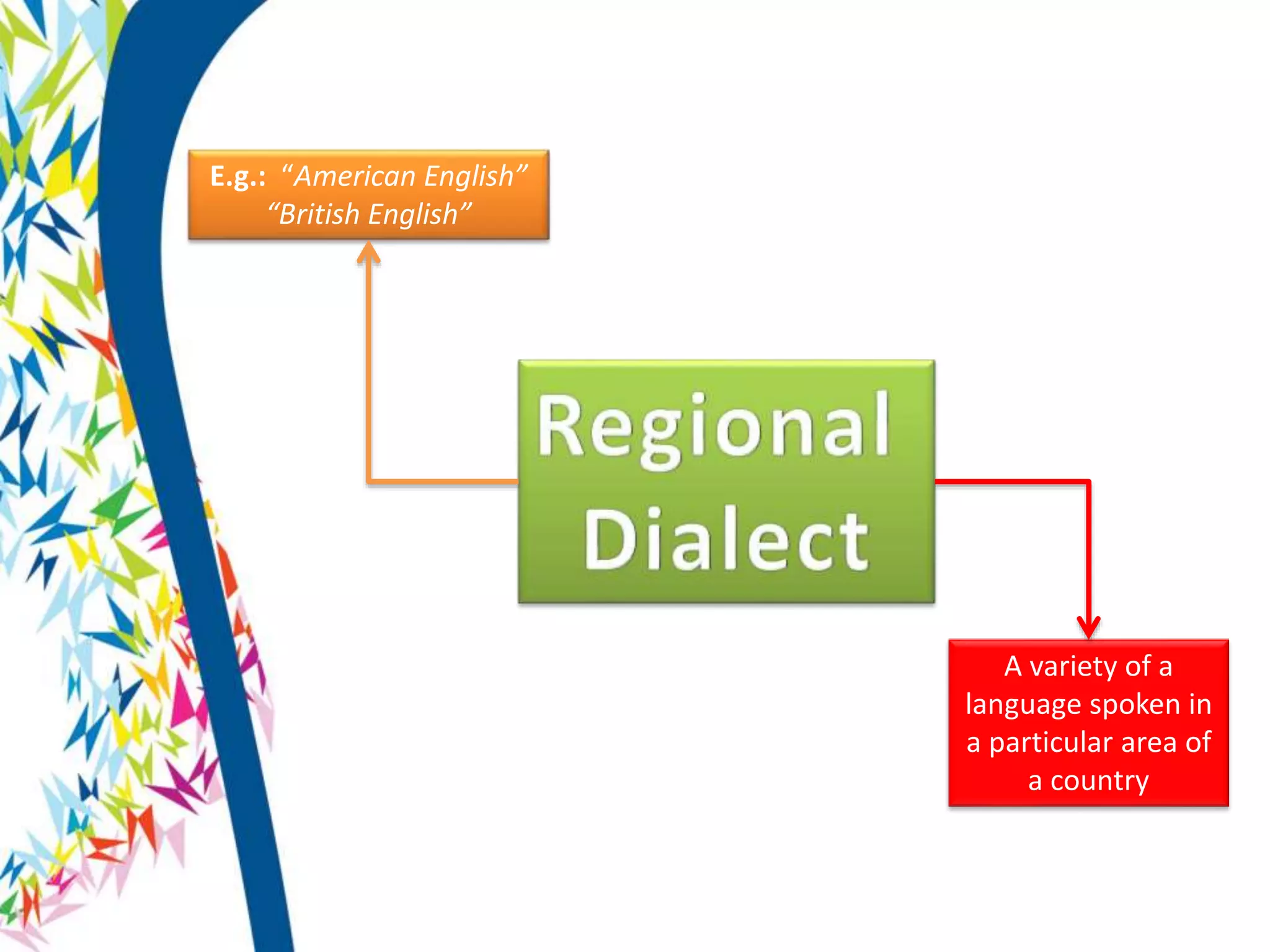
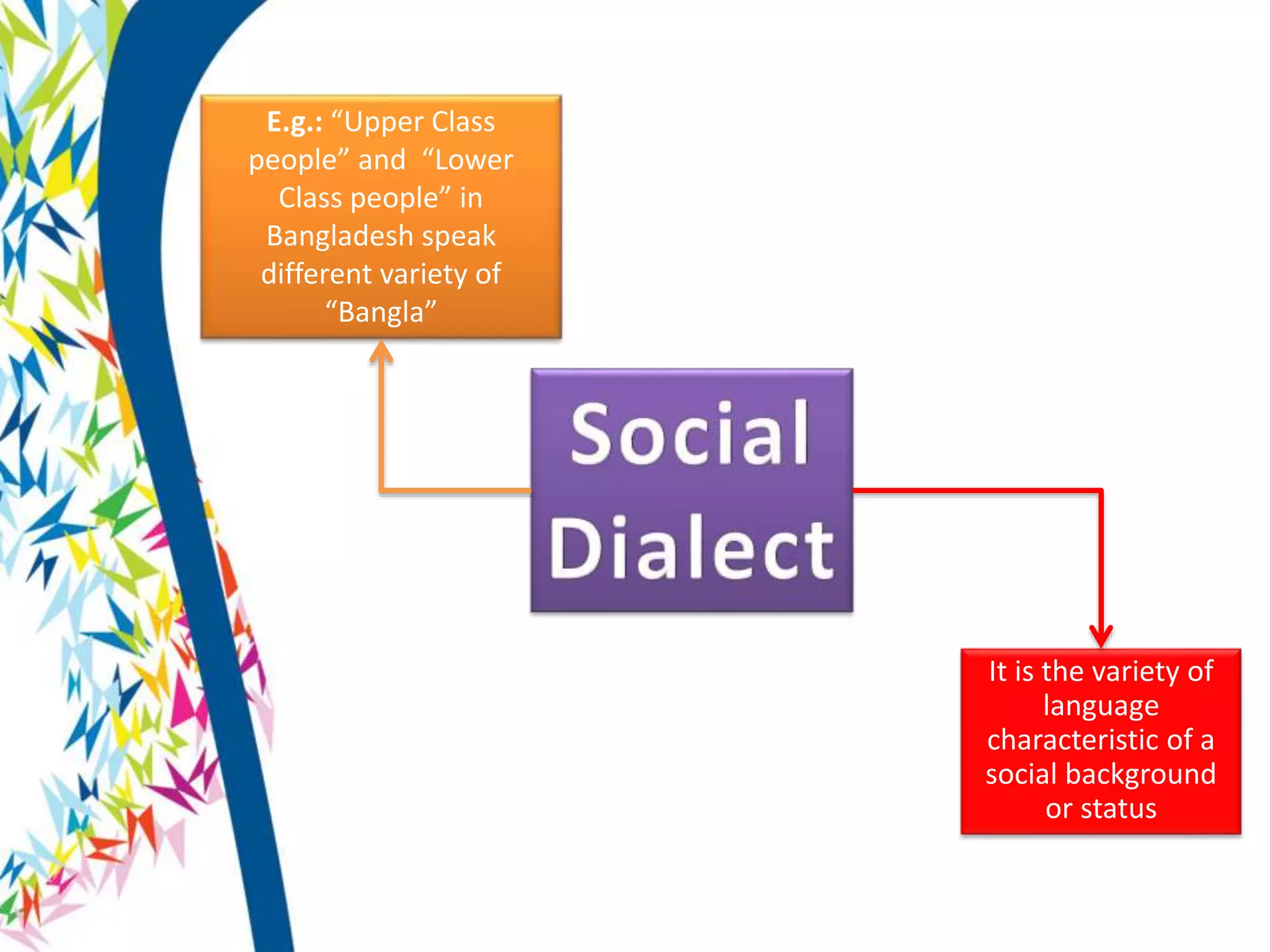
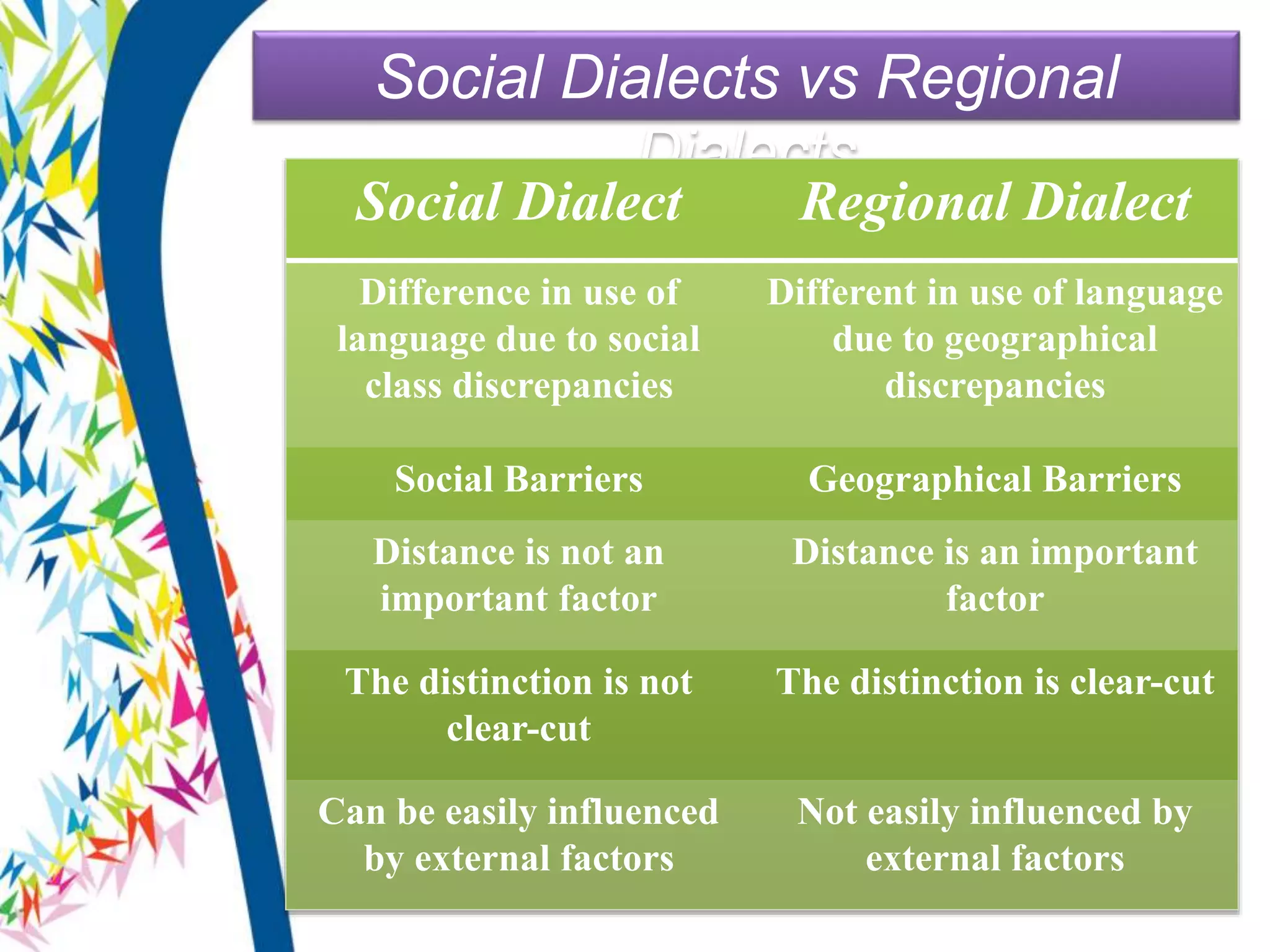
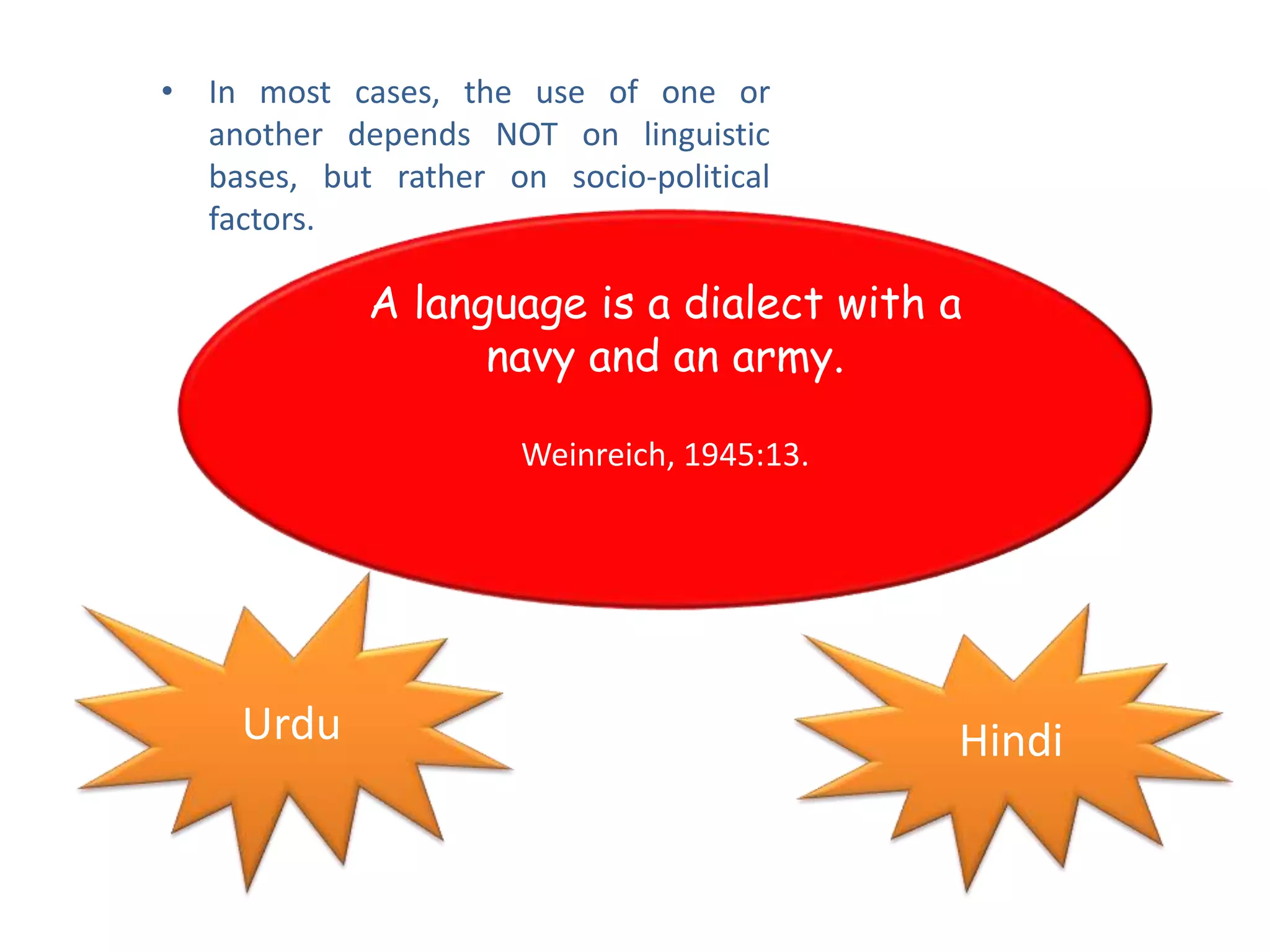
