Embed presentation
Download to read offline







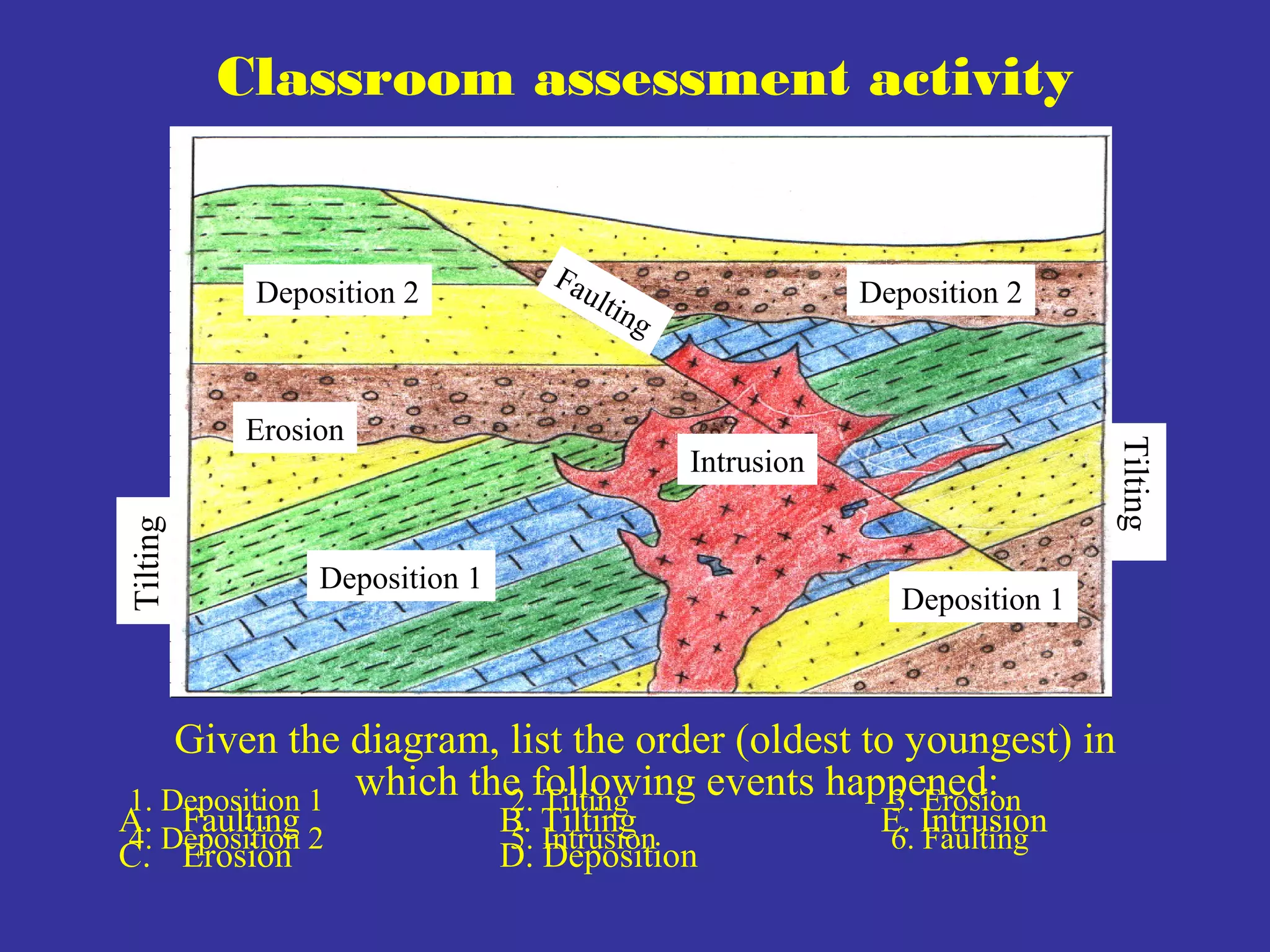
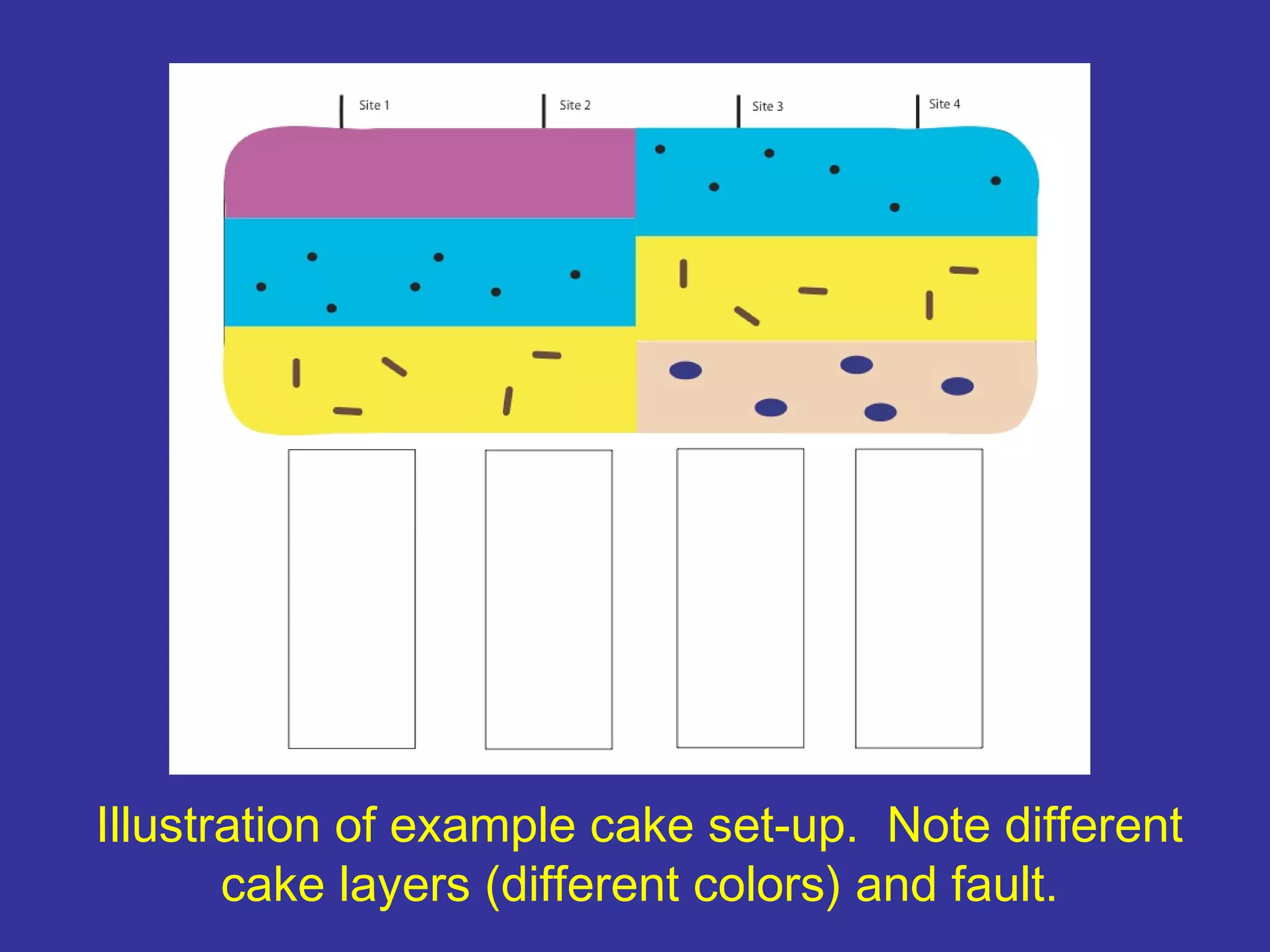

The document outlines a presentation for students to learn about minerals and the impact of mining through hands-on activities. It covers the principles of stratigraphy, including the laws governing sediment layers, their relationships, and faults. The presentation aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of geological processes and the historical context of rock formations.









