAL cytoplasmic inclusions. References: 1. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 2. Bradley’s Neurology in Clinical Practice CMC MAC 2021