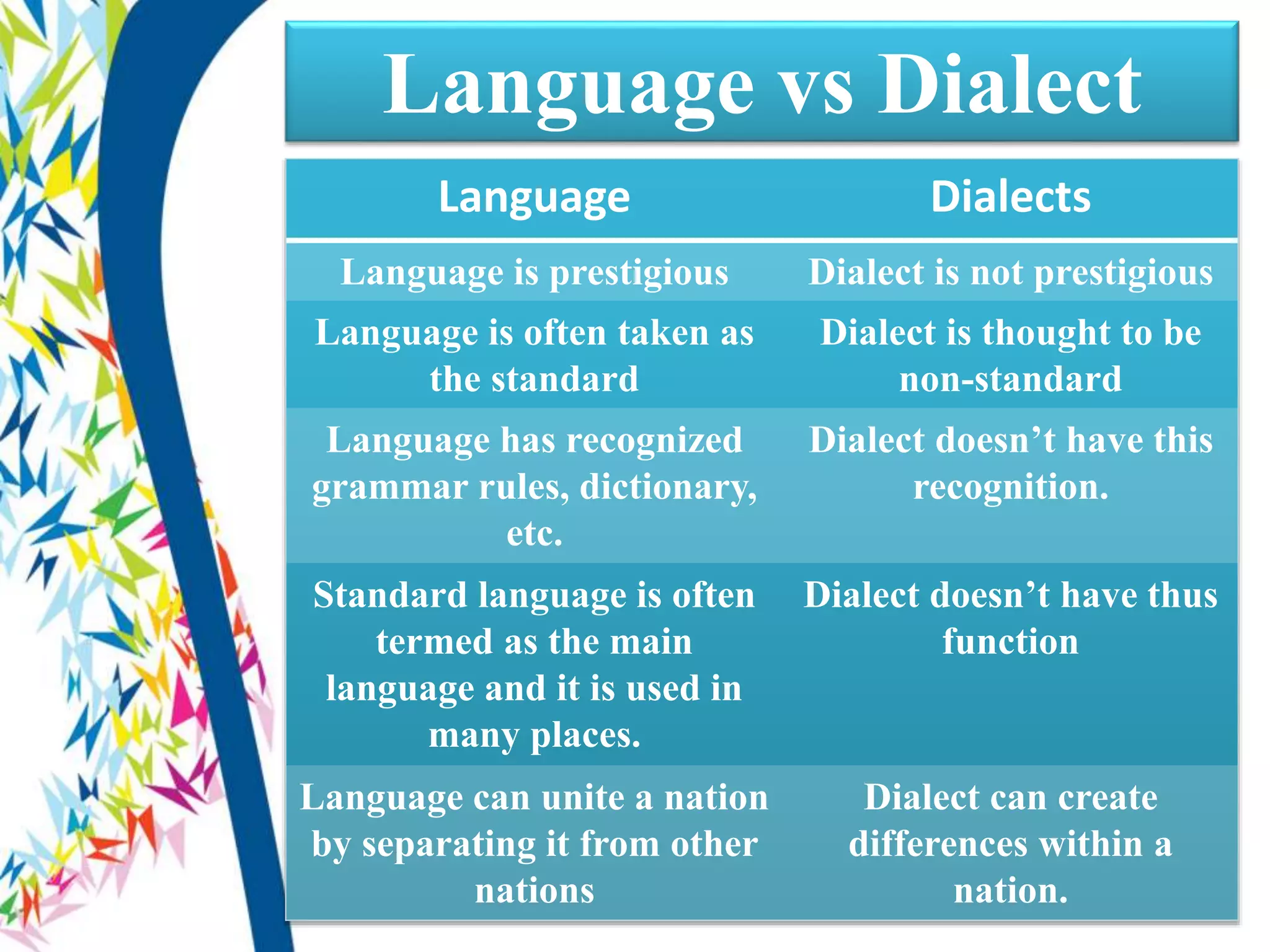
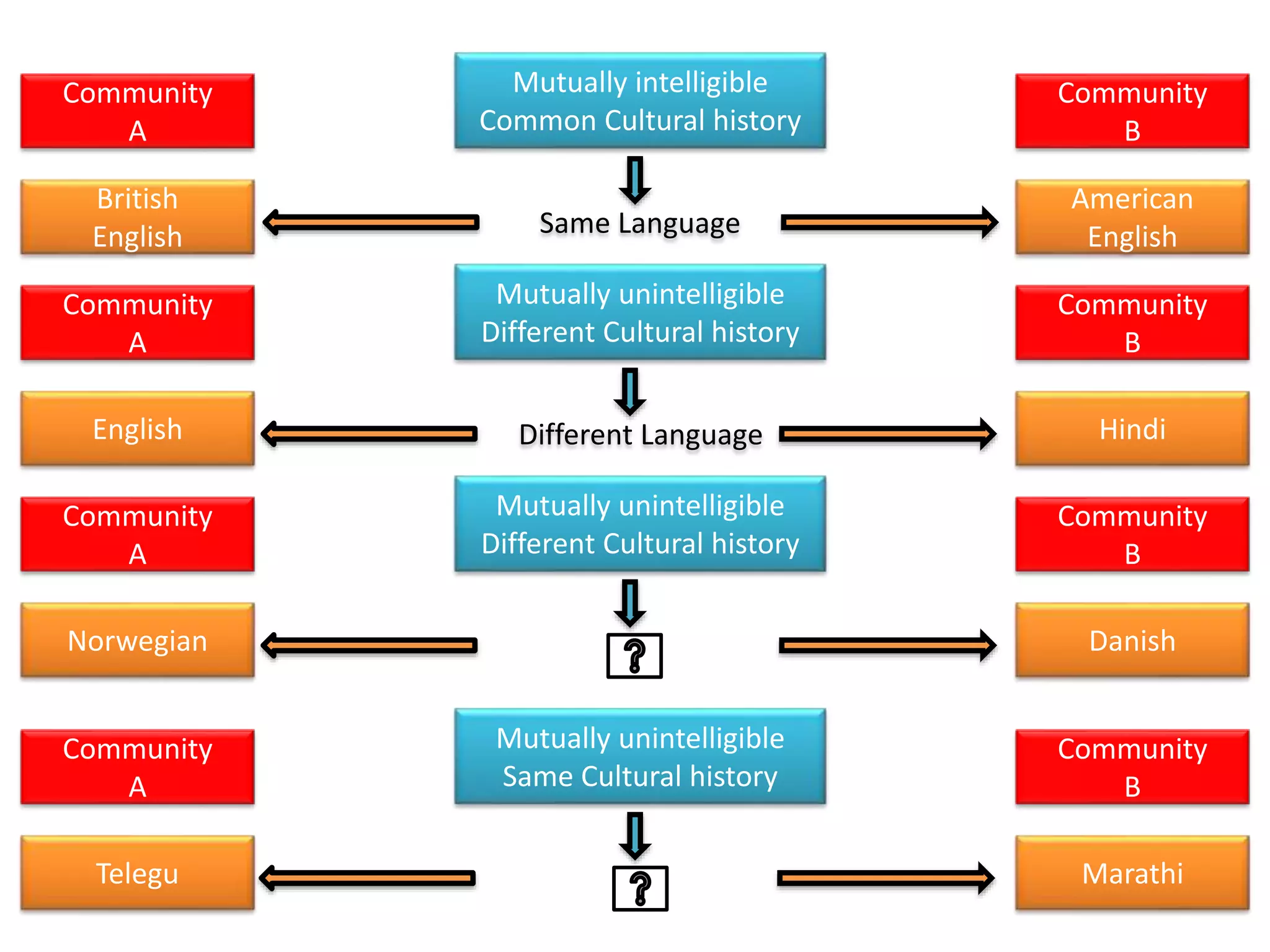
There are two main types of language varieties: dialects and languages. A dialect is a variety of a language that is characteristic of a particular group, such as a regional dialect like American English or a social dialect spoken by different social classes. The key difference between a dialect and a separate language is mutual intelligibility - varieties that are mutually intelligible are considered dialects, while mutually unintelligible varieties are considered separate languages. However, the distinction between dialects and languages is not always clear-cut and can depend on social and political factors as much as linguistic ones.